Rongqing Huang
Synthetic Cross-accent Data Augmentation for Automatic Speech Recognition
Mar 01, 2023


Abstract:The awareness for biased ASR datasets or models has increased notably in recent years. Even for English, despite a vast amount of available training data, systems perform worse for non-native speakers. In this work, we improve an accent-conversion model (ACM) which transforms native US-English speech into accented pronunciation. We include phonetic knowledge in the ACM training to provide accurate feedback about how well certain pronunciation patterns were recovered in the synthesized waveform. Furthermore, we investigate the feasibility of learned accent representations instead of static embeddings. Generated data was then used to train two state-of-the-art ASR systems. We evaluated our approach on native and non-native English datasets and found that synthetically accented data helped the ASR to better understand speech from seen accents. This observation did not translate to unseen accents, and it was not observed for a model that had been pre-trained exclusively with native speech.
Joint Audio/Text Training for Transformer Rescorer of Streaming Speech Recognition
Oct 31, 2022



Abstract:Recently, there has been an increasing interest in two-pass streaming end-to-end speech recognition (ASR) that incorporates a 2nd-pass rescoring model on top of the conventional 1st-pass streaming ASR model to improve recognition accuracy while keeping latency low. One of the latest 2nd-pass rescoring model, Transformer Rescorer, takes the n-best initial outputs and audio embeddings from the 1st-pass model, and then choose the best output by re-scoring the n-best initial outputs. However, training this Transformer Rescorer requires expensive paired audio-text training data because the model uses audio embeddings as input. In this work, we present our Joint Audio/Text training method for Transformer Rescorer, to leverage unpaired text-only data which is relatively cheaper than paired audio-text data. We evaluate Transformer Rescorer with our Joint Audio/Text training on Librispeech dataset as well as our large-scale in-house dataset and show that our training method can improve word error rate (WER) significantly compared to standard Transformer Rescorer without requiring any extra model parameters or latency.
Integrating Categorical Features in End-to-End ASR
Oct 06, 2021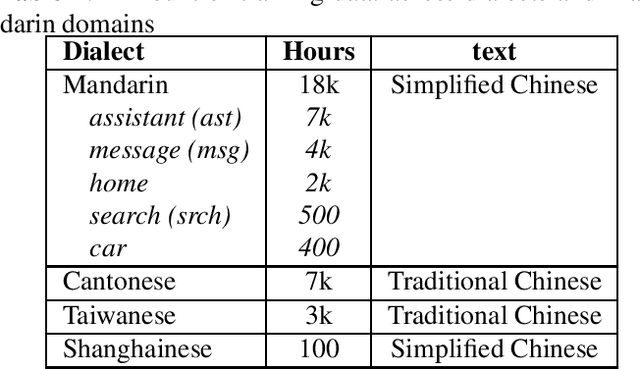
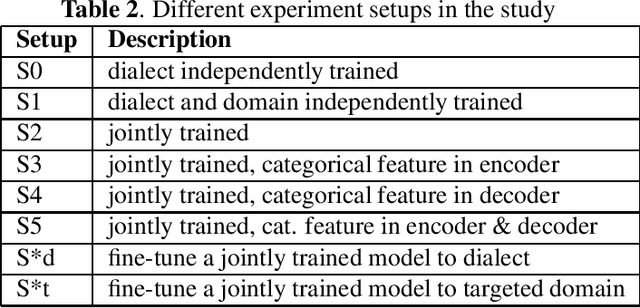
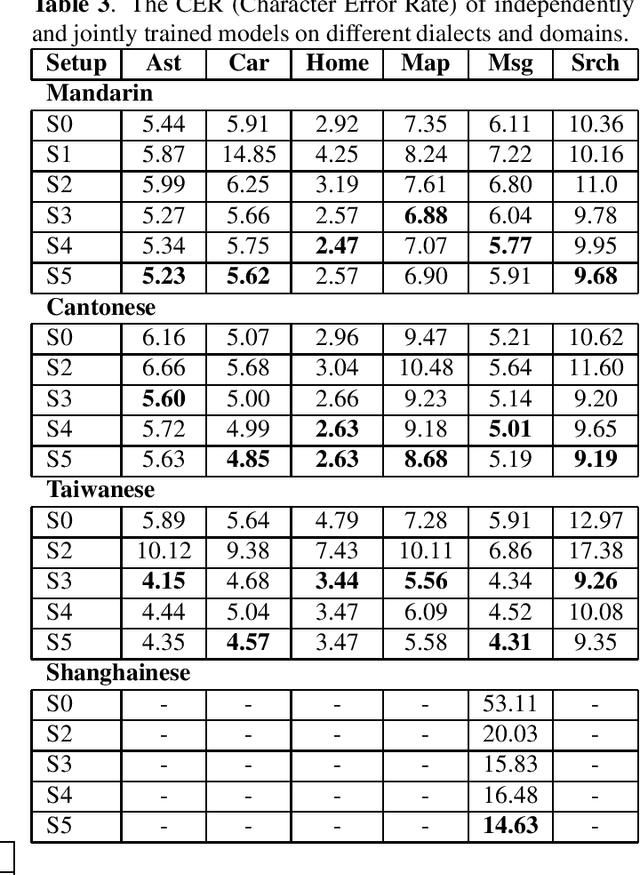
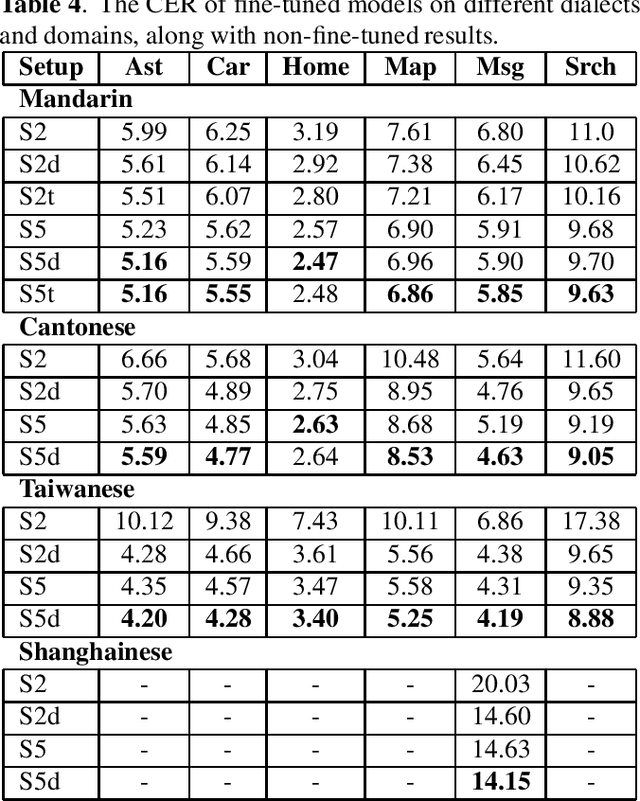
Abstract:All-neural, end-to-end ASR systems gained rapid interest from the speech recognition community. Such systems convert speech input to text units using a single trainable neural network model. E2E models require large amounts of paired speech text data that is expensive to obtain. The amount of data available varies across different languages and dialects. It is critical to make use of all these data so that both low resource languages and high resource languages can be improved. When we want to deploy an ASR system for a new application domain, the amount of domain specific training data is very limited. To be able to leverage data from existing domains is important for ASR accuracy in the new domain. In this paper, we treat all these aspects as categorical information in an ASR system, and propose a simple yet effective way to integrate categorical features into E2E model. We perform detailed analysis on various training strategies, and find that building a joint model that includes categorical features can be more accurate than multiple independently trained models.
Class LM and word mapping for contextual biasing in End-to-End ASR
Jul 10, 2020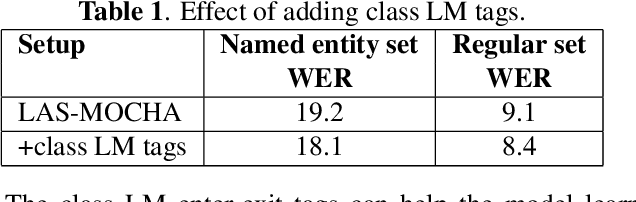
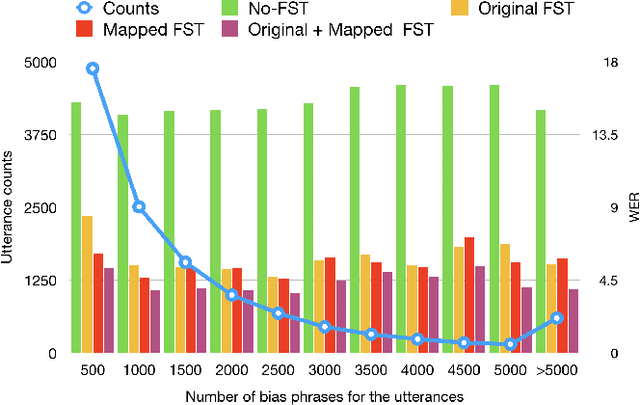
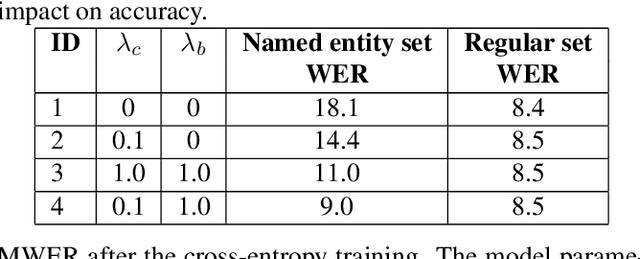
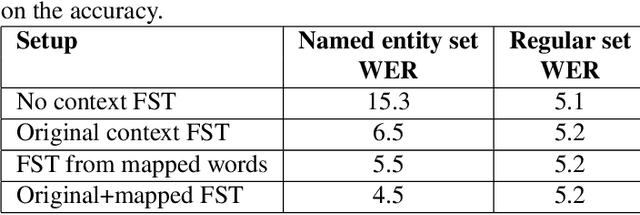
Abstract:In recent years, all-neural, end-to-end (E2E) ASR systems gained rapid interest in the speech recognition community. They convert speech input to text units in a single trainable Neural Network model. In ASR, many utterances contain rich named entities. Such named entities may be user or location specific and they are not seen during training. A single model makes it inflexible to utilize dynamic contextual information during inference. In this paper, we propose to train a context aware E2E model and allow the beam search to traverse into the context FST during inference. We also propose a simple method to adjust the cost discrepancy between the context FST and the base model. This algorithm is able to reduce the named entity utterance WER by 57% with little accuracy degradation on regular utterances. Although an E2E model does not need pronunciation dictionary, it's interesting to make use of existing pronunciation knowledge to improve accuracy. In this paper, we propose an algorithm to map the rare entity words to common words via pronunciation and treat the mapped words as an alternative form to the original word during recognition. This algorithm further reduces the WER on the named entity utterances by another 31%.
Kernel Regression with Sparse Metric Learning
Dec 25, 2017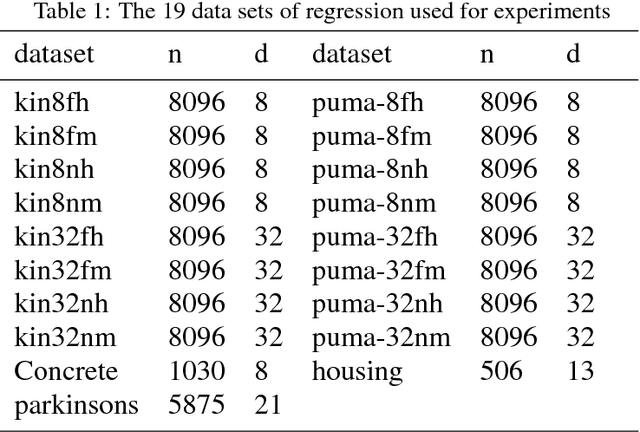
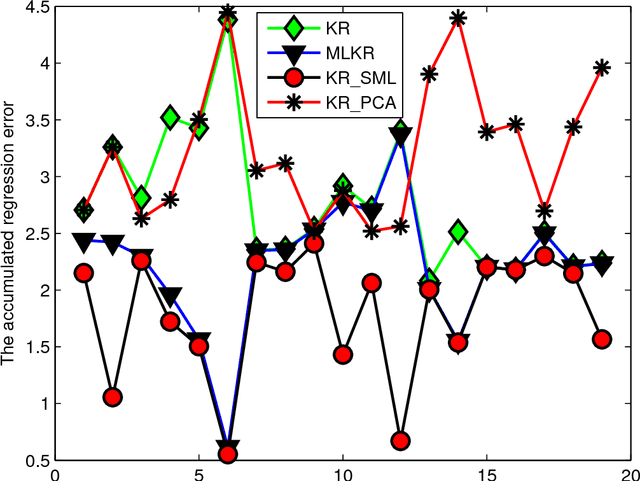
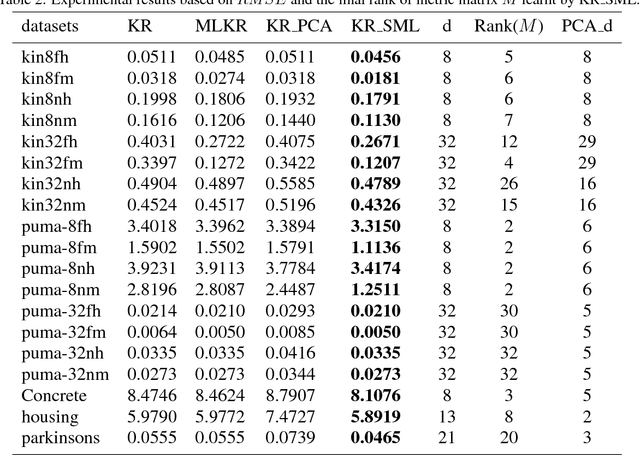
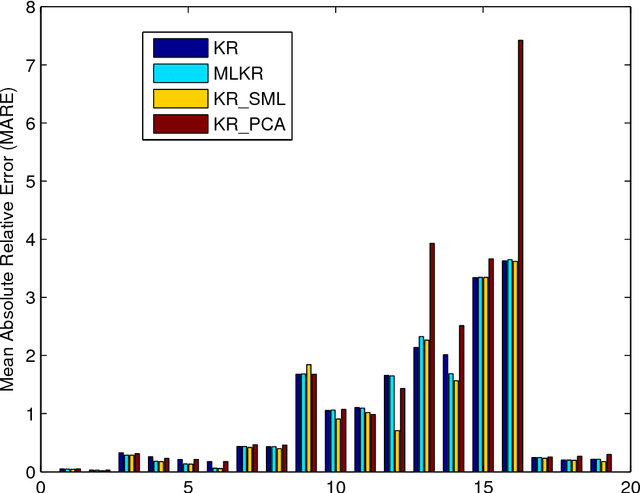
Abstract:Kernel regression is a popular non-parametric fitting technique. It aims at learning a function which estimates the targets for test inputs as precise as possible. Generally, the function value for a test input is estimated by a weighted average of the surrounding training examples. The weights are typically computed by a distance-based kernel function and they strongly depend on the distances between examples. In this paper, we first review the latest developments of sparse metric learning and kernel regression. Then a novel kernel regression method involving sparse metric learning, which is called kernel regression with sparse metric learning (KR$\_$SML), is proposed. The sparse kernel regression model is established by enforcing a mixed $(2,1)$-norm regularization over the metric matrix. It learns a Mahalanobis distance metric by a gradient descent procedure, which can simultaneously conduct dimensionality reduction and lead to good prediction results. Our work is the first to combine kernel regression with sparse metric learning. To verify the effectiveness of the proposed method, it is evaluated on 19 data sets for regression. Furthermore, the new method is also applied to solving practical problems of forecasting short-term traffic flows. In the end, we compare the proposed method with other three related kernel regression methods on all test data sets under two criterions. Experimental results show that the proposed method is much more competitive.
Network-Scale Traffic Modeling and Forecasting with Graphical Lasso and Neural Networks
Dec 25, 2017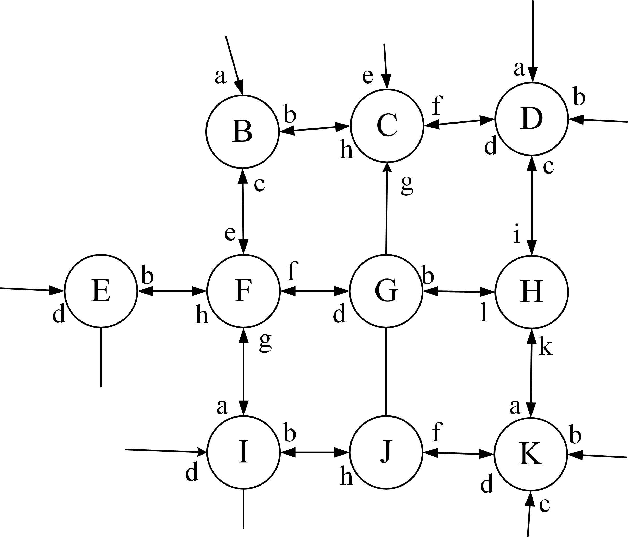
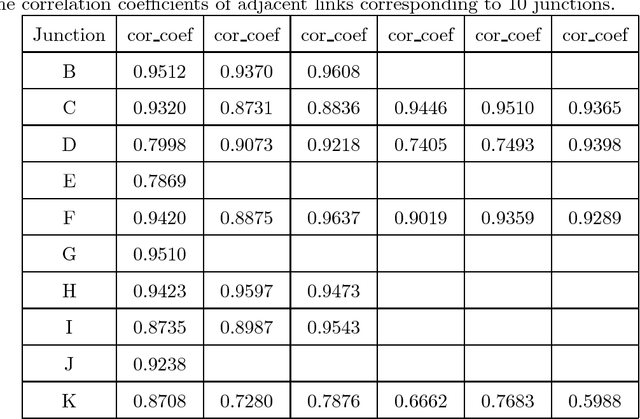
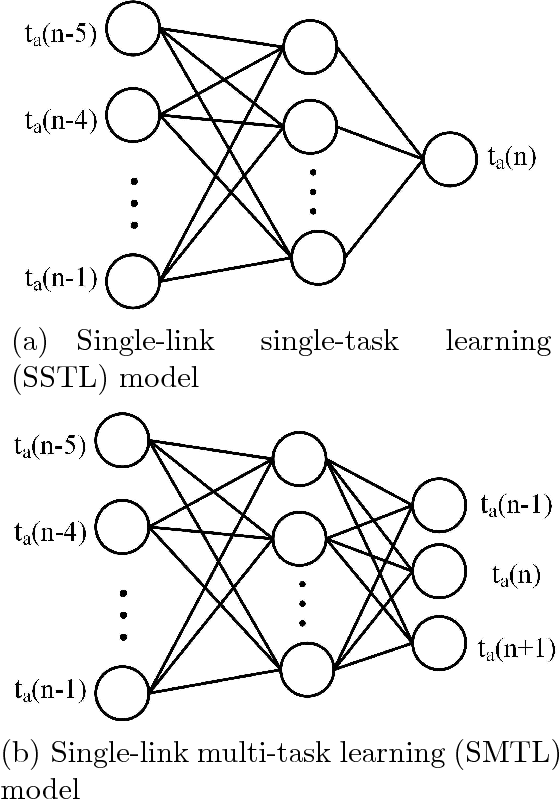
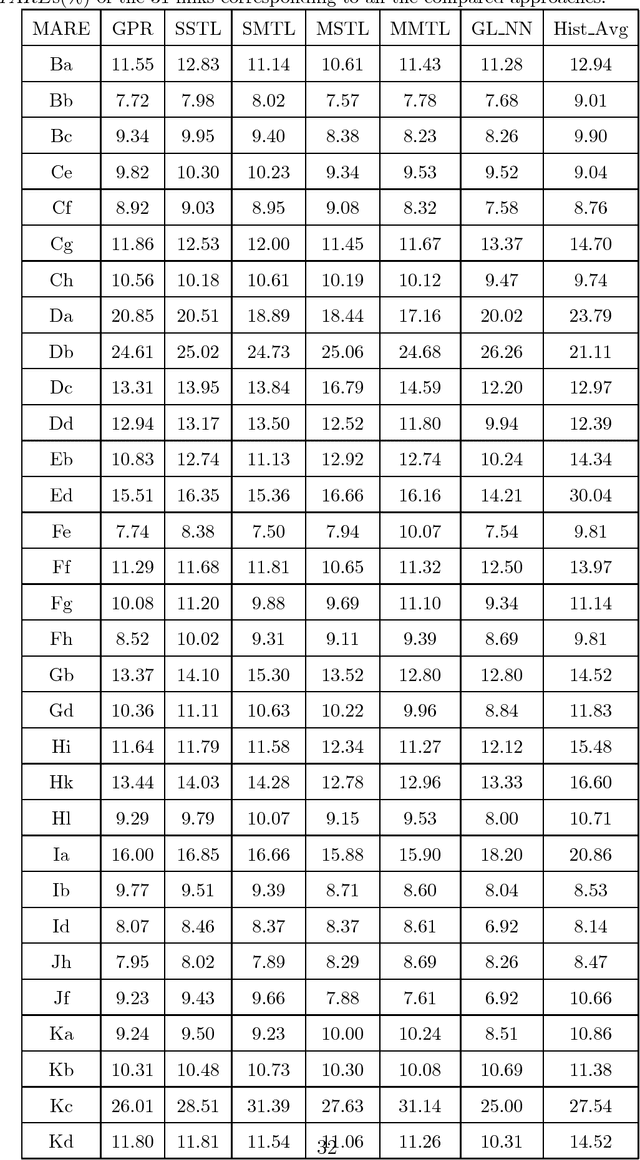
Abstract:Traffic flow forecasting, especially the short-term case, is an important topic in intelligent transportation systems (ITS). This paper does a lot of research on network-scale modeling and forecasting of short-term traffic flows. Firstly, we propose the concepts of single-link and multi-link models of traffic flow forecasting. Secondly, we construct four prediction models by combining the two models with single-task learning and multi-task learning. The combination of the multi-link model and multi-task learning not only improves the experimental efficiency but also the prediction accuracy. Moreover, a new multi-link single-task approach that combines graphical lasso (GL) with neural network (NN) is proposed. GL provides a general methodology for solving problems involving lots of variables. Using L1 regularization, GL builds a sparse graphical model making use of the sparse inverse covariance matrix. In addition, Gaussian process regression (GPR) is a classic regression algorithm in Bayesian machine learning. Although there is wide research on GPR, there are few applications of GPR in traffic flow forecasting. In this paper, we apply GPR to traffic flow forecasting and show its potential. Through sufficient experiments, we compare all of the proposed approaches and make an overall assessment at last.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge