Zhaohua Yang
MUA-RL: Multi-turn User-interacting Agent Reinforcement Learning for agentic tool use
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:With the recent rapid advancement of Agentic Intelligence, agentic tool use in LLMs has become increasingly important. During multi-turn interactions between agents and users, the dynamic, uncertain, and stochastic nature of user demands poses significant challenges to the agent's tool invocation capabilities. Agents are no longer expected to simply call tools to deliver a result; rather, they must iteratively refine their understanding of user needs through communication while simultaneously invoking tools to resolve user queries. Existing reinforcement learning (RL) approaches for tool use lack the integration of genuinely dynamic users during the RL training process. To bridge this gap, we introduce MUA-RL (Multi-turn User-interacting Agent Reinforcement Learning for agentic tool use), a novel reinforcement learning framework that, for the first time in the field of agentic tool use, integrates LLM-simulated users into the reinforcement learning loop. MUA-RL aims to enable autonomous learning of models to communicate with users efficiently and use various tools to solve practical problems in dynamic multi-turn interactions. Evaluations are done on several multi-turn tool-using benchmarks (see Figure 1). Specifically, MUA-RL-32B achieves 67.3 on TAU2 Retail, 45.4 on TAU2 Airline, 28.3 on TAU2 Telecom, 28.4 on BFCL-V3 Multi Turn, and 82.5 on ACEBench Agent -- outperforming or matching the performance of larger open-source models such as DeepSeek-V3-0324 and Qwen3-235B-A22B in non-thinking settings.
Learning-based Detection of GPS Spoofing Attack for Quadrotors
Jan 10, 2025Abstract:Safety-critical cyber-physical systems (CPS), such as quadrotor UAVs, are particularly prone to cyber attacks, which can result in significant consequences if not detected promptly and accurately. During outdoor operations, the nonlinear dynamics of UAV systems, combined with non-Gaussian noise, pose challenges to the effectiveness of conventional statistical and machine learning methods. To overcome these limitations, we present QUADFormer, an advanced attack detection framework for quadrotor UAVs leveraging a transformer-based architecture. This framework features a residue generator that produces sequences sensitive to anomalies, which are then analyzed by the transformer to capture statistical patterns for detection and classification. Furthermore, an alert mechanism ensures UAVs can operate safely even when under attack. Extensive simulations and experimental evaluations highlight that QUADFormer outperforms existing state-of-the-art techniques in detection accuracy.
Coastal Underwater Evidence Search System with Surface-Underwater Collaboration
Oct 03, 2024

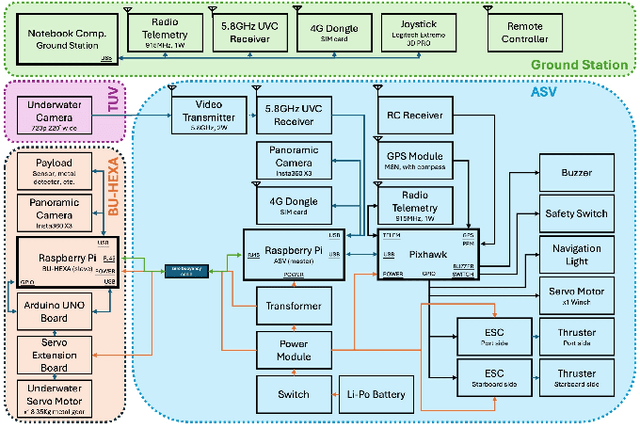

Abstract:The Coastal underwater evidence search system with surface-underwater collaboration is designed to revolutionize the search for artificial objects in coastal underwater environments, overcoming limitations associated with traditional methods such as divers and tethered remotely operated vehicles. Our innovative multi-robot collaborative system consists of three parts, an autonomous surface vehicle as a mission control center, a towed underwater vehicle for wide-area search, and a biomimetic underwater robot inspired by marine organisms for detailed inspections of identified areas. We conduct extensive simulations and real-world experiments in pond environments and coastal fields to demonstrate the system potential to surpass the limitations of conventional underwater search methods, offering a robust and efficient solution for law enforcement and recovery operations in marine settings.
Recent Advances in Data-driven Intelligent Control for Wireless Communication: A Comprehensive Survey
Aug 06, 2024Abstract:The advent of next-generation wireless communication systems heralds an era characterized by high data rates, low latency, massive connectivity, and superior energy efficiency. These systems necessitate innovative and adaptive strategies for resource allocation and device behavior control in wireless networks. Traditional optimization-based methods have been found inadequate in meeting the complex demands of these emerging systems. As the volume of data continues to escalate, the integration of data-driven methods has become indispensable for enabling adaptive and intelligent control mechanisms in future wireless communication systems. This comprehensive survey explores recent advancements in data-driven methodologies applied to wireless communication networks. It focuses on developments over the past five years and their application to various control objectives within wireless cyber-physical systems. It encompasses critical areas such as link adaptation, user scheduling, spectrum allocation, beam management, power control, and the co-design of communication and control systems. We provide an in-depth exploration of the technical underpinnings that support these data-driven approaches, including the algorithms, models, and frameworks developed to enhance network performance and efficiency. We also examine the challenges that current data-driven algorithms face, particularly in the context of the dynamic and heterogeneous nature of next-generation wireless networks. The paper provides a critical analysis of these challenges and offers insights into potential solutions and future research directions. This includes discussing the adaptability, integration with 6G, and security of data-driven methods in the face of increasing network complexity and data volume.
QUADFormer: Learning-based Detection of Cyber Attacks in Quadrotor UAVs
Jun 02, 2024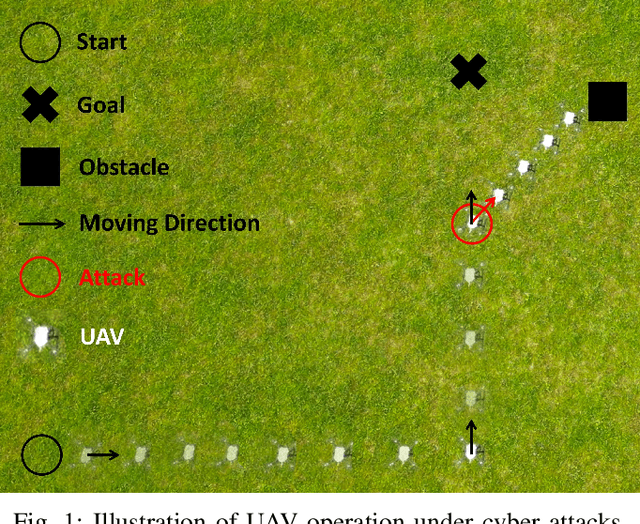
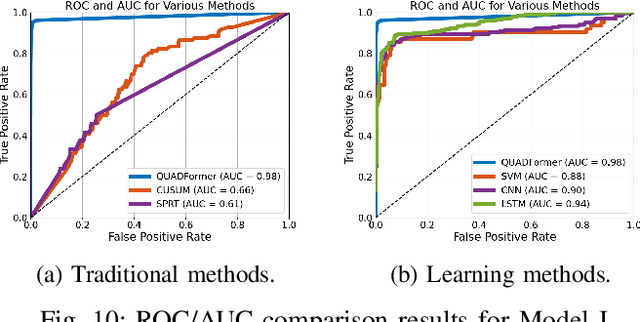
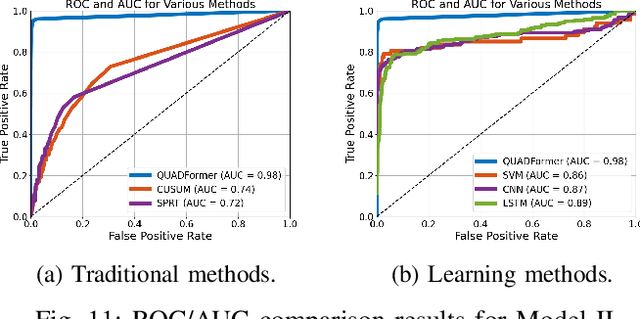
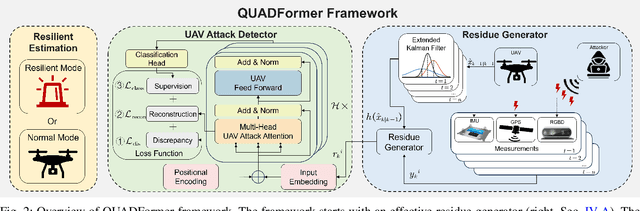
Abstract:Safety-critical intelligent cyber-physical systems, such as quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), are vulnerable to different types of cyber attacks, and the absence of timely and accurate attack detection can lead to severe consequences. When UAVs are engaged in large outdoor maneuvering flights, their system constitutes highly nonlinear dynamics that include non-Gaussian noises. Therefore, the commonly employed traditional statistics-based and emerging learning-based attack detection methods do not yield satisfactory results. In response to the above challenges, we propose QUADFormer, a novel Quadrotor UAV Attack Detection framework with transFormer-based architecture. This framework includes a residue generator designed to generate a residue sequence sensitive to anomalies. Subsequently, this sequence is fed into a transformer structure with disparity in correlation to specifically learn its statistical characteristics for the purpose of classification and attack detection. Finally, we design an alert module to ensure the safe execution of tasks by UAVs under attack conditions. We conduct extensive simulations and real-world experiments, and the results show that our method has achieved superior detection performance compared with many state-of-the-art methods.
GCOF: Self-iterative Text Generation for Copywriting Using Large Language Model
Feb 21, 2024
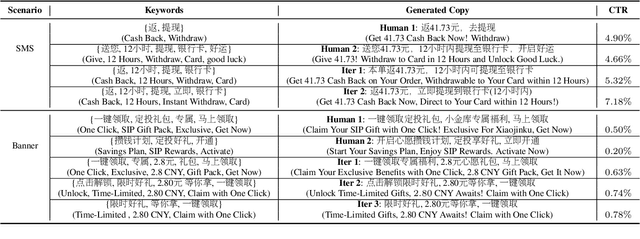
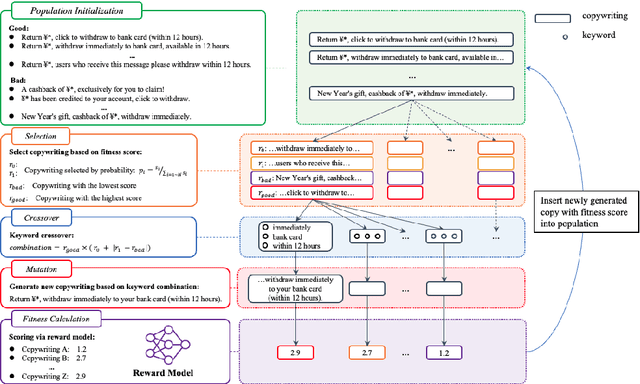
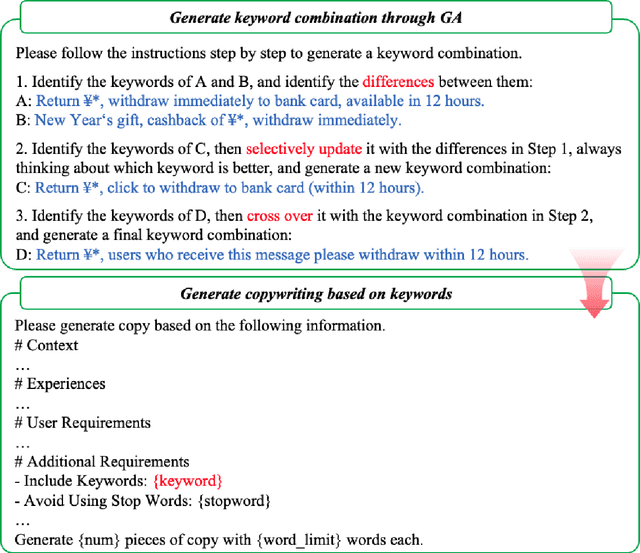
Abstract:Large language models(LLM) such as ChatGPT have substantially simplified the generation of marketing copy, yet producing content satisfying domain specific requirements, such as effectively engaging customers, remains a significant challenge. In this work, we introduce the Genetic Copy Optimization Framework (GCOF) designed to enhance both efficiency and engagememnt of marketing copy creation. We conduct explicit feature engineering within the prompts of LLM. Additionally, we modify the crossover operator in Genetic Algorithm (GA), integrating it into the GCOF to enable automatic feature engineering. This integration facilitates a self-iterative refinement of the marketing copy. Compared to human curated copy, Online results indicate that copy produced by our framework achieves an average increase in click-through rate (CTR) of over $50\%$.
Self-supervised Learning for Electroencephalogram: A Systematic Survey
Jan 09, 2024



Abstract:Electroencephalogram (EEG) is a non-invasive technique to record bioelectrical signals. Integrating supervised deep learning techniques with EEG signals has recently facilitated automatic analysis across diverse EEG-based tasks. However, the label issues of EEG signals have constrained the development of EEG-based deep models. Obtaining EEG annotations is difficult that requires domain experts to guide collection and labeling, and the variability of EEG signals among different subjects causes significant label shifts. To solve the above challenges, self-supervised learning (SSL) has been proposed to extract representations from unlabeled samples through well-designed pretext tasks. This paper concentrates on integrating SSL frameworks with temporal EEG signals to achieve efficient representation and proposes a systematic review of the SSL for EEG signals. In this paper, 1) we introduce the concept and theory of self-supervised learning and typical SSL frameworks. 2) We provide a comprehensive review of SSL for EEG analysis, including taxonomy, methodology, and technique details of the existing EEG-based SSL frameworks, and discuss the difference between these methods. 3) We investigate the adaptation of the SSL approach to various downstream tasks, including the task description and related benchmark datasets. 4) Finally, we discuss the potential directions for future SSL-EEG research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge