Min He
StarWhisper Telescope: Agent-Based Observation Assistant System to Approach AI Astrophysicist
Dec 09, 2024



Abstract:With the rapid advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs), LLM-based agents have introduced convenient and user-friendly methods for leveraging tools across various domains. In the field of astronomical observation, the construction of new telescopes has significantly increased astronomers' workload. Deploying LLM-powered agents can effectively alleviate this burden and reduce the costs associated with training personnel. Within the Nearby Galaxy Supernovae Survey (NGSS) project, which encompasses eight telescopes across three observation sites, aiming to find the transients from the galaxies in 50 mpc, we have developed the \textbf{StarWhisper Telescope System} to manage the entire observation process. This system automates tasks such as generating observation lists, conducting observations, analyzing data, and providing feedback to the observer. Observation lists are customized for different sites and strategies to ensure comprehensive coverage of celestial objects. After manual verification, these lists are uploaded to the telescopes via the agents in the system, which initiates observations upon neutral language. The observed images are analyzed in real-time, and the transients are promptly communicated to the observer. The agent modifies them into a real-time follow-up observation proposal and send to the Xinglong observatory group chat, then add them to the next-day observation lists. Additionally, the integration of AI agents within the system provides online accessibility, saving astronomers' time and encouraging greater participation from amateur astronomers in the NGSS project.
M4: Multi-Proxy Multi-Gate Mixture of Experts Network for Multiple Instance Learning in Histopathology Image Analysis
Jul 24, 2024



Abstract:Multiple instance learning (MIL) has been successfully applied for whole slide images (WSIs) analysis in computational pathology, enabling a wide range of prediction tasks from tumor subtyping to inferring genetic mutations and multi-omics biomarkers. However, existing MIL methods predominantly focus on single-task learning, resulting in not only overall low efficiency but also the overlook of inter-task relatedness. To address these issues, we proposed an adapted architecture of Multi-gate Mixture-of-experts with Multi-proxy for Multiple instance learning (M4), and applied this framework for simultaneous prediction of multiple genetic mutations from WSIs. The proposed M4 model has two main innovations: (1) utilizing a mixture of experts with multiple gating strategies for multi-genetic mutation prediction on a single pathological slide; (2) constructing multi-proxy expert network and gate network for comprehensive and effective modeling of pathological image information. Our model achieved significant improvements across five tested TCGA datasets in comparison to current state-of-the-art single-task methods. The code is available at:https://github.com/Bigyehahaha/M4.
Hypergraph Multi-modal Large Language Model: Exploiting EEG and Eye-tracking Modalities to Evaluate Heterogeneous Responses for Video Understanding
Jul 11, 2024



Abstract:Understanding of video creativity and content often varies among individuals, with differences in focal points and cognitive levels across different ages, experiences, and genders. There is currently a lack of research in this area, and most existing benchmarks suffer from several drawbacks: 1) a limited number of modalities and answers with restrictive length; 2) the content and scenarios within the videos are excessively monotonous, transmitting allegories and emotions that are overly simplistic. To bridge the gap to real-world applications, we introduce a large-scale \textbf{S}ubjective \textbf{R}esponse \textbf{I}ndicators for \textbf{A}dvertisement \textbf{V}ideos dataset, namely SRI-ADV. Specifically, we collected real changes in Electroencephalographic (EEG) and eye-tracking regions from different demographics while they viewed identical video content. Utilizing this multi-modal dataset, we developed tasks and protocols to analyze and evaluate the extent of cognitive understanding of video content among different users. Along with the dataset, we designed a \textbf{H}ypergraph \textbf{M}ulti-modal \textbf{L}arge \textbf{L}anguage \textbf{M}odel (HMLLM) to explore the associations among different demographics, video elements, EEG and eye-tracking indicators. HMLLM could bridge semantic gaps across rich modalities and integrate information beyond different modalities to perform logical reasoning. Extensive experimental evaluations on SRI-ADV and other additional video-based generative performance benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. The codes and dataset will be released at \url{https://github.com/suay1113/HMLLM}.
BatmanNet: Bi-branch Masked Graph Transformer Autoencoder for Molecular Representation
Nov 29, 2022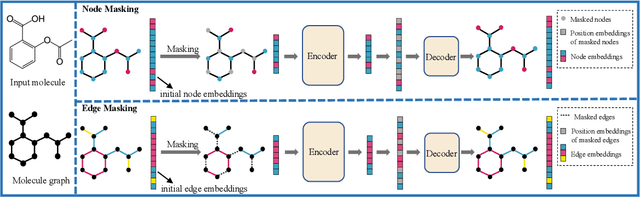
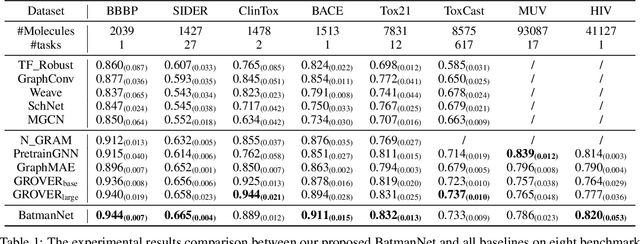
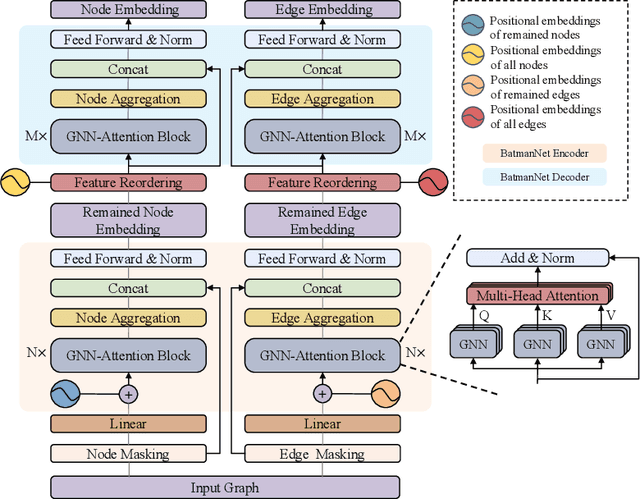
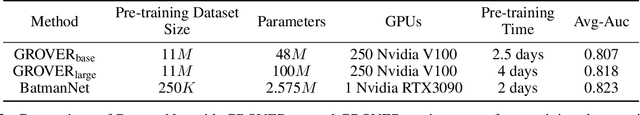
Abstract:Although substantial efforts have been made using graph neural networks (GNNs) for AI-driven drug discovery (AIDD), effective molecular representation learning remains an open challenge, especially in the case of insufficient labeled molecules. Recent studies suggest that big GNN models pre-trained by self-supervised learning on unlabeled datasets enable better transfer performance in downstream molecular property prediction tasks. However, they often require large-scale datasets and considerable computational resources, which is time-consuming, computationally expensive, and environmentally unfriendly. To alleviate these limitations, we propose a novel pre-training model for molecular representation learning, Bi-branch Masked Graph Transformer Autoencoder (BatmanNet). BatmanNet features two tailored and complementary graph autoencoders to reconstruct the missing nodes and edges from a masked molecular graph. To our surprise, BatmanNet discovered that the highly masked proportion (60%) of the atoms and bonds achieved the best performance. We further propose an asymmetric graph-based encoder-decoder architecture for either nodes and edges, where a transformer-based encoder only takes the visible subset of nodes or edges, and a lightweight decoder reconstructs the original molecule from the latent representation and mask tokens. With this simple yet effective asymmetrical design, our BatmanNet can learn efficiently even from a much smaller-scale unlabeled molecular dataset to capture the underlying structural and semantic information, overcoming a major limitation of current deep neural networks for molecular representation learning. For instance, using only 250K unlabelled molecules as pre-training data, our BatmanNet with 2.575M parameters achieves a 0.5% improvement on the average AUC compared with the current state-of-the-art method with 100M parameters pre-trained on 11M molecules.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge