Dialog Act Classification
Papers and Code
Grounding is All You Need? Dual Temporal Grounding for Video Dialog
Oct 08, 2024
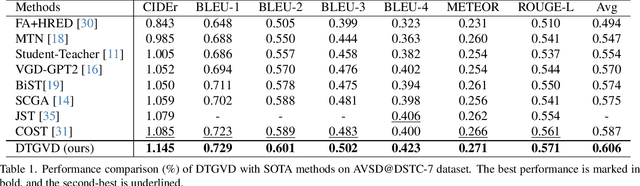
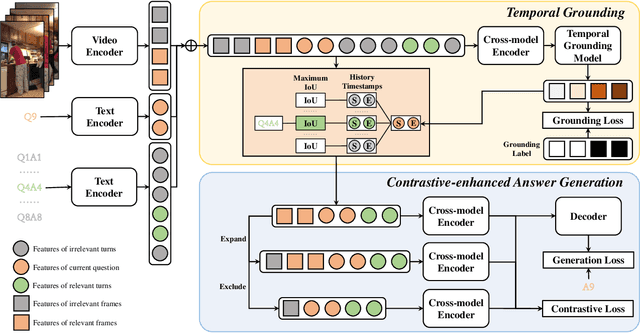
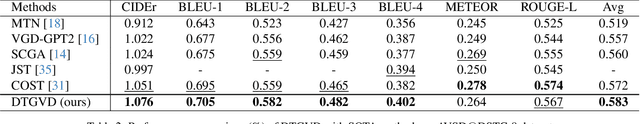
In the realm of video dialog response generation, the understanding of video content and the temporal nuances of conversation history are paramount. While a segment of current research leans heavily on large-scale pretrained visual-language models and often overlooks temporal dynamics, another delves deep into spatial-temporal relationships within videos but demands intricate object trajectory pre-extractions and sidelines dialog temporal dynamics. This paper introduces the Dual Temporal Grounding-enhanced Video Dialog model (DTGVD), strategically designed to merge the strengths of both dominant approaches. It emphasizes dual temporal relationships by predicting dialog turn-specific temporal regions, filtering video content accordingly, and grounding responses in both video and dialog contexts. One standout feature of DTGVD is its heightened attention to chronological interplay. By recognizing and acting upon the dependencies between different dialog turns, it captures more nuanced conversational dynamics. To further bolster the alignment between video and dialog temporal dynamics, we've implemented a list-wise contrastive learning strategy. Within this framework, accurately grounded turn-clip pairings are designated as positive samples, while less precise pairings are categorized as negative. This refined classification is then funneled into our holistic end-to-end response generation mechanism. Evaluations using AVSD@DSTC-7 and AVSD@DSTC-8 datasets underscore the superiority of our methodology.
TOD-Flow: Modeling the Structure of Task-Oriented Dialogues
Dec 07, 2023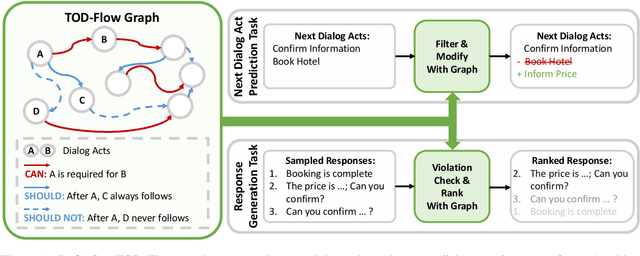
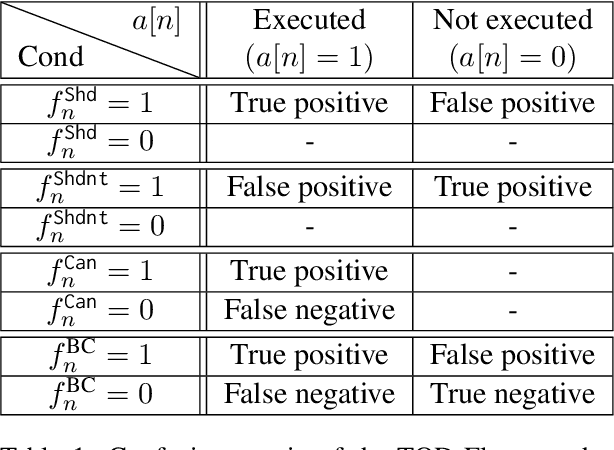
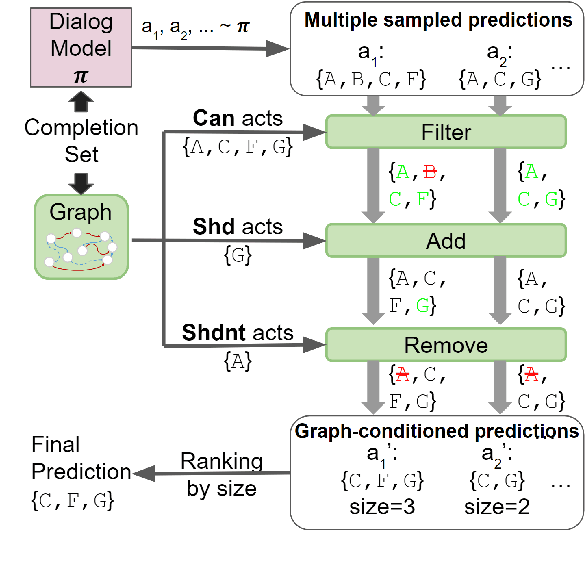
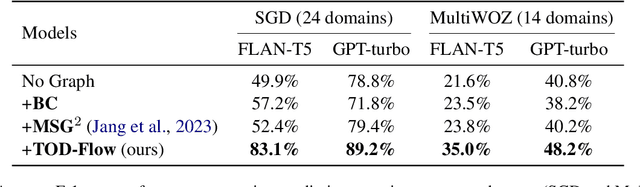
Task-Oriented Dialogue (TOD) systems have become crucial components in interactive artificial intelligence applications. While recent advances have capitalized on pre-trained language models (PLMs), they exhibit limitations regarding transparency and controllability. To address these challenges, we propose a novel approach focusing on inferring the TOD-Flow graph from dialogue data annotated with dialog acts, uncovering the underlying task structure in the form of a graph. The inferred TOD-Flow graph can be easily integrated with any dialogue model to improve its prediction performance, transparency, and controllability. Our TOD-Flow graph learns what a model can, should, and should not predict, effectively reducing the search space and providing a rationale for the model's prediction. We show that the proposed TOD-Flow graph better resembles human-annotated graphs compared to prior approaches. Furthermore, when combined with several dialogue policies and end-to-end dialogue models, we demonstrate that our approach significantly improves dialog act classification and end-to-end response generation performance in the MultiWOZ and SGD benchmarks. Code available at: https://github.com/srsohn/TOD-Flow
A Bi-directional Multi-hop Inference Model for Joint Dialog Sentiment Classification and Act Recognition
Aug 12, 2023



The joint task of Dialog Sentiment Classification (DSC) and Act Recognition (DAR) aims to predict the sentiment label and act label for each utterance in a dialog simultaneously. However, current methods encode the dialog context in only one direction, which limits their ability to thoroughly comprehend the context. Moreover, these methods overlook the explicit correlations between sentiment and act labels, which leads to an insufficient ability to capture rich sentiment and act clues and hinders effective and accurate reasoning. To address these issues, we propose a Bi-directional Multi-hop Inference Model (BMIM) that leverages a feature selection network and a bi-directional multi-hop inference network to iteratively extract and integrate rich sentiment and act clues in a bi-directional manner. We also employ contrastive learning and dual learning to explicitly model the correlations of sentiment and act labels. Our experiments on two widely-used datasets show that BMIM outperforms state-of-the-art baselines by at least 2.6% on F1 score in DAR and 1.4% on F1 score in DSC. Additionally, Our proposed model not only improves the performance but also enhances the interpretability of the joint sentiment and act prediction task.
InterroLang: Exploring NLP Models and Datasets through Dialogue-based Explanations
Oct 23, 2023While recently developed NLP explainability methods let us open the black box in various ways (Madsen et al., 2022), a missing ingredient in this endeavor is an interactive tool offering a conversational interface. Such a dialogue system can help users explore datasets and models with explanations in a contextualized manner, e.g. via clarification or follow-up questions, and through a natural language interface. We adapt the conversational explanation framework TalkToModel (Slack et al., 2022) to the NLP domain, add new NLP-specific operations such as free-text rationalization, and illustrate its generalizability on three NLP tasks (dialogue act classification, question answering, hate speech detection). To recognize user queries for explanations, we evaluate fine-tuned and few-shot prompting models and implement a novel Adapter-based approach. We then conduct two user studies on (1) the perceived correctness and helpfulness of the dialogues, and (2) the simulatability, i.e. how objectively helpful dialogical explanations are for humans in figuring out the model's predicted label when it's not shown. We found rationalization and feature attribution were helpful in explaining the model behavior. Moreover, users could more reliably predict the model outcome based on an explanation dialogue rather than one-off explanations.
D-CALM: A Dynamic Clustering-based Active Learning Approach for Mitigating Bias
May 26, 2023
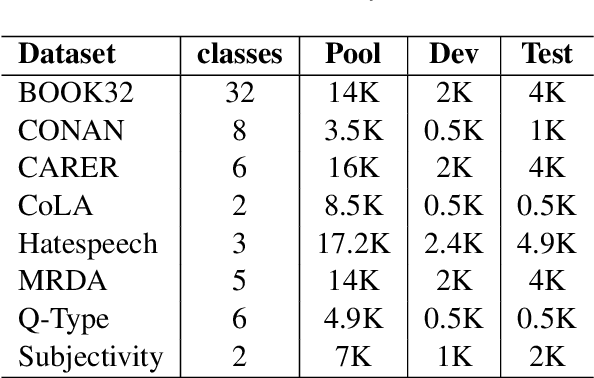
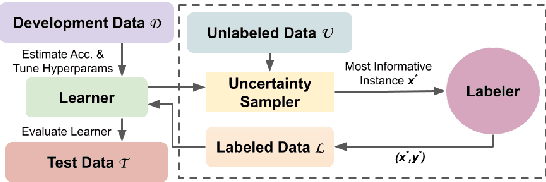
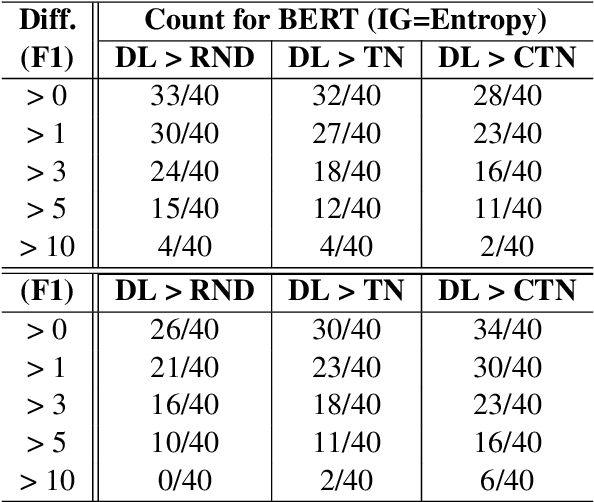
Despite recent advancements, NLP models continue to be vulnerable to bias. This bias often originates from the uneven distribution of real-world data and can propagate through the annotation process. Escalated integration of these models in our lives calls for methods to mitigate bias without overbearing annotation costs. While active learning (AL) has shown promise in training models with a small amount of annotated data, AL's reliance on the model's behavior for selective sampling can lead to an accumulation of unwanted bias rather than bias mitigation. However, infusing clustering with AL can overcome the bias issue of both AL and traditional annotation methods while exploiting AL's annotation efficiency. In this paper, we propose a novel adaptive clustering-based active learning algorithm, D-CALM, that dynamically adjusts clustering and annotation efforts in response to an estimated classifier error-rate. Experiments on eight datasets for a diverse set of text classification tasks, including emotion, hatespeech, dialog act, and book type detection, demonstrate that our proposed algorithm significantly outperforms baseline AL approaches with both pretrained transformers and traditional Support Vector Machines. D-CALM showcases robustness against different measures of information gain and, as evident from our analysis of label and error distribution, can significantly reduce unwanted model bias.
SLUE Phase-2: A Benchmark Suite of Diverse Spoken Language Understanding Tasks
Dec 20, 2022Spoken language understanding (SLU) tasks have been studied for many decades in the speech research community, but have not received as much attention as lower-level tasks like speech and speaker recognition. In particular, there are not nearly as many SLU task benchmarks, and many of the existing ones use data that is not freely available to all researchers. Recent work has begun to introduce such benchmark datasets for several tasks. In this work, we introduce several new annotated SLU benchmark tasks based on freely available speech data, which complement existing benchmarks and address gaps in the SLU evaluation landscape. We contribute four tasks: question answering and summarization involve inference over longer speech sequences; named entity localization addresses the speech-specific task of locating the targeted content in the signal; dialog act classification identifies the function of a given speech utterance. We follow the blueprint of the Spoken Language Understanding Evaluation (SLUE) benchmark suite. In order to facilitate the development of SLU models that leverage the success of pre-trained speech representations, we will be publishing for each task (i) annotations for a relatively small fine-tuning set, (ii) annotated development and test sets, and (iii) baseline models for easy reproducibility and comparisons. In this work, we present the details of data collection and annotation and the performance of the baseline models. We also perform sensitivity analysis of pipeline models' performance (speech recognizer + text model) to the speech recognition accuracy, using more than 20 state-of-the-art speech recognition models.
A Universality-Individuality Integration Model for Dialog Act Classification
Apr 13, 2022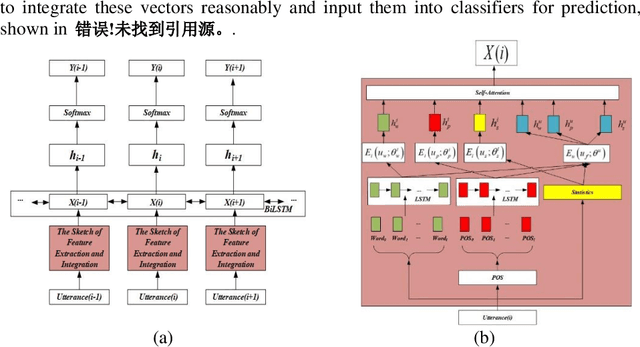

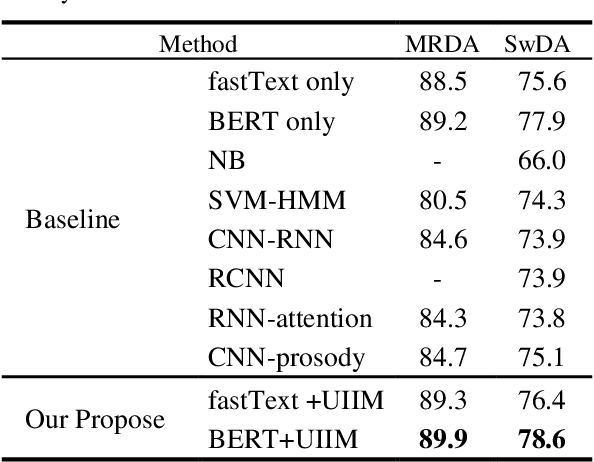
Dialog Act (DA) reveals the general intent of the speaker utterance in a conversation. Accurately predicting DAs can greatly facilitate the development of dialog agents. Although researchers have done extensive research on dialog act classification, the feature information of classification has not been fully considered. This paper suggests that word cues, part-of-speech cues and statistical cues can complement each other to improve the basis for recognition. In addition, the different types of the three lead to the diversity of their distribution forms, which hinders the mining of feature information. To solve this problem, we propose a novel model based on universality and individuality strategies, called Universality-Individuality Integration Model (UIIM). UIIM not only deepens the connection between the clues by learning universality, but also utilizes the learning of individuality to capture the characteristics of the clues themselves. Experiments were made over two most popular benchmark data sets SwDA and MRDA for dialogue act classification, and the results show that extracting the universalities and individualities between cues can more fully excavate the hidden information in the utterance, and improve the accuracy of automatic dialogue act recognition.
NatCS: Eliciting Natural Customer Support Dialogues
May 04, 2023



Despite growing interest in applications based on natural customer support conversations, there exist remarkably few publicly available datasets that reflect the expected characteristics of conversations in these settings. Existing task-oriented dialogue datasets, which were collected to benchmark dialogue systems mainly in written human-to-bot settings, are not representative of real customer support conversations and do not provide realistic benchmarks for systems that are applied to natural data. To address this gap, we introduce NatCS, a multi-domain collection of spoken customer service conversations. We describe our process for collecting synthetic conversations between customers and agents based on natural language phenomena observed in real conversations. Compared to previous dialogue datasets, the conversations collected with our approach are more representative of real human-to-human conversations along multiple metrics. Finally, we demonstrate potential uses of NatCS, including dialogue act classification and intent induction from conversations as potential applications, showing that dialogue act annotations in NatCS provide more effective training data for modeling real conversations compared to existing synthetic written datasets. We publicly release NatCS to facilitate research in natural dialog systems
Relational Temporal Graph Reasoning for Dual-task Dialogue Language Understanding
Jun 15, 2023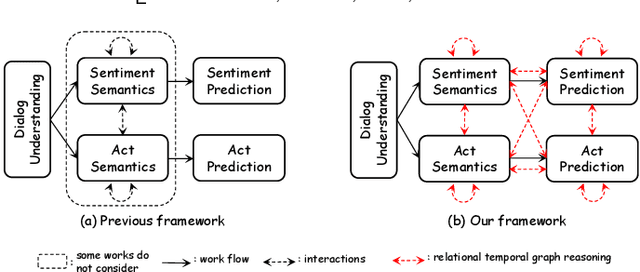
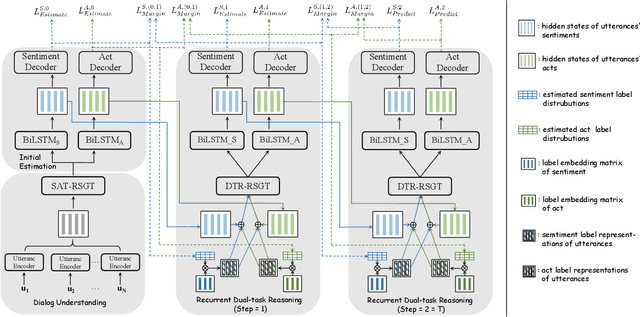
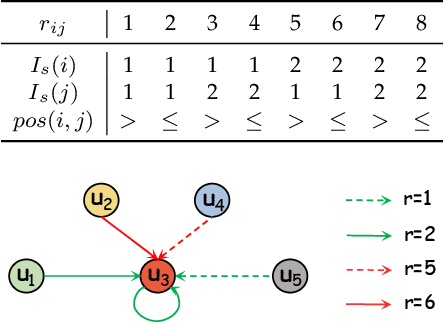
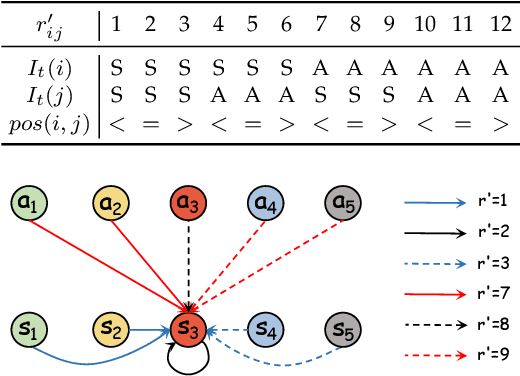
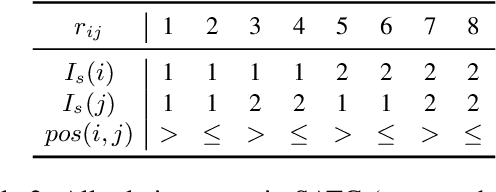
Dual-task dialog language understanding aims to tackle two correlative dialog language understanding tasks simultaneously via leveraging their inherent correlations. In this paper, we put forward a new framework, whose core is relational temporal graph reasoning.We propose a speaker-aware temporal graph (SATG) and a dual-task relational temporal graph (DRTG) to facilitate relational temporal modeling in dialog understanding and dual-task reasoning. Besides, different from previous works that only achieve implicit semantics-level interactions, we propose to model the explicit dependencies via integrating prediction-level interactions. To implement our framework, we first propose a novel model Dual-tAsk temporal Relational rEcurrent Reasoning network (DARER), which first generates the context-, speaker- and temporal-sensitive utterance representations through relational temporal modeling of SATG, then conducts recurrent dual-task relational temporal graph reasoning on DRTG, in which process the estimated label distributions act as key clues in prediction-level interactions. And the relational temporal modeling in DARER is achieved by relational convolutional networks (RGCNs). Then we further propose Relational Temporal Transformer (ReTeFormer), which achieves fine-grained relational temporal modeling via Relation- and Structure-aware Disentangled Multi-head Attention. Accordingly, we propose DARER with ReTeFormer (DARER2), which adopts two variants of ReTeFormer to achieve the relational temporal modeling of SATG and DTRG, respectively. The extensive experiments on different scenarios verify that our models outperform state-of-the-art models by a large margin. Remarkably, on the dialog sentiment classification task in the Mastodon dataset, DARER and DARER2 gain relative improvements of about 28% and 34% over the previous best model in terms of F1.
DARER: Dual-task Temporal Relational Recurrent Reasoning Network for Joint Dialog Sentiment Classification and Act Recognition
Mar 08, 2022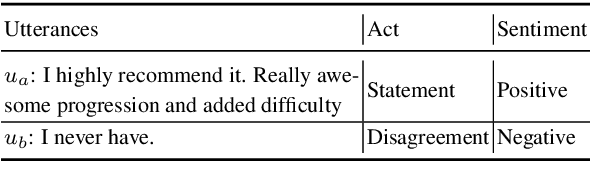
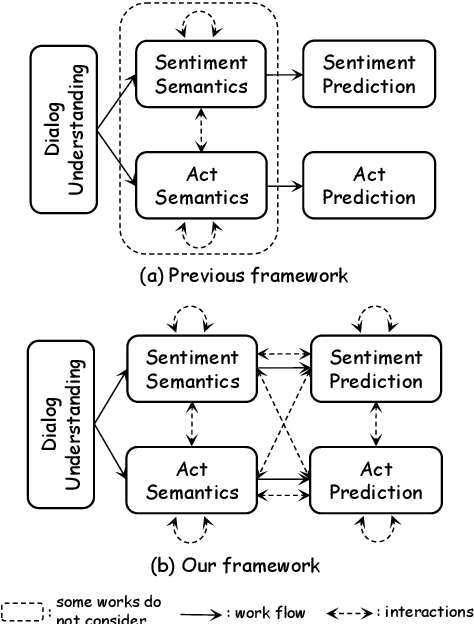
The task of joint dialog sentiment classification (DSC) and act recognition (DAR) aims to simultaneously predict the sentiment label and act label for each utterance in a dialog. In this paper, we put forward a new framework which models the explicit dependencies via integrating \textit{prediction-level interactions} other than semantics-level interactions, more consistent with human intuition. Besides, we propose a speaker-aware temporal graph (SATG) and a dual-task relational temporal graph (DRTG) to introduce \textit{temporal relations} into dialog understanding and dual-task reasoning. To implement our framework, we propose a novel model dubbed DARER, which first generates the context-, speaker- and temporal-sensitive utterance representations via modeling SATG, then conducts recurrent dual-task relational reasoning on DRTG, in which process the estimated label distributions act as key clues in prediction-level interactions. Experiment results show that DARER outperforms existing models by large margins while requiring much less computation resource and costing less training time. Remarkably, on DSC task in Mastodon, DARER gains a relative improvement of about 25% over previous best model in terms of F1, with less than 50% parameters and about only 60% required GPU memory.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge