Suwon Shon
WearVox: An Egocentric Multichannel Voice Assistant Benchmark for Wearables
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:Wearable devices such as AI glasses are transforming voice assistants into always-available, hands-free collaborators that integrate seamlessly with daily life, but they also introduce challenges like egocentric audio affected by motion and noise, rapid micro-interactions, and the need to distinguish device-directed speech from background conversations. Existing benchmarks largely overlook these complexities, focusing instead on clean or generic conversational audio. To bridge this gap, we present WearVox, the first benchmark designed to rigorously evaluate voice assistants in realistic wearable scenarios. WearVox comprises 3,842 multi-channel, egocentric audio recordings collected via AI glasses across five diverse tasks including Search-Grounded QA, Closed-Book QA, Side-Talk Rejection, Tool Calling, and Speech Translation, spanning a wide range of indoor and outdoor environments and acoustic conditions. Each recording is accompanied by rich metadata, enabling nuanced analysis of model performance under real-world constraints. We benchmark leading proprietary and open-source speech Large Language Models (SLLMs) and find that most real-time SLLMs achieve accuracies on WearVox ranging from 29% to 59%, with substantial performance degradation on noisy outdoor audio, underscoring the difficulty and realism of the benchmark. Additionally, we conduct a case study with two new SLLMs that perform inference with single-channel and multi-channel audio, demonstrating that multi-channel audio inputs significantly enhance model robustness to environmental noise and improve discrimination between device-directed and background speech. Our results highlight the critical importance of spatial audio cues for context-aware voice assistants and establish WearVox as a comprehensive testbed for advancing wearable voice AI research.
Multi-Channel Differential ASR for Robust Wearer Speech Recognition on Smart Glasses
Sep 17, 2025Abstract:With the growing adoption of wearable devices such as smart glasses for AI assistants, wearer speech recognition (WSR) is becoming increasingly critical to next-generation human-computer interfaces. However, in real environments, interference from side-talk speech remains a significant challenge to WSR and may cause accumulated errors for downstream tasks such as natural language processing. In this work, we introduce a novel multi-channel differential automatic speech recognition (ASR) method for robust WSR on smart glasses. The proposed system takes differential inputs from different frontends that complement each other to improve the robustness of WSR, including a beamformer, microphone selection, and a lightweight side-talk detection model. Evaluations on both simulated and real datasets demonstrate that the proposed system outperforms the traditional approach, achieving up to an 18.0% relative reduction in word error rate.
Dynamic-SUPERB Phase-2: A Collaboratively Expanding Benchmark for Measuring the Capabilities of Spoken Language Models with 180 Tasks
Nov 08, 2024



Abstract:Multimodal foundation models, such as Gemini and ChatGPT, have revolutionized human-machine interactions by seamlessly integrating various forms of data. Developing a universal spoken language model that comprehends a wide range of natural language instructions is critical for bridging communication gaps and facilitating more intuitive interactions. However, the absence of a comprehensive evaluation benchmark poses a significant challenge. We present Dynamic-SUPERB Phase-2, an open and evolving benchmark for the comprehensive evaluation of instruction-based universal speech models. Building upon the first generation, this second version incorporates 125 new tasks contributed collaboratively by the global research community, expanding the benchmark to a total of 180 tasks, making it the largest benchmark for speech and audio evaluation. While the first generation of Dynamic-SUPERB was limited to classification tasks, Dynamic-SUPERB Phase-2 broadens its evaluation capabilities by introducing a wide array of novel and diverse tasks, including regression and sequence generation, across speech, music, and environmental audio. Evaluation results indicate that none of the models performed well universally. SALMONN-13B excelled in English ASR, while WavLLM demonstrated high accuracy in emotion recognition, but current models still require further innovations to handle a broader range of tasks. We will soon open-source all task data and the evaluation pipeline.
Speech vs. Transcript: Does It Matter for Human Annotators in Speech Summarization?
Aug 12, 2024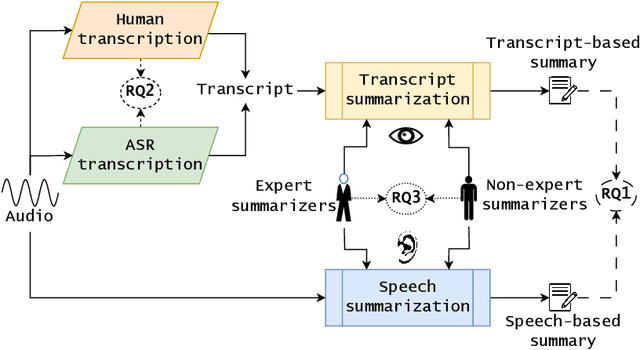
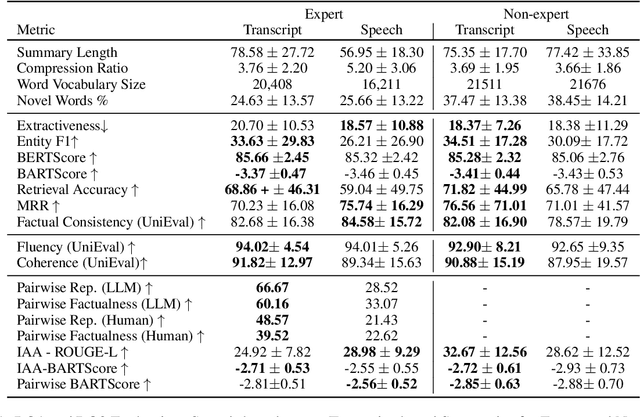
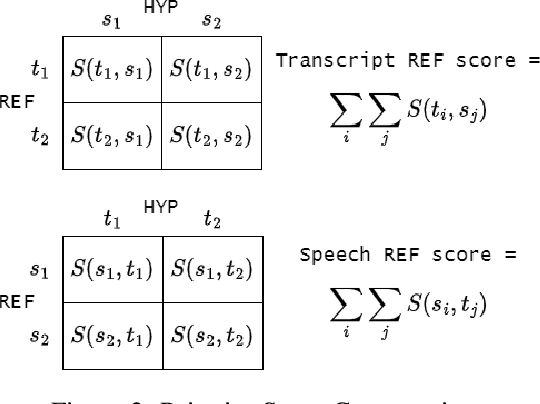
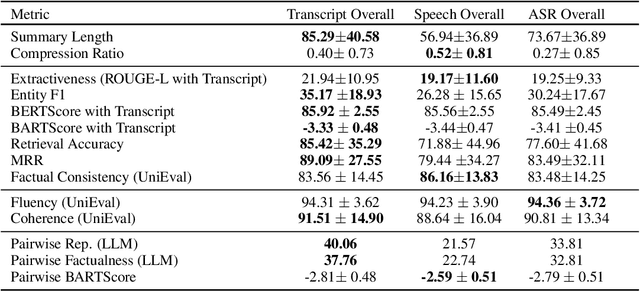
Abstract:Reference summaries for abstractive speech summarization require human annotation, which can be performed by listening to an audio recording or by reading textual transcripts of the recording. In this paper, we examine whether summaries based on annotators listening to the recordings differ from those based on annotators reading transcripts. Using existing intrinsic evaluation based on human evaluation, automatic metrics, LLM-based evaluation, and a retrieval-based reference-free method. We find that summaries are indeed different based on the source modality, and that speech-based summaries are more factually consistent and information-selective than transcript-based summaries. Meanwhile, transcript-based summaries are impacted by recognition errors in the source, and expert-written summaries are more informative and reliable. We make all the collected data and analysis code public(https://github.com/cmu-mlsp/interview_humanssum) to facilitate the reproduction of our work and advance research in this area.
On the Evaluation of Speech Foundation Models for Spoken Language Understanding
Jun 14, 2024Abstract:The Spoken Language Understanding Evaluation (SLUE) suite of benchmark tasks was recently introduced to address the need for open resources and benchmarking of complex spoken language understanding (SLU) tasks, including both classification and sequence generation tasks, on natural speech. The benchmark has demonstrated preliminary success in using pre-trained speech foundation models (SFM) for these SLU tasks. However, the community still lacks a fine-grained understanding of the comparative utility of different SFMs. Inspired by this, we ask: which SFMs offer the most benefits for these complex SLU tasks, and what is the most effective approach for incorporating these SFMs? To answer this, we perform an extensive evaluation of multiple supervised and self-supervised SFMs using several evaluation protocols: (i) frozen SFMs with a lightweight prediction head, (ii) frozen SFMs with a complex prediction head, and (iii) fine-tuned SFMs with a lightweight prediction head. Although the supervised SFMs are pre-trained on much more speech recognition data (with labels), they do not always outperform self-supervised SFMs; the latter tend to perform at least as well as, and sometimes better than, supervised SFMs, especially on the sequence generation tasks in SLUE. While there is no universally optimal way of incorporating SFMs, the complex prediction head gives the best performance for most tasks, although it increases the inference time. We also introduce an open-source toolkit and performance leaderboard, SLUE-PERB, for these tasks and modeling strategies.
DiscreteSLU: A Large Language Model with Self-Supervised Discrete Speech Units for Spoken Language Understanding
Jun 13, 2024



Abstract:The integration of pre-trained text-based large language models (LLM) with speech input has enabled instruction-following capabilities for diverse speech tasks. This integration requires the use of a speech encoder, a speech adapter, and an LLM, trained on diverse tasks. We propose the use of discrete speech units (DSU), rather than continuous-valued speech encoder outputs, that are converted to the LLM token embedding space using the speech adapter. We generate DSU using a self-supervised speech encoder followed by k-means clustering. The proposed model shows robust performance on speech inputs from seen/unseen domains and instruction-following capability in spoken question answering. We also explore various types of DSU extracted from different layers of the self-supervised speech encoder, as well as Mel frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCC). Our findings suggest that the ASR task and datasets are not crucial in instruction-tuning for spoken question answering tasks.
Improving ASR Contextual Biasing with Guided Attention
Jan 16, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we propose a Guided Attention (GA) auxiliary training loss, which improves the effectiveness and robustness of automatic speech recognition (ASR) contextual biasing without introducing additional parameters. A common challenge in previous literature is that the word error rate (WER) reduction brought by contextual biasing diminishes as the number of bias phrases increases. To address this challenge, we employ a GA loss as an additional training objective besides the Transducer loss. The proposed GA loss aims to teach the cross attention how to align bias phrases with text tokens or audio frames. Compared to studies with similar motivations, the proposed loss operates directly on the cross attention weights and is easier to implement. Through extensive experiments based on Conformer Transducer with Contextual Adapter, we demonstrate that the proposed method not only leads to a lower WER but also retains its effectiveness as the number of bias phrases increases. Specifically, the GA loss decreases the WER of rare vocabularies by up to 19.2% on LibriSpeech compared to the contextual biasing baseline, and up to 49.3% compared to a vanilla Transducer.
Generative Context-aware Fine-tuning of Self-supervised Speech Models
Dec 15, 2023



Abstract:When performing tasks like automatic speech recognition or spoken language understanding for a given utterance, access to preceding text or audio provides contextual information can improve performance. Considering the recent advances in generative large language models (LLM), we hypothesize that an LLM could generate useful context information using the preceding text. With appropriate prompts, LLM could generate a prediction of the next sentence or abstractive text like titles or topics. In this paper, we study the use of LLM-generated context information and propose an approach to distill the generated information during fine-tuning of self-supervised speech models, which we refer to as generative context-aware fine-tuning. This approach allows the fine-tuned model to make improved predictions without access to the true surrounding segments or to the LLM at inference time, while requiring only a very small additional context module. We evaluate the proposed approach using the SLUE and Libri-light benchmarks for several downstream tasks: automatic speech recognition, named entity recognition, and sentiment analysis. The results show that generative context-aware fine-tuning outperforms a context injection fine-tuning approach that accesses the ground-truth previous text, and is competitive with a generative context injection fine-tuning approach that requires the LLM at inference time.
A Comparative Study on E-Branchformer vs Conformer in Speech Recognition, Translation, and Understanding Tasks
May 18, 2023Abstract:Conformer, a convolution-augmented Transformer variant, has become the de facto encoder architecture for speech processing due to its superior performance in various tasks, including automatic speech recognition (ASR), speech translation (ST) and spoken language understanding (SLU). Recently, a new encoder called E-Branchformer has outperformed Conformer in the LibriSpeech ASR benchmark, making it promising for more general speech applications. This work compares E-Branchformer and Conformer through extensive experiments using different types of end-to-end sequence-to-sequence models. Results demonstrate that E-Branchformer achieves comparable or better performance than Conformer in almost all evaluation sets across 15 ASR, 2 ST, and 3 SLU benchmarks, while being more stable during training. We will release our training configurations and pre-trained models for reproducibility, which can benefit the speech community.
SLUE Phase-2: A Benchmark Suite of Diverse Spoken Language Understanding Tasks
Dec 20, 2022Abstract:Spoken language understanding (SLU) tasks have been studied for many decades in the speech research community, but have not received as much attention as lower-level tasks like speech and speaker recognition. In particular, there are not nearly as many SLU task benchmarks, and many of the existing ones use data that is not freely available to all researchers. Recent work has begun to introduce such benchmark datasets for several tasks. In this work, we introduce several new annotated SLU benchmark tasks based on freely available speech data, which complement existing benchmarks and address gaps in the SLU evaluation landscape. We contribute four tasks: question answering and summarization involve inference over longer speech sequences; named entity localization addresses the speech-specific task of locating the targeted content in the signal; dialog act classification identifies the function of a given speech utterance. We follow the blueprint of the Spoken Language Understanding Evaluation (SLUE) benchmark suite. In order to facilitate the development of SLU models that leverage the success of pre-trained speech representations, we will be publishing for each task (i) annotations for a relatively small fine-tuning set, (ii) annotated development and test sets, and (iii) baseline models for easy reproducibility and comparisons. In this work, we present the details of data collection and annotation and the performance of the baseline models. We also perform sensitivity analysis of pipeline models' performance (speech recognizer + text model) to the speech recognition accuracy, using more than 20 state-of-the-art speech recognition models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge