Zhi Yang
Chain of Mindset: Reasoning with Adaptive Cognitive Modes
Feb 10, 2026Abstract:Human problem-solving is never the repetition of a single mindset, by which we mean a distinct mode of cognitive processing. When tackling a specific task, we do not rely on a single mindset; instead, we integrate multiple mindsets within the single solution process. However, existing LLM reasoning methods fall into a common trap: they apply the same fixed mindset across all steps, overlooking that different stages of solving the same problem require fundamentally different mindsets. This single-minded assumption prevents models from reaching the next level of intelligence. To address this limitation, we propose Chain of Mindset (CoM), a training-free agentic framework that enables step-level adaptive mindset orchestration. CoM decomposes reasoning into four functionally heterogeneous mindsets: Spatial, Convergent, Divergent, and Algorithmic. A Meta-Agent dynamically selects the optimal mindset based on the evolving reasoning state, while a bidirectional Context Gate filters cross-module information flow to maintain effectiveness and efficiency. Experiments across six challenging benchmarks spanning mathematics, code generation, scientific QA, and spatial reasoning demonstrate that CoM achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming the strongest baseline by 4.96\% and 4.72\% in overall accuracy on Qwen3-VL-32B-Instruct and Gemini-2.0-Flash, while balancing reasoning efficiency. Our code is publicly available at \href{https://github.com/QuantaAlpha/chain-of-mindset}{https://github.com/QuantaAlpha/chain-of-mindset}.
QuantaAlpha: An Evolutionary Framework for LLM-Driven Alpha Mining
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:Financial markets are noisy and non-stationary, making alpha mining highly sensitive to noise in backtesting results and sudden market regime shifts. While recent agentic frameworks improve alpha mining automation, they often lack controllable multi-round search and reliable reuse of validated experience. To address these challenges, we propose QuantaAlpha, an evolutionary alpha mining framework that treats each end-to-end mining run as a trajectory and improves factors through trajectory-level mutation and crossover operations. QuantaAlpha localizes suboptimal steps in each trajectory for targeted revision and recombines complementary high-reward segments to reuse effective patterns, enabling structured exploration and refinement across mining iterations. During factor generation, QuantaAlpha enforces semantic consistency across the hypothesis, factor expression, and executable code, while constraining the complexity and redundancy of the generated factor to mitigate crowding. Extensive experiments on the China Securities Index 300 (CSI 300) demonstrate consistent gains over strong baseline models and prior agentic systems. When utilizing GPT-5.2, QuantaAlpha achieves an Information Coefficient (IC) of 0.1501, with an Annualized Rate of Return (ARR) of 27.75% and a Maximum Drawdown (MDD) of 7.98%. Moreover, factors mined on CSI 300 transfer effectively to the China Securities Index 500 (CSI 500) and the Standard & Poor's 500 Index (S&P 500), delivering 160% and 137% cumulative excess return over four years, respectively, which indicates strong robustness of QuantaAlpha under market distribution shifts.
Spider-Sense: Intrinsic Risk Sensing for Efficient Agent Defense with Hierarchical Adaptive Screening
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) evolve into autonomous agents, their real-world applicability has expanded significantly, accompanied by new security challenges. Most existing agent defense mechanisms adopt a mandatory checking paradigm, in which security validation is forcibly triggered at predefined stages of the agent lifecycle. In this work, we argue that effective agent security should be intrinsic and selective rather than architecturally decoupled and mandatory. We propose Spider-Sense framework, an event-driven defense framework based on Intrinsic Risk Sensing (IRS), which allows agents to maintain latent vigilance and trigger defenses only upon risk perception. Once triggered, the Spider-Sense invokes a hierarchical defence mechanism that trades off efficiency and precision: it resolves known patterns via lightweight similarity matching while escalating ambiguous cases to deep internal reasoning, thereby eliminating reliance on external models. To facilitate rigorous evaluation, we introduce S$^2$Bench, a lifecycle-aware benchmark featuring realistic tool execution and multi-stage attacks. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Spider-Sense achieves competitive or superior defense performance, attaining the lowest Attack Success Rate (ASR) and False Positive Rate (FPR), with only a marginal latency overhead of 8.3\%.
BinaryDemoire: Moiré-Aware Binarization for Image Demoiréing
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Image demoiréing aims to remove structured moiré artifacts in recaptured imagery, where degradations are highly frequency-dependent and vary across scales and directions. While recent deep networks achieve high-quality restoration, their full-precision designs remain costly for deployment. Binarization offers an extreme compression regime by quantizing both activations and weights to 1-bit. Yet, it has been rarely studied for demoiréing and performs poorly when naively applied. In this work, we propose BinaryDemoire, a binarized demoiréing framework that explicitly accommodates the frequency structure of moiré degradations. First, we introduce a moiré-aware binary gate (MABG) that extracts lightweight frequency descriptors together with activation statistics. It predicts channel-wise gating coefficients to condition the aggregation of binary convolution responses. Second, we design a shuffle-grouped residual adapter (SGRA) that performs structured sparse shortcut alignment. It further integrates interleaved mixing to promote information exchange across different channel partitions. Extensive experiments on four benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed BinaryDemoire surpasses current binarization methods. Code: https://github.com/zhengchen1999/BinaryDemoire.
EvoFSM: Controllable Self-Evolution for Deep Research with Finite State Machines
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:While LLM-based agents have shown promise for deep research, most existing approaches rely on fixed workflows that struggle to adapt to real-world, open-ended queries. Recent work therefore explores self-evolution by allowing agents to rewrite their own code or prompts to improve problem-solving ability, but unconstrained optimization often triggers instability, hallucinations, and instruction drift. We propose EvoFSM, a structured self-evolving framework that achieves both adaptability and control by evolving an explicit Finite State Machine (FSM) instead of relying on free-form rewriting. EvoFSM decouples the optimization space into macroscopic Flow (state-transition logic) and microscopic Skill (state-specific behaviors), enabling targeted improvements under clear behavioral boundaries. Guided by a critic mechanism, EvoFSM refines the FSM through a small set of constrained operations, and further incorporates a self-evolving memory that distills successful trajectories as reusable priors and failure patterns as constraints for future queries. Extensive evaluations on five multi-hop QA benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of EvoFSM. In particular, EvoFSM reaches 58.0% accuracy on the DeepSearch benchmark. Additional results on interactive decision-making tasks further validate its generalization.
RLPO: Residual Listwise Preference Optimization for Long-Context Review Ranking
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Review ranking is pivotal in e-commerce for prioritizing diagnostic and authentic feedback from the deluge of user-generated content. While large language models have improved semantic assessment, existing ranking paradigms face a persistent trade-off in long-context settings. Pointwise scoring is efficient but often fails to account for list-level interactions, leading to miscalibrated top-$k$ rankings. Listwise approaches can leverage global context, yet they are computationally expensive and become unstable as candidate lists grow. To address this, we propose Residual Listwise Preference Optimization (RLPO), which formulates ranking as listwise representation-level residual correction over a strong pointwise LLM scorer. RLPO first produces calibrated pointwise scores and item representations, then applies a lightweight encoder over the representations to predict listwise score residuals, avoiding full token-level listwise processing. We also introduce a large-scale benchmark for long-context review ranking with human verification. Experiments show RLPO improves NDCG@k over strong pointwise and listwise baselines and remains robust as list length increases.
BizFinBench.v2: A Unified Dual-Mode Bilingual Benchmark for Expert-Level Financial Capability Alignment
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:Large language models have undergone rapid evolution, emerging as a pivotal technology for intelligence in financial operations. However, existing benchmarks are often constrained by pitfalls such as reliance on simulated or general-purpose samples and a focus on singular, offline static scenarios. Consequently, they fail to align with the requirements for authenticity and real-time responsiveness in financial services, leading to a significant discrepancy between benchmark performance and actual operational efficacy. To address this, we introduce BizFinBench.v2, the first large-scale evaluation benchmark grounded in authentic business data from both Chinese and U.S. equity markets, integrating online assessment. We performed clustering analysis on authentic user queries from financial platforms, resulting in eight fundamental tasks and two online tasks across four core business scenarios, totaling 29,578 expert-level Q&A pairs. Experimental results demonstrate that ChatGPT-5 achieves a prominent 61.5% accuracy in main tasks, though a substantial gap relative to financial experts persists; in online tasks, DeepSeek-R1 outperforms all other commercial LLMs. Error analysis further identifies the specific capability deficiencies of existing models within practical financial business contexts. BizFinBench.v2 transcends the limitations of current benchmarks, achieving a business-level deconstruction of LLM financial capabilities and providing a precise basis for evaluating efficacy in the widespread deployment of LLMs within the financial domain. The data and code are available at https://github.com/HiThink-Research/BizFinBench.v2.
RLinf: Flexible and Efficient Large-scale Reinforcement Learning via Macro-to-Micro Flow Transformation
Sep 19, 2025



Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has demonstrated immense potential in advancing artificial general intelligence, agentic intelligence, and embodied intelligence. However, the inherent heterogeneity and dynamicity of RL workflows often lead to low hardware utilization and slow training on existing systems. In this paper, we present RLinf, a high-performance RL training system based on our key observation that the major roadblock to efficient RL training lies in system flexibility. To maximize flexibility and efficiency, RLinf is built atop a novel RL system design paradigm called macro-to-micro flow transformation (M2Flow), which automatically breaks down high-level, easy-to-compose RL workflows at both the temporal and spatial dimensions, and recomposes them into optimized execution flows. Supported by RLinf worker's adaptive communication capability, we devise context switching and elastic pipelining to realize M2Flow transformation, and a profiling-guided scheduling policy to generate optimal execution plans. Extensive evaluations on both reasoning RL and embodied RL tasks demonstrate that RLinf consistently outperforms state-of-the-art systems, achieving 1.1x-2.13x speedup in end-to-end training throughput.
VoxAging: Continuously Tracking Speaker Aging with a Large-Scale Longitudinal Dataset in English and Mandarin
May 27, 2025Abstract:The performance of speaker verification systems is adversely affected by speaker aging. However, due to challenges in data collection, particularly the lack of sustained and large-scale longitudinal data for individuals, research on speaker aging remains difficult. In this paper, we present VoxAging, a large-scale longitudinal dataset collected from 293 speakers (226 English speakers and 67 Mandarin speakers) over several years, with the longest time span reaching 17 years (approximately 900 weeks). For each speaker, the data were recorded at weekly intervals. We studied the phenomenon of speaker aging and its effects on advanced speaker verification systems, analyzed individual speaker aging processes, and explored the impact of factors such as age group and gender on speaker aging research.
ExploreGS: a vision-based low overhead framework for 3D scene reconstruction
May 14, 2025
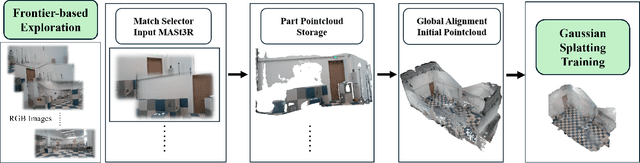


Abstract:This paper proposes a low-overhead, vision-based 3D scene reconstruction framework for drones, named ExploreGS. By using RGB images, ExploreGS replaces traditional lidar-based point cloud acquisition process with a vision model, achieving a high-quality reconstruction at a lower cost. The framework integrates scene exploration and model reconstruction, and leverags a Bag-of-Words(BoW) model to enable real-time processing capabilities, therefore, the 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) training can be executed on-board. Comprehensive experiments in both simulation and real-world environments demonstrate the efficiency and applicability of the ExploreGS framework on resource-constrained devices, while maintaining reconstruction quality comparable to state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge