Zhenwen Li
Data and System Perspectives of Sustainable Artificial Intelligence
Jan 13, 2025Abstract:Sustainable AI is a subfield of AI for concerning developing and using AI systems in ways of aiming to reduce environmental impact and achieve sustainability. Sustainable AI is increasingly important given that training of and inference with AI models such as large langrage models are consuming a large amount of computing power. In this article, we discuss current issues, opportunities and example solutions for addressing these issues, and future challenges to tackle, from the data and system perspectives, related to data acquisition, data processing, and AI model training and inference.
Using LLM to select the right SQL Query from candidates
Jan 04, 2024Abstract:Text-to-SQL models can generate a list of candidate SQL queries, and the best query is often in the candidate list, but not at the top of the list. An effective re-rank method can select the right SQL query from the candidate list and improve the model's performance. Previous studies on code generation automatically generate test cases and use them to re-rank candidate codes. However, automatic test case generation for text-to-SQL is an understudied field. We propose an automatic test case generation method that first generates a database and then uses LLMs to predict the ground truth, which is the expected execution results of the ground truth SQL query on this database. To reduce the difficulty for LLMs to predict, we conduct experiments to search for ways to generate easy databases for LLMs and design easy-to-understand prompts. Based on our test case generation method, we propose a re-rank method to select the right SQL query from the candidate list. Given a candidate list, our method can generate test cases and re-rank the candidate list according to their pass numbers on these test cases and their generation probabilities. The experiment results on the validation dataset of Spider show that the performance of some state-of-the-art models can get a 3.6\% improvement after applying our re-rank method.
Data Transformation to Construct a Dataset for Generating Entity-Relationship Model from Natural Language
Dec 21, 2023Abstract:In order to reduce the manual cost of designing ER models, recent approaches have been proposed to address the task of NL2ERM, i.e., automatically generating entity-relationship (ER) models from natural language (NL) utterances such as software requirements. These approaches are typically rule-based ones, which rely on rigid heuristic rules; these approaches cannot generalize well to various linguistic ways of describing the same requirement. Despite having better generalization capability than rule-based approaches, deep-learning-based models are lacking for NL2ERM due to lacking a large-scale dataset. To address this issue, in this paper, we report our insight that there exists a high similarity between the task of NL2ERM and the increasingly popular task of text-to-SQL, and propose a data transformation algorithm that transforms the existing data of text-to-SQL into the data of NL2ERM. We apply our data transformation algorithm on Spider, one of the most popular text-to-SQL datasets, and we also collect some data entries with different NL types, to obtain a large-scale NL2ERM dataset. Because NL2ERM can be seen as a special information extraction (IE) task, we train two state-of-the-art IE models on our dataset. The experimental results show that both the two models achieve high performance and outperform existing baselines.
AutoShrink: A Topology-aware NAS for Discovering Efficient Neural Architecture
Nov 21, 2019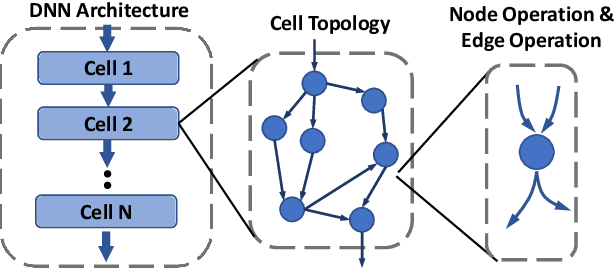
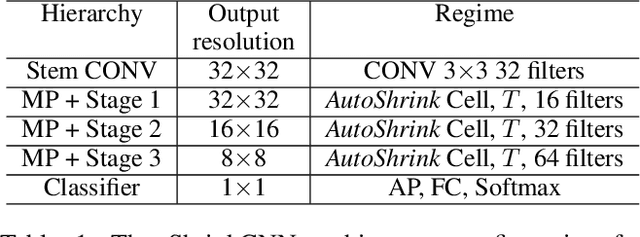
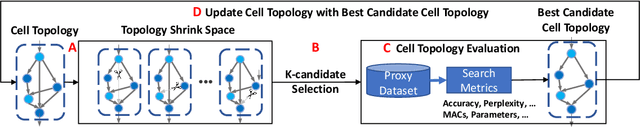
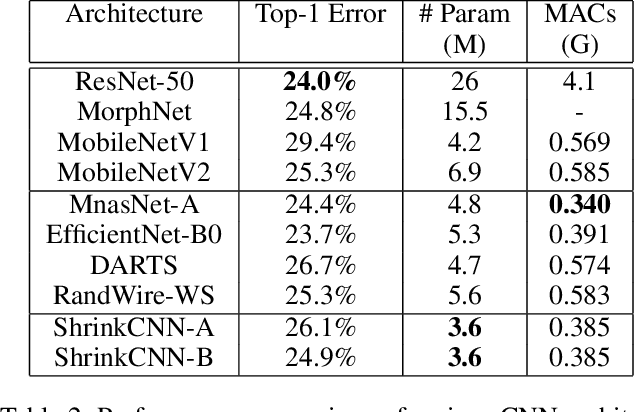
Abstract:Resource is an important constraint when deploying Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) on mobile and edge devices. Existing works commonly adopt the cell-based search approach, which limits the flexibility of network patterns in learned cell structures. Moreover, due to the topology-agnostic nature of existing works, including both cell-based and node-based approaches, the search process is time consuming and the performance of found architecture may be sub-optimal. To address these problems, we propose AutoShrink, a topology-aware Neural Architecture Search(NAS) for searching efficient building blocks of neural architectures. Our method is node-based and thus can learn flexible network patterns in cell structures within a topological search space. Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) are used to abstract DNN architectures and progressively optimize the cell structure through edge shrinking. As the search space intrinsically reduces as the edges are progressively shrunk, AutoShrink explores more flexible search space with even less search time. We evaluate AutoShrink on image classification and language tasks by crafting ShrinkCNN and ShrinkRNN models. ShrinkCNN is able to achieve up to 48% parameter reduction and save 34% Multiply-Accumulates (MACs) on ImageNet-1K with comparable accuracy of state-of-the-art (SOTA) models. Specifically, both ShrinkCNN and ShrinkRNN are crafted within 1.5 GPU hours, which is 7.2x and 6.7x faster than the crafting time of SOTA CNN and RNN models, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge