Maoliang Li
Eric
EaqVLA: Encoding-aligned Quantization for Vision-Language-Action Models
May 27, 2025Abstract:With the development of Embodied Artificial intelligence, the end-to-end control policy such as Vision-Language-Action (VLA) model has become the mainstream. Existing VLA models faces expensive computing/storage cost, which need to be optimized. Quantization is considered as the most effective method which can not only reduce the memory cost but also achieve computation acceleration. However, we find the token alignment of VLA models hinders the application of existing quantization methods. To address this, we proposed an optimized framework called EaqVLA, which apply encoding-aligned quantization to VLA models. Specifically, we propose an complete analysis method to find the misalignment in various granularity. Based on the analysis results, we propose a mixed precision quantization with the awareness of encoding alignment. Experiments shows that the porposed EaqVLA achieves better quantization performance (with the minimal quantization loss for end-to-end action control and xxx times acceleration) than existing quantization methods.
FedHQ: Hybrid Runtime Quantization for Federated Learning
May 17, 2025Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) is a decentralized model training approach that preserves data privacy but struggles with low efficiency. Quantization, a powerful training optimization technique, has been widely explored for integration into FL. However, many studies fail to consider the distinct performance attribution between particular quantization strategies, such as post-training quantization (PTQ) or quantization-aware training (QAT). As a result, existing FL quantization methods rely solely on either PTQ or QAT, optimizing for speed or accuracy while compromising the other. To efficiently accelerate FL and maintain distributed convergence accuracy across various FL settings, this paper proposes a hybrid quantitation approach combining PTQ and QAT for FL systems. We conduct case studies to validate the effectiveness of using hybrid quantization in FL. To solve the difficulty of modeling speed and accuracy caused by device and data heterogeneity, we propose a hardware-related analysis and data-distribution-related analysis to help identify the trade-off boundaries for strategy selection. Based on these, we proposed a novel framework named FedHQ to automatically adopt optimal hybrid strategy allocation for FL systems. Specifically, FedHQ develops a coarse-grained global initialization and fine-grained ML-based adjustment to ensure efficiency and robustness. Experiments show that FedHQ achieves up to 2.47x times training acceleration and up to 11.15% accuracy improvement and negligible extra overhead.
MoQa: Rethinking MoE Quantization with Multi-stage Data-model Distribution Awareness
Mar 27, 2025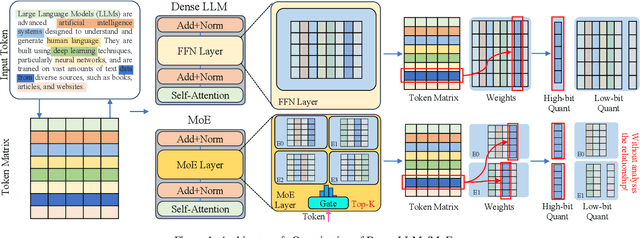
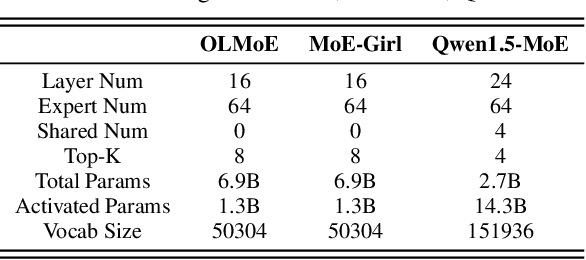
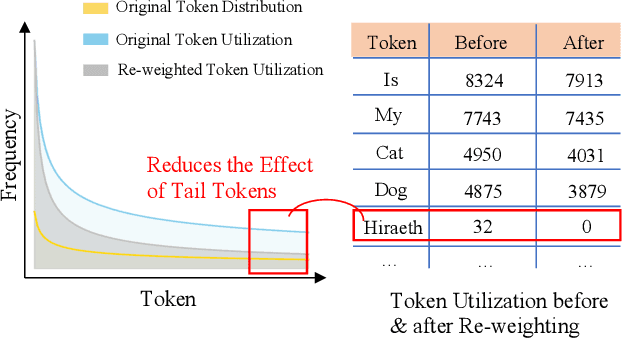
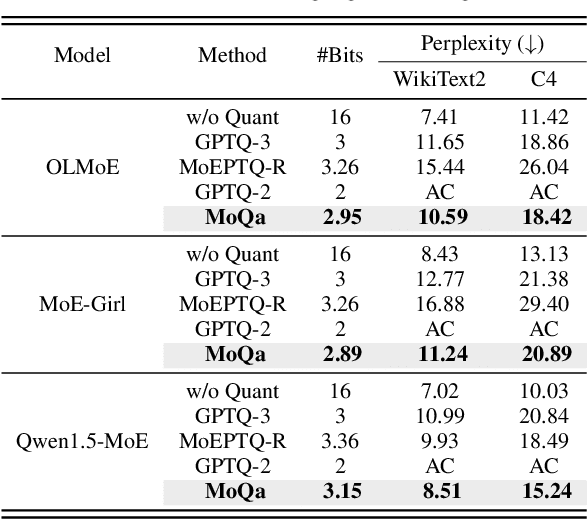
Abstract:With the advances in artificial intelligence, Mix-of-Experts (MoE) has become the main form of Large Language Models (LLMs), and its demand for model compression is increasing. Quantization is an effective method that not only compresses the models but also significantly accelerates their performance. Existing quantization methods have gradually shifted the focus from parameter scaling to the analysis of data distributions. However, their analysis is designed for dense LLMs and relies on the simple one-model-all-data mapping, which is unsuitable for MoEs. This paper proposes a new quantization framework called MoQa. MoQa decouples the data-model distribution complexity of MoEs in multiple analysis stages, quantitively revealing the dynamics during sparse data activation, data-parameter mapping, and inter-expert correlations. Based on these, MoQa identifies particular experts' and parameters' significance with optimal data-model distribution awareness and proposes a series of fine-grained mix-quantization strategies adaptive to various data activation and expert combination scenarios. Moreover, MoQa discusses the limitations of existing quantization and analyzes the impact of each stage analysis, showing novel insights for MoE quantization. Experiments show that MoQa achieves a 1.69~2.18 perplexity decrease in language modeling tasks and a 1.58%~8.91% accuracy improvement in zero-shot inference tasks. We believe MoQa will play a role in future MoE construction, optimization, and compression.
Data and System Perspectives of Sustainable Artificial Intelligence
Jan 13, 2025Abstract:Sustainable AI is a subfield of AI for concerning developing and using AI systems in ways of aiming to reduce environmental impact and achieve sustainability. Sustainable AI is increasingly important given that training of and inference with AI models such as large langrage models are consuming a large amount of computing power. In this article, we discuss current issues, opportunities and example solutions for addressing these issues, and future challenges to tackle, from the data and system perspectives, related to data acquisition, data processing, and AI model training and inference.
Infinite-Dimensional Feature Interaction
May 22, 2024



Abstract:The past neural network design has largely focused on feature representation space dimension and its capacity scaling (e.g., width, depth), but overlooked the feature interaction space scaling. Recent advancements have shown shifted focus towards element-wise multiplication to facilitate higher-dimensional feature interaction space for better information transformation. Despite this progress, multiplications predominantly capture low-order interactions, thus remaining confined to a finite-dimensional interaction space. To transcend this limitation, classic kernel methods emerge as a promising solution to engage features in an infinite-dimensional space. We introduce InfiNet, a model architecture that enables feature interaction within an infinite-dimensional space created by RBF kernel. Our experiments reveal that InfiNet achieves new state-of-the-art, owing to its capability to leverage infinite-dimensional interactions, significantly enhancing model performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge