Yining Shi
Tsinghua University
COME: Adding Scene-Centric Forecasting Control to Occupancy World Model
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:World models are critical for autonomous driving to simulate environmental dynamics and generate synthetic data. Existing methods struggle to disentangle ego-vehicle motion (perspective shifts) from scene evolvement (agent interactions), leading to suboptimal predictions. Instead, we propose to separate environmental changes from ego-motion by leveraging the scene-centric coordinate systems. In this paper, we introduce COME: a framework that integrates scene-centric forecasting Control into the Occupancy world ModEl. Specifically, COME first generates ego-irrelevant, spatially consistent future features through a scene-centric prediction branch, which are then converted into scene condition using a tailored ControlNet. These condition features are subsequently injected into the occupancy world model, enabling more accurate and controllable future occupancy predictions. Experimental results on the nuScenes-Occ3D dataset show that COME achieves consistent and significant improvements over state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods across diverse configurations, including different input sources (ground-truth, camera-based, fusion-based occupancy) and prediction horizons (3s and 8s). For example, under the same settings, COME achieves 26.3% better mIoU metric than DOME and 23.7% better mIoU metric than UniScene. These results highlight the efficacy of disentangled representation learning in enhancing spatio-temporal prediction fidelity for world models. Code and videos will be available at https://github.com/synsin0/COME.
DriveCamSim: Generalizable Camera Simulation via Explicit Camera Modeling for Autonomous Driving
May 26, 2025Abstract:Camera sensor simulation serves as a critical role for autonomous driving (AD), e.g. evaluating vision-based AD algorithms. While existing approaches have leveraged generative models for controllable image/video generation, they remain constrained to generating multi-view video sequences with fixed camera viewpoints and video frequency, significantly limiting their downstream applications. To address this, we present a generalizable camera simulation framework DriveCamSim, whose core innovation lies in the proposed Explicit Camera Modeling (ECM) mechanism. Instead of implicit interaction through vanilla attention, ECM establishes explicit pixel-wise correspondences across multi-view and multi-frame dimensions, decoupling the model from overfitting to the specific camera configurations (intrinsic/extrinsic parameters, number of views) and temporal sampling rates presented in the training data. For controllable generation, we identify the issue of information loss inherent in existing conditional encoding and injection pipelines, proposing an information-preserving control mechanism. This control mechanism not only improves conditional controllability, but also can be extended to be identity-aware to enhance temporal consistency in foreground object rendering. With above designs, our model demonstrates superior performance in both visual quality and controllability, as well as generalization capability across spatial-level (camera parameters variations) and temporal-level (video frame rate variations), enabling flexible user-customizable camera simulation tailored to diverse application scenarios. Code will be avaliable at https://github.com/swc-17/DriveCamSim for facilitating future research.
AgentThink: A Unified Framework for Tool-Augmented Chain-of-Thought Reasoning in Vision-Language Models for Autonomous Driving
May 21, 2025



Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) show promise for autonomous driving, yet their struggle with hallucinations, inefficient reasoning, and limited real-world validation hinders accurate perception and robust step-by-step reasoning. To overcome this, we introduce \textbf{AgentThink}, a pioneering unified framework that, for the first time, integrates Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning with dynamic, agent-style tool invocation for autonomous driving tasks. AgentThink's core innovations include: \textbf{(i) Structured Data Generation}, by establishing an autonomous driving tool library to automatically construct structured, self-verified reasoning data explicitly incorporating tool usage for diverse driving scenarios; \textbf{(ii) A Two-stage Training Pipeline}, employing Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) with Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) to equip VLMs with the capability for autonomous tool invocation; and \textbf{(iii) Agent-style Tool-Usage Evaluation}, introducing a novel multi-tool assessment protocol to rigorously evaluate the model's tool invocation and utilization. Experiments on the DriveLMM-o1 benchmark demonstrate AgentThink significantly boosts overall reasoning scores by \textbf{53.91\%} and enhances answer accuracy by \textbf{33.54\%}, while markedly improving reasoning quality and consistency. Furthermore, ablation studies and robust zero-shot/few-shot generalization experiments across various benchmarks underscore its powerful capabilities. These findings highlight a promising trajectory for developing trustworthy and tool-aware autonomous driving models.
TileLang: A Composable Tiled Programming Model for AI Systems
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Modern AI workloads rely heavily on optimized computing kernels for both training and inference. These AI kernels follow well-defined data-flow patterns, such as moving tiles between DRAM and SRAM and performing a sequence of computations on those tiles. However, writing high-performance kernels remains complex despite the clarity of these patterns. Achieving peak performance requires careful, hardware-centric optimizations to fully leverage modern accelerators. While domain-specific compilers attempt to reduce the burden of writing high-performance kernels, they often struggle with usability and expressiveness gaps. In this paper, we present TileLang, a generalized tiled programming model for more efficient AI Kernel programming. TileLang decouples scheduling space (thread binding, layout, tensorize and pipeline) from dataflow, and encapsulated them as a set of customization annotations and primitives. This approach allows users to focus on the kernel's data-flow itself, while leaving most other optimizations to compilers. We conduct comprehensive experiments on commonly-used devices, across numerous experiments, our evaluation shows that TileLang can achieve state-of-the-art performance in key kernels, demonstrating that its unified block-and-thread paradigm and transparent scheduling capabilities deliver both the power and flexibility demanded by modern AI system development.
CleanMAP: Distilling Multimodal LLMs for Confidence-Driven Crowdsourced HD Map Updates
Apr 14, 2025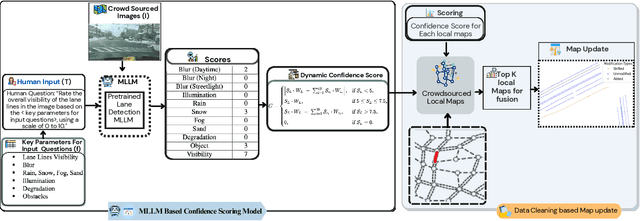
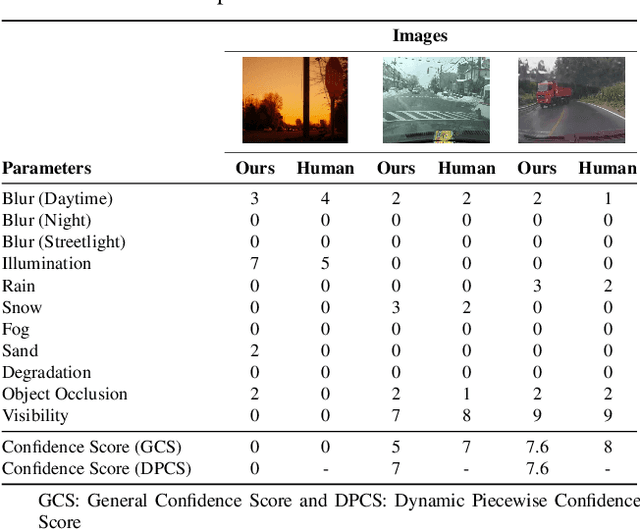
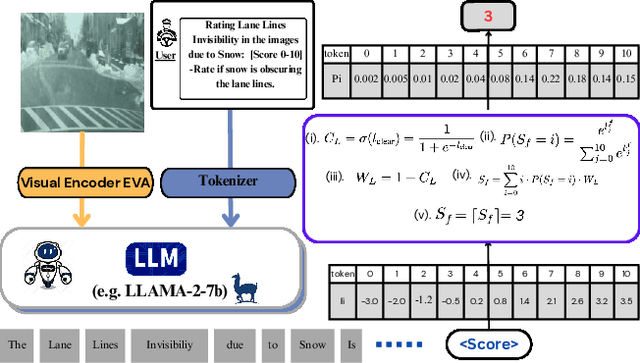

Abstract:The rapid growth of intelligent connected vehicles (ICVs) and integrated vehicle-road-cloud systems has increased the demand for accurate, real-time HD map updates. However, ensuring map reliability remains challenging due to inconsistencies in crowdsourced data, which suffer from motion blur, lighting variations, adverse weather, and lane marking degradation. This paper introduces CleanMAP, a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM)-based distillation framework designed to filter and refine crowdsourced data for high-confidence HD map updates. CleanMAP leverages an MLLM-driven lane visibility scoring model that systematically quantifies key visual parameters, assigning confidence scores (0-10) based on their impact on lane detection. A novel dynamic piecewise confidence-scoring function adapts scores based on lane visibility, ensuring strong alignment with human evaluations while effectively filtering unreliable data. To further optimize map accuracy, a confidence-driven local map fusion strategy ranks and selects the top-k highest-scoring local maps within an optimal confidence range (best score minus 10%), striking a balance between data quality and quantity. Experimental evaluations on a real-world autonomous vehicle dataset validate CleanMAP's effectiveness, demonstrating that fusing the top three local maps achieves the lowest mean map update error of 0.28m, outperforming the baseline (0.37m) and meeting stringent accuracy thresholds (<= 0.32m). Further validation with real-vehicle data confirms 84.88% alignment with human evaluators, reinforcing the model's robustness and reliability. This work establishes CleanMAP as a scalable and deployable solution for crowdsourced HD map updates, ensuring more precise and reliable autonomous navigation. The code will be available at https://Ankit-Zefan.github.io/CleanMap/
POD: Predictive Object Detection with Single-Frame FMCW LiDAR Point Cloud
Apr 08, 2025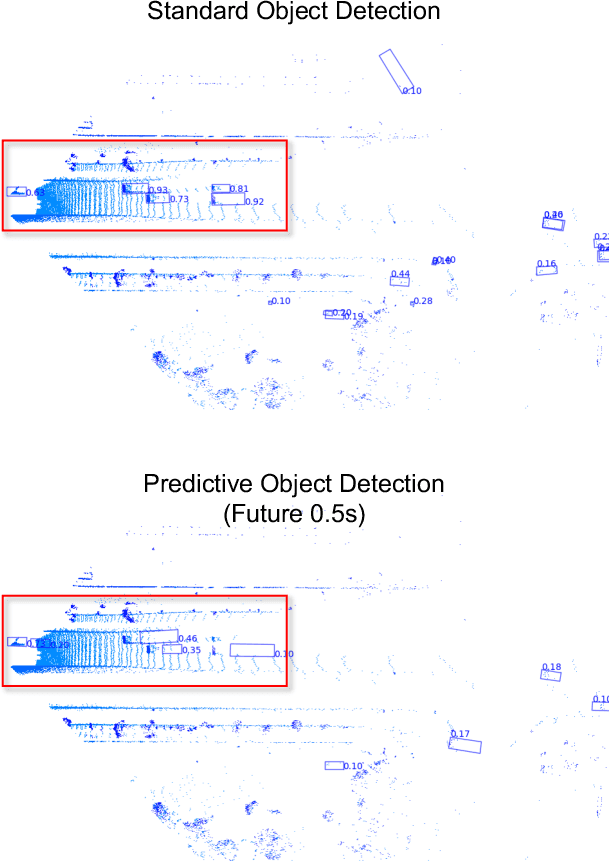
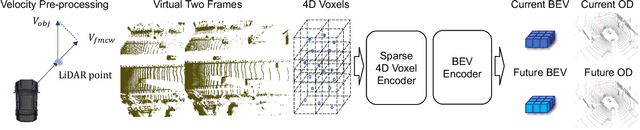
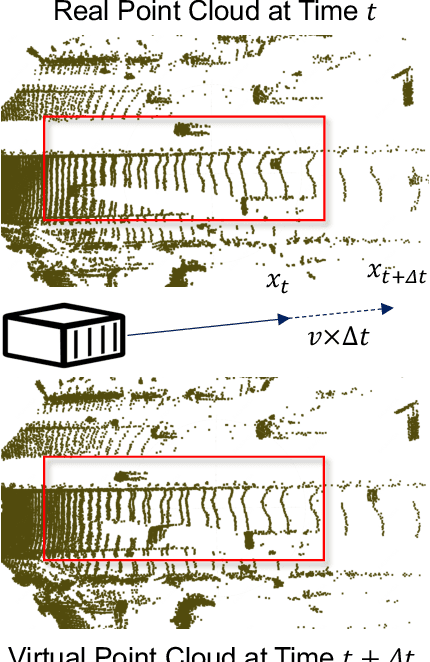
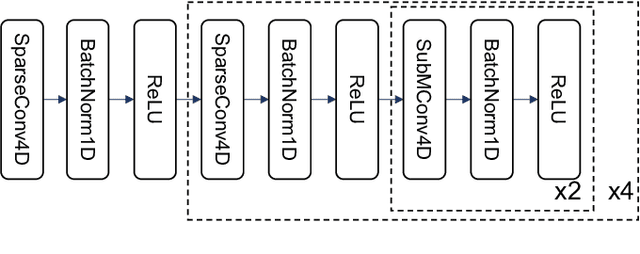
Abstract:LiDAR-based 3D object detection is a fundamental task in the field of autonomous driving. This paper explores the unique advantage of Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave (FMCW) LiDAR in autonomous perception. Given a single frame FMCW point cloud with radial velocity measurements, we expect that our object detector can detect the short-term future locations of objects using only the current frame sensor data and demonstrate a fast ability to respond to intermediate danger. To achieve this, we extend the standard object detection task to a novel task named predictive object detection (POD), which aims to predict the short-term future location and dimensions of objects based solely on current observations. Typically, a motion prediction task requires historical sensor information to process the temporal contexts of each object, while our detector's avoidance of multi-frame historical information enables a much faster response time to potential dangers. The core advantage of FMCW LiDAR lies in the radial velocity associated with every reflected point. We propose a novel POD framework, the core idea of which is to generate a virtual future point using a ray casting mechanism, create virtual two-frame point clouds with the current and virtual future frames, and encode these two-frame voxel features with a sparse 4D encoder. Subsequently, the 4D voxel features are separated by temporal indices and remapped into two Bird's Eye View (BEV) features: one decoded for standard current frame object detection and the other for future predictive object detection. Extensive experiments on our in-house dataset demonstrate the state-of-the-art standard and predictive detection performance of the proposed POD framework.
FASIONAD++ : Integrating High-Level Instruction and Information Bottleneck in FAt-Slow fusION Systems for Enhanced Safety in Autonomous Driving with Adaptive Feedback
Mar 11, 2025



Abstract:Ensuring safe, comfortable, and efficient planning is crucial for autonomous driving systems. While end-to-end models trained on large datasets perform well in standard driving scenarios, they struggle with complex low-frequency events. Recent Large Language Models (LLMs) and Vision Language Models (VLMs) advancements offer enhanced reasoning but suffer from computational inefficiency. Inspired by the dual-process cognitive model "Thinking, Fast and Slow", we propose $\textbf{FASIONAD}$ -- a novel dual-system framework that synergizes a fast end-to-end planner with a VLM-based reasoning module. The fast system leverages end-to-end learning to achieve real-time trajectory generation in common scenarios, while the slow system activates through uncertainty estimation to perform contextual analysis and complex scenario resolution. Our architecture introduces three key innovations: (1) A dynamic switching mechanism enabling slow system intervention based on real-time uncertainty assessment; (2) An information bottleneck with high-level plan feedback that optimizes the slow system's guidance capability; (3) A bidirectional knowledge exchange where visual prompts enhance the slow system's reasoning while its feedback refines the fast planner's decision-making. To strengthen VLM reasoning, we develop a question-answering mechanism coupled with reward-instruct training strategy. In open-loop experiments, FASIONAD achieves a $6.7\%$ reduction in average $L2$ trajectory error and $28.1\%$ lower collision rate.
LEGO-Motion: Learning-Enhanced Grids with Occupancy Instance Modeling for Class-Agnostic Motion Prediction
Mar 10, 2025



Abstract:Accurate and reliable spatial and motion information plays a pivotal role in autonomous driving systems. However, object-level perception models struggle with handling open scenario categories and lack precise intrinsic geometry. On the other hand, occupancy-based class-agnostic methods excel in representing scenes but fail to ensure physics consistency and ignore the importance of interactions between traffic participants, hindering the model's ability to learn accurate and reliable motion. In this paper, we introduce a novel occupancy-instance modeling framework for class-agnostic motion prediction tasks, named LEGO-Motion, which incorporates instance features into Bird's Eye View (BEV) space. Our model comprises (1) a BEV encoder, (2) an Interaction-Augmented Instance Encoder, and (3) an Instance-Enhanced BEV Encoder, improving both interaction relationships and physics consistency within the model, thereby ensuring a more accurate and robust understanding of the environment. Extensive experiments on the nuScenes dataset demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming existing approaches. Furthermore, the effectiveness of our framework is validated on the advanced FMCW LiDAR benchmark, showcasing its practical applicability and generalization capabilities. The code will be made publicly available to facilitate further research.
PriorMotion: Generative Class-Agnostic Motion Prediction with Raster-Vector Motion Field Priors
Dec 05, 2024Abstract:Reliable perception of spatial and motion information is crucial for safe autonomous navigation. Traditional approaches typically fall into two categories: object-centric and class-agnostic methods. While object-centric methods often struggle with missed detections, leading to inaccuracies in motion prediction, many class-agnostic methods focus heavily on encoder design, often overlooking important priors like rigidity and temporal consistency, leading to suboptimal performance, particularly with sparse LiDAR data at distant region. To address these issues, we propose $\textbf{PriorMotion}$, a generative framework that extracts rasterized and vectorized scene representations to model spatio-temporal priors. Our model comprises a BEV encoder, an Raster-Vector prior Encoder, and a Spatio-Temporal prior Generator, improving both spatial and temporal consistency in motion prediction. Additionally, we introduce a standardized evaluation protocol for class-agnostic motion prediction. Experiments on the nuScenes dataset show that PriorMotion achieves state-of-the-art performance, with further validation on advanced FMCW LiDAR confirming its robustness.
FASIONAD : FAst and Slow FusION Thinking Systems for Human-Like Autonomous Driving with Adaptive Feedback
Nov 27, 2024



Abstract:Ensuring safe, comfortable, and efficient navigation is a critical goal for autonomous driving systems. While end-to-end models trained on large-scale datasets excel in common driving scenarios, they often struggle with rare, long-tail events. Recent progress in large language models (LLMs) has introduced enhanced reasoning capabilities, but their computational demands pose challenges for real-time decision-making and precise planning. This paper presents FASIONAD, a novel dual-system framework inspired by the cognitive model "Thinking, Fast and Slow." The fast system handles routine navigation tasks using rapid, data-driven path planning, while the slow system focuses on complex reasoning and decision-making in challenging or unfamiliar situations. A dynamic switching mechanism based on score distribution and feedback allows seamless transitions between the two systems. Visual prompts generated by the fast system enable human-like reasoning in the slow system, which provides high-quality feedback to enhance the fast system's decision-making. To evaluate FASIONAD, we introduce a new benchmark derived from the nuScenes dataset, specifically designed to differentiate fast and slow scenarios. FASIONAD achieves state-of-the-art performance on this benchmark, establishing a new standard for frameworks integrating fast and slow cognitive processes in autonomous driving. This approach paves the way for more adaptive, human-like autonomous driving systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge