Sifa Zheng
ForSim: Stepwise Forward Simulation for Traffic Policy Fine-Tuning
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:As the foundation of closed-loop training and evaluation in autonomous driving, traffic simulation still faces two fundamental challenges: covariate shift introduced by open-loop imitation learning and limited capacity to reflect the multimodal behaviors observed in real-world traffic. Although recent frameworks such as RIFT have partially addressed these issues through group-relative optimization, their forward simulation procedures remain largely non-reactive, leading to unrealistic agent interactions within the virtual domain and ultimately limiting simulation fidelity. To address these issues, we propose ForSim, a stepwise closed-loop forward simulation paradigm. At each virtual timestep, the traffic agent propagates the virtual candidate trajectory that best spatiotemporally matches the reference trajectory through physically grounded motion dynamics, thereby preserving multimodal behavioral diversity while ensuring intra-modality consistency. Other agents are updated with stepwise predictions, yielding coherent and interaction-aware evolution. When incorporated into the RIFT traffic simulation framework, ForSim operates in conjunction with group-relative optimization to fine-tune traffic policy. Extensive experiments confirm that this integration consistently improves safety while maintaining efficiency, realism, and comfort. These results underscore the importance of modeling closed-loop multimodal interactions within forward simulation and enhance the fidelity and reliability of traffic simulation for autonomous driving. Project Page: https://currychen77.github.io/ForSim/
Listen, Look, Drive: Coupling Audio Instructions for User-aware VLA-based Autonomous Driving
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:Vision Language Action (VLA) models promise an open-vocabulary interface that can translate perceptual ambiguity into semantically grounded driving decisions, yet they still treat language as a static prior fixed at inference time. As a result, the model must infer continuously shifting objectives from pixels alone, yielding delayed or overly conservative maneuvers. We argue that effective VLAs for autonomous driving need an online channel in which users can influence driving with specific intentions. To this end, we present EchoVLA, a user-aware VLA that couples camera streams with in situ audio instructions. We augment the nuScenes dataset with temporally aligned, intent-specific speech commands generated by converting ego-motion descriptions into synthetic audios. Further, we compose emotional speech-trajectory pairs into a multimodal Chain-of-Thought (CoT) for fine-tuning a Multimodal Large Model (MLM) based on Qwen2.5-Omni. Specifically, we synthesize the audio-augmented dataset with different emotion types paired with corresponding driving behaviors, leveraging the emotional cues embedded in tone, pitch, and speech tempo to reflect varying user states, such as urgent or hesitant intentions, thus enabling our EchoVLA to interpret not only the semantic content but also the emotional context of audio commands for more nuanced and emotionally adaptive driving behavior. In open-loop benchmarks, our approach reduces the average L2 error by $59.4\%$ and the collision rate by $74.4\%$ compared to the baseline of vision-only perception. More experiments on nuScenes dataset validate that EchoVLA not only steers the trajectory through audio instructions, but also modulates driving behavior in response to the emotions detected in the user's speech.
Modified-Emergency Index (MEI): A Criticality Metric for Autonomous Driving in Lateral Conflict
Oct 31, 2025Abstract:Effective, reliable, and efficient evaluation of autonomous driving safety is essential to demonstrate its trustworthiness. Criticality metrics provide an objective means of assessing safety. However, as existing metrics primarily target longitudinal conflicts, accurately quantifying the risks of lateral conflicts - prevalent in urban settings - remains challenging. This paper proposes the Modified-Emergency Index (MEI), a metric designed to quantify evasive effort in lateral conflicts. Compared to the original Emergency Index (EI), MEI refines the estimation of the time available for evasive maneuvers, enabling more precise risk quantification. We validate MEI on a public lateral conflict dataset based on Argoverse-2, from which we extract over 1,500 high-quality AV conflict cases, including more than 500 critical events. MEI is then compared with the well-established ACT and the widely used PET metrics. Results show that MEI consistently outperforms them in accurately quantifying criticality and capturing risk evolution. Overall, these findings highlight MEI as a promising metric for evaluating urban conflicts and enhancing the safety assessment framework for autonomous driving. The open-source implementation is available at https://github.com/AutoChengh/MEI.
DriveCamSim: Generalizable Camera Simulation via Explicit Camera Modeling for Autonomous Driving
May 26, 2025Abstract:Camera sensor simulation serves as a critical role for autonomous driving (AD), e.g. evaluating vision-based AD algorithms. While existing approaches have leveraged generative models for controllable image/video generation, they remain constrained to generating multi-view video sequences with fixed camera viewpoints and video frequency, significantly limiting their downstream applications. To address this, we present a generalizable camera simulation framework DriveCamSim, whose core innovation lies in the proposed Explicit Camera Modeling (ECM) mechanism. Instead of implicit interaction through vanilla attention, ECM establishes explicit pixel-wise correspondences across multi-view and multi-frame dimensions, decoupling the model from overfitting to the specific camera configurations (intrinsic/extrinsic parameters, number of views) and temporal sampling rates presented in the training data. For controllable generation, we identify the issue of information loss inherent in existing conditional encoding and injection pipelines, proposing an information-preserving control mechanism. This control mechanism not only improves conditional controllability, but also can be extended to be identity-aware to enhance temporal consistency in foreground object rendering. With above designs, our model demonstrates superior performance in both visual quality and controllability, as well as generalization capability across spatial-level (camera parameters variations) and temporal-level (video frame rate variations), enabling flexible user-customizable camera simulation tailored to diverse application scenarios. Code will be avaliable at https://github.com/swc-17/DriveCamSim for facilitating future research.
RIFT: Closed-Loop RL Fine-Tuning for Realistic and Controllable Traffic Simulation
May 06, 2025



Abstract:Achieving both realism and controllability in interactive closed-loop traffic simulation remains a key challenge in autonomous driving. Data-driven simulation methods reproduce realistic trajectories but suffer from covariate shift in closed-loop deployment, compounded by simplified dynamics models that further reduce reliability. Conversely, physics-based simulation methods enhance reliable and controllable closed-loop interactions but often lack expert demonstrations, compromising realism. To address these challenges, we introduce a dual-stage AV-centered simulation framework that conducts open-loop imitation learning pre-training in a data-driven simulator to capture trajectory-level realism and multimodality, followed by closed-loop reinforcement learning fine-tuning in a physics-based simulator to enhance controllability and mitigate covariate shift. In the fine-tuning stage, we propose RIFT, a simple yet effective closed-loop RL fine-tuning strategy that preserves the trajectory-level multimodality through a GRPO-style group-relative advantage formulation, while enhancing controllability and training stability by replacing KL regularization with the dual-clip mechanism. Extensive experiments demonstrate that RIFT significantly improves the realism and controllability of generated traffic scenarios, providing a robust platform for evaluating autonomous vehicle performance in diverse and interactive scenarios.
Passenger hazard perception based on EEG signals for highly automated driving vehicles
Aug 29, 2024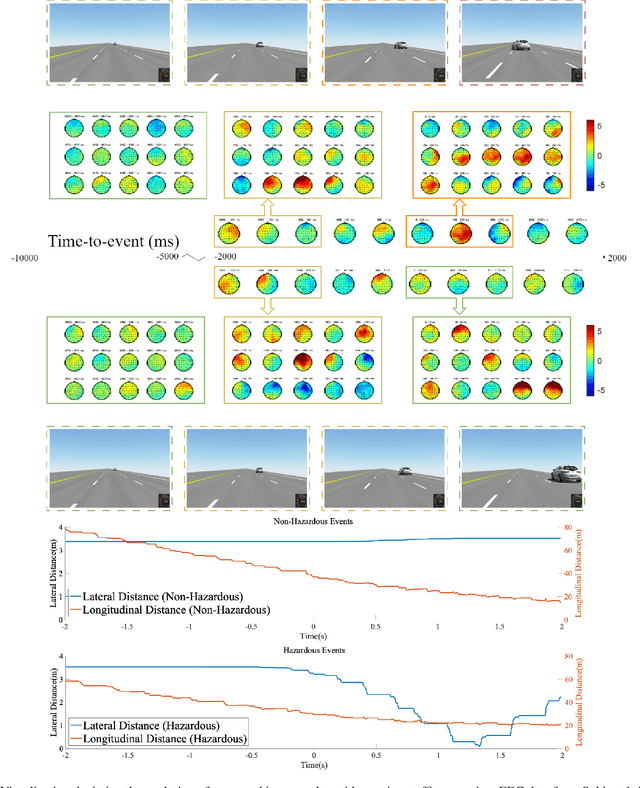
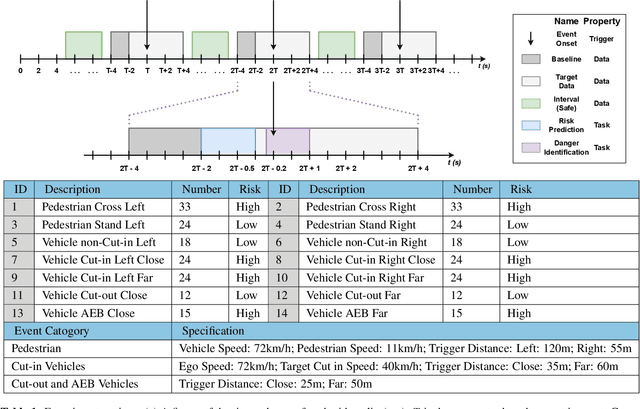
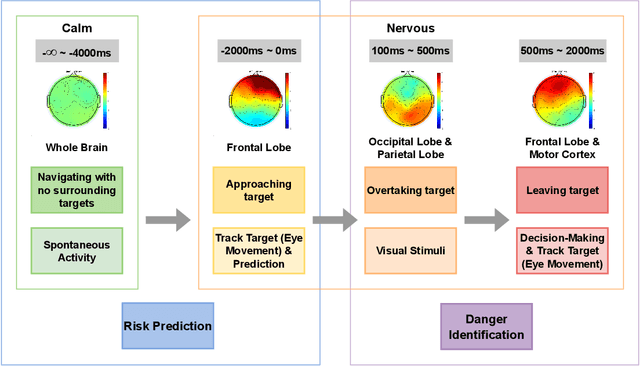
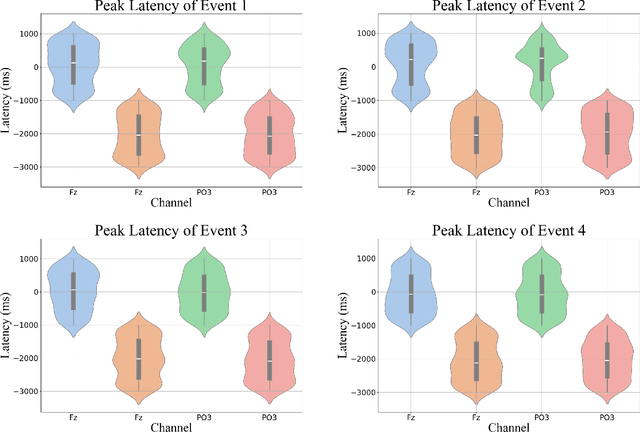
Abstract:Enhancing the safety of autonomous vehicles is crucial, especially given recent accidents involving automated systems. As passengers in these vehicles, humans' sensory perception and decision-making can be integrated with autonomous systems to improve safety. This study explores neural mechanisms in passenger-vehicle interactions, leading to the development of a Passenger Cognitive Model (PCM) and the Passenger EEG Decoding Strategy (PEDS). Central to PEDS is a novel Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network (CRNN) that captures spatial and temporal EEG data patterns. The CRNN, combined with stacking algorithms, achieves an accuracy of $85.0\% \pm 3.18\%$. Our findings highlight the predictive power of pre-event EEG data, enhancing the detection of hazardous scenarios and offering a network-driven framework for safer autonomous vehicles.
FREA: Feasibility-Guided Generation of Safety-Critical Scenarios with Reasonable Adversariality
Jun 05, 2024



Abstract:Generating safety-critical scenarios, which are essential yet difficult to collect at scale, offers an effective method to evaluate the robustness of autonomous vehicles (AVs). Existing methods focus on optimizing adversariality while preserving the naturalness of scenarios, aiming to achieve a balance through data-driven approaches. However, without an appropriate upper bound for adversariality, the scenarios might exhibit excessive adversariality, potentially leading to unavoidable collisions. In this paper, we introduce FREA, a novel safety-critical scenarios generation method that incorporates the Largest Feasible Region (LFR) of AV as guidance to ensure the reasonableness of the adversarial scenarios. Concretely, FREA initially pre-calculates the LFR of AV from offline datasets. Subsequently, it learns a reasonable adversarial policy that controls critical background vehicles (CBVs) in the scene to generate adversarial yet AV-feasible scenarios by maximizing a novel feasibility-dependent objective function. Extensive experiments illustrate that FREA can effectively generate safety-critical scenarios, yielding considerable near-miss events while ensuring AV's feasibility. Generalization analysis also confirms the robustness of FREA in AV testing across various surrogate AV methods and traffic environments.
SparseDrive: End-to-End Autonomous Driving via Sparse Scene Representation
May 31, 2024
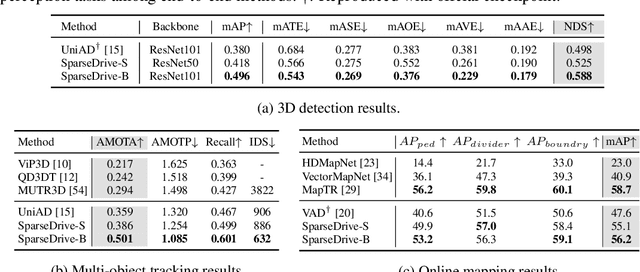
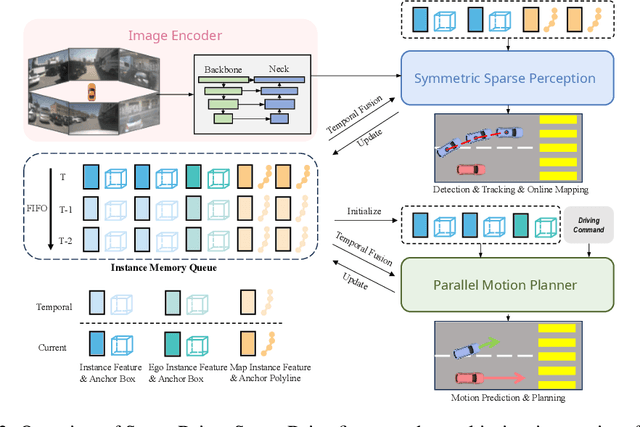
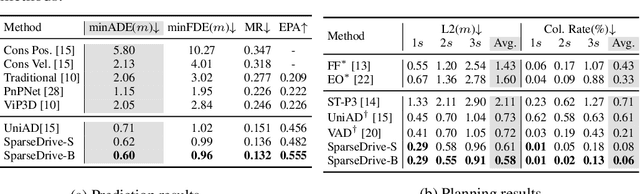
Abstract:The well-established modular autonomous driving system is decoupled into different standalone tasks, e.g. perception, prediction and planning, suffering from information loss and error accumulation across modules. In contrast, end-to-end paradigms unify multi-tasks into a fully differentiable framework, allowing for optimization in a planning-oriented spirit. Despite the great potential of end-to-end paradigms, both the performance and efficiency of existing methods are not satisfactory, particularly in terms of planning safety. We attribute this to the computationally expensive BEV (bird's eye view) features and the straightforward design for prediction and planning. To this end, we explore the sparse representation and review the task design for end-to-end autonomous driving, proposing a new paradigm named SparseDrive. Concretely, SparseDrive consists of a symmetric sparse perception module and a parallel motion planner. The sparse perception module unifies detection, tracking and online mapping with a symmetric model architecture, learning a fully sparse representation of the driving scene. For motion prediction and planning, we review the great similarity between these two tasks, leading to a parallel design for motion planner. Based on this parallel design, which models planning as a multi-modal problem, we propose a hierarchical planning selection strategy , which incorporates a collision-aware rescore module, to select a rational and safe trajectory as the final planning output. With such effective designs, SparseDrive surpasses previous state-of-the-arts by a large margin in performance of all tasks, while achieving much higher training and inference efficiency. Code will be avaliable at https://github.com/swc-17/SparseDrive for facilitating future research.
Neural Radiance Field in Autonomous Driving: A Survey
Apr 26, 2024



Abstract:Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) has garnered significant attention from both academia and industry due to its intrinsic advantages, particularly its implicit representation and novel view synthesis capabilities. With the rapid advancements in deep learning, a multitude of methods have emerged to explore the potential applications of NeRF in the domain of Autonomous Driving (AD). However, a conspicuous void is apparent within the current literature. To bridge this gap, this paper conducts a comprehensive survey of NeRF's applications in the context of AD. Our survey is structured to categorize NeRF's applications in Autonomous Driving (AD), specifically encompassing perception, 3D reconstruction, simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM), and simulation. We delve into in-depth analysis and summarize the findings for each application category, and conclude by providing insights and discussions on future directions in this field. We hope this paper serves as a comprehensive reference for researchers in this domain. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first survey specifically focused on the applications of NeRF in the Autonomous Driving domain.
What Truly Matters in Trajectory Prediction for Autonomous Driving?
Jun 27, 2023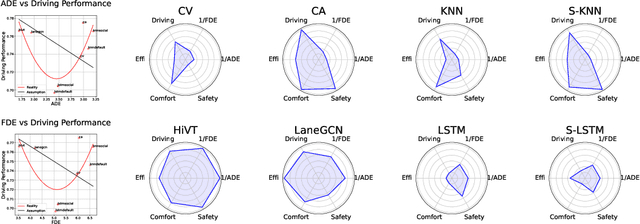



Abstract:In the autonomous driving system, trajectory prediction plays a vital role in ensuring safety and facilitating smooth navigation. However, we observe a substantial discrepancy between the accuracy of predictors on fixed datasets and their driving performance when used in downstream tasks. This discrepancy arises from two overlooked factors in the current evaluation protocols of trajectory prediction: 1) the dynamics gap between the dataset and real driving scenario; and 2) the computational efficiency of predictors. In real-world scenarios, prediction algorithms influence the behavior of autonomous vehicles, which, in turn, alter the behaviors of other agents on the road. This interaction results in predictor-specific dynamics that directly impact prediction results. As other agents' responses are predetermined on datasets, a significant dynamics gap arises between evaluations conducted on fixed datasets and actual driving scenarios. Furthermore, focusing solely on accuracy fails to address the demand for computational efficiency, which is critical for the real-time response required by the autonomous driving system. Therefore, in this paper, we demonstrate that an interactive, task-driven evaluation approach for trajectory prediction is crucial to reflect its efficacy for autonomous driving.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge