Diange Yang
Tsinghua University
LSRE: Latent Semantic Rule Encoding for Real-Time Semantic Risk Detection in Autonomous Driving
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Real-world autonomous driving must adhere to complex human social rules that extend beyond legally codified traffic regulations. Many of these semantic constraints, such as yielding to emergency vehicles, complying with traffic officers' gestures, or stopping for school buses, are intuitive for humans yet difficult to encode explicitly. Although large vision-language models (VLMs) can interpret such semantics, their inference cost makes them impractical for real-time deployment.This work proposes LSRE, a Latent Semantic Rule Encoding framework that converts sparsely sampled VLM judgments into decision boundaries within the latent space of a recurrent world model. By encoding language-defined safety semantics into a lightweight latent classifier, LSRE enables real-time semantic risk assessment at 10 Hz without per-frame VLM queries. Experiments on six semantic-failure scenarios in CARLA demonstrate that LSRE attains semantic risk detection accuracy comparable to a large VLM baseline, while providing substantially earlier hazard anticipation and maintaining low computational latency. LSRE further generalizes to rarely seen semantic-similar test cases, indicating that language-guided latent classification offers an effective and deployable mechanism for semantic safety monitoring in autonomous driving.
DTCCL: Disengagement-Triggered Contrastive Continual Learning for Autonomous Bus Planners
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Autonomous buses run on fixed routes but must operate in open, dynamic urban environments. Disengagement events on these routes are often geographically concentrated and typically arise from planner failures in highly interactive regions. Such policy-level failures are difficult to correct using conventional imitation learning, which easily overfits to sparse disengagement data. To address this issue, this paper presents a Disengagement-Triggered Contrastive Continual Learning (DTCCL) framework that enables autonomous buses to improve planning policies through real-world operation. Each disengagement triggers cloud-based data augmentation that generates positive and negative samples by perturbing surrounding agents while preserving route context. Contrastive learning refines policy representations to better distinguish safe and unsafe behaviors, and continual updates are applied in a cloud-edge loop without human supervision. Experiments on urban bus routes demonstrate that DTCCL improves overall planning performance by 48.6 percent compared with direct retraining, validating its effectiveness for scalable, closed-loop policy improvement in autonomous public transport.
Are All Data Necessary? Efficient Data Pruning for Large-scale Autonomous Driving Dataset via Trajectory Entropy Maximization
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Collecting large-scale naturalistic driving data is essential for training robust autonomous driving planners. However, real-world datasets often contain a substantial amount of repetitive and low-value samples, which lead to excessive storage costs and bring limited benefits to policy learning. To address this issue, we propose an information-theoretic data pruning method that effectively reduces the training data volume without compromising model performance. Our approach evaluates the trajectory distribution information entropy of driving data and iteratively selects high-value samples that preserve the statistical characteristics of the original dataset in a model-agnostic manner. From a theoretical perspective, we show that maximizing trajectory entropy effectively constrains the Kullback-Leibler divergence between the pruned subset and the original data distribution, thereby maintaining generalization ability. Comprehensive experiments on the NuPlan benchmark with a large-scale imitation learning framework demonstrate that the proposed method can reduce the dataset size by up to 40% while maintaining closed-loop performance. This work provides a lightweight and theoretically grounded approach for scalable data management and efficient policy learning in autonomous driving systems.
COME: Adding Scene-Centric Forecasting Control to Occupancy World Model
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:World models are critical for autonomous driving to simulate environmental dynamics and generate synthetic data. Existing methods struggle to disentangle ego-vehicle motion (perspective shifts) from scene evolvement (agent interactions), leading to suboptimal predictions. Instead, we propose to separate environmental changes from ego-motion by leveraging the scene-centric coordinate systems. In this paper, we introduce COME: a framework that integrates scene-centric forecasting Control into the Occupancy world ModEl. Specifically, COME first generates ego-irrelevant, spatially consistent future features through a scene-centric prediction branch, which are then converted into scene condition using a tailored ControlNet. These condition features are subsequently injected into the occupancy world model, enabling more accurate and controllable future occupancy predictions. Experimental results on the nuScenes-Occ3D dataset show that COME achieves consistent and significant improvements over state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods across diverse configurations, including different input sources (ground-truth, camera-based, fusion-based occupancy) and prediction horizons (3s and 8s). For example, under the same settings, COME achieves 26.3% better mIoU metric than DOME and 23.7% better mIoU metric than UniScene. These results highlight the efficacy of disentangled representation learning in enhancing spatio-temporal prediction fidelity for world models. Code and videos will be available at https://github.com/synsin0/COME.
AgentThink: A Unified Framework for Tool-Augmented Chain-of-Thought Reasoning in Vision-Language Models for Autonomous Driving
May 21, 2025



Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) show promise for autonomous driving, yet their struggle with hallucinations, inefficient reasoning, and limited real-world validation hinders accurate perception and robust step-by-step reasoning. To overcome this, we introduce \textbf{AgentThink}, a pioneering unified framework that, for the first time, integrates Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning with dynamic, agent-style tool invocation for autonomous driving tasks. AgentThink's core innovations include: \textbf{(i) Structured Data Generation}, by establishing an autonomous driving tool library to automatically construct structured, self-verified reasoning data explicitly incorporating tool usage for diverse driving scenarios; \textbf{(ii) A Two-stage Training Pipeline}, employing Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) with Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) to equip VLMs with the capability for autonomous tool invocation; and \textbf{(iii) Agent-style Tool-Usage Evaluation}, introducing a novel multi-tool assessment protocol to rigorously evaluate the model's tool invocation and utilization. Experiments on the DriveLMM-o1 benchmark demonstrate AgentThink significantly boosts overall reasoning scores by \textbf{53.91\%} and enhances answer accuracy by \textbf{33.54\%}, while markedly improving reasoning quality and consistency. Furthermore, ablation studies and robust zero-shot/few-shot generalization experiments across various benchmarks underscore its powerful capabilities. These findings highlight a promising trajectory for developing trustworthy and tool-aware autonomous driving models.
CleanMAP: Distilling Multimodal LLMs for Confidence-Driven Crowdsourced HD Map Updates
Apr 14, 2025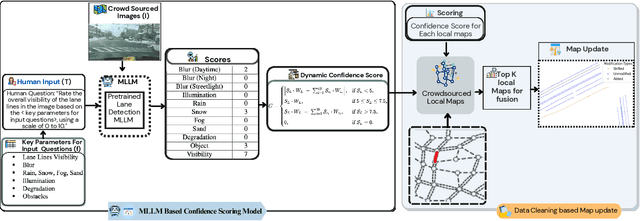
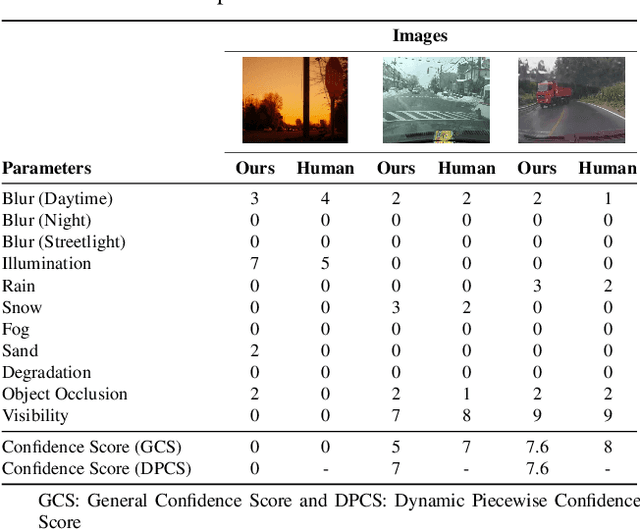
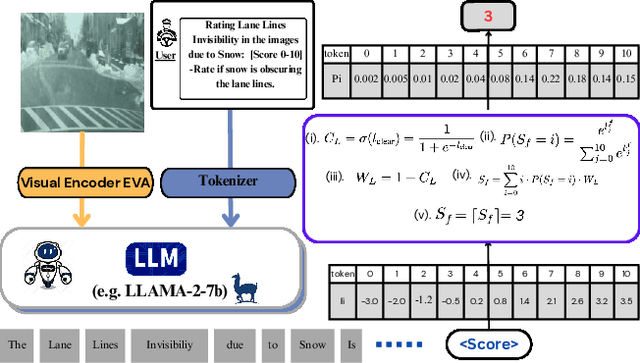

Abstract:The rapid growth of intelligent connected vehicles (ICVs) and integrated vehicle-road-cloud systems has increased the demand for accurate, real-time HD map updates. However, ensuring map reliability remains challenging due to inconsistencies in crowdsourced data, which suffer from motion blur, lighting variations, adverse weather, and lane marking degradation. This paper introduces CleanMAP, a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM)-based distillation framework designed to filter and refine crowdsourced data for high-confidence HD map updates. CleanMAP leverages an MLLM-driven lane visibility scoring model that systematically quantifies key visual parameters, assigning confidence scores (0-10) based on their impact on lane detection. A novel dynamic piecewise confidence-scoring function adapts scores based on lane visibility, ensuring strong alignment with human evaluations while effectively filtering unreliable data. To further optimize map accuracy, a confidence-driven local map fusion strategy ranks and selects the top-k highest-scoring local maps within an optimal confidence range (best score minus 10%), striking a balance between data quality and quantity. Experimental evaluations on a real-world autonomous vehicle dataset validate CleanMAP's effectiveness, demonstrating that fusing the top three local maps achieves the lowest mean map update error of 0.28m, outperforming the baseline (0.37m) and meeting stringent accuracy thresholds (<= 0.32m). Further validation with real-vehicle data confirms 84.88% alignment with human evaluators, reinforcing the model's robustness and reliability. This work establishes CleanMAP as a scalable and deployable solution for crowdsourced HD map updates, ensuring more precise and reliable autonomous navigation. The code will be available at https://Ankit-Zefan.github.io/CleanMap/
POD: Predictive Object Detection with Single-Frame FMCW LiDAR Point Cloud
Apr 08, 2025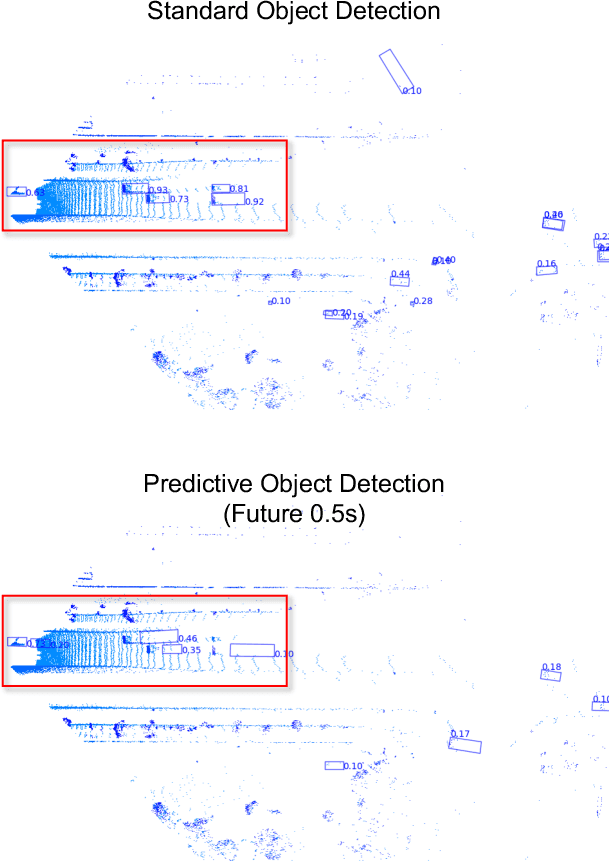
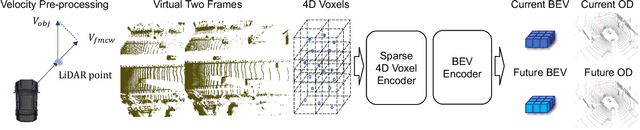
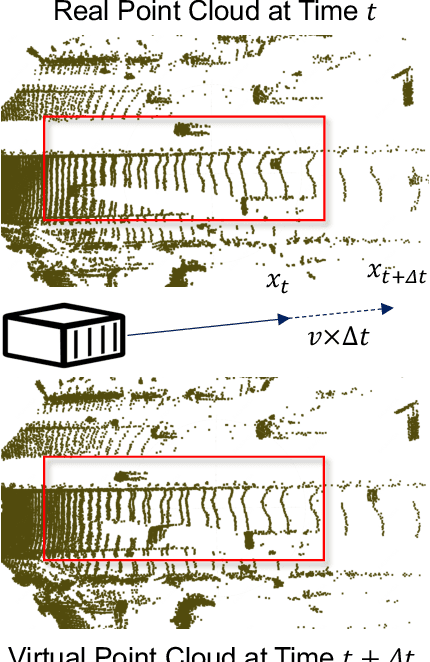
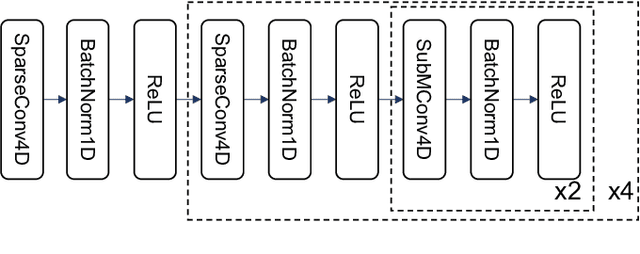
Abstract:LiDAR-based 3D object detection is a fundamental task in the field of autonomous driving. This paper explores the unique advantage of Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave (FMCW) LiDAR in autonomous perception. Given a single frame FMCW point cloud with radial velocity measurements, we expect that our object detector can detect the short-term future locations of objects using only the current frame sensor data and demonstrate a fast ability to respond to intermediate danger. To achieve this, we extend the standard object detection task to a novel task named predictive object detection (POD), which aims to predict the short-term future location and dimensions of objects based solely on current observations. Typically, a motion prediction task requires historical sensor information to process the temporal contexts of each object, while our detector's avoidance of multi-frame historical information enables a much faster response time to potential dangers. The core advantage of FMCW LiDAR lies in the radial velocity associated with every reflected point. We propose a novel POD framework, the core idea of which is to generate a virtual future point using a ray casting mechanism, create virtual two-frame point clouds with the current and virtual future frames, and encode these two-frame voxel features with a sparse 4D encoder. Subsequently, the 4D voxel features are separated by temporal indices and remapped into two Bird's Eye View (BEV) features: one decoded for standard current frame object detection and the other for future predictive object detection. Extensive experiments on our in-house dataset demonstrate the state-of-the-art standard and predictive detection performance of the proposed POD framework.
FASIONAD++ : Integrating High-Level Instruction and Information Bottleneck in FAt-Slow fusION Systems for Enhanced Safety in Autonomous Driving with Adaptive Feedback
Mar 11, 2025



Abstract:Ensuring safe, comfortable, and efficient planning is crucial for autonomous driving systems. While end-to-end models trained on large datasets perform well in standard driving scenarios, they struggle with complex low-frequency events. Recent Large Language Models (LLMs) and Vision Language Models (VLMs) advancements offer enhanced reasoning but suffer from computational inefficiency. Inspired by the dual-process cognitive model "Thinking, Fast and Slow", we propose $\textbf{FASIONAD}$ -- a novel dual-system framework that synergizes a fast end-to-end planner with a VLM-based reasoning module. The fast system leverages end-to-end learning to achieve real-time trajectory generation in common scenarios, while the slow system activates through uncertainty estimation to perform contextual analysis and complex scenario resolution. Our architecture introduces three key innovations: (1) A dynamic switching mechanism enabling slow system intervention based on real-time uncertainty assessment; (2) An information bottleneck with high-level plan feedback that optimizes the slow system's guidance capability; (3) A bidirectional knowledge exchange where visual prompts enhance the slow system's reasoning while its feedback refines the fast planner's decision-making. To strengthen VLM reasoning, we develop a question-answering mechanism coupled with reward-instruct training strategy. In open-loop experiments, FASIONAD achieves a $6.7\%$ reduction in average $L2$ trajectory error and $28.1\%$ lower collision rate.
LEGO-Motion: Learning-Enhanced Grids with Occupancy Instance Modeling for Class-Agnostic Motion Prediction
Mar 10, 2025



Abstract:Accurate and reliable spatial and motion information plays a pivotal role in autonomous driving systems. However, object-level perception models struggle with handling open scenario categories and lack precise intrinsic geometry. On the other hand, occupancy-based class-agnostic methods excel in representing scenes but fail to ensure physics consistency and ignore the importance of interactions between traffic participants, hindering the model's ability to learn accurate and reliable motion. In this paper, we introduce a novel occupancy-instance modeling framework for class-agnostic motion prediction tasks, named LEGO-Motion, which incorporates instance features into Bird's Eye View (BEV) space. Our model comprises (1) a BEV encoder, (2) an Interaction-Augmented Instance Encoder, and (3) an Instance-Enhanced BEV Encoder, improving both interaction relationships and physics consistency within the model, thereby ensuring a more accurate and robust understanding of the environment. Extensive experiments on the nuScenes dataset demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming existing approaches. Furthermore, the effectiveness of our framework is validated on the advanced FMCW LiDAR benchmark, showcasing its practical applicability and generalization capabilities. The code will be made publicly available to facilitate further research.
Advancing Autonomous Vehicle Intelligence: Deep Learning and Multimodal LLM for Traffic Sign Recognition and Robust Lane Detection
Mar 08, 2025Abstract:Autonomous vehicles (AVs) require reliable traffic sign recognition and robust lane detection capabilities to ensure safe navigation in complex and dynamic environments. This paper introduces an integrated approach combining advanced deep learning techniques and Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) for comprehensive road perception. For traffic sign recognition, we systematically evaluate ResNet-50, YOLOv8, and RT-DETR, achieving state-of-the-art performance of 99.8% with ResNet-50, 98.0% accuracy with YOLOv8, and achieved 96.6% accuracy in RT-DETR despite its higher computational complexity. For lane detection, we propose a CNN-based segmentation method enhanced by polynomial curve fitting, which delivers high accuracy under favorable conditions. Furthermore, we introduce a lightweight, Multimodal, LLM-based framework that directly undergoes instruction tuning using small yet diverse datasets, eliminating the need for initial pretraining. This framework effectively handles various lane types, complex intersections, and merging zones, significantly enhancing lane detection reliability by reasoning under adverse conditions. Despite constraints in available training resources, our multimodal approach demonstrates advanced reasoning capabilities, achieving a Frame Overall Accuracy (FRM) of 53.87%, a Question Overall Accuracy (QNS) of 82.83%, lane detection accuracies of 99.6% in clear conditions and 93.0% at night, and robust performance in reasoning about lane invisibility due to rain (88.4%) or road degradation (95.6%). The proposed comprehensive framework markedly enhances AV perception reliability, thus contributing significantly to safer autonomous driving across diverse and challenging road scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge