Junze Wen
LSRE: Latent Semantic Rule Encoding for Real-Time Semantic Risk Detection in Autonomous Driving
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Real-world autonomous driving must adhere to complex human social rules that extend beyond legally codified traffic regulations. Many of these semantic constraints, such as yielding to emergency vehicles, complying with traffic officers' gestures, or stopping for school buses, are intuitive for humans yet difficult to encode explicitly. Although large vision-language models (VLMs) can interpret such semantics, their inference cost makes them impractical for real-time deployment.This work proposes LSRE, a Latent Semantic Rule Encoding framework that converts sparsely sampled VLM judgments into decision boundaries within the latent space of a recurrent world model. By encoding language-defined safety semantics into a lightweight latent classifier, LSRE enables real-time semantic risk assessment at 10 Hz without per-frame VLM queries. Experiments on six semantic-failure scenarios in CARLA demonstrate that LSRE attains semantic risk detection accuracy comparable to a large VLM baseline, while providing substantially earlier hazard anticipation and maintaining low computational latency. LSRE further generalizes to rarely seen semantic-similar test cases, indicating that language-guided latent classification offers an effective and deployable mechanism for semantic safety monitoring in autonomous driving.
DTCCL: Disengagement-Triggered Contrastive Continual Learning for Autonomous Bus Planners
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Autonomous buses run on fixed routes but must operate in open, dynamic urban environments. Disengagement events on these routes are often geographically concentrated and typically arise from planner failures in highly interactive regions. Such policy-level failures are difficult to correct using conventional imitation learning, which easily overfits to sparse disengagement data. To address this issue, this paper presents a Disengagement-Triggered Contrastive Continual Learning (DTCCL) framework that enables autonomous buses to improve planning policies through real-world operation. Each disengagement triggers cloud-based data augmentation that generates positive and negative samples by perturbing surrounding agents while preserving route context. Contrastive learning refines policy representations to better distinguish safe and unsafe behaviors, and continual updates are applied in a cloud-edge loop without human supervision. Experiments on urban bus routes demonstrate that DTCCL improves overall planning performance by 48.6 percent compared with direct retraining, validating its effectiveness for scalable, closed-loop policy improvement in autonomous public transport.
Are All Data Necessary? Efficient Data Pruning for Large-scale Autonomous Driving Dataset via Trajectory Entropy Maximization
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Collecting large-scale naturalistic driving data is essential for training robust autonomous driving planners. However, real-world datasets often contain a substantial amount of repetitive and low-value samples, which lead to excessive storage costs and bring limited benefits to policy learning. To address this issue, we propose an information-theoretic data pruning method that effectively reduces the training data volume without compromising model performance. Our approach evaluates the trajectory distribution information entropy of driving data and iteratively selects high-value samples that preserve the statistical characteristics of the original dataset in a model-agnostic manner. From a theoretical perspective, we show that maximizing trajectory entropy effectively constrains the Kullback-Leibler divergence between the pruned subset and the original data distribution, thereby maintaining generalization ability. Comprehensive experiments on the NuPlan benchmark with a large-scale imitation learning framework demonstrate that the proposed method can reduce the dataset size by up to 40% while maintaining closed-loop performance. This work provides a lightweight and theoretically grounded approach for scalable data management and efficient policy learning in autonomous driving systems.
Dynamically Local-Enhancement Planner for Large-Scale Autonomous Driving
Feb 28, 2025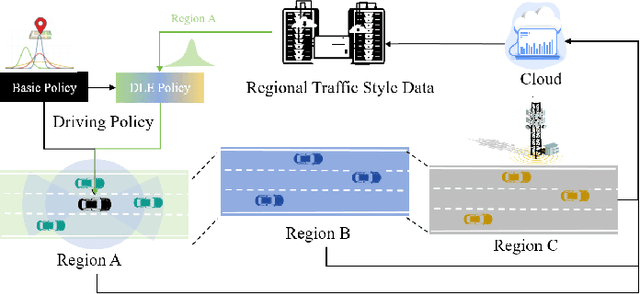
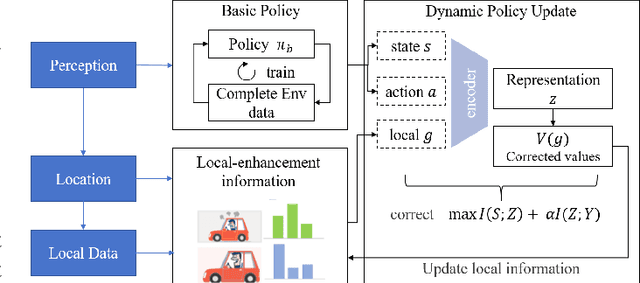
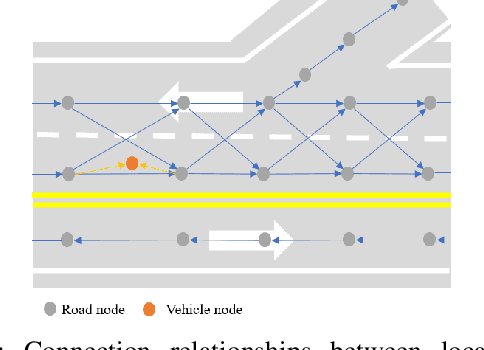
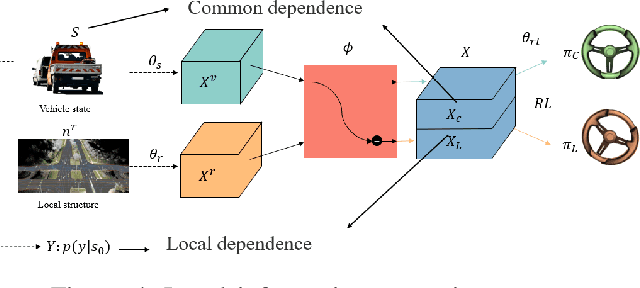
Abstract:Current autonomous vehicles operate primarily within limited regions, but there is increasing demand for broader applications. However, as models scale, their limited capacity becomes a significant challenge for adapting to novel scenarios. It is increasingly difficult to improve models for new situations using a single monolithic model. To address this issue, we introduce the concept of dynamically enhancing a basic driving planner with local driving data, without permanently modifying the planner itself. This approach, termed the Dynamically Local-Enhancement (DLE) Planner, aims to improve the scalability of autonomous driving systems without significantly expanding the planner's size. Our approach introduces a position-varying Markov Decision Process formulation coupled with a graph neural network that extracts region-specific driving features from local observation data. The learned features describe the local behavior of the surrounding objects, which is then leveraged to enhance a basic reinforcement learning-based policy. We evaluated our approach in multiple scenarios and compared it with a one-for-all driving model. The results show that our method outperforms the baseline policy in both safety (collision rate) and average reward, while maintaining a lighter scale. This approach has the potential to benefit large-scale autonomous vehicles without the need for largely expanding on-device driving models.
Grid-Centric Traffic Scenario Perception for Autonomous Driving: A Comprehensive Review
Mar 02, 2023



Abstract:Grid-centric perception is a crucial field for mobile robot perception and navigation. Nonetheless, grid-centric perception is less prevalent than object-centric perception for autonomous driving as autonomous vehicles need to accurately perceive highly dynamic, large-scale outdoor traffic scenarios and the complexity and computational costs of grid-centric perception are high. The rapid development of deep learning techniques and hardware gives fresh insights into the evolution of grid-centric perception and enables the deployment of many real-time algorithms. Current industrial and academic research demonstrates the great advantages of grid-centric perception, such as comprehensive fine-grained environmental representation, greater robustness to occlusion, more efficient sensor fusion, and safer planning policies. Given the lack of current surveys for this rapidly expanding field, we present a hierarchically-structured review of grid-centric perception for autonomous vehicles. We organize previous and current knowledge of occupancy grid techniques and provide a systematic in-depth analysis of algorithms in terms of three aspects: feature representation, data utility, and applications in autonomous driving systems. Lastly, we present a summary of the current research trend and provide some probable future outlooks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge