Zhengping Jiang
How Grounded is Wikipedia? A Study on Structured Evidential Support
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:Wikipedia is a critical resource for modern NLP, serving as a rich repository of up-to-date and citation-backed information on a wide variety of subjects. The reliability of Wikipedia -- its groundedness in its cited sources -- is vital to this purpose. This work provides a quantitative analysis of the extent to which Wikipedia *is* so grounded and of how readily grounding evidence may be retrieved. To this end, we introduce PeopleProfiles -- a large-scale, multi-level dataset of claim support annotations on Wikipedia articles of notable people. We show that roughly 20% of claims in Wikipedia *lead* sections are unsupported by the article body; roughly 27% of annotated claims in the article *body* are unsupported by their (publicly accessible) cited sources; and >80% of lead claims cannot be traced to these sources via annotated body evidence. Further, we show that recovery of complex grounding evidence for claims that *are* supported remains a challenge for standard retrieval methods.
Always Tell Me The Odds: Fine-grained Conditional Probability Estimation
May 02, 2025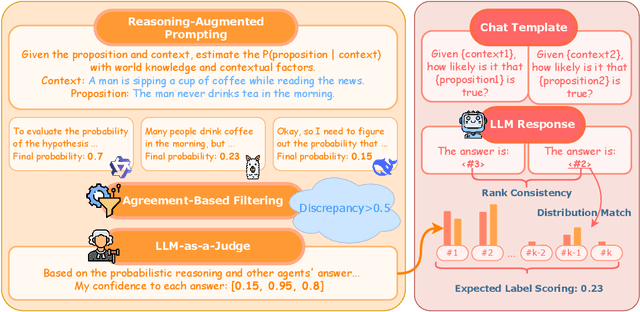
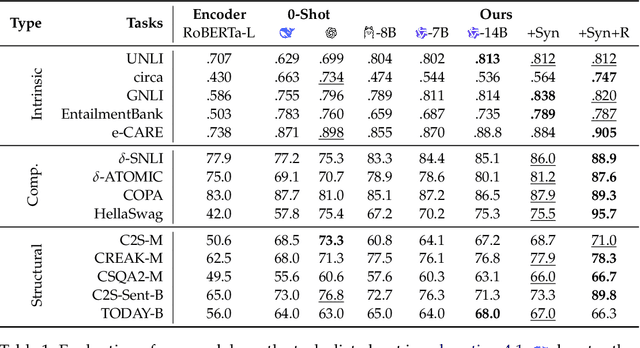
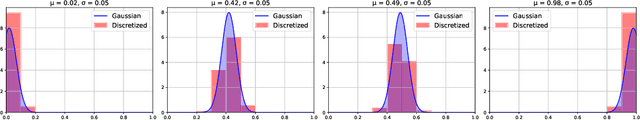
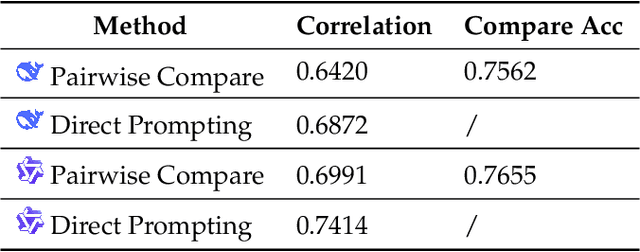
Abstract:We present a state-of-the-art model for fine-grained probability estimation of propositions conditioned on context. Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have significantly enhanced their reasoning capabilities, particularly on well-defined tasks with complete information. However, LLMs continue to struggle with making accurate and well-calibrated probabilistic predictions under uncertainty or partial information. While incorporating uncertainty into model predictions often boosts performance, obtaining reliable estimates of that uncertainty remains understudied. In particular, LLM probability estimates tend to be coarse and biased towards more frequent numbers. Through a combination of human and synthetic data creation and assessment, scaling to larger models, and better supervision, we propose a set of strong and precise probability estimation models. We conduct systematic evaluations across tasks that rely on conditional probability estimation and show that our approach consistently outperforms existing fine-tuned and prompting-based methods by a large margin.
CLAIMCHECK: How Grounded are LLM Critiques of Scientific Papers?
Mar 27, 2025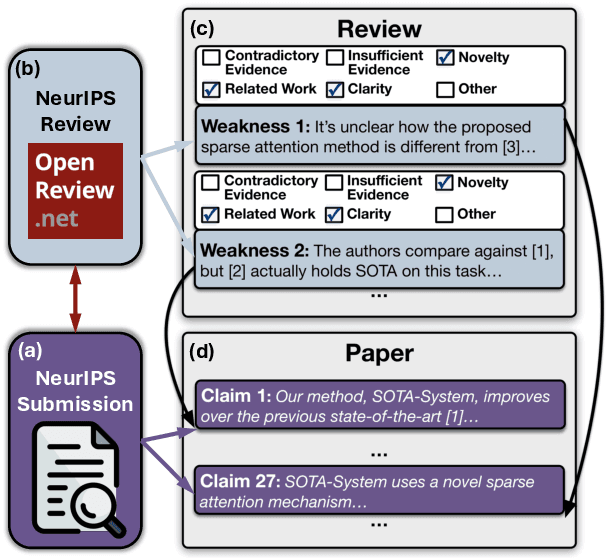
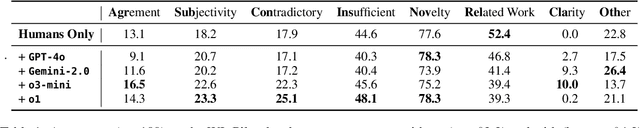
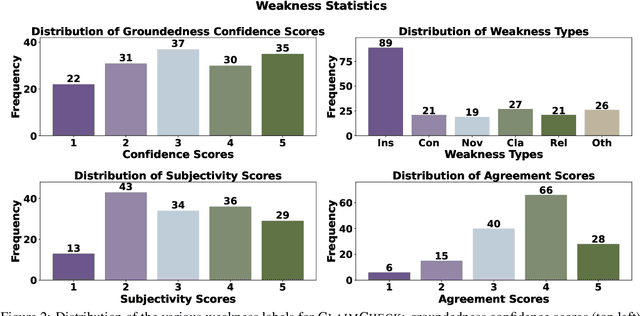
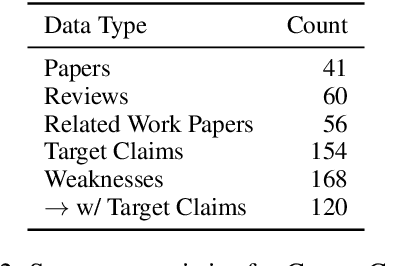
Abstract:A core part of scientific peer review involves providing expert critiques that directly assess the scientific claims a paper makes. While it is now possible to automatically generate plausible (if generic) reviews, ensuring that these reviews are sound and grounded in the papers' claims remains challenging. To facilitate LLM benchmarking on these challenges, we introduce CLAIMCHECK, an annotated dataset of NeurIPS 2023 and 2024 submissions and reviews mined from OpenReview. CLAIMCHECK is richly annotated by ML experts for weakness statements in the reviews and the paper claims that they dispute, as well as fine-grained labels of the validity, objectivity, and type of the identified weaknesses. We benchmark several LLMs on three claim-centric tasks supported by CLAIMCHECK, requiring models to (1) associate weaknesses with the claims they dispute, (2) predict fine-grained labels for weaknesses and rewrite the weaknesses to enhance their specificity, and (3) verify a paper's claims with grounded reasoning. Our experiments reveal that cutting-edge LLMs, while capable of predicting weakness labels in (2), continue to underperform relative to human experts on all other tasks.
Conformal Linguistic Calibration: Trading-off between Factuality and Specificity
Feb 26, 2025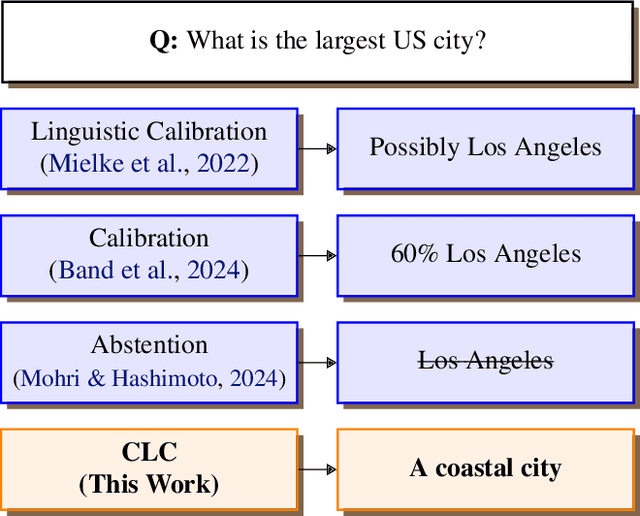
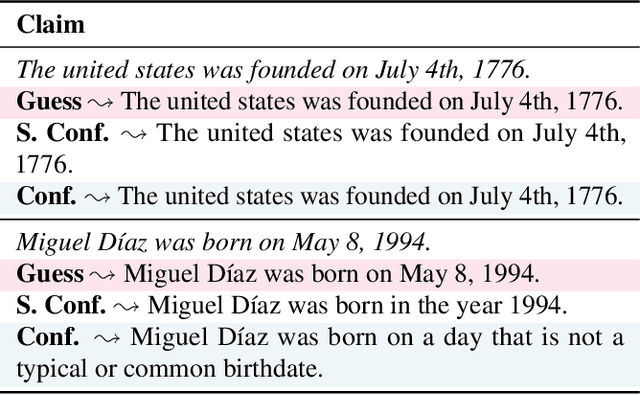
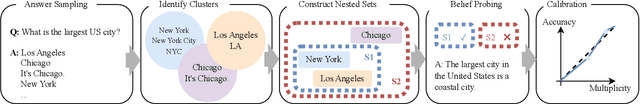
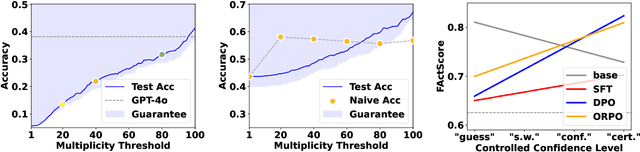
Abstract:Language model outputs are not always reliable; this prompts research into methods for adapting model responses based on uncertainty. Common approaches include: \emph{abstention}, where models refrain from generating responses when uncertain; and \emph{linguistic calibration}, where models hedge their statements using uncertainty quantifiers. However, abstention can withhold valuable information, while linguistically calibrated responses are often challenging to leverage in downstream tasks. We propose a unifying view of both approaches, Conformal Linguistic Calibration (CLC), reinterpreting linguistic calibration as answer set prediction. We begin by presenting a unified framework that connects abstention and linguistic calibration through the lens of linguistic pragmatics. We then describe an implementation that allows for controlling the level of imprecision in model responses. Experimental results show that our method produces calibrated outputs with conformal guarantees on factual accuracy. Furthermore, our approach enables fine-tuning models to perform uncertainty-aware adaptive claim rewriting, offering a controllable balance between factuality and specificity.
Core: Robust Factual Precision Scoring with Informative Sub-Claim Identification
Jul 04, 2024

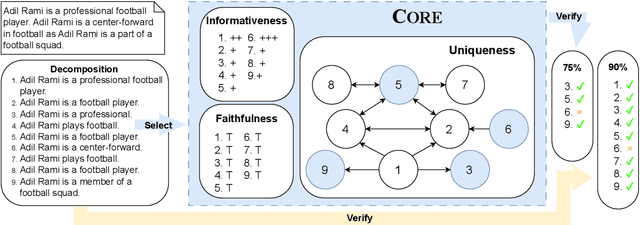
Abstract:Hallucinations -- the generation of untrue claims -- pose a challenge to the application of large language models (LLMs) [1] thereby motivating the development of metrics to evaluate factual precision. We observe that popular metrics using the Decompose-Then-Verify framework, such as FActScore [2], can be manipulated by adding obvious or repetitive claims to artificially inflate scores. We expand the FActScore dataset to design and analyze factual precision metrics, demonstrating that models can be trained to achieve high scores under existing metrics through exploiting the issues we identify. This motivates our new customizable plug-and-play subclaim selection component called Core, which filters down individual subclaims according to their uniqueness and informativeness. Metrics augmented by Core are substantially more robust as shown in head-to-head comparisons. We release an evaluation framework supporting the modular use of Core (https://github.com/zipJiang/Core) and various decomposition strategies, and we suggest its adoption by the LLM community. [1] Hong et al., "The Hallucinations Leaderboard -- An Open Effort to Measure Hallucinations in Large Language Models", arXiv:2404.05904v2 [cs.CL]. [2] Min et al., "FActScore: Fine-grained Atomic Evaluation of Factual Precision in Long Form Text Generation", arXiv:2305.14251v2 [cs.CL].
A Closer Look at Claim Decomposition
Mar 18, 2024



Abstract:As generated text becomes more commonplace, it is increasingly important to evaluate how well-supported such text is by external knowledge sources. Many approaches for evaluating textual support rely on some method for decomposing text into its individual subclaims which are scored against a trusted reference. We investigate how various methods of claim decomposition -- especially LLM-based methods -- affect the result of an evaluation approach such as the recently proposed FActScore, finding that it is sensitive to the decomposition method used. This sensitivity arises because such metrics attribute overall textual support to the model that generated the text even though error can also come from the metric's decomposition step. To measure decomposition quality, we introduce an adaptation of FActScore, which we call DecompScore. We then propose an LLM-based approach to generating decompositions inspired by Bertrand Russell's theory of logical atomism and neo-Davidsonian semantics and demonstrate its improved decomposition quality over previous methods.
RORA: Robust Free-Text Rationale Evaluation
Mar 01, 2024



Abstract:Free-text rationales play a pivotal role in explainable NLP, bridging the knowledge and reasoning gaps behind a model's decision-making. However, due to the diversity of potential reasoning paths and a corresponding lack of definitive ground truth, their evaluation remains a challenge. Existing evaluation metrics rely on the degree to which a rationale supports a target label, but we find these fall short in evaluating rationales that inadvertently leak the labels. To address this problem, we propose RORA, a Robust free-text Rationale evaluation against label leakage. RORA quantifies the new information supplied by a rationale to justify the label. This is achieved by assessing the conditional V-information \citep{hewitt-etal-2021-conditional} with a predictive family robust against leaky features that can be exploited by a small model. RORA consistently outperforms existing approaches in evaluating human-written, synthetic, or model-generated rationales, particularly demonstrating robustness against label leakage. We also show that RORA aligns well with human judgment, providing a more reliable and accurate measurement across diverse free-text rationales.
Enhancing Systematic Decompositional Natural Language Inference Using Informal Logic
Feb 27, 2024Abstract:Contemporary language models enable new opportunities for structured reasoning with text, such as the construction and evaluation of intuitive, proof-like textual entailment trees without relying on brittle formal logic. However, progress in this direction has been hampered by a long-standing lack of a clear protocol for determining what valid compositional entailment is. This absence causes noisy datasets and limited performance gains by modern neuro-symbolic engines. To address these problems, we formulate a consistent and theoretically grounded approach to annotating decompositional entailment datasets, and evaluate its impact on LLM-based textual inference. We find that our resulting dataset, RDTE (Recognizing Decompositional Textual Entailment), has a substantially higher internal consistency (+9%) than prior decompositional entailment datasets, suggesting that RDTE is a significant step forward in the long-standing problem of forming a clear protocol for discerning entailment. We also find that training an RDTE-oriented entailment classifier via knowledge distillation and employing it in a modern neuro-symbolic reasoning engine significantly improves results (both accuracy and proof quality) over other entailment classifier baselines, illustrating the practical benefit of this advance for textual inference.
MegaWika: Millions of reports and their sources across 50 diverse languages
Jul 13, 2023Abstract:To foster the development of new models for collaborative AI-assisted report generation, we introduce MegaWika, consisting of 13 million Wikipedia articles in 50 diverse languages, along with their 71 million referenced source materials. We process this dataset for a myriad of applications, going beyond the initial Wikipedia citation extraction and web scraping of content, including translating non-English articles for cross-lingual applications and providing FrameNet parses for automated semantic analysis. MegaWika is the largest resource for sentence-level report generation and the only report generation dataset that is multilingual. We manually analyze the quality of this resource through a semantically stratified sample. Finally, we provide baseline results and trained models for crucial steps in automated report generation: cross-lingual question answering and citation retrieval.
Segmenting Subtitles for Correcting ASR Segmentation Errors
Apr 16, 2021



Abstract:Typical ASR systems segment the input audio into utterances using purely acoustic information, which may not resemble the sentence-like units that are expected by conventional machine translation (MT) systems for Spoken Language Translation. In this work, we propose a model for correcting the acoustic segmentation of ASR models for low-resource languages to improve performance on downstream tasks. We propose the use of subtitles as a proxy dataset for correcting ASR acoustic segmentation, creating synthetic acoustic utterances by modeling common error modes. We train a neural tagging model for correcting ASR acoustic segmentation and show that it improves downstream performance on MT and audio-document cross-language information retrieval (CLIR).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge