David Wan
Multimodal Fact-Level Attribution for Verifiable Reasoning
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) are increasingly used for real-world tasks involving multi-step reasoning and long-form generation, where reliability requires grounding model outputs in heterogeneous input sources and verifying individual factual claims. However, existing multimodal grounding benchmarks and evaluation methods focus on simplified, observation-based scenarios or limited modalities and fail to assess attribution in complex multimodal reasoning. We introduce MuRGAt (Multimodal Reasoning with Grounded Attribution), a benchmark for evaluating fact-level multimodal attribution in settings that require reasoning beyond direct observation. Given inputs spanning video, audio, and other modalities, MuRGAt requires models to generate answers with explicit reasoning and precise citations, where each citation specifies both modality and temporal segments. To enable reliable assessment, we introduce an automatic evaluation framework that strongly correlates with human judgments. Benchmarking with human and automated scores reveals that even strong MLLMs frequently hallucinate citations despite correct reasoning. Moreover, we observe a key trade-off: increasing reasoning depth or enforcing structured grounding often degrades accuracy, highlighting a significant gap between internal reasoning and verifiable attribution.
GenerationPrograms: Fine-grained Attribution with Executable Programs
Jun 17, 2025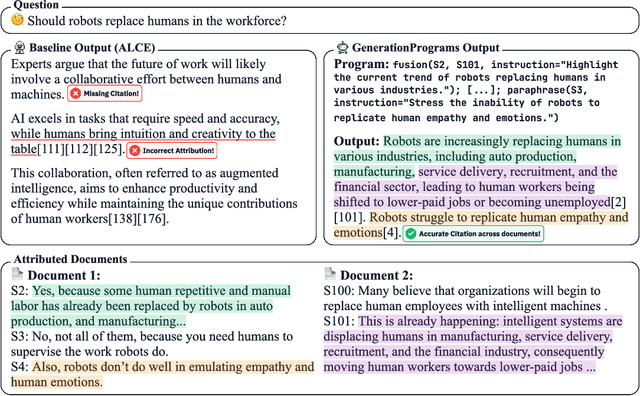
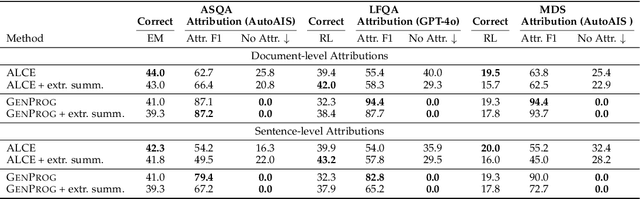
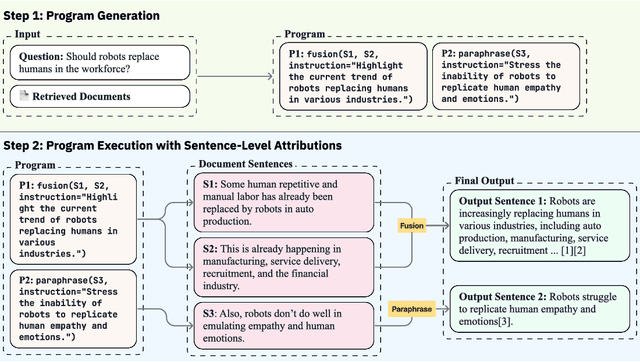
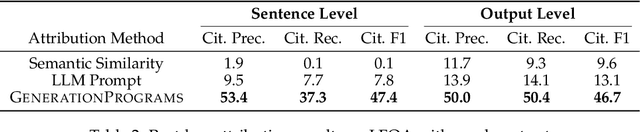
Abstract:Recent large language models (LLMs) achieve impressive performance in source-conditioned text generation but often fail to correctly provide fine-grained attributions for their outputs, undermining verifiability and trust. Moreover, existing attribution methods do not explain how and why models leverage the provided source documents to generate their final responses, limiting interpretability. To overcome these challenges, we introduce a modular generation framework, GenerationPrograms, inspired by recent advancements in executable "code agent" architectures. Unlike conventional generation methods that simultaneously generate outputs and attributions or rely on post-hoc attribution, GenerationPrograms decomposes the process into two distinct stages: first, creating an executable program plan composed of modular text operations (such as paraphrasing, compression, and fusion) explicitly tailored to the query, and second, executing these operations following the program's specified instructions to produce the final response. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that GenerationPrograms significantly improves attribution quality at both the document level and sentence level across two long-form question-answering tasks and a multi-document summarization task. We further demonstrate that GenerationPrograms can effectively function as a post-hoc attribution method, outperforming traditional techniques in recovering accurate attributions. In addition, the interpretable programs generated by GenerationPrograms enable localized refinement through modular-level improvements that further enhance overall attribution quality.
CLaMR: Contextualized Late-Interaction for Multimodal Content Retrieval
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Online video web content is richly multimodal: a single video blends vision, speech, ambient audio, and on-screen text. Retrieval systems typically treat these modalities as independent retrieval sources, which can lead to noisy and subpar retrieval. We explore multimodal video content retrieval, where relevance can be scored from one particular modality or jointly across multiple modalities simultaneously. Consequently, an effective retriever must dynamically choose which modality (or set of modalities) best addresses the query. We introduce CLaMR, a multimodal, late-interaction retriever that jointly indexes 4 modalities: video frames, transcribed speech, on-screen text, and metadata. CLaMR jointly encodes all modalities with a unified multimodal backbone for improved contextualization and is trained to enhance dynamic modality selection via two key innovations. First, given the lack of training data for multimodal retrieval, we introduce MultiVENT 2.0++, a large-scale synthetic training dataset built on MultiVENT 2.0 (event-centric videos in various languages paired with queries) with modality-targeted queries. Next, we propose a modality-aware loss that jointly trains according to a standard contrastive objective alongside an objective for learning correct modality usage. On the test sets of MultiVENT 2.0++ and MSRVTT, conventional aggregation strategies, such as averaging similarities for baseline retrievers, degrade performance by introducing noise from irrelevant modalities. In contrast, CLaMR consistently outperforms existing retrievers: on MultiVENT 2.0++, CLaMR improves nDCG@10 by 25.6 over the best single-modality retriever and by 35.4 over the best multi-modality retriever. We illustrate CLaMR's downstream utility on long-video QA, retrieving relevant frames and obtaining a 3.50% boost over LanguageBind on Video-MME and 1.42% over dense sampling on LongVideoBench.
MAMM-Refine: A Recipe for Improving Faithfulness in Generation with Multi-Agent Collaboration
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:Multi-agent collaboration among models has shown promise in reasoning tasks but is underexplored in long-form generation tasks like summarization and question-answering. We extend multi-agent multi-model reasoning to generation, specifically to improving faithfulness through refinement, i.e., revising model-generated outputs to remove factual inconsistencies. We investigate how iterative collaboration among multiple instances and types of large language models (LLMs) enhances subtasks in the refinement process, such as error detection, critiquing unfaithful sentences, and making corrections based on critiques. We design intrinsic evaluations for each subtask, with our findings indicating that both multi-agent (multiple instances) and multi-model (diverse LLM types) approaches benefit error detection and critiquing. Additionally, reframing critiquing and refinement as reranking rather than generation tasks improves multi-agent performance. We consolidate these insights into a final "recipe" called Multi-Agent Multi-Model Refinement (MAMM-Refine), where multi-agent and multi-model collaboration significantly boosts performance on three summarization datasets as well as on long-form question answering, demonstrating the effectiveness and generalizability of our recipe.
QAPyramid: Fine-grained Evaluation of Content Selection for Text Summarization
Dec 10, 2024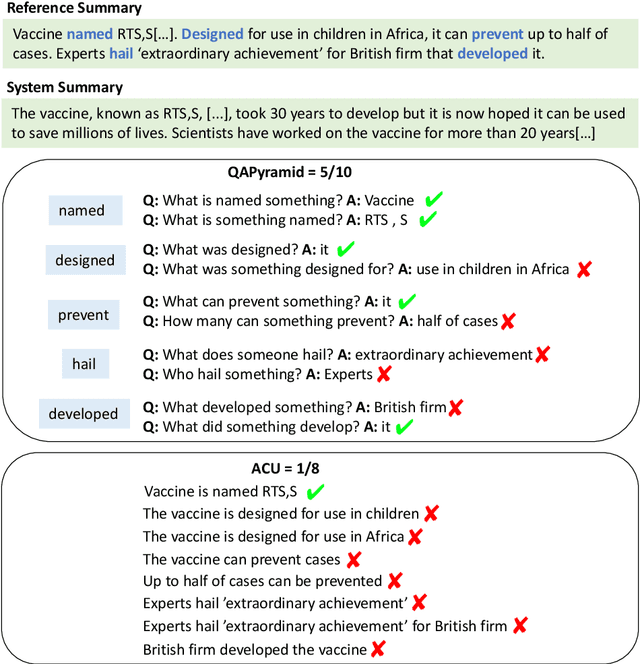
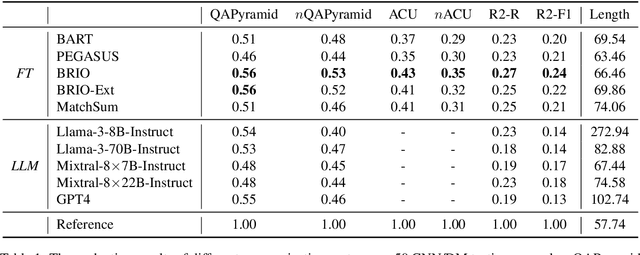
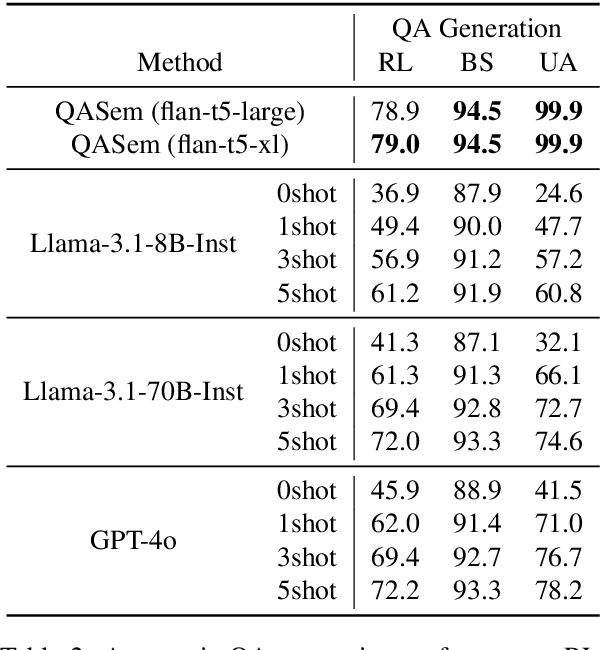
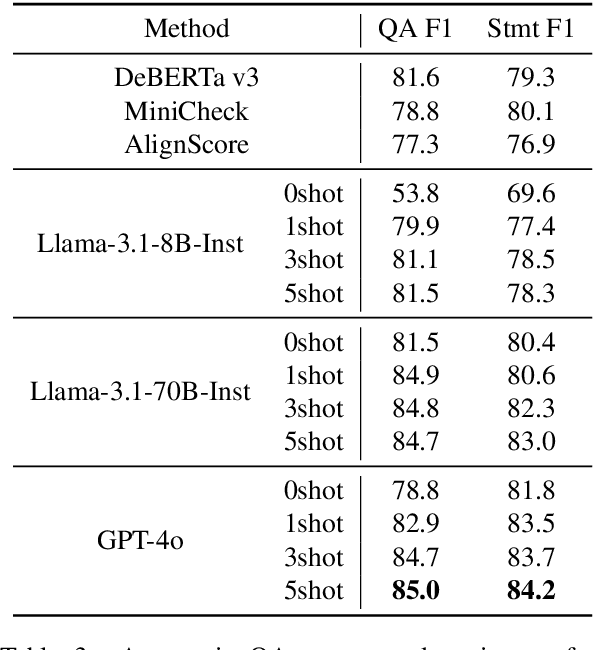
Abstract:How to properly conduct human evaluations for text summarization is a longstanding challenge. The Pyramid human evaluation protocol, which assesses content selection by breaking the reference summary into sub-units and verifying their presence in the system summary, has been widely adopted. However, it suffers from a lack of systematicity in the definition and granularity of the sub-units. We address these problems by proposing QAPyramid, which decomposes each reference summary into finer-grained question-answer (QA) pairs according to the QA-SRL framework. We collect QA-SRL annotations for reference summaries from CNN/DM and evaluate 10 summarization systems, resulting in 8.9K QA-level annotations. We show that, compared to Pyramid, QAPyramid provides more systematic and fine-grained content selection evaluation while maintaining high inter-annotator agreement without needing expert annotations. Furthermore, we propose metrics that automate the evaluation pipeline and achieve higher correlations with QAPyramid than other widely adopted metrics, allowing future work to accurately and efficiently benchmark summarization systems.
On Positional Bias of Faithfulness for Long-form Summarization
Oct 31, 2024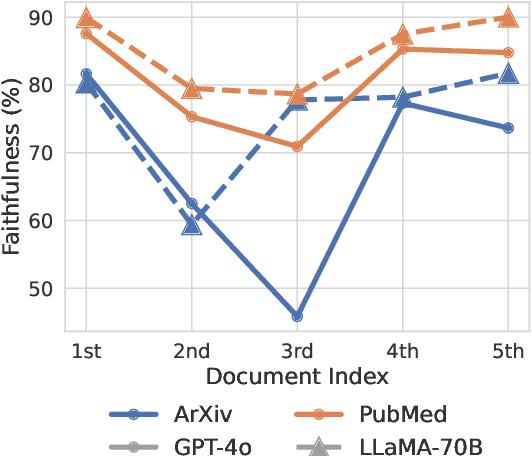
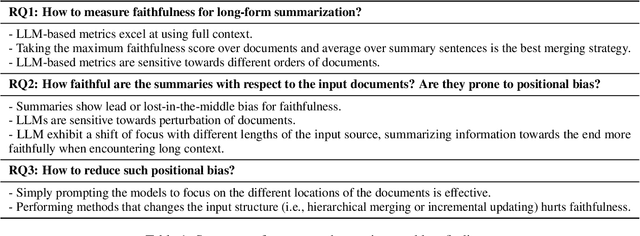
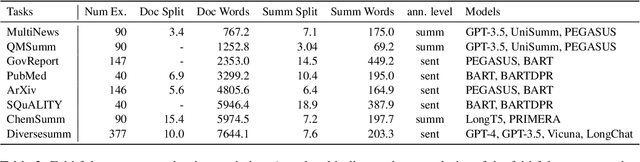

Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) often exhibit positional bias in long-context settings, under-attending to information in the middle of inputs. We investigate the presence of this bias in long-form summarization, its impact on faithfulness, and various techniques to mitigate this bias. To consistently evaluate faithfulness, we first compile a benchmark of eight human-annotated long-form summarization datasets and perform a meta-evaluation of faithfulness metrics. We show that LLM-based faithfulness metrics, though effective with full-context inputs, remain sensitive to document order, indicating positional bias. Analyzing LLM-generated summaries across six datasets, we find a "U-shaped" trend in faithfulness, where LLMs faithfully summarize the beginning and end of documents but neglect middle content. Perturbing document order similarly reveals models are less faithful when important documents are placed in the middle of the input. We find that this behavior is partly due to shifting focus with context length: as context increases, summaries become less faithful, but beyond a certain length, faithfulness improves as the model focuses on the end. Finally, we experiment with different generation techniques to reduce positional bias and find that prompting techniques effectively direct model attention to specific positions, whereas more sophisticated approaches offer limited improvements. Our data and code are available in https://github.com/meetdavidwan/longformfact.
Localizing Factual Inconsistencies in Attributable Text Generation
Oct 09, 2024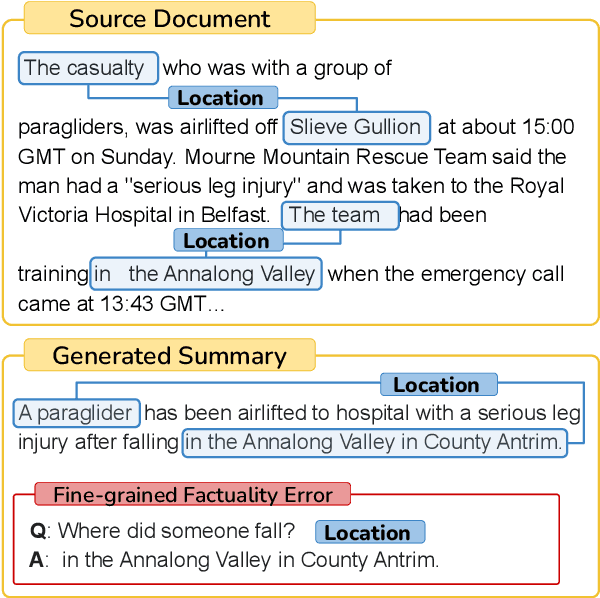
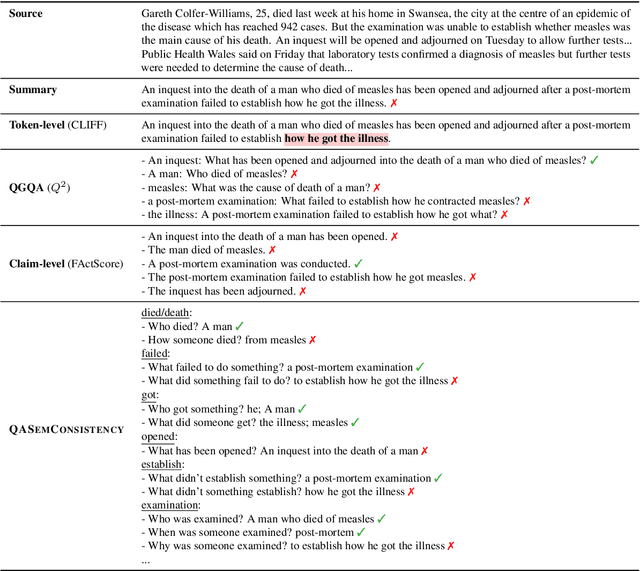

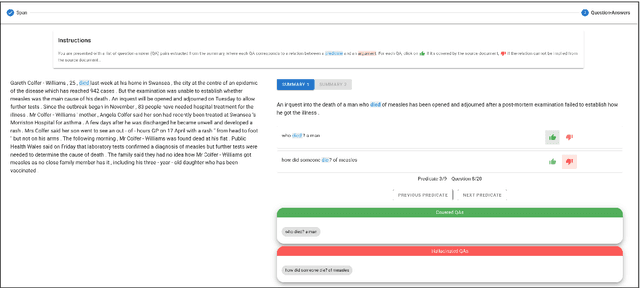
Abstract:There has been an increasing interest in detecting hallucinations in model-generated texts, both manually and automatically, at varying levels of granularity. However, most existing methods fail to precisely pinpoint the errors. In this work, we introduce QASemConsistency, a new formalism for localizing factual inconsistencies in attributable text generation, at a fine-grained level. Drawing inspiration from Neo-Davidsonian formal semantics, we propose decomposing the generated text into minimal predicate-argument level propositions, expressed as simple question-answer (QA) pairs, and assess whether each individual QA pair is supported by a trusted reference text. As each QA pair corresponds to a single semantic relation between a predicate and an argument, QASemConsistency effectively localizes the unsupported information. We first demonstrate the effectiveness of the QASemConsistency methodology for human annotation, by collecting crowdsourced annotations of granular consistency errors, while achieving a substantial inter-annotator agreement ($\kappa > 0.7)$. Then, we implement several methods for automatically detecting localized factual inconsistencies, with both supervised entailment models and open-source LLMs.
Contrastive Region Guidance: Improving Grounding in Vision-Language Models without Training
Mar 04, 2024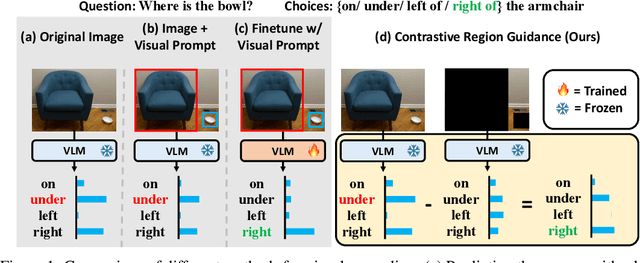
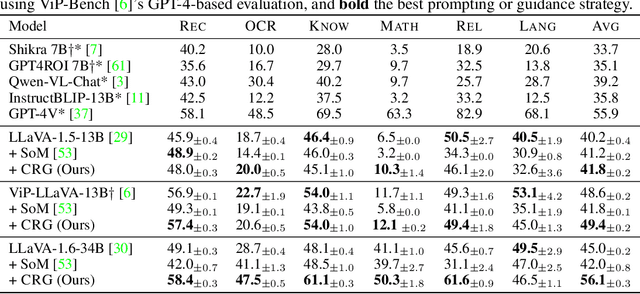
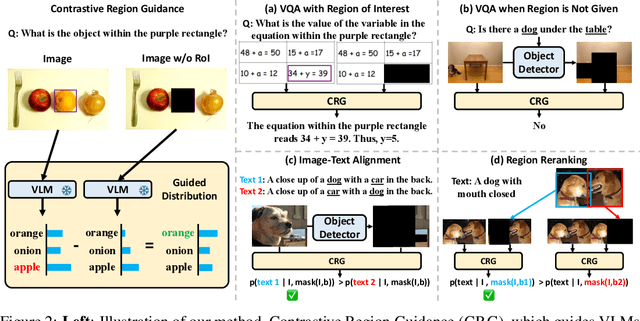
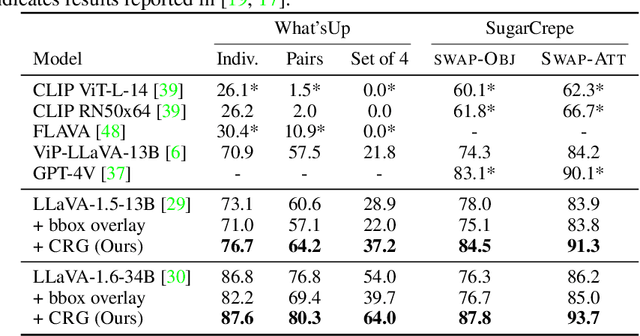
Abstract:Highlighting particularly relevant regions of an image can improve the performance of vision-language models (VLMs) on various vision-language (VL) tasks by guiding the model to attend more closely to these regions of interest. For example, VLMs can be given a "visual prompt", where visual markers such as bounding boxes delineate key image regions. However, current VLMs that can incorporate visual guidance are either proprietary and expensive or require costly training on curated data that includes visual prompts. We introduce Contrastive Region Guidance (CRG), a training-free guidance method that enables open-source VLMs to respond to visual prompts. CRG contrasts model outputs produced with and without visual prompts, factoring out biases revealed by the model when answering without the information required to produce a correct answer (i.e., the model's prior). CRG achieves substantial improvements in a wide variety of VL tasks: When region annotations are provided, CRG increases absolute accuracy by up to 11.1% on ViP-Bench, a collection of six diverse region-based tasks such as recognition, math, and object relationship reasoning. We also show CRG's applicability to spatial reasoning, with 10% improvement on What'sUp, as well as to compositional generalization -- improving accuracy by 11.5% and 7.5% on two challenging splits from SugarCrepe -- and to image-text alignment for generated images, where we improve by up to 8.4 AUROC and 6.8 F1 points on SeeTRUE. When reference regions are absent, CRG allows us to re-rank proposed regions in referring expression comprehension and phrase grounding benchmarks like RefCOCO/+/g and Flickr30K Entities, with an average gain of 3.2% in accuracy. Our analysis explores alternative masking strategies for CRG, quantifies CRG's probability shift, and evaluates the role of region guidance strength, empirically validating CRG's design choices.
HistAlign: Improving Context Dependency in Language Generation by Aligning with History
May 08, 2023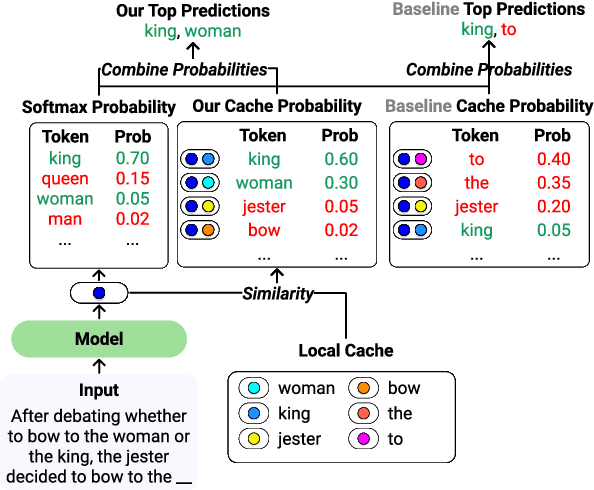
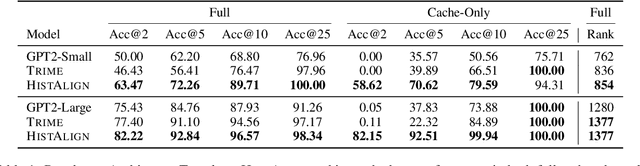
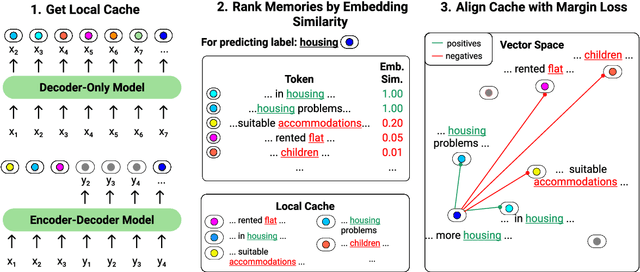

Abstract:Language models (LMs) can generate hallucinations and incoherent outputs, which highlights their weak context dependency. Cache-LMs, which augment LMs with a memory of recent history, can increase context dependency and have shown remarkable performance in diverse language generation tasks. However, we find that even with training, the performance gain stemming from the cache component of current cache-LMs is suboptimal due to the misalignment between the current hidden states and those stored in the memory. In this work, we present HistAlign, a new training approach to ensure good cache alignment such that the model receives useful signals from the history. We first prove our concept on a simple and synthetic task where the memory is essential for correct predictions, and we show that the cache component of HistAlign is better aligned and improves overall performance. Next, we evaluate HistAlign on diverse downstream language generation tasks, including prompt continuation, abstractive summarization, and data-to-text. We demonstrate that HistAlign improves text coherence and faithfulness in open-ended and conditional generation settings respectively. HistAlign is also generalizable across different model families, showcasing its strength in improving context dependency of LMs in diverse scenarios. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/meetdavidwan/histalign
Faithfulness-Aware Decoding Strategies for Abstractive Summarization
Mar 06, 2023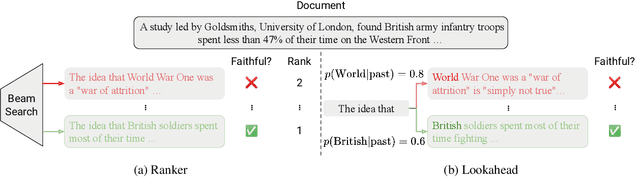
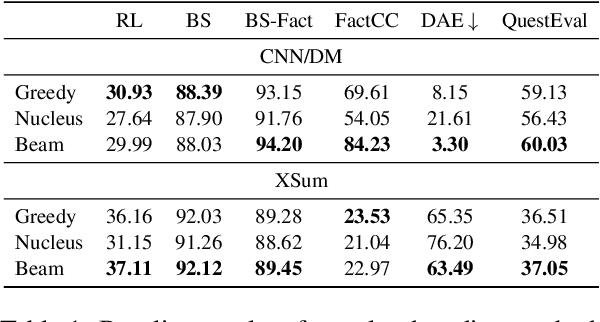
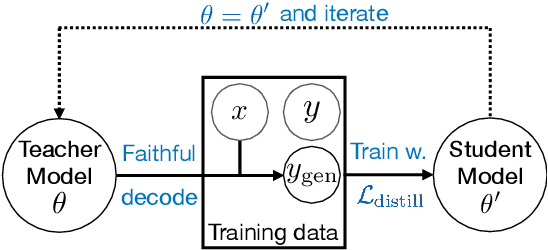
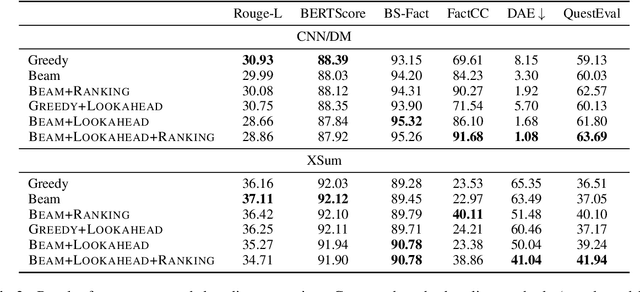
Abstract:Despite significant progress in understanding and improving faithfulness in abstractive summarization, the question of how decoding strategies affect faithfulness is less studied. We present a systematic study of the effect of generation techniques such as beam search and nucleus sampling on faithfulness in abstractive summarization. We find a consistent trend where beam search with large beam sizes produces the most faithful summaries while nucleus sampling generates the least faithful ones. We propose two faithfulness-aware generation methods to further improve faithfulness over current generation techniques: (1) ranking candidates generated by beam search using automatic faithfulness metrics and (2) incorporating lookahead heuristics that produce a faithfulness score on the future summary. We show that both generation methods significantly improve faithfulness across two datasets as evaluated by four automatic faithfulness metrics and human evaluation. To reduce computational cost, we demonstrate a simple distillation approach that allows the model to generate faithful summaries with just greedy decoding. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/amazon-science/faithful-summarization-generation
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge