Xuehai Pan
Rethinking Information Structures in RLHF: Reward Generalization from a Graph Theory Perspective
Feb 20, 2024Abstract:There is a trilemma in reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF): the incompatibility between highly diverse contexts, low labeling cost, and reliable alignment performance. Here we aim to mitigate such incompatibility through the design of dataset information structures during reward modeling, and meanwhile propose new, generalizable methods of analysis that have wider applications, including potentially shedding light on goal misgeneralization. Specifically, we first reexamine the RLHF process and propose a theoretical framework portraying it as an autoencoding process over text distributions. Our framework formalizes the RLHF objective of ensuring distributional consistency between human preference and large language model (LLM) behavior. Based on this framework, we introduce a new method to model generalization in the reward modeling stage of RLHF, the induced Bayesian network (IBN). Drawing from random graph theory and causal analysis, it enables empirically grounded derivation of generalization error bounds, a key improvement over classical methods of generalization analysis. An insight from our analysis is the superiority of the tree-based information structure in reward modeling, compared to chain-based baselines in conventional RLHF methods. We derive that in complex contexts with limited data, the tree-based reward model (RM) induces up to $\Theta(\log n/\log\log n)$ times less variance than chain-based RM where $n$ is the dataset size. As validation, we demonstrate that on three NLP tasks, the tree-based RM achieves 65% win rate on average against chain-based baselines. Looking ahead, we hope to extend the IBN analysis to help understand the phenomenon of goal misgeneralization.
Aligner: Achieving Efficient Alignment through Weak-to-Strong Correction
Feb 06, 2024Abstract:Efforts to align Large Language Models (LLMs) are mainly conducted via Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) methods. However, RLHF encounters major challenges including training reward models, actor-critic engineering, and importantly, it requires access to LLM parameters. Here we introduce Aligner, a new efficient alignment paradigm that bypasses the whole RLHF process by learning the correctional residuals between the aligned and the unaligned answers. Our Aligner offers several key advantages. Firstly, it is an autoregressive seq2seq model that is trained on the query-answer-correction dataset via supervised learning; this offers a parameter-efficient alignment solution with minimal resources. Secondly, the Aligner facilitates weak-to-strong generalization; finetuning large pretrained models by Aligner's supervisory signals demonstrates strong performance boost. Thirdly, Aligner functions as a model-agnostic plug-and-play module, allowing for its direct application on different open-source and API-based models. Remarkably, Aligner-7B improves 11 different LLMs by 21.9% in helpfulness and 23.8% in harmlessness on average (GPT-4 by 17.5% and 26.9%). When finetuning (strong) Llama2-70B with (weak) Aligner-13B's supervision, we can improve Llama2 by 8.2% in helpfulness and 61.6% in harmlessness. See our dataset and code at https://aligner2024.github.io
AI Alignment: A Comprehensive Survey
Nov 01, 2023Abstract:AI alignment aims to make AI systems behave in line with human intentions and values. As AI systems grow more capable, the potential large-scale risks associated with misaligned AI systems become salient. Hundreds of AI experts and public figures have expressed concerns about AI risks, arguing that "mitigating the risk of extinction from AI should be a global priority, alongside other societal-scale risks such as pandemics and nuclear war". To provide a comprehensive and up-to-date overview of the alignment field, in this survey paper, we delve into the core concepts, methodology, and practice of alignment. We identify the RICE principles as the key objectives of AI alignment: Robustness, Interpretability, Controllability, and Ethicality. Guided by these four principles, we outline the landscape of current alignment research and decompose them into two key components: forward alignment and backward alignment. The former aims to make AI systems aligned via alignment training, while the latter aims to gain evidence about the systems' alignment and govern them appropriately to avoid exacerbating misalignment risks. Forward alignment and backward alignment form a recurrent process where the alignment of AI systems from the forward process is verified in the backward process, meanwhile providing updated objectives for forward alignment in the next round. On forward alignment, we discuss learning from feedback and learning under distribution shift. On backward alignment, we discuss assurance techniques and governance practices that apply to every stage of AI systems' lifecycle. We also release and continually update the website (www.alignmentsurvey.com) which features tutorials, collections of papers, blog posts, and other resources.
Safety-Gymnasium: A Unified Safe Reinforcement Learning Benchmark
Oct 19, 2023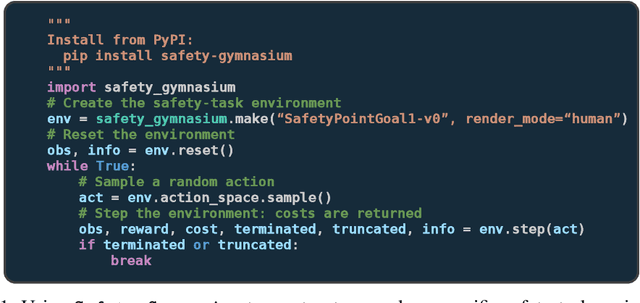
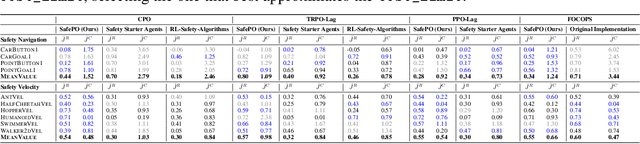
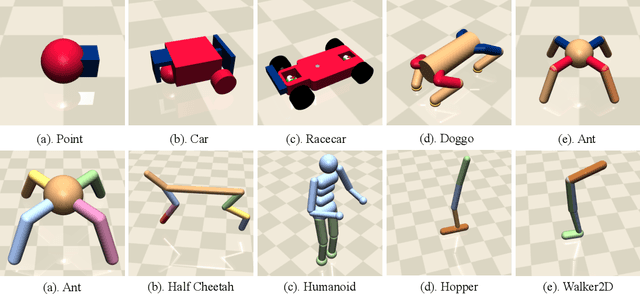
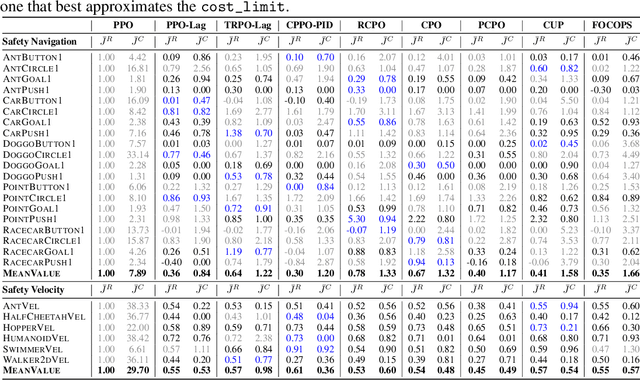
Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) systems possess significant potential to drive societal progress. However, their deployment often faces obstacles due to substantial safety concerns. Safe reinforcement learning (SafeRL) emerges as a solution to optimize policies while simultaneously adhering to multiple constraints, thereby addressing the challenge of integrating reinforcement learning in safety-critical scenarios. In this paper, we present an environment suite called Safety-Gymnasium, which encompasses safety-critical tasks in both single and multi-agent scenarios, accepting vector and vision-only input. Additionally, we offer a library of algorithms named Safe Policy Optimization (SafePO), comprising 16 state-of-the-art SafeRL algorithms. This comprehensive library can serve as a validation tool for the research community. By introducing this benchmark, we aim to facilitate the evaluation and comparison of safety performance, thus fostering the development of reinforcement learning for safer, more reliable, and responsible real-world applications. The website of this project can be accessed at https://sites.google.com/view/safety-gymnasium.
Safe RLHF: Safe Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback
Oct 19, 2023



Abstract:With the development of large language models (LLMs), striking a balance between the performance and safety of AI systems has never been more critical. However, the inherent tension between the objectives of helpfulness and harmlessness presents a significant challenge during LLM training. To address this issue, we propose Safe Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (Safe RLHF), a novel algorithm for human value alignment. Safe RLHF explicitly decouples human preferences regarding helpfulness and harmlessness, effectively avoiding the crowdworkers' confusion about the tension and allowing us to train separate reward and cost models. We formalize the safety concern of LLMs as an optimization task of maximizing the reward function while satisfying specified cost constraints. Leveraging the Lagrangian method to solve this constrained problem, Safe RLHF dynamically adjusts the balance between the two objectives during fine-tuning. Through a three-round fine-tuning using Safe RLHF, we demonstrate a superior ability to mitigate harmful responses while enhancing model performance compared to existing value-aligned algorithms. Experimentally, we fine-tuned the Alpaca-7B using Safe RLHF and aligned it with collected human preferences, significantly improving its helpfulness and harmlessness according to human evaluations.
Red Teaming Game: A Game-Theoretic Framework for Red Teaming Language Models
Oct 10, 2023Abstract:Deployable Large Language Models (LLMs) must conform to the criterion of helpfulness and harmlessness, thereby achieving consistency between LLMs outputs and human values. Red-teaming techniques constitute a critical way towards this criterion. Existing work rely solely on manual red team designs and heuristic adversarial prompts for vulnerability detection and optimization. These approaches lack rigorous mathematical formulation, thus limiting the exploration of diverse attack strategy within quantifiable measure and optimization of LLMs under convergence guarantees. In this paper, we present Red-teaming Game (RTG), a general game-theoretic framework without manual annotation. RTG is designed for analyzing the multi-turn attack and defense interactions between Red-team language Models (RLMs) and Blue-team Language Model (BLM). Within the RTG, we propose Gamified Red-teaming Solver (GRTS) with diversity measure of the semantic space. GRTS is an automated red teaming technique to solve RTG towards Nash equilibrium through meta-game analysis, which corresponds to the theoretically guaranteed optimization direction of both RLMs and BLM. Empirical results in multi-turn attacks with RLMs show that GRTS autonomously discovered diverse attack strategies and effectively improved security of LLMs, outperforming existing heuristic red-team designs. Overall, RTG has established a foundational framework for red teaming tasks and constructed a new scalable oversight technique for alignment.
Baichuan 2: Open Large-scale Language Models
Sep 20, 2023Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance on a variety of natural language tasks based on just a few examples of natural language instructions, reducing the need for extensive feature engineering. However, most powerful LLMs are closed-source or limited in their capability for languages other than English. In this technical report, we present Baichuan 2, a series of large-scale multilingual language models containing 7 billion and 13 billion parameters, trained from scratch, on 2.6 trillion tokens. Baichuan 2 matches or outperforms other open-source models of similar size on public benchmarks like MMLU, CMMLU, GSM8K, and HumanEval. Furthermore, Baichuan 2 excels in vertical domains such as medicine and law. We will release all pre-training model checkpoints to benefit the research community in better understanding the training dynamics of Baichuan 2.
BeaverTails: Towards Improved Safety Alignment of LLM via a Human-Preference Dataset
Jul 10, 2023



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce the BeaverTails dataset, aimed at fostering research on safety alignment in large language models (LLMs). This dataset uniquely separates annotations of helpfulness and harmlessness for question-answering pairs, thus offering distinct perspectives on these crucial attributes. In total, we have compiled safety meta-labels for 30,207 question-answer (QA) pairs and gathered 30,144 pairs of expert comparison data for both the helpfulness and harmlessness metrics. We further showcase applications of BeaverTails in content moderation and reinforcement learning with human feedback (RLHF), emphasizing its potential for practical safety measures in LLMs. We believe this dataset provides vital resources for the community, contributing towards the safe development and deployment of LLMs. Our project page is available at the following URL: https://sites.google.com/view/pku-beavertails.
OmniSafe: An Infrastructure for Accelerating Safe Reinforcement Learning Research
May 16, 2023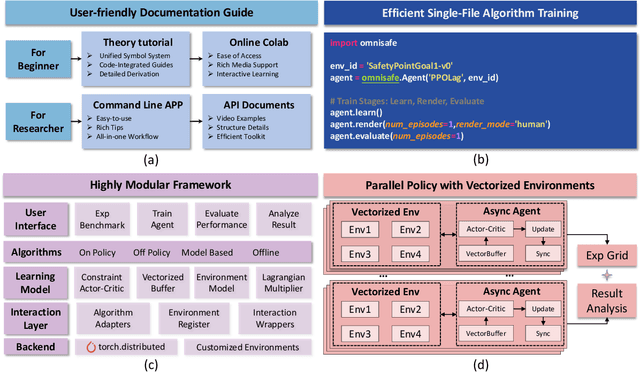
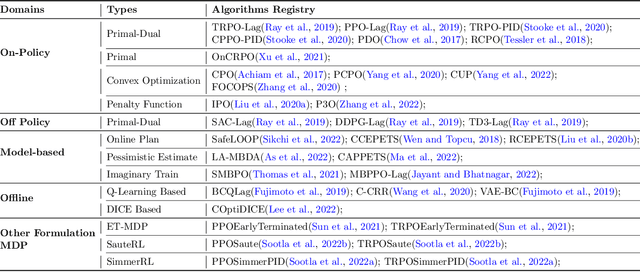
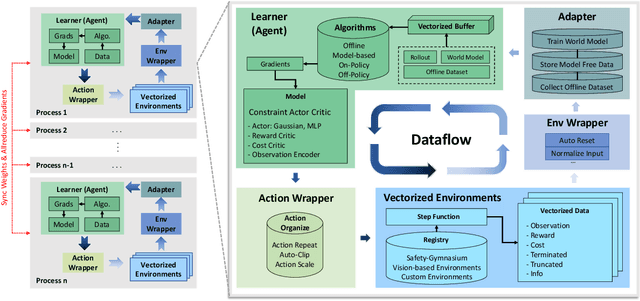
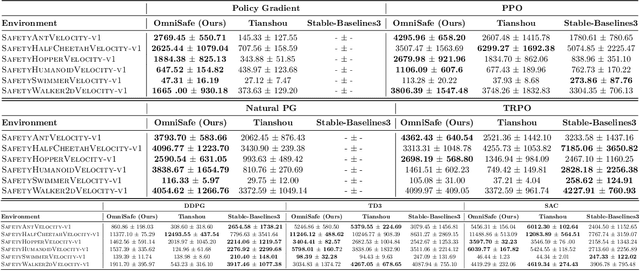
Abstract:AI systems empowered by reinforcement learning (RL) algorithms harbor the immense potential to catalyze societal advancement, yet their deployment is often impeded by significant safety concerns. Particularly in safety-critical applications, researchers have raised concerns about unintended harms or unsafe behaviors of unaligned RL agents. The philosophy of safe reinforcement learning (SafeRL) is to align RL agents with harmless intentions and safe behavioral patterns. In SafeRL, agents learn to develop optimal policies by receiving feedback from the environment, while also fulfilling the requirement of minimizing the risk of unintended harm or unsafe behavior. However, due to the intricate nature of SafeRL algorithm implementation, combining methodologies across various domains presents a formidable challenge. This had led to an absence of a cohesive and efficacious learning framework within the contemporary SafeRL research milieu. In this work, we introduce a foundational framework designed to expedite SafeRL research endeavors. Our comprehensive framework encompasses an array of algorithms spanning different RL domains and places heavy emphasis on safety elements. Our efforts are to make the SafeRL-related research process more streamlined and efficient, therefore facilitating further research in AI safety. Our project is released at: https://github.com/PKU-Alignment/omnisafe.
Proactive Multi-Camera Collaboration For 3D Human Pose Estimation
Mar 07, 2023



Abstract:This paper presents a multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) scheme for proactive Multi-Camera Collaboration in 3D Human Pose Estimation in dynamic human crowds. Traditional fixed-viewpoint multi-camera solutions for human motion capture (MoCap) are limited in capture space and susceptible to dynamic occlusions. Active camera approaches proactively control camera poses to find optimal viewpoints for 3D reconstruction. However, current methods still face challenges with credit assignment and environment dynamics. To address these issues, our proposed method introduces a novel Collaborative Triangulation Contribution Reward (CTCR) that improves convergence and alleviates multi-agent credit assignment issues resulting from using 3D reconstruction accuracy as the shared reward. Additionally, we jointly train our model with multiple world dynamics learning tasks to better capture environment dynamics and encourage anticipatory behaviors for occlusion avoidance. We evaluate our proposed method in four photo-realistic UE4 environments to ensure validity and generalizability. Empirical results show that our method outperforms fixed and active baselines in various scenarios with different numbers of cameras and humans.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge