Xiaoyan Cai
ASPO: Adaptive Sentence-Level Preference Optimization for Fine-Grained Multimodal Reasoning
May 25, 2025Abstract:Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) has gained significant attention for its simplicity and computational efficiency in aligning large language models (LLMs). Recent advancements have extended DPO to multimodal scenarios, achieving strong performance. However, traditional DPO relies on binary preference optimization, rewarding or penalizing entire responses without considering fine-grained segment correctness, leading to suboptimal solutions. The root of this issue lies in the absence of fine-grained supervision during the optimization process. To address this, we propose Adaptive Sentence-level Preference Optimization (ASPO), which evaluates individual sentences for more precise preference optimization. By dynamically calculating adaptive rewards at the sentence level based on model predictions, ASPO enhances response content assessment without additional models or parameters. This significantly improves the alignment of multimodal features. Extensive experiments show that ASPO substantially enhances the overall performance of multimodal models.
Instruction-Aligned Visual Attention for Mitigating Hallucinations in Large Vision-Language Models
Mar 24, 2025Abstract:Despite the significant success of Large Vision-Language models(LVLMs), these models still suffer hallucinations when describing images, generating answers that include non-existent objects. It is reported that these models tend to over-focus on certain irrelevant image tokens that do not contain critical information for answering the question and distort the output. To address this, we propose an Instruction-Aligned Visual Attention(IAVA) approach, which identifies irrelevant tokens by comparing changes in attention weights under two different instructions. By applying contrastive decoding, we dynamically adjust the logits generated from original image tokens and irrelevant image tokens, reducing the model's over-attention to irrelevant information. The experimental results demonstrate that IAVA consistently outperforms existing decoding techniques on benchmarks such as MME, POPE, and TextVQA in mitigating object hallucinations. Our IAVA approach is available online at https://github.com/Lee-lab558/IAVA.
CoF: Coarse to Fine-Grained Image Understanding for Multi-modal Large Language Models
Dec 22, 2024



Abstract:The impressive performance of Large Language Model (LLM) has prompted researchers to develop Multi-modal LLM (MLLM), which has shown great potential for various multi-modal tasks. However, current MLLM often struggles to effectively address fine-grained multi-modal challenges. We argue that this limitation is closely linked to the models' visual grounding capabilities. The restricted spatial awareness and perceptual acuity of visual encoders frequently lead to interference from irrelevant background information in images, causing the models to overlook subtle but crucial details. As a result, achieving fine-grained regional visual comprehension becomes difficult. In this paper, we break down multi-modal understanding into two stages, from Coarse to Fine (CoF). In the first stage, we prompt the MLLM to locate the approximate area of the answer. In the second stage, we further enhance the model's focus on relevant areas within the image through visual prompt engineering, adjusting attention weights of pertinent regions. This, in turn, improves both visual grounding and overall performance in downstream tasks. Our experiments show that this approach significantly boosts the performance of baseline models, demonstrating notable generalization and effectiveness. Our CoF approach is available online at https://github.com/Gavin001201/CoF.
Enhancing Fine-Grained Vision-Language Pretraining with Negative Augmented Samples
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:Existing Vision-Language Pretraining (VLP) methods have achieved remarkable improvements across a variety of vision-language tasks, confirming their effectiveness in capturing coarse-grained semantic correlations. However, their capability for fine-grained understanding, which is critical for many nuanced vision-language applications, remains limited. Prevailing VLP models often overlook the intricate distinctions in expressing different modal features and typically depend on the similarity of holistic features for cross-modal interactions. Moreover, these models directly align and integrate features from different modalities, focusing more on coarse-grained general representations, thus failing to capture the nuanced differences necessary for tasks demanding a more detailed perception. In response to these limitations, we introduce Negative Augmented Samples(NAS), a refined vision-language pretraining model that innovatively incorporates NAS to specifically address the challenge of fine-grained understanding. NAS utilizes a Visual Dictionary(VD) as a semantic bridge between visual and linguistic domains. Additionally, it employs a Negative Visual Augmentation(NVA) method based on the VD to generate challenging negative image samples. These samples deviate from positive samples exclusively at the token level, thereby necessitating that the model discerns the subtle disparities between positive and negative samples with greater precision. Comprehensive experiments validate the efficacy of NAS components and underscore its potential to enhance fine-grained vision-language comprehension.
MoDULA: Mixture of Domain-Specific and Universal LoRA for Multi-Task Learning
Dec 10, 2024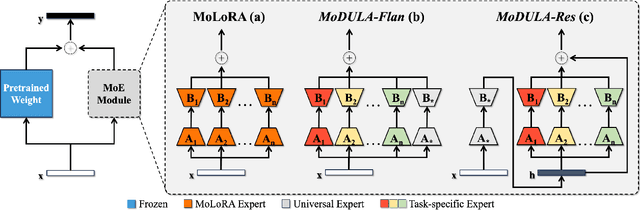
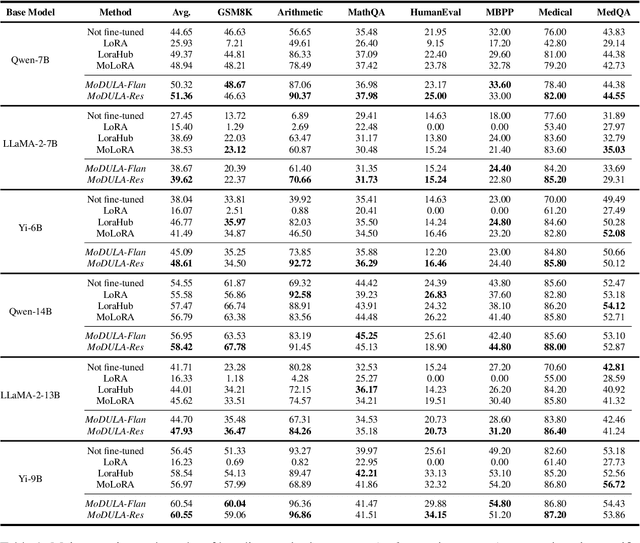
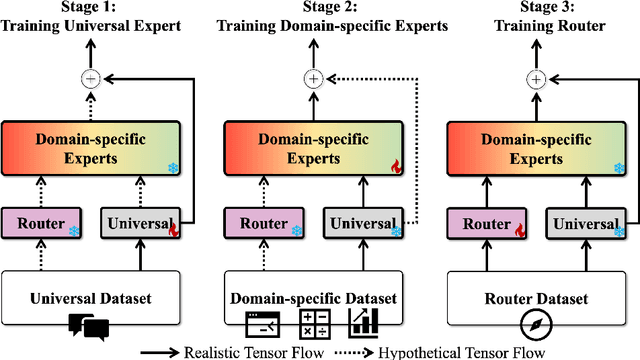
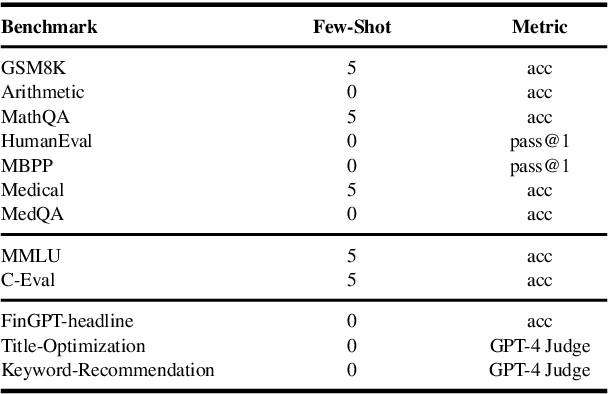
Abstract:The growing demand for larger-scale models in the development of \textbf{L}arge \textbf{L}anguage \textbf{M}odels (LLMs) poses challenges for efficient training within limited computational resources. Traditional fine-tuning methods often exhibit instability in multi-task learning and rely heavily on extensive training resources. Here, we propose MoDULA (\textbf{M}ixture \textbf{o}f \textbf{D}omain-Specific and \textbf{U}niversal \textbf{L}oR\textbf{A}), a novel \textbf{P}arameter \textbf{E}fficient \textbf{F}ine-\textbf{T}uning (PEFT) \textbf{M}ixture-\textbf{o}f-\textbf{E}xpert (MoE) paradigm for improved fine-tuning and parameter efficiency in multi-task learning. The paradigm effectively improves the multi-task capability of the model by training universal experts, domain-specific experts, and routers separately. MoDULA-Res is a new method within the MoDULA paradigm, which maintains the model's general capability by connecting universal and task-specific experts through residual connections. The experimental results demonstrate that the overall performance of the MoDULA-Flan and MoDULA-Res methods surpasses that of existing fine-tuning methods on various LLMs. Notably, MoDULA-Res achieves more significant performance improvements in multiple tasks while reducing training costs by over 80\% without losing general capability. Moreover, MoDULA displays flexible pluggability, allowing for the efficient addition of new tasks without retraining existing experts from scratch. This progressive training paradigm circumvents data balancing issues, enhancing training efficiency and model stability. Overall, MoDULA provides a scalable, cost-effective solution for fine-tuning LLMs with enhanced parameter efficiency and generalization capability.
MLoRA: Multi-Domain Low-Rank Adaptive Network for CTR Prediction
Aug 14, 2024



Abstract:Click-through rate (CTR) prediction is one of the fundamental tasks in the industry, especially in e-commerce, social media, and streaming media. It directly impacts website revenues, user satisfaction, and user retention. However, real-world production platforms often encompass various domains to cater for diverse customer needs. Traditional CTR prediction models struggle in multi-domain recommendation scenarios, facing challenges of data sparsity and disparate data distributions across domains. Existing multi-domain recommendation approaches introduce specific-domain modules for each domain, which partially address these issues but often significantly increase model parameters and lead to insufficient training. In this paper, we propose a Multi-domain Low-Rank Adaptive network (MLoRA) for CTR prediction, where we introduce a specialized LoRA module for each domain. This approach enhances the model's performance in multi-domain CTR prediction tasks and is able to be applied to various deep-learning models. We evaluate the proposed method on several multi-domain datasets. Experimental results demonstrate our MLoRA approach achieves a significant improvement compared with state-of-the-art baselines. Furthermore, we deploy it in the production environment of the Alibaba.COM. The online A/B testing results indicate the superiority and flexibility in real-world production environments. The code of our MLoRA is publicly available.
General2Specialized LLMs Translation for E-commerce
Mar 06, 2024Abstract:Existing Neural Machine Translation (NMT) models mainly handle translation in the general domain, while overlooking domains with special writing formulas, such as e-commerce and legal documents. Taking e-commerce as an example, the texts usually include amounts of domain-related words and have more grammar problems, which leads to inferior performances of current NMT methods. To address these problems, we collect two domain-related resources, including a set of term pairs (aligned Chinese-English bilingual terms) and a parallel corpus annotated for the e-commerce domain. Furthermore, we propose a two-step fine-tuning paradigm (named G2ST) with self-contrastive semantic enhancement to transfer one general NMT model to the specialized NMT model for e-commerce. The paradigm can be used for the NMT models based on Large language models (LLMs). Extensive evaluations on real e-commerce titles demonstrate the superior translation quality and robustness of our G2ST approach, as compared with state-of-the-art NMT models such as LLaMA, Qwen, GPT-3.5, and even GPT-4.
ChatRadio-Valuer: A Chat Large Language Model for Generalizable Radiology Report Generation Based on Multi-institution and Multi-system Data
Oct 10, 2023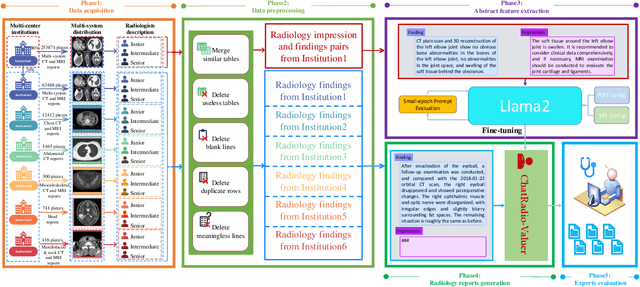
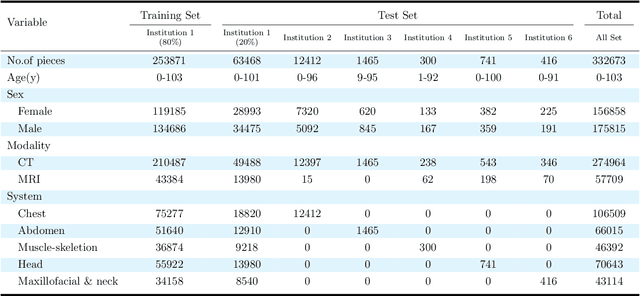
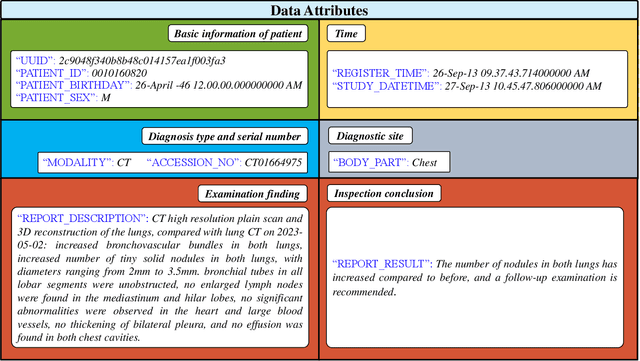
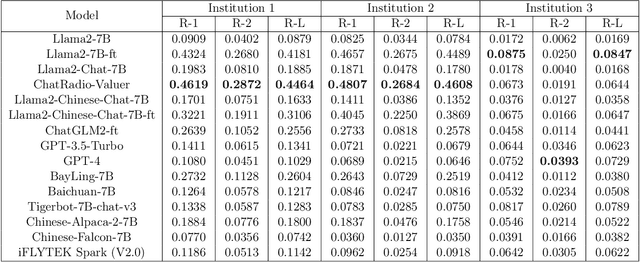
Abstract:Radiology report generation, as a key step in medical image analysis, is critical to the quantitative analysis of clinically informed decision-making levels. However, complex and diverse radiology reports with cross-source heterogeneity pose a huge generalizability challenge to the current methods under massive data volume, mainly because the style and normativity of radiology reports are obviously distinctive among institutions, body regions inspected and radiologists. Recently, the advent of large language models (LLM) offers great potential for recognizing signs of health conditions. To resolve the above problem, we collaborate with the Second Xiangya Hospital in China and propose ChatRadio-Valuer based on the LLM, a tailored model for automatic radiology report generation that learns generalizable representations and provides a basis pattern for model adaptation in sophisticated analysts' cases. Specifically, ChatRadio-Valuer is trained based on the radiology reports from a single institution by means of supervised fine-tuning, and then adapted to disease diagnosis tasks for human multi-system evaluation (i.e., chest, abdomen, muscle-skeleton, head, and maxillofacial $\&$ neck) from six different institutions in clinical-level events. The clinical dataset utilized in this study encompasses a remarkable total of \textbf{332,673} observations. From the comprehensive results on engineering indicators, clinical efficacy and deployment cost metrics, it can be shown that ChatRadio-Valuer consistently outperforms state-of-the-art models, especially ChatGPT (GPT-3.5-Turbo) and GPT-4 et al., in terms of the diseases diagnosis from radiology reports. ChatRadio-Valuer provides an effective avenue to boost model generalization performance and alleviate the annotation workload of experts to enable the promotion of clinical AI applications in radiology reports.
Evaluating Large Language Models for Radiology Natural Language Processing
Jul 27, 2023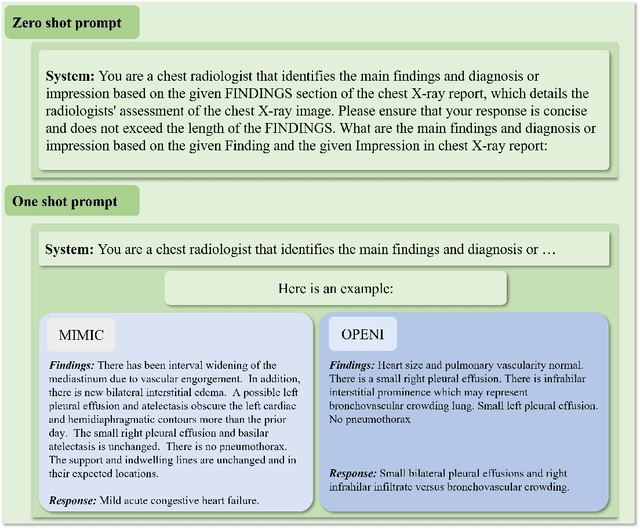
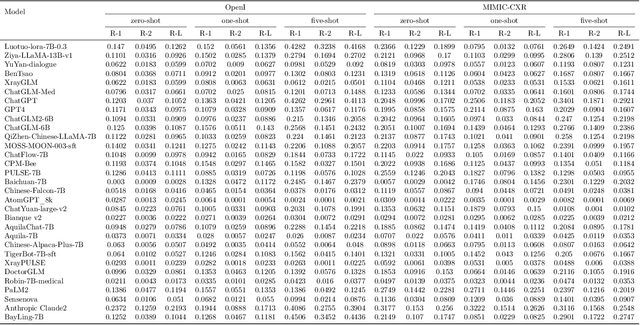
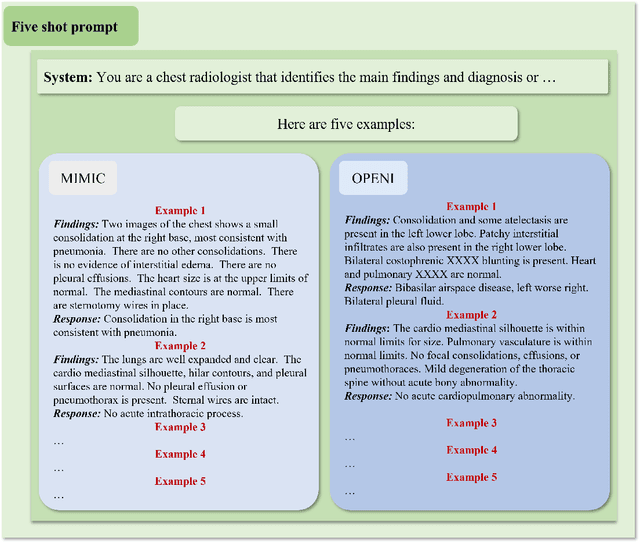
Abstract:The rise of large language models (LLMs) has marked a pivotal shift in the field of natural language processing (NLP). LLMs have revolutionized a multitude of domains, and they have made a significant impact in the medical field. Large language models are now more abundant than ever, and many of these models exhibit bilingual capabilities, proficient in both English and Chinese. However, a comprehensive evaluation of these models remains to be conducted. This lack of assessment is especially apparent within the context of radiology NLP. This study seeks to bridge this gap by critically evaluating thirty two LLMs in interpreting radiology reports, a crucial component of radiology NLP. Specifically, the ability to derive impressions from radiologic findings is assessed. The outcomes of this evaluation provide key insights into the performance, strengths, and weaknesses of these LLMs, informing their practical applications within the medical domain.
ImpressionGPT: An Iterative Optimizing Framework for Radiology Report Summarization with ChatGPT
May 03, 2023Abstract:The 'Impression' section of a radiology report is a critical basis for communication between radiologists and other physicians, and it is typically written by radiologists based on the 'Findings' section. However, writing numerous impressions can be laborious and error-prone for radiologists. Although recent studies have achieved promising results in automatic impression generation using large-scale medical text data for pre-training and fine-tuning pre-trained language models, such models often require substantial amounts of medical text data and have poor generalization performance. While large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT have shown strong generalization capabilities and performance, their performance in specific domains, such as radiology, remains under-investigated and potentially limited. To address this limitation, we propose ImpressionGPT, which leverages the in-context learning capability of LLMs by constructing dynamic contexts using domain-specific, individualized data. This dynamic prompt approach enables the model to learn contextual knowledge from semantically similar examples from existing data. Additionally, we design an iterative optimization algorithm that performs automatic evaluation on the generated impression results and composes the corresponding instruction prompts to further optimize the model. The proposed ImpressionGPT model achieves state-of-the-art performance on both MIMIC-CXR and OpenI datasets without requiring additional training data or fine-tuning the LLMs. This work presents a paradigm for localizing LLMs that can be applied in a wide range of similar application scenarios, bridging the gap between general-purpose LLMs and the specific language processing needs of various domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge