Jinxia Zhang
The Bitter Lesson of Diffusion Language Models for Agentic Workflows: A Comprehensive Reality Check
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:The pursuit of real-time agentic interaction has driven interest in Diffusion-based Large Language Models (dLLMs) as alternatives to auto-regressive backbones, promising to break the sequential latency bottleneck. However, does such efficiency gains translate into effective agentic behavior? In this work, we present a comprehensive evaluation of dLLMs (e.g., LLaDA, Dream) across two distinct agentic paradigms: Embodied Agents (requiring long-horizon planning) and Tool-Calling Agents (requiring precise formatting). Contrary to the efficiency hype, our results on Agentboard and BFCL reveal a "bitter lesson": current dLLMs fail to serve as reliable agentic backbones, frequently leading to systematically failure. (1) In Embodied settings, dLLMs suffer repeated attempts, failing to branch under temporal feedback. (2) In Tool-Calling settings, dLLMs fail to maintain symbolic precision (e.g. strict JSON schemas) under diffusion noise. To assess the potential of dLLMs in agentic workflows, we introduce DiffuAgent, a multi-agent evaluation framework that integrates dLLMs as plug-and-play cognitive cores. Our analysis shows that dLLMs are effective in non-causal roles (e.g., memory summarization and tool selection) but require the incorporation of causal, precise, and logically grounded reasoning mechanisms into the denoising process to be viable for agentic tasks.
Runaway is Ashamed, But Helpful: On the Early-Exit Behavior of Large Language Model-based Agents in Embodied Environments
May 23, 2025Abstract:Agents powered by large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong planning and decision-making capabilities in complex embodied environments. However, such agents often suffer from inefficiencies in multi-turn interactions, frequently trapped in repetitive loops or issuing ineffective commands, leading to redundant computational overhead. Instead of relying solely on learning from trajectories, we take a first step toward exploring the early-exit behavior for LLM-based agents. We propose two complementary approaches: 1. an $\textbf{intrinsic}$ method that injects exit instructions during generation, and 2. an $\textbf{extrinsic}$ method that verifies task completion to determine when to halt an agent's trial. To evaluate early-exit mechanisms, we introduce two metrics: one measures the reduction of $\textbf{redundant steps}$ as a positive effect, and the other evaluates $\textbf{progress degradation}$ as a negative effect. Experiments with 4 different LLMs across 5 embodied environments show significant efficiency improvements, with only minor drops in agent performance. We also validate a practical strategy where a stronger agent assists after an early-exit agent, achieving better performance with the same total steps. We will release our code to support further research.
MADiff: Text-Guided Fashion Image Editing with Mask Prediction and Attention-Enhanced Diffusion
Dec 28, 2024
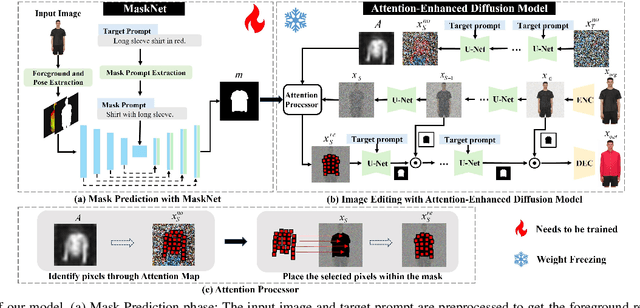

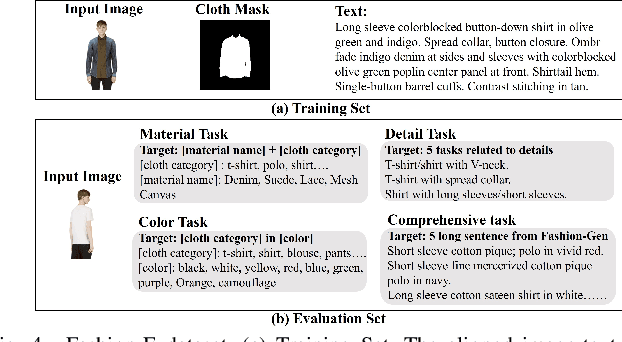
Abstract:Text-guided image editing model has achieved great success in general domain. However, directly applying these models to the fashion domain may encounter two issues: (1) Inaccurate localization of editing region; (2) Weak editing magnitude. To address these issues, the MADiff model is proposed. Specifically, to more accurately identify editing region, the MaskNet is proposed, in which the foreground region, densepose and mask prompts from large language model are fed into a lightweight UNet to predict the mask for editing region. To strengthen the editing magnitude, the Attention-Enhanced Diffusion Model is proposed, where the noise map, attention map, and the mask from MaskNet are fed into the proposed Attention Processor to produce a refined noise map. By integrating the refined noise map into the diffusion model, the edited image can better align with the target prompt. Given the absence of benchmarks in fashion image editing, we constructed a dataset named Fashion-E, comprising 28390 image-text pairs in the training set, and 2639 image-text pairs for four types of fashion tasks in the evaluation set. Extensive experiments on Fashion-E demonstrate that our proposed method can accurately predict the mask of editing region and significantly enhance editing magnitude in fashion image editing compared to the state-of-the-art methods.
FashionFAE: Fine-grained Attributes Enhanced Fashion Vision-Language Pre-training
Dec 28, 2024Abstract:Large-scale Vision-Language Pre-training (VLP) has demonstrated remarkable success in the general domain. However, in the fashion domain, items are distinguished by fine-grained attributes like texture and material, which are crucial for tasks such as retrieval. Existing models often fail to leverage these fine-grained attributes from both text and image modalities. To address the above issues, we propose a novel approach for the fashion domain, Fine-grained Attributes Enhanced VLP (FashionFAE), which focuses on the detailed characteristics of fashion data. An attribute-emphasized text prediction task is proposed to predict fine-grained attributes of the items. This forces the model to focus on the salient attributes from the text modality. Additionally, a novel attribute-promoted image reconstruction task is proposed, which further enhances the fine-grained ability of the model by leveraging the representative attributes from the image modality. Extensive experiments show that FashionFAE significantly outperforms State-Of-The-Art (SOTA) methods, achieving 2.9% and 5.2% improvements in retrieval on sub-test and full test sets, respectively, and a 1.6% average improvement in recognition tasks.
CoF: Coarse to Fine-Grained Image Understanding for Multi-modal Large Language Models
Dec 22, 2024



Abstract:The impressive performance of Large Language Model (LLM) has prompted researchers to develop Multi-modal LLM (MLLM), which has shown great potential for various multi-modal tasks. However, current MLLM often struggles to effectively address fine-grained multi-modal challenges. We argue that this limitation is closely linked to the models' visual grounding capabilities. The restricted spatial awareness and perceptual acuity of visual encoders frequently lead to interference from irrelevant background information in images, causing the models to overlook subtle but crucial details. As a result, achieving fine-grained regional visual comprehension becomes difficult. In this paper, we break down multi-modal understanding into two stages, from Coarse to Fine (CoF). In the first stage, we prompt the MLLM to locate the approximate area of the answer. In the second stage, we further enhance the model's focus on relevant areas within the image through visual prompt engineering, adjusting attention weights of pertinent regions. This, in turn, improves both visual grounding and overall performance in downstream tasks. Our experiments show that this approach significantly boosts the performance of baseline models, demonstrating notable generalization and effectiveness. Our CoF approach is available online at https://github.com/Gavin001201/CoF.
Enhancing Fine-Grained Vision-Language Pretraining with Negative Augmented Samples
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:Existing Vision-Language Pretraining (VLP) methods have achieved remarkable improvements across a variety of vision-language tasks, confirming their effectiveness in capturing coarse-grained semantic correlations. However, their capability for fine-grained understanding, which is critical for many nuanced vision-language applications, remains limited. Prevailing VLP models often overlook the intricate distinctions in expressing different modal features and typically depend on the similarity of holistic features for cross-modal interactions. Moreover, these models directly align and integrate features from different modalities, focusing more on coarse-grained general representations, thus failing to capture the nuanced differences necessary for tasks demanding a more detailed perception. In response to these limitations, we introduce Negative Augmented Samples(NAS), a refined vision-language pretraining model that innovatively incorporates NAS to specifically address the challenge of fine-grained understanding. NAS utilizes a Visual Dictionary(VD) as a semantic bridge between visual and linguistic domains. Additionally, it employs a Negative Visual Augmentation(NVA) method based on the VD to generate challenging negative image samples. These samples deviate from positive samples exclusively at the token level, thereby necessitating that the model discerns the subtle disparities between positive and negative samples with greater precision. Comprehensive experiments validate the efficacy of NAS components and underscore its potential to enhance fine-grained vision-language comprehension.
MQM-APE: Toward High-Quality Error Annotation Predictors with Automatic Post-Editing in LLM Translation Evaluators
Sep 22, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown significant potential as judges for Machine Translation (MT) quality assessment, providing both scores and fine-grained feedback. Although approaches such as GEMBA-MQM has shown SOTA performance on reference-free evaluation, the predicted errors do not align well with those annotated by human, limiting their interpretability as feedback signals. To enhance the quality of error annotations predicted by LLM evaluators, we introduce a universal and training-free framework, $\textbf{MQM-APE}$, based on the idea of filtering out non-impactful errors by Automatically Post-Editing (APE) the original translation based on each error, leaving only those errors that contribute to quality improvement. Specifically, we prompt the LLM to act as 1) $\textit{evaluator}$ to provide error annotations, 2) $\textit{post-editor}$ to determine whether errors impact quality improvement and 3) $\textit{pairwise quality verifier}$ as the error filter. Experiments show that our approach consistently improves both the reliability and quality of error spans against GEMBA-MQM, across eight LLMs in both high- and low-resource languages. Orthogonal to trained approaches, MQM-APE complements translation-specific evaluators such as Tower, highlighting its broad applicability. Further analysis confirm the effectiveness of each module and offer valuable insights into evaluator design and LLMs selection. The code will be released to facilitate the community.
Shifting Spotlight for Co-supervision: A Simple yet Efficient Single-branch Network to See Through Camouflage
Apr 13, 2024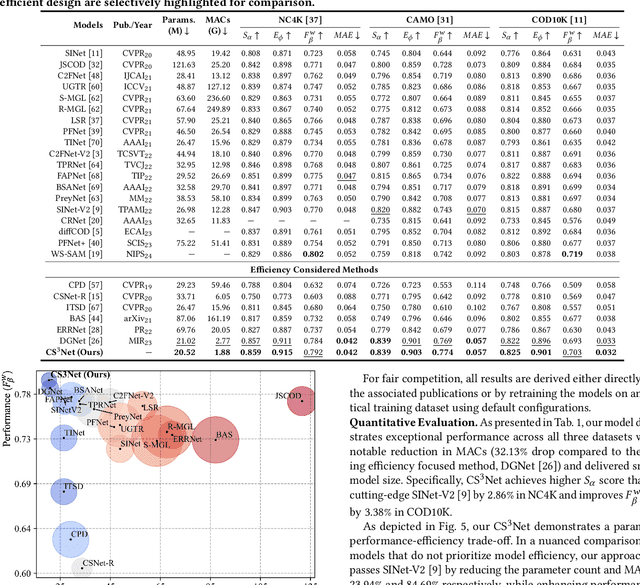
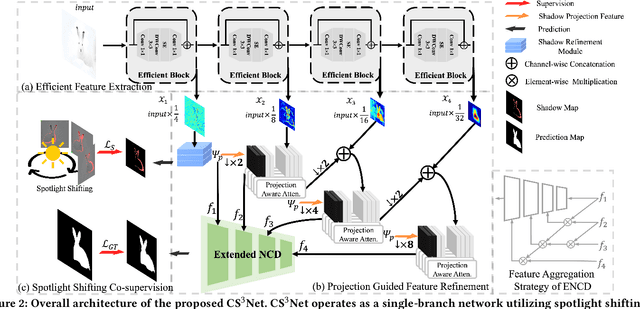
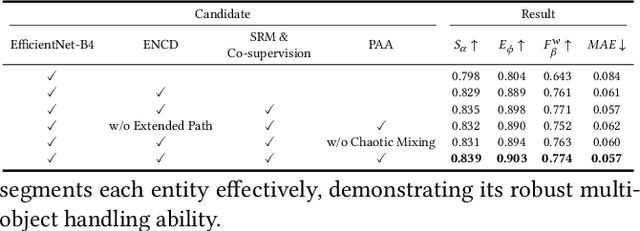
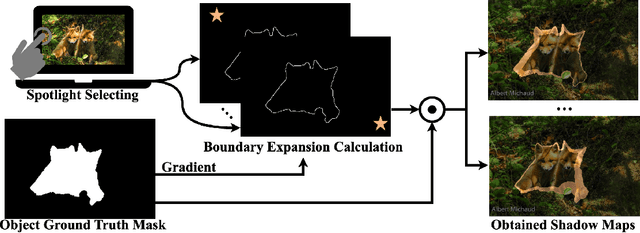
Abstract:Efficient and accurate camouflaged object detection (COD) poses a challenge in the field of computer vision. Recent approaches explored the utility of edge information for network co-supervision, achieving notable advancements. However, these approaches introduce an extra branch for complex edge extraction, complicate the model architecture and increases computational demands. Addressing this issue, our work replicates the effect that animal's camouflage can be easily revealed under a shifting spotlight, and leverages it for network co-supervision to form a compact yet efficient single-branch network, the Co-Supervised Spotlight Shifting Network (CS$^3$Net). The spotlight shifting strategy allows CS$^3$Net to learn additional prior within a single-branch framework, obviating the need for resource demanding multi-branch design. To leverage the prior of spotlight shifting co-supervision, we propose Shadow Refinement Module (SRM) and Projection Aware Attention (PAA) for feature refinement and enhancement. To ensure the continuity of multi-scale features aggregation, we utilize the Extended Neighbor Connection Decoder (ENCD) for generating the final predictions. Empirical evaluations on public datasets confirm that our CS$^3$Net offers an optimal balance between efficiency and performance: it accomplishes a 32.13% reduction in Multiply-Accumulate (MACs) operations compared to leading efficient COD models, while also delivering superior performance.
A lightweight network for photovoltaic cell defect detection in electroluminescence images based on neural architecture search and knowledge distillation
Feb 15, 2023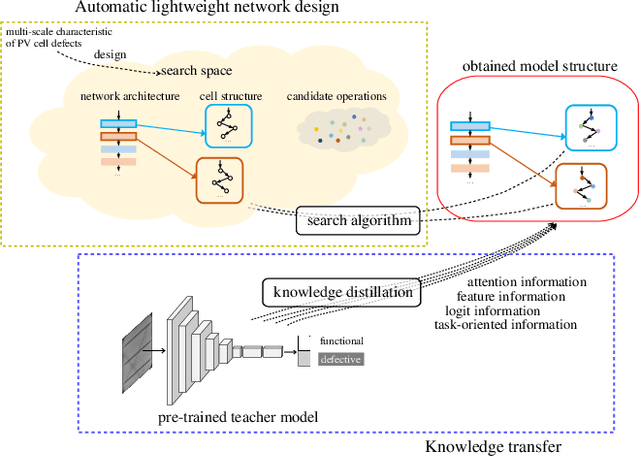
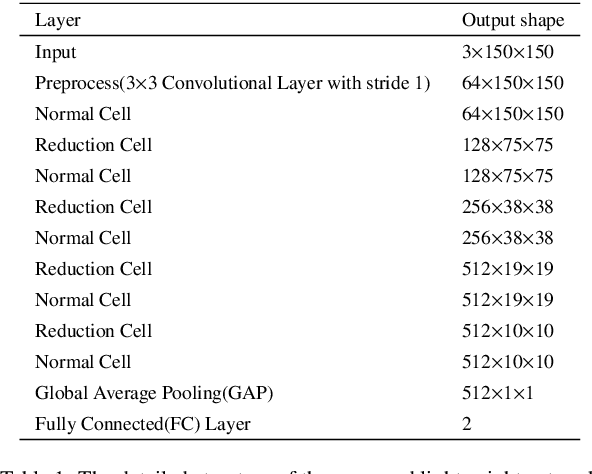
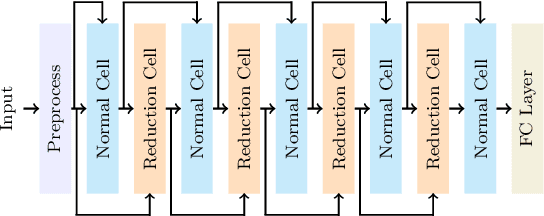
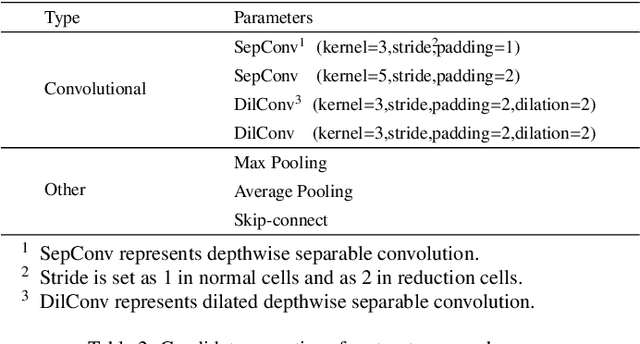
Abstract:Nowadays, the rapid development of photovoltaic(PV) power stations requires increasingly reliable maintenance and fault diagnosis of PV modules in the field. Due to the effectiveness, convolutional neural network (CNN) has been widely used in the existing automatic defect detection of PV cells. However, the parameters of these CNN-based models are very large, which require stringent hardware resources and it is difficult to be applied in actual industrial projects. To solve these problems, we propose a novel lightweight high-performance model for automatic defect detection of PV cells in electroluminescence(EL) images based on neural architecture search and knowledge distillation. To auto-design an effective lightweight model, we introduce neural architecture search to the field of PV cell defect classification for the first time. Since the defect can be any size, we design a proper search structure of network to better exploit the multi-scale characteristic. To improve the overall performance of the searched lightweight model, we further transfer the knowledge learned by the existing pre-trained large-scale model based on knowledge distillation. Different kinds of knowledge are exploited and transferred, including attention information, feature information, logit information and task-oriented information. Experiments have demonstrated that the proposed model achieves the state-of-the-art performance on the public PV cell dataset of EL images under online data augmentation with accuracy of 91.74% and the parameters of 1.85M. The proposed lightweight high-performance model can be easily deployed to the end devices of the actual industrial projects and retain the accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge