Xuebo Liu
PACE: Defying the Scaling Hypothesis of Exploration in Iterative Alignment for Mathematical Reasoning
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Iterative Direct Preference Optimization has emerged as the state-of-the-art paradigm for aligning Large Language Models on reasoning tasks. Standard implementations (DPO-R1) rely on Best-of-N sampling (e.g., $N \ge 8$) to mine golden trajectories from the distribution tail. In this paper, we challenge this scaling hypothesis and reveal a counter-intuitive phenomenon: in mathematical reasoning, aggressive exploration yields diminishing returns and even catastrophic policy collapse. We theoretically demonstrate that scaling $N$ amplifies verifier noise and induces detrimental distribution shifts. To resolve this, we introduce \textbf{PACE} (Proximal Alignment via Corrective Exploration), which replaces brute-force mining with a generation-based corrective strategy. Operating with a minimal budget ($2<N<3$), PACE synthesizes high-fidelity preference pairs from failed explorations. Empirical evaluations show that PACE outperforms DPO-R1 $(N=16)$ while using only about $1/5$ of the compute, demonstrating superior robustness against reward hacking and label noise.
Stop Rewarding Hallucinated Steps: Faithfulness-Aware Step-Level Reinforcement Learning for Small Reasoning Models
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:As large language models become smaller and more efficient, small reasoning models (SRMs) are crucial for enabling chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning in resource-constrained settings. However, they are prone to faithfulness hallucinations, especially in intermediate reasoning steps. Existing mitigation methods based on online reinforcement learning rely on outcome-based rewards or coarse-grained CoT evaluation, which can inadvertently reinforce unfaithful reasoning when the final answer is correct. To address these limitations, we propose Faithfulness-Aware Step-Level Reinforcement Learning (FaithRL), introducing step-level supervision via explicit faithfulness rewards from a process reward model, together with an implicit truncated resampling strategy that generates contrastive signals from faithful prefixes. Experiments across multiple SRMs and Open-Book QA benchmarks demonstrate that FaithRL consistently reduces hallucinations in both the CoT and final answers, leading to more faithful and reliable reasoning. Code is available at https://github.com/Easy195/FaithRL.
Think Dense, Not Long: Dynamic Decoupled Conditional Advantage for Efficient Reasoning
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) can elicit strong multi-step reasoning, yet it often encourages overly verbose traces. Moreover, naive length penalties in group-relative optimization can severely hurt accuracy. We attribute this failure to two structural issues: (i) Dilution of Length Baseline, where incorrect responses (with zero length reward) depress the group baseline and over-penalize correct solutions; and (ii) Difficulty-Penalty Mismatch, where a static penalty cannot adapt to problem difficulty, suppressing necessary reasoning on hard instances while leaving redundancy on easy ones. We propose Dynamic Decoupled Conditional Advantage (DDCA) to decouple efficiency optimization from correctness. DDCA computes length advantages conditionally within the correct-response cluster to eliminate baseline dilution, and dynamically scales the penalty strength using the group pass rate as a proxy for difficulty. Experiments on GSM8K, MATH500, AMC23, and AIME25 show that DDCA consistently improves the efficiency--accuracy trade-off relative to adaptive baselines, reducing generated tokens by approximately 60% on simpler tasks (e.g., GSM8K) versus over 20% on harder benchmarks (e.g., AIME25), thereby maintaining or improving accuracy. Code is available at https://github.com/alphadl/DDCA.
CVeDRL: An Efficient Code Verifier via Difficulty-aware Reinforcement Learning
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Code verifiers play a critical role in post-verification for LLM-based code generation, yet existing supervised fine-tuning methods suffer from data scarcity, high failure rates, and poor inference efficiency. While reinforcement learning (RL) offers a promising alternative by optimizing models through execution-driven rewards without labeled supervision, our preliminary results show that naive RL with only functionality rewards fails to generate effective unit tests for difficult branches and samples. We first theoretically analyze showing that branch coverage, sample difficulty, syntactic and functional correctness can be jointly modeled as RL rewards, where optimizing these signals can improve the reliability of unit-test-based verification. Guided by this analysis, we design syntax- and functionality-aware rewards and further propose branch- and sample-difficulty--aware RL using exponential reward shaping and static analysis metrics. With this formulation, CVeDRL achieves state-of-the-art performance with only 0.6B parameters, yielding up to 28.97% higher pass rate and 15.08% higher branch coverage than GPT-3.5, while delivering over $20\times$ faster inference than competitive baselines. Code is available at https://github.com/LIGHTCHASER1/CVeDRL.git
Exposing the Cracks: Vulnerabilities of Retrieval-Augmented LLM-based Machine Translation
Oct 01, 2025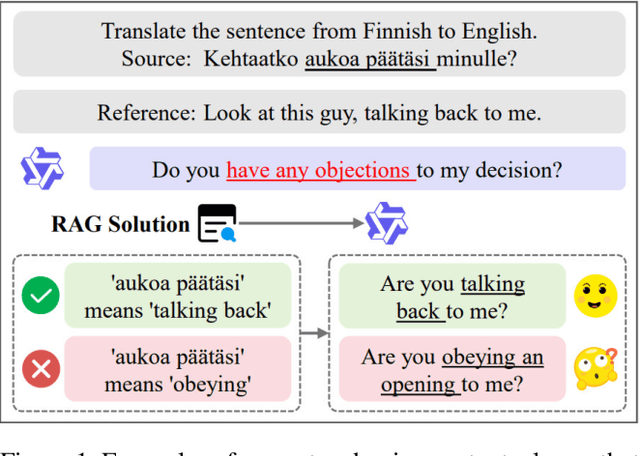

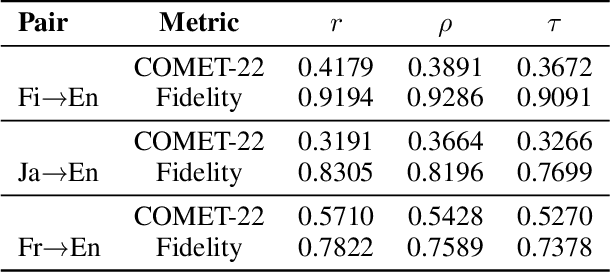
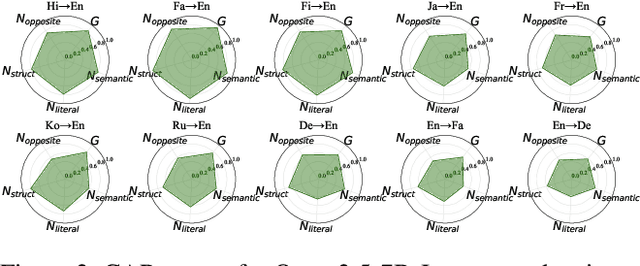
Abstract:\textbf{RE}trieval-\textbf{A}ugmented \textbf{L}LM-based \textbf{M}achine \textbf{T}ranslation (REAL-MT) shows promise for knowledge-intensive tasks like idiomatic translation, but its reliability under noisy retrieval contexts remains poorly understood despite this being a common challenge in real-world deployment. To address this gap, we propose a noise synthesis framework and new metrics to evaluate the robustness of REAL-MT systematically. Using this framework, we instantiate REAL-MT with Qwen-series models, including standard LLMs and large reasoning models (LRMs) with enhanced reasoning, and evaluate their performance on idiomatic translation across high-, medium-, and low-resource language pairs under synthesized noise. Our results show that low-resource language pairs, which rely more heavily on retrieved context, degrade more severely under noise than high-resource ones and often produce nonsensical translations. Although LRMs possess enhanced reasoning capabilities, they show no improvement in error correction and are even more susceptible to noise, tending to rationalize incorrect contexts. We find that this stems from an attention shift away from the source idiom to noisy content, while confidence increases despite declining accuracy, indicating poor calibration. To mitigate these issues, we investigate training-free and fine-tuning strategies, which improve robustness at the cost of performance in clean contexts, revealing a fundamental trade-off. Our findings highlight the limitations of current approaches, underscoring the need for self-verifying integration mechanisms.
AQuilt: Weaving Logic and Self-Inspection into Low-Cost, High-Relevance Data Synthesis for Specialist LLMs
Jul 24, 2025Abstract:Despite the impressive performance of large language models (LLMs) in general domains, they often underperform in specialized domains. Existing approaches typically rely on data synthesis methods and yield promising results by using unlabeled data to capture domain-specific features. However, these methods either incur high computational costs or suffer from performance limitations, while also demonstrating insufficient generalization across different tasks. To address these challenges, we propose AQuilt, a framework for constructing instruction-tuning data for any specialized domains from corresponding unlabeled data, including Answer, Question, Unlabeled data, Inspection, Logic, and Task type. By incorporating logic and inspection, we encourage reasoning processes and self-inspection to enhance model performance. Moreover, customizable task instructions enable high-quality data generation for any task. As a result, we construct a dataset of 703k examples to train a powerful data synthesis model. Experiments show that AQuilt is comparable to DeepSeek-V3 while utilizing just 17% of the production cost. Further analysis demonstrates that our generated data exhibits higher relevance to downstream tasks. Source code, models, and scripts are available at https://github.com/Krueske/AQuilt.
REA-RL: Reflection-Aware Online Reinforcement Learning for Efficient Large Reasoning Models
May 26, 2025Abstract:Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) demonstrate strong performance in complex tasks but often face the challenge of overthinking, leading to substantially high inference costs. Existing approaches synthesize shorter reasoning responses for LRMs to learn, but are inefficient for online usage due to the time-consuming data generation and filtering processes. Meanwhile, online reinforcement learning mainly adopts a length reward to encourage short reasoning responses, but tends to lose the reflection ability and harm the performance. To address these issues, we propose REA-RL, which introduces a small reflection model for efficient scaling in online training, offering both parallel sampling and sequential revision. Besides, a reflection reward is designed to further prevent LRMs from favoring short yet non-reflective responses. Experiments show that both methods maintain or enhance performance while significantly improving inference efficiency. Their combination achieves a good balance between performance and efficiency, reducing inference costs by 35% without compromising performance. Further analysis demonstrates that our methods are effective by maintaining reflection frequency for hard problems while appropriately reducing it for simpler ones without losing reflection ability. Codes are available at https://github.com/hexuandeng/REA-RL.
Runaway is Ashamed, But Helpful: On the Early-Exit Behavior of Large Language Model-based Agents in Embodied Environments
May 23, 2025Abstract:Agents powered by large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong planning and decision-making capabilities in complex embodied environments. However, such agents often suffer from inefficiencies in multi-turn interactions, frequently trapped in repetitive loops or issuing ineffective commands, leading to redundant computational overhead. Instead of relying solely on learning from trajectories, we take a first step toward exploring the early-exit behavior for LLM-based agents. We propose two complementary approaches: 1. an $\textbf{intrinsic}$ method that injects exit instructions during generation, and 2. an $\textbf{extrinsic}$ method that verifies task completion to determine when to halt an agent's trial. To evaluate early-exit mechanisms, we introduce two metrics: one measures the reduction of $\textbf{redundant steps}$ as a positive effect, and the other evaluates $\textbf{progress degradation}$ as a negative effect. Experiments with 4 different LLMs across 5 embodied environments show significant efficiency improvements, with only minor drops in agent performance. We also validate a practical strategy where a stronger agent assists after an early-exit agent, achieving better performance with the same total steps. We will release our code to support further research.
Dynamic Sampling that Adapts: Iterative DPO for Self-Aware Mathematical Reasoning
May 22, 2025Abstract:In the realm of data selection for reasoning tasks, existing approaches predominantly rely on externally predefined static metrics such as difficulty and diversity, which are often designed for supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and lack adaptability to continuous training processes. A critical limitation of these methods is their inability to dynamically align with the evolving capabilities of models during online training, a gap that becomes increasingly pronounced with the rise of dynamic training paradigms and online reinforcement learning (RL) frameworks (e.g., R1 models). To address this, we introduce SAI-DPO, an algorithm that dynamically selects training data by continuously assessing a model's stage-specific reasoning abilities across different training phases. By integrating real-time model performance feedback, SAI-DPO adaptively adapts data selection to the evolving strengths and weaknesses of the model, thus enhancing both data utilization efficiency and final task performance. Extensive experiments on three state-of-the-art models and eight mathematical reasoning benchmarks, including challenging competition-level datasets (e.g., AIME24 and AMC23), demonstrate that SAI-DPO achieves an average performance boost of up to 21.3 percentage points, with particularly notable improvements of 10 and 15 points on AIME24 and AMC23, respectively. These results highlight the superiority of dynamic, model-adaptive data selection over static, externally defined strategies in advancing reasoning.
AgentDropout: Dynamic Agent Elimination for Token-Efficient and High-Performance LLM-Based Multi-Agent Collaboration
Mar 24, 2025Abstract:Multi-agent systems (MAS) based on large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated significant potential in collaborative problem-solving. However, they still face substantial challenges of low communication efficiency and suboptimal task performance, making the careful design of the agents' communication topologies particularly important. Inspired by the management theory that roles in an efficient team are often dynamically adjusted, we propose AgentDropout, which identifies redundant agents and communication across different communication rounds by optimizing the adjacency matrices of the communication graphs and eliminates them to enhance both token efficiency and task performance. Compared to state-of-the-art methods, AgentDropout achieves an average reduction of 21.6% in prompt token consumption and 18.4% in completion token consumption, along with a performance improvement of 1.14 on the tasks. Furthermore, the extended experiments demonstrate that AgentDropout achieves notable domain transferability and structure robustness, revealing its reliability and effectiveness. We release our code at https://github.com/wangzx1219/AgentDropout.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge