Xiabin Zhou
DynamicKV: Task-Aware Adaptive KV Cache Compression for Long Context LLMs
Dec 19, 2024Abstract:Efficient KV cache management in LLMs is crucial for long-context tasks like RAG and summarization. Existing KV cache compression methods enforce a fixed pattern, neglecting task-specific characteristics and reducing the retention of essential information. However, we observe distinct activation patterns across layers in various tasks, highlighting the need for adaptive strategies tailored to each task's unique demands. Based on this insight, we propose DynamicKV, a method that dynamically optimizes token retention by adjusting the number of tokens retained at each layer to adapt to the specific task. DynamicKV establishes global and per-layer maximum KV cache budgets, temporarily retaining the maximum budget for the current layer, and periodically updating the KV cache sizes of all preceding layers during inference. Our method retains only 1.7% of the KV cache size while achieving ~85% of the Full KV cache performance on LongBench. Notably, even under extreme compression (0.9%), DynamicKV surpasses state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods by 11% in the Needle-in-a-Haystack test using Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2. The code will be released.
Divide, Conquer and Combine: A Training-Free Framework for High-Resolution Image Perception in Multimodal Large Language Models
Aug 28, 2024Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have experienced significant advancements recently, but still struggle to recognize and interpret intricate details in high-resolution (HR) images effectively. While state-of-the-art (SOTA) MLLMs claim to process images at 4K resolution, existing MLLM benchmarks only support up to 2K, leaving the capabilities of SOTA models on true HR images largely untested. Furthermore, existing methods for enhancing HR image perception in MLLMs rely on computationally expensive visual instruction tuning. To address these limitations, we introduce HR-Bench, the first deliberately designed benchmark to rigorously evaluate MLLM performance on 4K&8K images. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that while downsampling HR images leads to vision information loss, leveraging complementary modalities, e.g., text, can effectively compensate for this loss. Building upon this insight, we propose Divide, Conquer and Combine (DC$^2$), a novel training-free framework for enhancing MLLM perception of HR images. DC$^2$ follows a three-staged approach: 1) Divide: recursively partitioning the HR image into patches and merging similar patches to minimize computational overhead, 2) Conquer: leveraging the MLLM to generate accurate textual descriptions for each image patch, and 3) Combine: utilizing the generated text descriptions to enhance the MLLM's understanding of the overall HR image. Extensive experiments show that: 1) the SOTA MLLM achieves 63% accuracy, which is markedly lower than the 87% accuracy achieved by humans on HR-Bench; 2) our DC$^2$ brings consistent and significant improvements (a relative increase of +6% on HR-Bench and +8% on general multimodal benchmarks). The benchmark and code will be released to facilitate the multimodal R&D community.
DB-LLM: Accurate Dual-Binarization for Efficient LLMs
Feb 19, 2024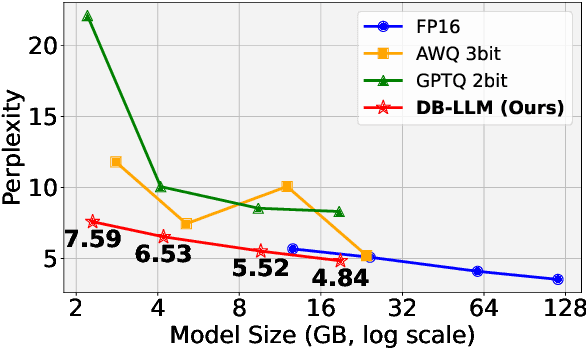
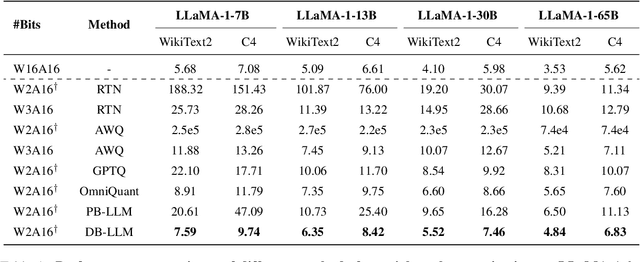
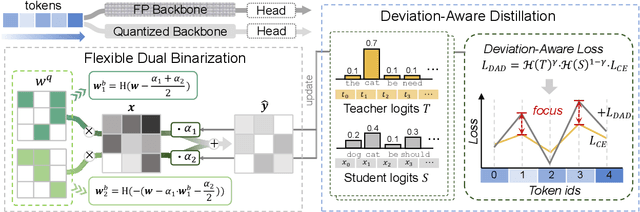
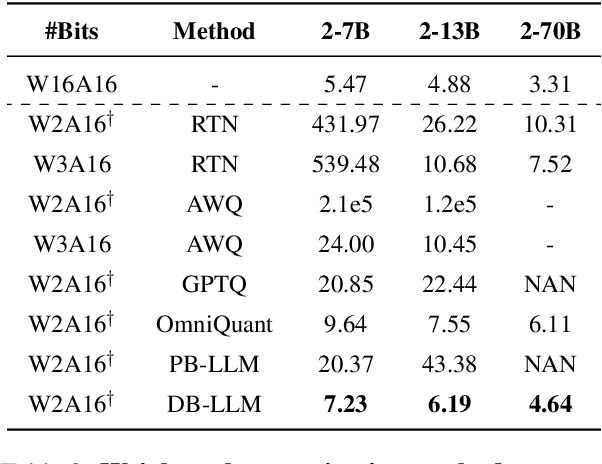
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have significantly advanced the field of natural language processing, while the expensive memory and computation consumption impede their practical deployment. Quantization emerges as one of the most effective methods for improving the computational efficiency of LLMs. However, existing ultra-low-bit quantization always causes severe accuracy drops. In this paper, we empirically relieve the micro and macro characteristics of ultra-low bit quantization and present a novel Dual-Binarization method for LLMs, namely DB-LLM. For the micro-level, we take both the accuracy advantage of 2-bit-width and the efficiency advantage of binarization into account, introducing Flexible Dual Binarization (FDB). By splitting 2-bit quantized weights into two independent sets of binaries, FDB ensures the accuracy of representations and introduces flexibility, utilizing the efficient bitwise operations of binarization while retaining the inherent high sparsity of ultra-low bit quantization. For the macro-level, we find the distortion that exists in the prediction of LLM after quantization, which is specified as the deviations related to the ambiguity of samples. We propose the Deviation-Aware Distillation (DAD) method, enabling the model to focus differently on various samples. Comprehensive experiments show that our DB-LLM not only significantly surpasses the current State-of-The-Art (SoTA) in ultra-low bit quantization (eg, perplexity decreased from 9.64 to 7.23), but also achieves an additional 20\% reduction in computational consumption compared to the SOTA method under the same bit-width. Our code will be released soon.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge