Siyi Cao
Runaway is Ashamed, But Helpful: On the Early-Exit Behavior of Large Language Model-based Agents in Embodied Environments
May 23, 2025Abstract:Agents powered by large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong planning and decision-making capabilities in complex embodied environments. However, such agents often suffer from inefficiencies in multi-turn interactions, frequently trapped in repetitive loops or issuing ineffective commands, leading to redundant computational overhead. Instead of relying solely on learning from trajectories, we take a first step toward exploring the early-exit behavior for LLM-based agents. We propose two complementary approaches: 1. an $\textbf{intrinsic}$ method that injects exit instructions during generation, and 2. an $\textbf{extrinsic}$ method that verifies task completion to determine when to halt an agent's trial. To evaluate early-exit mechanisms, we introduce two metrics: one measures the reduction of $\textbf{redundant steps}$ as a positive effect, and the other evaluates $\textbf{progress degradation}$ as a negative effect. Experiments with 4 different LLMs across 5 embodied environments show significant efficiency improvements, with only minor drops in agent performance. We also validate a practical strategy where a stronger agent assists after an early-exit agent, achieving better performance with the same total steps. We will release our code to support further research.
Complementary Advantages of ChatGPTs and Human Readers in Reasoning: Evidence from English Text Reading Comprehension
Nov 17, 2023


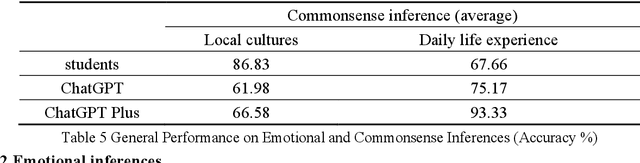
Abstract:ChatGPT has shown its great power in text processing, including its reasoning ability from text reading. However, there has not been any direct comparison between human readers and ChatGPT in reasoning ability related to text reading. This study was undertaken to investigate how ChatGPTs (i.e., ChatGPT and ChatGPT Plus) and Chinese senior school students as ESL learners exhibited their reasoning ability from English narrative texts. Additionally, we compared the two ChatGPTs in the reasoning performances when commands were updated elaborately. The whole study was composed of three reasoning tests: Test 1 for commonsense inference, Test 2 for emotional inference, and Test 3 for causal inference. The results showed that in Test 1, the students outdid the two ChatGPT versions in local-culture-related inferences but performed worse than the chatbots in daily-life inferences. In Test 2, ChatGPT Plus excelled whereas ChatGPT lagged behind in accuracy. In association with both accuracy and frequency of correct responses, the students were inferior to the two chatbots. Compared with ChatGPTs' better performance in positive emotions, the students showed their superiority in inferring negative emotions. In Test 3, the students demonstrated better logical analysis, outdoing both chatbots. In updating command condition, ChatGPT Plus displayed good causal reasoning ability while ChatGPT kept unchanged. Our study reveals that human readers and ChatGPTs have their respective advantages and disadvantages in drawing inferences from text reading comprehension, unlocking a complementary relationship in text-based reasoning.
Nine-year-old children outperformed ChatGPT in emotion: Evidence from Chinese writing
Oct 01, 2023Abstract:ChatGPT has been demonstrated to possess significant capabilities in generating intricate, human-like text, and recent studies have established that its performance in theory of mind tasks is comparable to that of a nine-year-old child. However, it remains uncertain whether ChatGPT surpasses nine-year-old children in Chinese writing proficiency. To explore this, our study juxtaposed the Chinese writing performance of ChatGPT and nine-year-old children on both narrative and scientific topics, aiming to uncover the relative strengths and weaknesses of ChatGPT in writing. The collected data were analyzed across five linguistic dimensions: fluency, accuracy, complexity, cohesion, and emotion. Each dimension underwent assessment through precise indices. The findings revealed that nine-year-old children excelled beyond ChatGPT in terms of fluency and cohesion within their writing. In contrast, ChatGPT manifested a superior performance in accuracy compared to the children. Concerning complexity, children exhibited superior skills in science-themed writing, while ChatGPT prevailed in nature-themed writing. Significantly, this research is pioneering in revealing that nine-year-old children convey stronger emotions than ChatGPT in their Chinese compositions.
Exploring the effectiveness of ChatGPT-based feedback compared with teacher feedback and self-feedback: Evidence from Chinese to English translation
Sep 04, 2023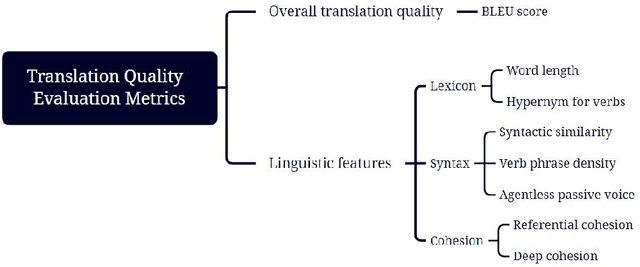
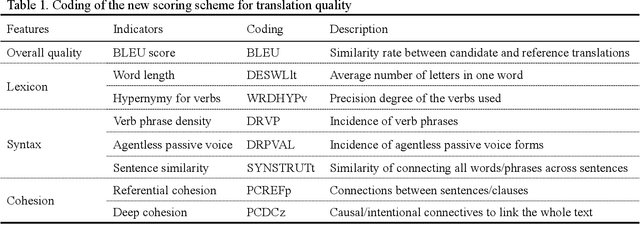
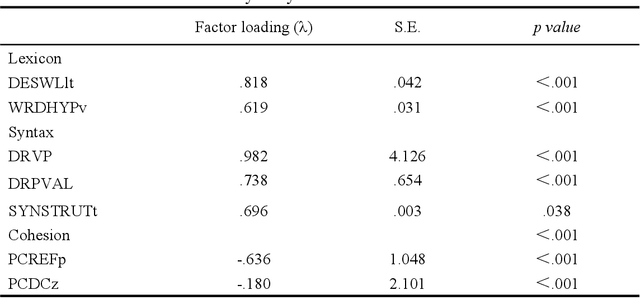
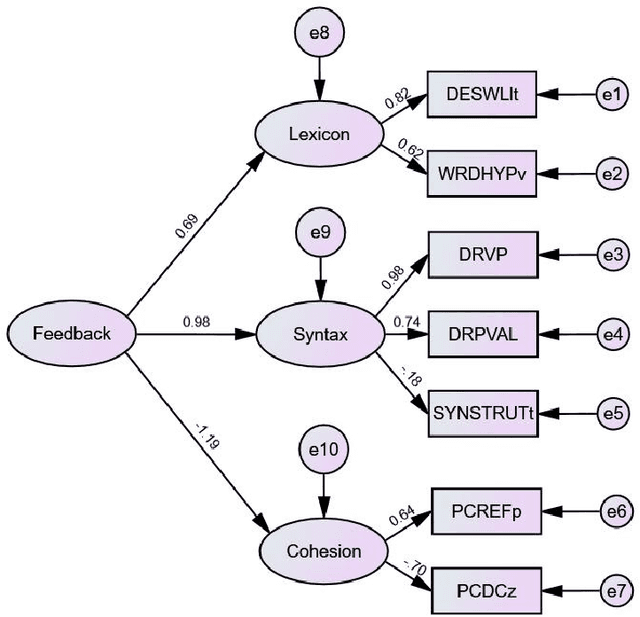
Abstract:ChatGPT,a cutting-edge AI-powered Chatbot,can quickly generate responses on given commands. While it was reported that ChatGPT had the capacity to deliver useful feedback, it is still unclear about its effectiveness compared with conventional feedback approaches,such as teacher feedback (TF) and self-feedback (SF). To address this issue, this study compared the revised Chinese to English translation texts produced by Chinese Master of Translation and Interpretation (MTI) students,who learned English as a Second/Foreign Language (ESL/EFL), based on three feedback types (i.e., ChatGPT-based feedback, TF and SF). The data was analyzed using BLEU score to gauge the overall translation quality as well as Coh-Metrix to examine linguistic features across three dimensions: lexicon, syntax, and cohesion.The findings revealed that TF- and SF-guided translation texts surpassed those with ChatGPT-based feedback, as indicated by the BLEU score. In terms of linguistic features,ChatGPT-based feedback demonstrated superiority, particularly in enhancing lexical capability and referential cohesion in the translation texts. However, TF and SF proved more effective in developing syntax-related skills,as it addressed instances of incorrect usage of the passive voice. These diverse outcomes indicate ChatGPT's potential as a supplementary resource, complementing traditional teacher-led methods in translation practice.
Chinese Intermediate English Learners outdid ChatGPT in deep cohesion: Evidence from English narrative writing
Mar 21, 2023
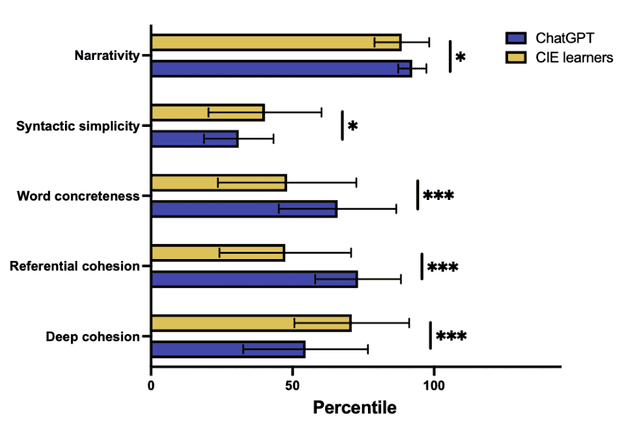
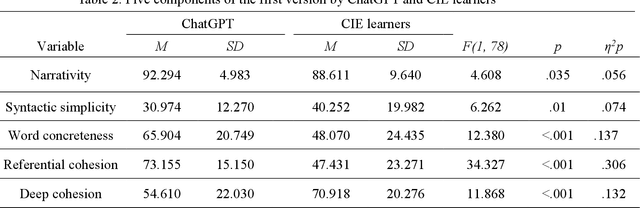
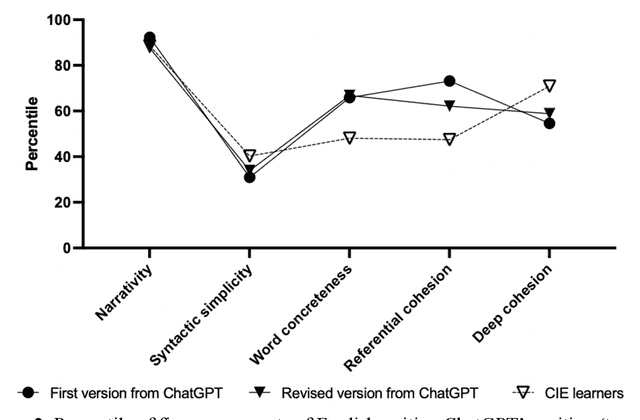
Abstract:ChatGPT is a publicly available chatbot that can quickly generate texts on given topics, but it is unknown whether the chatbot is really superior to human writers in all aspects of writing and whether its writing quality can be prominently improved on the basis of updating commands. Consequently, this study compared the writing performance on a narrative topic by ChatGPT and Chinese intermediate English (CIE) learners so as to reveal the chatbot's advantage and disadvantage in writing. The data were analyzed in terms of five discourse components using Coh-Metrix (a special instrument for analyzing language discourses), and the results revealed that ChatGPT performed better than human writers in narrativity, word concreteness, and referential cohesion, but worse in syntactic simplicity and deep cohesion in its initial version. After more revision commands were updated, while the resulting version was facilitated in syntactic simplicity, yet it is still lagged far behind CIE learners' writing in deep cohesion. In addition, the correlation analysis of the discourse components suggests that narrativity was correlated with referential cohesion in both ChatGPT and human writers, but the correlations varied within each group.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge