Luwei Yang
GURecon: Learning Detailed 3D Geometric Uncertainties for Neural Surface Reconstruction
Dec 19, 2024Abstract:Neural surface representation has demonstrated remarkable success in the areas of novel view synthesis and 3D reconstruction. However, assessing the geometric quality of 3D reconstructions in the absence of ground truth mesh remains a significant challenge, due to its rendering-based optimization process and entangled learning of appearance and geometry with photometric losses. In this paper, we present a novel framework, i.e, GURecon, which establishes a geometric uncertainty field for the neural surface based on geometric consistency. Different from existing methods that rely on rendering-based measurement, GURecon models a continuous 3D uncertainty field for the reconstructed surface, and is learned by an online distillation approach without introducing real geometric information for supervision. Moreover, in order to mitigate the interference of illumination on geometric consistency, a decoupled field is learned and exploited to finetune the uncertainty field. Experiments on various datasets demonstrate the superiority of GURecon in modeling 3D geometric uncertainty, as well as its plug-and-play extension to various neural surface representations and improvement on downstream tasks such as incremental reconstruction. The code and supplementary material are available on the project website: https://zju3dv.github.io/GURecon/.
MLoRA: Multi-Domain Low-Rank Adaptive Network for CTR Prediction
Aug 14, 2024



Abstract:Click-through rate (CTR) prediction is one of the fundamental tasks in the industry, especially in e-commerce, social media, and streaming media. It directly impacts website revenues, user satisfaction, and user retention. However, real-world production platforms often encompass various domains to cater for diverse customer needs. Traditional CTR prediction models struggle in multi-domain recommendation scenarios, facing challenges of data sparsity and disparate data distributions across domains. Existing multi-domain recommendation approaches introduce specific-domain modules for each domain, which partially address these issues but often significantly increase model parameters and lead to insufficient training. In this paper, we propose a Multi-domain Low-Rank Adaptive network (MLoRA) for CTR prediction, where we introduce a specialized LoRA module for each domain. This approach enhances the model's performance in multi-domain CTR prediction tasks and is able to be applied to various deep-learning models. We evaluate the proposed method on several multi-domain datasets. Experimental results demonstrate our MLoRA approach achieves a significant improvement compared with state-of-the-art baselines. Furthermore, we deploy it in the production environment of the Alibaba.COM. The online A/B testing results indicate the superiority and flexibility in real-world production environments. The code of our MLoRA is publicly available.
Modeling User Intent Beyond Trigger: Incorporating Uncertainty for Trigger-Induced Recommendation
Aug 07, 2024



Abstract:To cater to users' desire for an immersive browsing experience, numerous e-commerce platforms provide various recommendation scenarios, with a focus on Trigger-Induced Recommendation (TIR) tasks. However, the majority of current TIR methods heavily rely on the trigger item to understand user intent, lacking a higher-level exploration and exploitation of user intent (e.g., popular items and complementary items), which may result in an overly convergent understanding of users' short-term intent and can be detrimental to users' long-term purchasing experiences. Moreover, users' short-term intent shows uncertainty and is affected by various factors such as browsing context and historical behaviors, which poses challenges to user intent modeling. To address these challenges, we propose a novel model called Deep Uncertainty Intent Network (DUIN), comprising three essential modules: i) Explicit Intent Exploit Module extracting explicit user intent using the contrastive learning paradigm; ii) Latent Intent Explore Module exploring latent user intent by leveraging the multi-view relationships between items; iii) Intent Uncertainty Measurement Module offering a distributional estimation and capturing the uncertainty associated with user intent. Experiments on three real-world datasets demonstrate the superior performance of DUIN compared to existing baselines. Notably, DUIN has been deployed across all TIR scenarios in our e-commerce platform, with online A/B testing results conclusively validating its superiority.
On Practical Diversified Recommendation with Controllable Category Diversity Framework
Feb 06, 2024



Abstract:Recommender systems have made significant strides in various industries, primarily driven by extensive efforts to enhance recommendation accuracy. However, this pursuit of accuracy has inadvertently given rise to echo chamber/filter bubble effects. Especially in industry, it could impair user's experiences and prevent user from accessing a wider range of items. One of the solutions is to take diversity into account. However, most of existing works focus on user's explicit preferences, while rarely exploring user's non-interaction preferences. These neglected non-interaction preferences are especially important for broadening user's interests in alleviating echo chamber/filter bubble effects.Therefore, in this paper, we first define diversity as two distinct definitions, i.e., user-explicit diversity (U-diversity) and user-item non-interaction diversity (N-diversity) based on user historical behaviors. Then, we propose a succinct and effective method, named as Controllable Category Diversity Framework (CCDF) to achieve both high U-diversity and N-diversity simultaneously.Specifically, CCDF consists of two stages, User-Category Matching and Constrained Item Matching. The User-Category Matching utilizes the DeepU2C model and a combined loss to capture user's preferences in categories, and then selects the top-$K$ categories with a controllable parameter $K$.These top-$K$ categories will be used as trigger information in Constrained Item Matching. Offline experimental results show that our proposed DeepU2C outperforms state-of-the-art diversity-oriented methods, especially on N-diversity task. The whole framework is validated in a real-world production environment by conducting online A/B testing.
* A Two-stage Controllable Category Diversity Framework for Recommendation
Deep Evolutional Instant Interest Network for CTR Prediction in Trigger-Induced Recommendation
Jan 17, 2024



Abstract:The recommendation has been playing a key role in many industries, e.g., e-commerce, streaming media, social media, etc. Recently, a new recommendation scenario, called Trigger-Induced Recommendation (TIR), where users are able to explicitly express their instant interests via trigger items, is emerging as an essential role in many e-commerce platforms, e.g., Alibaba.com and Amazon. Without explicitly modeling the user's instant interest, traditional recommendation methods usually obtain sub-optimal results in TIR. Even though there are a few methods considering the trigger and target items simultaneously to solve this problem, they still haven't taken into account temporal information of user behaviors, the dynamic change of user instant interest when the user scrolls down and the interactions between the trigger and target items. To tackle these problems, we propose a novel method -- Deep Evolutional Instant Interest Network (DEI2N), for click-through rate prediction in TIR scenarios. Specifically, we design a User Instant Interest Modeling Layer to predict the dynamic change of the intensity of instant interest when the user scrolls down. Temporal information is utilized in user behavior modeling. Moreover, an Interaction Layer is introduced to learn better interactions between the trigger and target items. We evaluate our method on several offline and real-world industrial datasets. Experimental results show that our proposed DEI2N outperforms state-of-the-art baselines. In addition, online A/B testing demonstrates the superiority over the existing baseline in real-world production environments.
PNeRFLoc: Visual Localization with Point-based Neural Radiance Fields
Dec 17, 2023
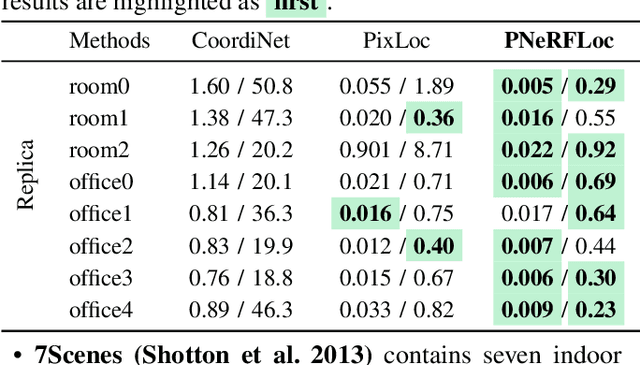

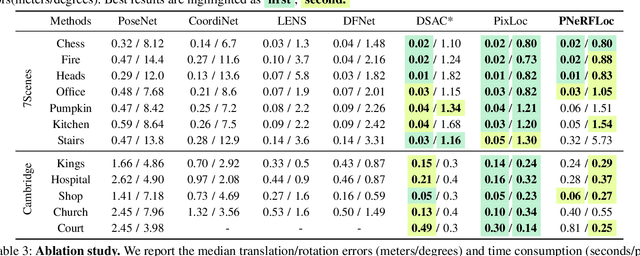
Abstract:Due to the ability to synthesize high-quality novel views, Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have been recently exploited to improve visual localization in a known environment. However, the existing methods mostly utilize NeRFs for data augmentation to improve the regression model training, and the performance on novel viewpoints and appearances is still limited due to the lack of geometric constraints. In this paper, we propose a novel visual localization framework, \ie, PNeRFLoc, based on a unified point-based representation. On the one hand, PNeRFLoc supports the initial pose estimation by matching 2D and 3D feature points as traditional structure-based methods; on the other hand, it also enables pose refinement with novel view synthesis using rendering-based optimization. Specifically, we propose a novel feature adaption module to close the gaps between the features for visual localization and neural rendering. To improve the efficacy and efficiency of neural rendering-based optimization, we also develop an efficient rendering-based framework with a warping loss function. Furthermore, several robustness techniques are developed to handle illumination changes and dynamic objects for outdoor scenarios. Experiments demonstrate that PNeRFLoc performs the best on synthetic data when the NeRF model can be well learned and performs on par with the SOTA method on the visual localization benchmark datasets.
Dense RGB SLAM with Neural Implicit Maps
Jan 21, 2023Abstract:There is an emerging trend of using neural implicit functions for map representation in Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM). Some pioneer works have achieved encouraging results on RGB-D SLAM. In this paper, we present a dense RGB SLAM method with neural implicit map representation. To reach this challenging goal without depth input, we introduce a hierarchical feature volume to facilitate the implicit map decoder. This design effectively fuses shape cues across different scales to facilitate map reconstruction. Our method simultaneously solves the camera motion and the neural implicit map by matching the rendered and input video frames. To facilitate optimization, we further propose a photometric warping loss in the spirit of multi-view stereo to better constrain the camera pose and scene geometry. We evaluate our method on commonly used benchmarks and compare it with modern RGB and RGB-D SLAM systems. Our method achieves favorable results than previous methods and even surpasses some recent RGB-D SLAM methods. Our source code will be publicly available.
Multiplex Bipartite Network Embedding using Dual Hypergraph Convolutional Networks
Feb 12, 2021



Abstract:A bipartite network is a graph structure where nodes are from two distinct domains and only inter-domain interactions exist as edges. A large number of network embedding methods exist to learn vectorial node representations from general graphs with both homogeneous and heterogeneous node and edge types, including some that can specifically model the distinct properties of bipartite networks. However, these methods are inadequate to model multiplex bipartite networks (e.g., in e-commerce), that have multiple types of interactions (e.g., click, inquiry, and buy) and node attributes. Most real-world multiplex bipartite networks are also sparse and have imbalanced node distributions that are challenging to model. In this paper, we develop an unsupervised Dual HyperGraph Convolutional Network (DualHGCN) model that scalably transforms the multiplex bipartite network into two sets of homogeneous hypergraphs and uses spectral hypergraph convolutional operators, along with intra- and inter-message passing strategies to promote information exchange within and across domains, to learn effective node embedding. We benchmark DualHGCN using four real-world datasets on link prediction and node classification tasks. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that DualHGCN significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods, and is robust to varying sparsity levels and imbalanced node distributions.
Modeling Dynamic Heterogeneous Network for Link Prediction using Hierarchical Attention with Temporal RNN
Apr 01, 2020



Abstract:Network embedding aims to learn low-dimensional representations of nodes while capturing structure information of networks. It has achieved great success on many tasks of network analysis such as link prediction and node classification. Most of existing network embedding algorithms focus on how to learn static homogeneous networks effectively. However, networks in the real world are more complex, e.g., networks may consist of several types of nodes and edges (called heterogeneous information) and may vary over time in terms of dynamic nodes and edges (called evolutionary patterns). Limited work has been done for network embedding of dynamic heterogeneous networks as it is challenging to learn both evolutionary and heterogeneous information simultaneously. In this paper, we propose a novel dynamic heterogeneous network embedding method, termed as DyHATR, which uses hierarchical attention to learn heterogeneous information and incorporates recurrent neural networks with temporal attention to capture evolutionary patterns. We benchmark our method on four real-world datasets for the task of link prediction. Experimental results show that DyHATR significantly outperforms several state-of-the-art baselines.
Attribute Recognition from Adaptive Parts
Jul 18, 2016


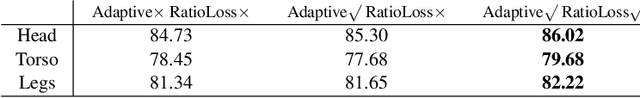
Abstract:Previous part-based attribute recognition approaches perform part detection and attribute recognition in separate steps. The parts are not optimized for attribute recognition and therefore could be sub-optimal. We present an end-to-end deep learning approach to overcome the limitation. It generates object parts from key points and perform attribute recognition accordingly, allowing adaptive spatial transform of the parts. Both key point estimation and attribute recognition are learnt jointly in a multi-task setting. Extensive experiments on two datasets verify the efficacy of proposed end-to-end approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge