PNeRFLoc: Visual Localization with Point-based Neural Radiance Fields
Paper and Code
Dec 17, 2023
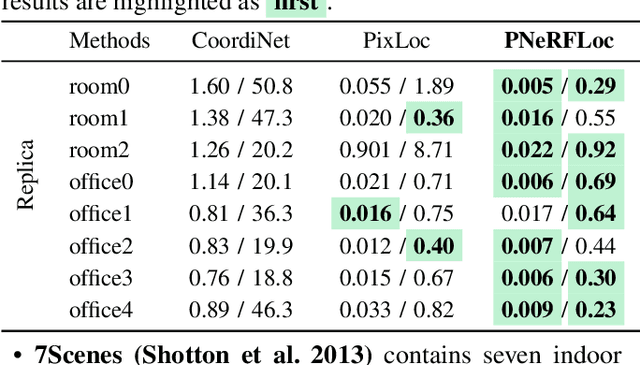

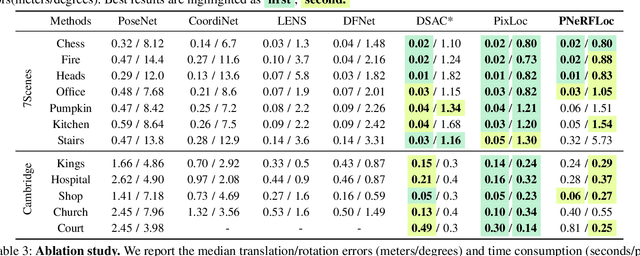
Due to the ability to synthesize high-quality novel views, Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have been recently exploited to improve visual localization in a known environment. However, the existing methods mostly utilize NeRFs for data augmentation to improve the regression model training, and the performance on novel viewpoints and appearances is still limited due to the lack of geometric constraints. In this paper, we propose a novel visual localization framework, \ie, PNeRFLoc, based on a unified point-based representation. On the one hand, PNeRFLoc supports the initial pose estimation by matching 2D and 3D feature points as traditional structure-based methods; on the other hand, it also enables pose refinement with novel view synthesis using rendering-based optimization. Specifically, we propose a novel feature adaption module to close the gaps between the features for visual localization and neural rendering. To improve the efficacy and efficiency of neural rendering-based optimization, we also develop an efficient rendering-based framework with a warping loss function. Furthermore, several robustness techniques are developed to handle illumination changes and dynamic objects for outdoor scenarios. Experiments demonstrate that PNeRFLoc performs the best on synthetic data when the NeRF model can be well learned and performs on par with the SOTA method on the visual localization benchmark datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge