Wenyu Zhang
CPiRi: Channel Permutation-Invariant Relational Interaction for Multivariate Time Series Forecasting
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Current methods for multivariate time series forecasting can be classified into channel-dependent and channel-independent models. Channel-dependent models learn cross-channel features but often overfit the channel ordering, which hampers adaptation when channels are added or reordered. Channel-independent models treat each channel in isolation to increase flexibility, yet this neglects inter-channel dependencies and limits performance. To address these limitations, we propose \textbf{CPiRi}, a \textbf{channel permutation invariant (CPI)} framework that infers cross-channel structure from data rather than memorizing a fixed ordering, enabling deployment in settings with structural and distributional co-drift without retraining. CPiRi couples \textbf{spatio-temporal decoupling architecture} with \textbf{permutation-invariant regularization training strategy}: a frozen pretrained temporal encoder extracts high-quality temporal features, a lightweight spatial module learns content-driven inter-channel relations, while a channel shuffling strategy enforces CPI during training. We further \textbf{ground CPiRi in theory} by analyzing permutation equivariance in multivariate time series forecasting. Experiments on multiple benchmarks show state-of-the-art results. CPiRi remains stable when channel orders are shuffled and exhibits strong \textbf{inductive generalization} to unseen channels even when trained on \textbf{only half} of the channels, while maintaining \textbf{practical efficiency} on large-scale datasets. The source code is released at https://github.com/JasonStraka/CPiRi.
LitVISTA: A Benchmark for Narrative Orchestration in Literary Text
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:Computational narrative analysis aims to capture rhythm, tension, and emotional dynamics in literary texts. Existing large language models can generate long stories but overly focus on causal coherence, neglecting the complex story arcs and orchestration inherent in human narratives. This creates a structural misalignment between model- and human-generated narratives. We propose VISTA Space, a high-dimensional representational framework for narrative orchestration that unifies human and model narrative perspectives. We further introduce LitVISTA, a structurally annotated benchmark grounded in literary texts, enabling systematic evaluation of models' narrative orchestration capabilities. We conduct oracle evaluations on a diverse selection of frontier LLMs, including GPT, Claude, Grok, and Gemini. Results reveal systematic deficiencies: existing models fail to construct a unified global narrative view, struggling to jointly capture narrative function and structure. Furthermore, even advanced thinking modes yield only limited gains for such literary narrative understanding.
Time-Aware Adaptive Side Information Fusion for Sequential Recommendation
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Incorporating item-side information, such as category and brand, into sequential recommendation is a well-established and effective approach for improving performance. However, despite significant advancements, current models are generally limited by three key challenges: they often overlook the fine-grained temporal dynamics inherent in timestamps, exhibit vulnerability to noise in user interaction sequences, and rely on computationally expensive fusion architectures. To systematically address these challenges, we propose the Time-Aware Adaptive Side Information Fusion (TASIF) framework. TASIF integrates three synergistic components: (1) a simple, plug-and-play time span partitioning mechanism to capture global temporal patterns; (2) an adaptive frequency filter that leverages a learnable gate to denoise feature sequences adaptively, thereby providing higher-quality inputs for subsequent fusion modules; and (3) an efficient adaptive side information fusion layer, this layer employs a "guide-not-mix" architecture, where attributes guide the attention mechanism without being mixed into the content-representing item embeddings, ensuring deep interaction while ensuring computational efficiency. Extensive experiments on four public datasets demonstrate that TASIF significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines while maintaining excellent efficiency in training. Our source code is available at https://github.com/jluo00/TASIF.
Mapping the Vanishing and Transformation of Urban Villages in China
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Urban villages (UVs), informal settlements embedded within China's urban fabric, have undergone widespread demolition and redevelopment in recent decades. However, there remains a lack of systematic evaluation of whether the demolished land has been effectively reused, raising concerns about the efficacy and sustainability of current redevelopment practices. To address the gap, this study proposes a deep learning-based framework to monitor the spatiotemporal changes of UVs in China. Specifically, semantic segmentation of multi-temporal remote sensing imagery is first used to map evolving UV boundaries, and then post-demolition land use is classified into six categories based on the "remained-demolished-redeveloped" phase: incomplete demolition, vacant land, construction sites, buildings, green spaces, and others. Four representative cities from China's four economic regions were selected as the study areas, i.e., Guangzhou (East), Zhengzhou (Central), Xi'an (West), and Harbin (Northeast). The results indicate: 1) UV redevelopment processes were frequently prolonged; 2) redevelopment transitions primarily occurred in peripheral areas, whereas urban cores remained relatively stable; and 3) three spatiotemporal transformation pathways, i.e., synchronized redevelopment, delayed redevelopment, and gradual optimization, were revealed. This study highlights the fragmented, complex and nonlinear nature of UV redevelopment, underscoring the need for tiered and context-sensitive planning strategies. By linking spatial dynamics with the context of redevelopment policies, the findings offer valuable empirical insights that support more inclusive, efficient, and sustainable urban renewal, while also contributing to a broader global understanding of informal settlement transformations.
* Appendix A. Supplementary data at https://ars.els-cdn.com/content/image/1-s2.0-S2210670725008418-mmc1.docx
Incorporating Contextual Paralinguistic Understanding in Large Speech-Language Models
Aug 10, 2025Abstract:Current large speech language models (Speech-LLMs) often exhibit limitations in empathetic reasoning, primarily due to the absence of training datasets that integrate both contextual content and paralinguistic cues. In this work, we propose two approaches to incorporate contextual paralinguistic information into model training: (1) an explicit method that provides paralinguistic metadata (e.g., emotion annotations) directly to the LLM, and (2) an implicit method that automatically generates novel training question-answer (QA) pairs using both categorical and dimensional emotion annotations alongside speech transcriptions. Our implicit method boosts performance (LLM-judged) by 38.41% on a human-annotated QA benchmark, reaching 46.02% when combined with the explicit approach, showing effectiveness in contextual paralinguistic understanding. We also validate the LLM judge by demonstrating its correlation with classification metrics, providing support for its reliability.
Beyond Classification: Towards Speech Emotion Reasoning with Multitask AudioLLMs
Jun 07, 2025Abstract:Audio Large Language Models (AudioLLMs) have achieved strong results in semantic tasks like speech recognition and translation, but remain limited in modeling paralinguistic cues such as emotion. Existing approaches often treat emotion understanding as a classification problem, offering little insight into the underlying rationale behind predictions. In this work, we explore emotion reasoning, a strategy that leverages the generative capabilities of AudioLLMs to enhance emotion recognition by producing semantically aligned, evidence-grounded explanations. To support this in multitask AudioLLMs, we introduce a unified framework combining reasoning-augmented data supervision, dual-encoder architecture, and task-alternating training. This approach enables AudioLLMs to effectively learn different tasks while incorporating emotional reasoning. Experiments on IEMOCAP and MELD show that our approach not only improves emotion prediction accuracy but also enhances the coherence and evidential grounding of the generated responses.
Mapping Urban Villages in China: Progress and Challenges
Mar 18, 2025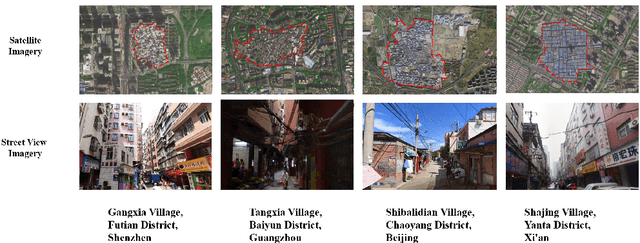
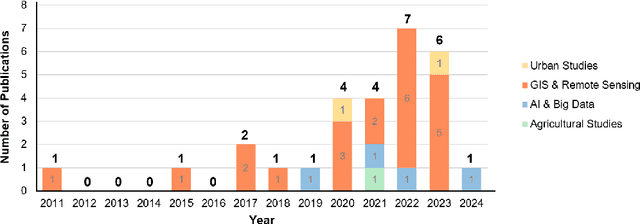
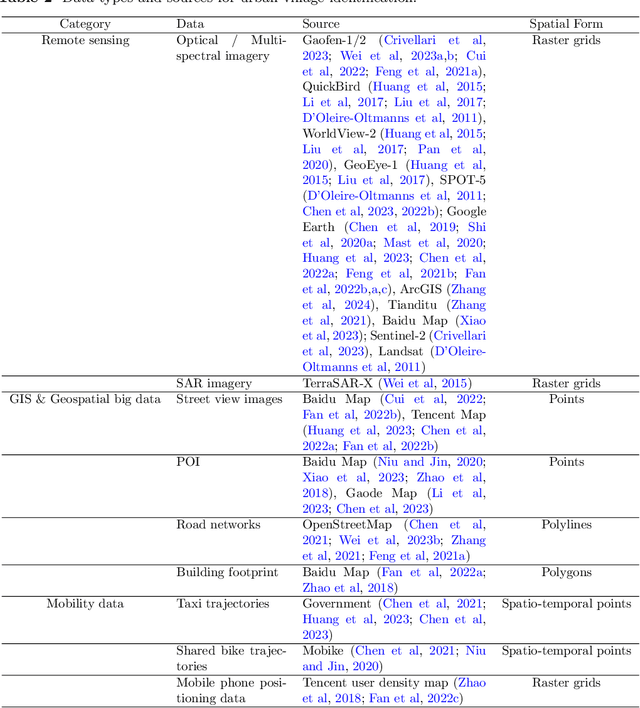
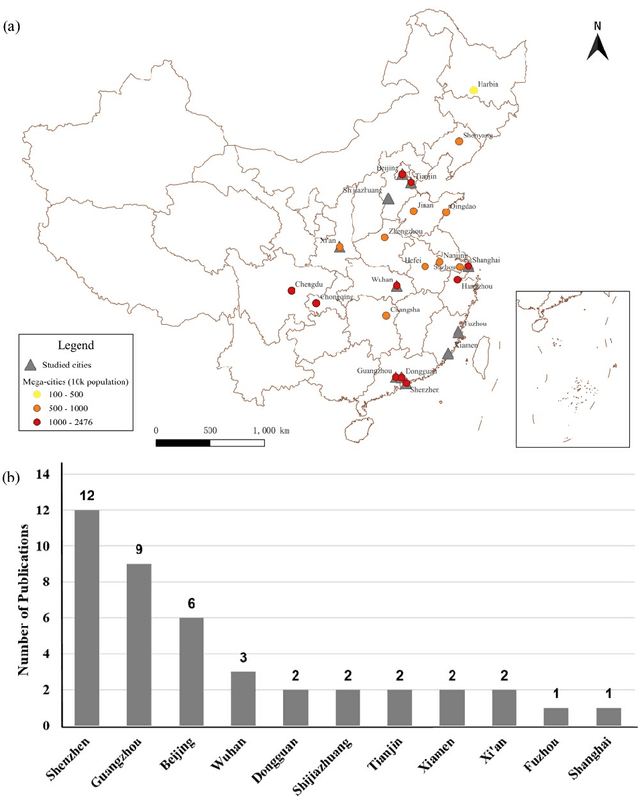
Abstract:The shift toward high-quality urbanization has brought increased attention to the issue of "urban villages", which has become a prominent social problem in China. However, there is a lack of available geospatial data on urban villages, making it crucial to prioritize urban village mapping. In order to assess the current progress in urban village mapping and identify challenges and future directions, we have conducted a comprehensive review, which to the best of our knowledge is the first of its kind in this field. Our review begins by providing a clear context for urban villages and elaborating the method for literature review, then summarizes the study areas, data sources, and approaches used for urban village mapping in China. We also address the challenges and future directions for further research. Through thorough investigation, we find that current studies only cover very limited study areas and periods and lack sufficient investigation into the scalability, transferability, and interpretability of identification approaches due to the challenges in concept fuzziness and variances, spatial heterogeneity and variances of urban villages, and data availability. Future research can complement and further the current research in the following potential directions in order to achieve large-area mapping across the whole nation...
* Updated review at https://github.com/rui-research/urban-village-review
Bridging Domain Gaps between Pretrained Multimodal Models and Recommendations
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:With the explosive growth of multimodal content online, pre-trained visual-language models have shown great potential for multimodal recommendation. However, while these models achieve decent performance when applied in a frozen manner, surprisingly, due to significant domain gaps (e.g., feature distribution discrepancy and task objective misalignment) between pre-training and personalized recommendation, adopting a joint training approach instead leads to performance worse than baseline. Existing approaches either rely on simple feature extraction or require computationally expensive full model fine-tuning, struggling to balance effectiveness and efficiency. To tackle these challenges, we propose \textbf{P}arameter-efficient \textbf{T}uning for \textbf{M}ultimodal \textbf{Rec}ommendation (\textbf{PTMRec}), a novel framework that bridges the domain gap between pre-trained models and recommendation systems through a knowledge-guided dual-stage parameter-efficient training strategy. This framework not only eliminates the need for costly additional pre-training but also flexibly accommodates various parameter-efficient tuning methods.
Fusion of Millimeter-wave Radar and Pulse Oximeter Data for Low-burden Diagnosis of Obstructive Sleep Apnea-Hypopnea Syndrome
Jan 25, 2025



Abstract:Objective: The aim of the study is to develop a novel method for improved diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome (OSAHS) in clinical or home settings, with the focus on achieving diagnostic performance comparable to the gold-standard polysomnography (PSG) with significantly reduced monitoring burden. Methods: We propose a method using millimeter-wave radar and pulse oximeter for OSAHS diagnosis (ROSA). It contains a sleep apnea-hypopnea events (SAE) detection network, which directly predicts the temporal localization of SAE, and a sleep staging network, which predicts the sleep stages throughout the night, based on radar signals. It also fuses oxygen saturation (SpO2) information from the pulse oximeter to adjust the score of SAE detected by radar. Results: Experimental results on a real-world dataset (>800 hours of overnight recordings, 100 subjects) demonstrated high agreement (ICC=0.9870) on apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) between ROSA and PSG. ROSA also exhibited excellent diagnostic performance, exceeding 90% in accuracy across AHI diagnostic thresholds of 5, 15 and 30 events/h. Conclusion: ROSA improves diagnostic accuracy by fusing millimeter-wave radar and pulse oximeter data. It provides a reliable and low-burden solution for OSAHS diagnosis. Significance: ROSA addresses the limitations of high complexity and monitoring burden associated with traditional PSG. The high accuracy and low burden of ROSA show its potential to improve the accessibility of OSAHS diagnosis among population.
Advancing Singlish Understanding: Bridging the Gap with Datasets and Multimodal Models
Jan 02, 2025



Abstract:Singlish, a Creole language rooted in English, is a key focus in linguistic research within multilingual and multicultural contexts. However, its spoken form remains underexplored, limiting insights into its linguistic structure and applications. To address this gap, we standardize and annotate the largest spoken Singlish corpus, introducing the Multitask National Speech Corpus (MNSC). These datasets support diverse tasks, including Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), Spoken Question Answering (SQA), Spoken Dialogue Summarization (SDS), and Paralinguistic Question Answering (PQA). We release standardized splits and a human-verified test set to facilitate further research. Additionally, we propose SingAudioLLM, a multi-task multimodal model leveraging multimodal large language models to handle these tasks concurrently. Experiments reveal our models adaptability to Singlish context, achieving state-of-the-art performance and outperforming prior models by 10-30% in comparison with other AudioLLMs and cascaded solutions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge