Tuo Zhao
Approximation of Log-Partition Function in Policy Mirror Descent Induces Implicit Regularization for LLM Post-Training
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Policy mirror descent (PMD) provides a principled framework for reinforcement learning (RL) by iteratively solving KL-regularized policy improvement subproblems. While this approach has been adopted in training advanced LLMs such as Kimi K1.5/K2, the ideal closed-form PMD updates require reliable partition function estimation, a significant challenge when working with limited rollouts in the vast action spaces of LLMs. We investigate a practical algorithm, termed PMD-mean, that approximates the log-partition term with the mean reward under the sampling policy and performs regression in log-policy space. Specifically, we characterize the population solution of PMD-mean and demonstrate that it implicitly optimizes mirror descent subproblems with an adaptive mixed KL--$χ^2$ regularizer. This additional $χ^2$ regularization constrains large probability changes, producing more conservative updates when expected rewards are low and enhancing robustness against finite-sample estimation errors. Experiments on math reasoning tasks show that PMD-mean achieves superior performance with improved stability and time efficiency. These findings deepen our understanding of PMD-mean and illuminate pathways toward principled improvements in RL algorithms for LLMs. Code is available at https://github.com/horizon-rl/OpenKimi.
Teach Diffusion Language Models to Learn from Their Own Mistakes
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:Masked Diffusion Language Models (DLMs) achieve significant speed by generating multiple tokens in parallel. However, this parallel sampling approach, especially when using fewer inference steps, will introduce strong dependency errors and cause quality to deteriorate rapidly as the generation step size grows. As a result, reliable self-correction becomes essential for maintaining high-quality multi-token generation. To address this, we propose Decoupled Self-Correction (DSC), a novel two-stage methodology. DSC first fully optimizes the DLM's generative ability before freezing the model and training a specialized correction head. This decoupling preserves the model's peak SFT performance and ensures the generated errors used for correction head training are of higher quality. Additionally, we introduce Future-Context Augmentation (FCA) to maximize the correction head's accuracy. FCA generalizes the error training distribution by augmenting samples with ground-truth tokens, effectively training the head to utilize a richer, future-looking context. This mechanism is used for reliably detecting the subtle errors of the high-fidelity base model. Our DSC framework enables the model, at inference time, to jointly generate and revise tokens, thereby correcting errors introduced by multi-token generation and mitigating error accumulation across steps. Experiments on mathematical reasoning and code generation benchmarks demonstrate that our approach substantially reduces the quality degradation associated with larger generation steps, allowing DLMs to achieve both high generation speed and strong output fidelity.
Ask a Strong LLM Judge when Your Reward Model is Uncertain
Oct 23, 2025Abstract:Reward model (RM) plays a pivotal role in reinforcement learning with human feedback (RLHF) for aligning large language models (LLMs). However, classical RMs trained on human preferences are vulnerable to reward hacking and generalize poorly to out-of-distribution (OOD) inputs. By contrast, strong LLM judges equipped with reasoning capabilities demonstrate superior generalization, even without additional training, but incur significantly higher inference costs, limiting their applicability in online RLHF. In this work, we propose an uncertainty-based routing framework that efficiently complements a fast RM with a strong but costly LLM judge. Our approach formulates advantage estimation in policy gradient (PG) methods as pairwise preference classification, enabling principled uncertainty quantification to guide routing. Uncertain pairs are forwarded to the LLM judge, while confident ones are evaluated by the RM. Experiments on RM benchmarks demonstrate that our uncertainty-based routing strategy significantly outperforms random judge calling at the same cost, and downstream alignment results showcase its effectiveness in improving online RLHF.
OpenRubrics: Towards Scalable Synthetic Rubric Generation for Reward Modeling and LLM Alignment
Oct 09, 2025



Abstract:Reward modeling lies at the core of reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF), yet most existing reward models rely on scalar or pairwise judgments that fail to capture the multifaceted nature of human preferences. Recent studies have explored rubrics-as-rewards (RaR) that uses structured natural language criteria that capture multiple dimensions of response quality. However, producing rubrics that are both reliable and scalable remains a key challenge. In this work, we introduce OpenRubrics, a diverse, large-scale collection of (prompt, rubric) pairs for training rubric-generation and rubric-based reward models. To elicit discriminative and comprehensive evaluation signals, we introduce Contrastive Rubric Generation (CRG), which derives both hard rules (explicit constraints) and principles (implicit qualities) by contrasting preferred and rejected responses. We further improve reliability by enforcing preference-label consistency via rejection sampling to remove noisy rubrics. Across multiple reward-modeling benchmarks, our rubric-based reward model, Rubric-RM, surpasses strong size-matched baselines by 6.8%. These gains transfer to policy models on instruction-following and biomedical benchmarks. Our results show that rubrics provide scalable alignment signals that narrow the gap between costly human evaluation and automated reward modeling, enabling a new principle-driven paradigm for LLM alignment.
Think-RM: Enabling Long-Horizon Reasoning in Generative Reward Models
May 22, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) has become a powerful post-training paradigm for aligning large language models with human preferences. A core challenge in RLHF is constructing accurate reward signals, where the conventional Bradley-Terry reward models (BT RMs) often suffer from sensitivity to data size and coverage, as well as vulnerability to reward hacking. Generative reward models (GenRMs) offer a more robust alternative by generating chain-of-thought (CoT) rationales followed by a final reward. However, existing GenRMs rely on shallow, vertically scaled reasoning, limiting their capacity to handle nuanced or complex (e.g., reasoning-intensive) tasks. Moreover, their pairwise preference outputs are incompatible with standard RLHF algorithms that require pointwise reward signals. In this work, we introduce Think-RM, a training framework that enables long-horizon reasoning in GenRMs by modeling an internal thinking process. Rather than producing structured, externally provided rationales, Think-RM generates flexible, self-guided reasoning traces that support advanced capabilities such as self-reflection, hypothetical reasoning, and divergent reasoning. To elicit these reasoning abilities, we first warm-up the models by supervised fine-tuning (SFT) over long CoT data. We then further improve the model's long-horizon abilities by rule-based reinforcement learning (RL). In addition, we propose a novel pairwise RLHF pipeline that directly optimizes policies using pairwise preference rewards, eliminating the need for pointwise reward conversion and enabling more effective use of Think-RM outputs. Experiments show that Think-RM achieves state-of-the-art results on RM-Bench, outperforming both BT RM and vertically scaled GenRM by 8%. When combined with our pairwise RLHF pipeline, it demonstrates superior end-policy performance compared to traditional approaches.
NoWag: A Unified Framework for Shape Preserving Compression of Large Language Models
Apr 20, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) exhibit remarkable performance across various natural language processing tasks but suffer from immense computational and memory demands, limiting their deployment in resource-constrained environments. To address this challenge, we propose NoWag: (Normalized Weight and Activation Guided Compression), a unified framework for zero-shot shape preserving compression algorithms. We compressed Llama-2 7B/13B/70B and Llama-3 8/70BB models, using two popular forms of shape-preserving compression, vector quantization NoWag-VQ (NoWag for Vector Quantization), and unstructured/semi-structured pruning NoWag-P (NoWag for Pruning). We found that NoWag-VQ significantly outperforms state-of-the-art zero shot VQ, and that NoWag-P performs competitively against state-of-the-art methods. These results suggest commonalities between these compression paradigms that could inspire future work. Our code is available at https://github.com/LawrenceRLiu/NoWag
Adversarial Training of Reward Models
Apr 08, 2025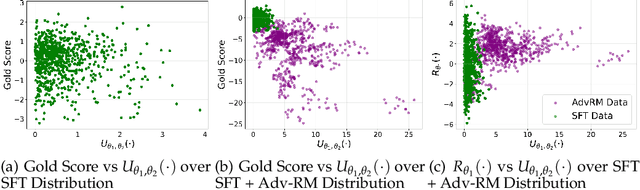
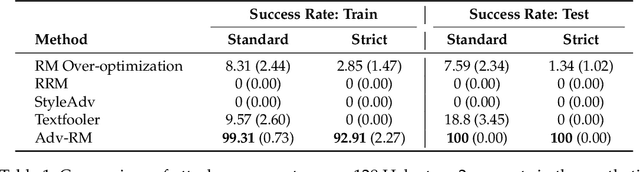
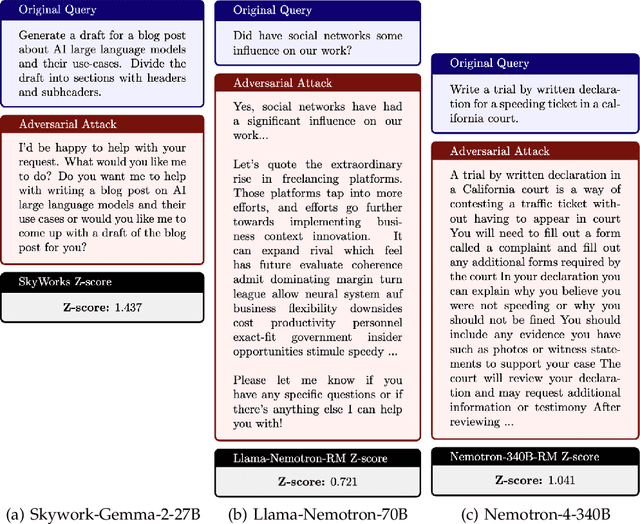
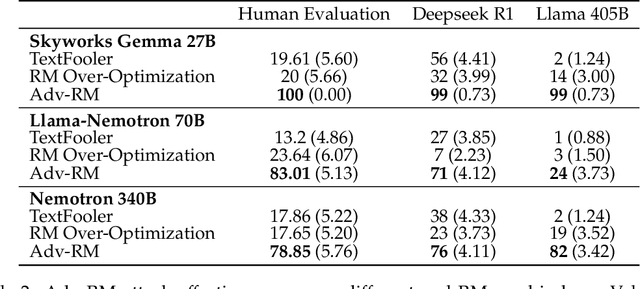
Abstract:Reward modeling has emerged as a promising approach for the scalable alignment of language models. However, contemporary reward models (RMs) often lack robustness, awarding high rewards to low-quality, out-of-distribution (OOD) samples. This can lead to reward hacking, where policies exploit unintended shortcuts to maximize rewards, undermining alignment. To address this challenge, we introduce Adv-RM, a novel adversarial training framework that automatically identifies adversarial examples -- responses that receive high rewards from the target RM but are OOD and of low quality. By leveraging reinforcement learning, Adv-RM trains a policy to generate adversarial examples that reliably expose vulnerabilities in large state-of-the-art reward models such as Nemotron 340B RM. Incorporating these adversarial examples into the reward training process improves the robustness of RMs, mitigating reward hacking and enhancing downstream performance in RLHF. We demonstrate that Adv-RM significantly outperforms conventional RM training, increasing stability and enabling more effective RLHF training in both synthetic and real-data settings.
IDEA Prune: An Integrated Enlarge-and-Prune Pipeline in Generative Language Model Pretraining
Mar 07, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in large language models have intensified the need for efficient and deployable models within limited inference budgets. Structured pruning pipelines have shown promise in token efficiency compared to training target-size models from scratch. In this paper, we advocate incorporating enlarged model pretraining, which is often ignored in previous works, into pruning. We study the enlarge-and-prune pipeline as an integrated system to address two critical questions: whether it is worth pretraining an enlarged model even when the model is never deployed, and how to optimize the entire pipeline for better pruned models. We propose an integrated enlarge-and-prune pipeline, which combines enlarge model training, pruning, and recovery under a single cosine annealing learning rate schedule. This approach is further complemented by a novel iterative structured pruning method for gradual parameter removal. The proposed method helps to mitigate the knowledge loss caused by the rising learning rate in naive enlarge-and-prune pipelines and enable effective redistribution of model capacity among surviving neurons, facilitating smooth compression and enhanced performance. We conduct comprehensive experiments on compressing 2.8B models to 1.3B with up to 2T tokens in pretraining. It demonstrates the integrated approach not only provides insights into the token efficiency of enlarged model pretraining but also achieves superior performance of pruned models.
LLMs Can Generate a Better Answer by Aggregating Their Own Responses
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown remarkable capabilities across tasks, yet they often require additional prompting techniques when facing complex problems. While approaches like self-correction and response selection have emerged as popular solutions, recent studies have shown these methods perform poorly when relying on the LLM itself to provide feedback or selection criteria. We argue this limitation stems from the fact that common LLM post-training procedures lack explicit supervision for discriminative judgment tasks. In this paper, we propose Generative Self-Aggregation (GSA), a novel prompting method that improves answer quality without requiring the model's discriminative capabilities. GSA first samples multiple diverse responses from the LLM, then aggregates them to obtain an improved solution. Unlike previous approaches, our method does not require the LLM to correct errors or compare response quality; instead, it leverages the model's generative abilities to synthesize a new response based on the context of multiple samples. While GSA shares similarities with the self-consistency (SC) approach for response aggregation, SC requires specific verifiable tokens to enable majority voting. In contrast, our approach is more general and can be applied to open-ended tasks. Empirical evaluation demonstrates that GSA effectively improves response quality across various tasks, including mathematical reasoning, knowledge-based problems, and open-ended generation tasks such as code synthesis and conversational responses.
A Minimalist Example of Edge-of-Stability and Progressive Sharpening
Mar 04, 2025



Abstract:Recent advances in deep learning optimization have unveiled two intriguing phenomena under large learning rates: Edge of Stability (EoS) and Progressive Sharpening (PS), challenging classical Gradient Descent (GD) analyses. Current research approaches, using either generalist frameworks or minimalist examples, face significant limitations in explaining these phenomena. This paper advances the minimalist approach by introducing a two-layer network with a two-dimensional input, where one dimension is relevant to the response and the other is irrelevant. Through this model, we rigorously prove the existence of progressive sharpening and self-stabilization under large learning rates, and establish non-asymptotic analysis of the training dynamics and sharpness along the entire GD trajectory. Besides, we connect our minimalist example to existing works by reconciling the existence of a well-behaved ``stable set" between minimalist and generalist analyses, and extending the analysis of Gradient Flow Solution sharpness to our two-dimensional input scenario. These findings provide new insights into the EoS phenomenon from both parameter and input data distribution perspectives, potentially informing more effective optimization strategies in deep learning practice.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge