Alexander Bukharin
NVIDIA Nemotron 3: Efficient and Open Intelligence
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:We introduce the Nemotron 3 family of models - Nano, Super, and Ultra. These models deliver strong agentic, reasoning, and conversational capabilities. The Nemotron 3 family uses a Mixture-of-Experts hybrid Mamba-Transformer architecture to provide best-in-class throughput and context lengths of up to 1M tokens. Super and Ultra models are trained with NVFP4 and incorporate LatentMoE, a novel approach that improves model quality. The two larger models also include MTP layers for faster text generation. All Nemotron 3 models are post-trained using multi-environment reinforcement learning enabling reasoning, multi-step tool use, and support granular reasoning budget control. Nano, the smallest model, outperforms comparable models in accuracy while remaining extremely cost-efficient for inference. Super is optimized for collaborative agents and high-volume workloads such as IT ticket automation. Ultra, the largest model, provides state-of-the-art accuracy and reasoning performance. Nano is released together with its technical report and this white paper, while Super and Ultra will follow in the coming months. We will openly release the model weights, pre- and post-training software, recipes, and all data for which we hold redistribution rights.
Nemotron 3 Nano: Open, Efficient Mixture-of-Experts Hybrid Mamba-Transformer Model for Agentic Reasoning
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:We present Nemotron 3 Nano 30B-A3B, a Mixture-of-Experts hybrid Mamba-Transformer language model. Nemotron 3 Nano was pretrained on 25 trillion text tokens, including more than 3 trillion new unique tokens over Nemotron 2, followed by supervised fine tuning and large-scale RL on diverse environments. Nemotron 3 Nano achieves better accuracy than our previous generation Nemotron 2 Nano while activating less than half of the parameters per forward pass. It achieves up to 3.3x higher inference throughput than similarly-sized open models like GPT-OSS-20B and Qwen3-30B-A3B-Thinking-2507, while also being more accurate on popular benchmarks. Nemotron 3 Nano demonstrates enhanced agentic, reasoning, and chat abilities and supports context lengths up to 1M tokens. We release both our pretrained Nemotron 3 Nano 30B-A3B Base and post-trained Nemotron 3 Nano 30B-A3B checkpoints on Hugging Face.
NVIDIA Nemotron Nano 2: An Accurate and Efficient Hybrid Mamba-Transformer Reasoning Model
Aug 21, 2025



Abstract:We introduce Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2, a hybrid Mamba-Transformer language model designed to increase throughput for reasoning workloads while achieving state-of-the-art accuracy compared to similarly-sized models. Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2 builds on the Nemotron-H architecture, in which the majority of the self-attention layers in the common Transformer architecture are replaced with Mamba-2 layers, to achieve improved inference speed when generating the long thinking traces needed for reasoning. We create Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2 by first pre-training a 12-billion-parameter model (Nemotron-Nano-12B-v2-Base) on 20 trillion tokens using an FP8 training recipe. After aligning Nemotron-Nano-12B-v2-Base, we employ the Minitron strategy to compress and distill the model with the goal of enabling inference on up to 128k tokens on a single NVIDIA A10G GPU (22GiB of memory, bfloat16 precision). Compared to existing similarly-sized models (e.g., Qwen3-8B), we show that Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2 achieves on-par or better accuracy on reasoning benchmarks while achieving up to 6x higher inference throughput in reasoning settings like 8k input and 16k output tokens. We are releasing Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2, Nemotron-Nano12B-v2-Base, and Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2-Base checkpoints along with the majority of our pre- and post-training datasets on Hugging Face.
HelpSteer3-Preference: Open Human-Annotated Preference Data across Diverse Tasks and Languages
May 16, 2025Abstract:Preference datasets are essential for training general-domain, instruction-following language models with Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). Each subsequent data release raises expectations for future data collection, meaning there is a constant need to advance the quality and diversity of openly available preference data. To address this need, we introduce HelpSteer3-Preference, a permissively licensed (CC-BY-4.0), high-quality, human-annotated preference dataset comprising of over 40,000 samples. These samples span diverse real-world applications of large language models (LLMs), including tasks relating to STEM, coding and multilingual scenarios. Using HelpSteer3-Preference, we train Reward Models (RMs) that achieve top performance on RM-Bench (82.4%) and JudgeBench (73.7%). This represents a substantial improvement (~10% absolute) over the previously best-reported results from existing RMs. We demonstrate HelpSteer3-Preference can also be applied to train Generative RMs and how policy models can be aligned with RLHF using our RMs. Dataset (CC-BY-4.0): https://huggingface.co/datasets/nvidia/HelpSteer3#preference
Llama-Nemotron: Efficient Reasoning Models
May 02, 2025



Abstract:We introduce the Llama-Nemotron series of models, an open family of heterogeneous reasoning models that deliver exceptional reasoning capabilities, inference efficiency, and an open license for enterprise use. The family comes in three sizes -- Nano (8B), Super (49B), and Ultra (253B) -- and performs competitively with state-of-the-art reasoning models such as DeepSeek-R1 while offering superior inference throughput and memory efficiency. In this report, we discuss the training procedure for these models, which entails using neural architecture search from Llama 3 models for accelerated inference, knowledge distillation, and continued pretraining, followed by a reasoning-focused post-training stage consisting of two main parts: supervised fine-tuning and large scale reinforcement learning. Llama-Nemotron models are the first open-source models to support a dynamic reasoning toggle, allowing users to switch between standard chat and reasoning modes during inference. To further support open research and facilitate model development, we provide the following resources: 1. We release the Llama-Nemotron reasoning models -- LN-Nano, LN-Super, and LN-Ultra -- under the commercially permissive NVIDIA Open Model License Agreement. 2. We release the complete post-training dataset: Llama-Nemotron-Post-Training-Dataset. 3. We also release our training codebases: NeMo, NeMo-Aligner, and Megatron-LM.
Adversarial Training of Reward Models
Apr 08, 2025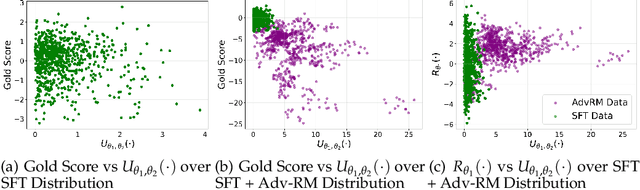
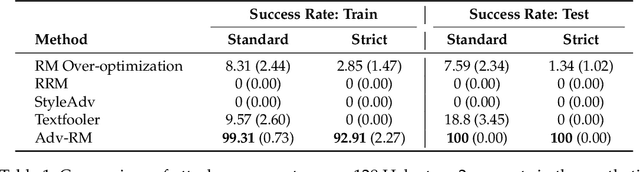
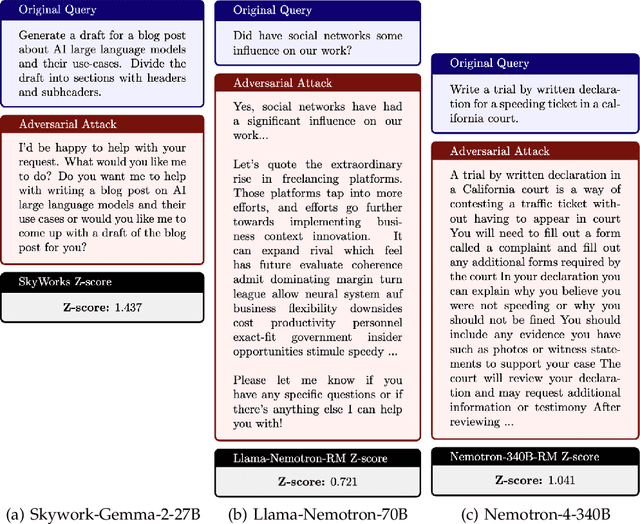
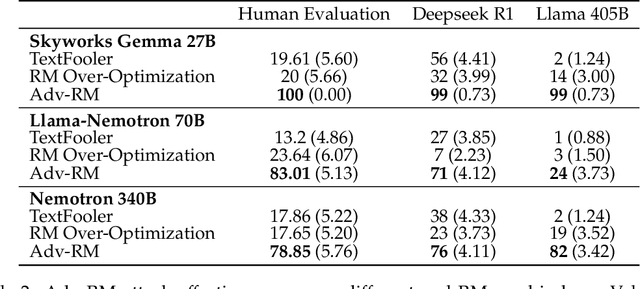
Abstract:Reward modeling has emerged as a promising approach for the scalable alignment of language models. However, contemporary reward models (RMs) often lack robustness, awarding high rewards to low-quality, out-of-distribution (OOD) samples. This can lead to reward hacking, where policies exploit unintended shortcuts to maximize rewards, undermining alignment. To address this challenge, we introduce Adv-RM, a novel adversarial training framework that automatically identifies adversarial examples -- responses that receive high rewards from the target RM but are OOD and of low quality. By leveraging reinforcement learning, Adv-RM trains a policy to generate adversarial examples that reliably expose vulnerabilities in large state-of-the-art reward models such as Nemotron 340B RM. Incorporating these adversarial examples into the reward training process improves the robustness of RMs, mitigating reward hacking and enhancing downstream performance in RLHF. We demonstrate that Adv-RM significantly outperforms conventional RM training, increasing stability and enabling more effective RLHF training in both synthetic and real-data settings.
HelpSteer2-Preference: Complementing Ratings with Preferences
Oct 02, 2024Abstract:Reward models are critical for aligning models to follow instructions, and are typically trained following one of two popular paradigms: Bradley-Terry style or Regression style. However, there is a lack of evidence that either approach is better than the other, when adequately matched for data. This is primarily because these approaches require data collected in different (but incompatible) formats, meaning that adequately matched data is not available in existing public datasets. To tackle this problem, we release preference annotations (designed for Bradley-Terry training) to complement existing ratings (designed for Regression style training) in the HelpSteer2 dataset. To improve data interpretability, preference annotations are accompanied with human-written justifications. Using this data, we conduct the first head-to-head comparison of Bradley-Terry and Regression models when adequately matched for data. Based on insights derived from such a comparison, we propose a novel approach to combine Bradley-Terry and Regression reward modeling. A Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct model tuned with this approach scores 94.1 on RewardBench, emerging top of more than 140 reward models as of 1 Oct 2024. We also demonstrate the effectiveness of this reward model at aligning models to follow instructions in RLHF. We open-source this dataset (CC-BY-4.0 license) at https://huggingface.co/datasets/nvidia/HelpSteer2 and openly release the trained Reward Model at https://huggingface.co/nvidia/Llama-3.1-Nemotron-70B-Reward
Robust Reinforcement Learning from Corrupted Human Feedback
Jun 21, 2024Abstract:Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) provides a principled framework for aligning AI systems with human preference data. For various reasons, e.g., personal bias, context ambiguity, lack of training, etc, human annotators may give incorrect or inconsistent preference labels. To tackle this challenge, we propose a robust RLHF approach -- $R^3M$, which models the potentially corrupted preference label as sparse outliers. Accordingly, we formulate the robust reward learning as an $\ell_1$-regularized maximum likelihood estimation problem. Computationally, we develop an efficient alternating optimization algorithm, which only incurs negligible computational overhead compared with the standard RLHF approach. Theoretically, we prove that under proper regularity conditions, $R^3M$ can consistently learn the underlying reward and identify outliers, provided that the number of outlier labels scales sublinearly with the preference sample size. Furthermore, we remark that $R^3M$ is versatile and can be extended to various preference optimization methods, including direct preference optimization (DPO). Our experiments on robotic control and natural language generation with large language models (LLMs) show that $R^3M$ improves robustness of the reward against several types of perturbations to the preference data.
Adaptive Preference Scaling for Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback
Jun 04, 2024Abstract:Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) is a prevalent approach to align AI systems with human values by learning rewards from human preference data. Due to various reasons, however, such data typically takes the form of rankings over pairs of trajectory segments, which fails to capture the varying strengths of preferences across different pairs. In this paper, we propose a novel adaptive preference loss, underpinned by distributionally robust optimization (DRO), designed to address this uncertainty in preference strength. By incorporating an adaptive scaling parameter into the loss for each pair, our method increases the flexibility of the reward function. Specifically, it assigns small scaling parameters to pairs with ambiguous preferences, leading to more comparable rewards, and large scaling parameters to those with clear preferences for more distinct rewards. Computationally, our proposed loss function is strictly convex and univariate with respect to each scaling parameter, enabling its efficient optimization through a simple second-order algorithm. Our method is versatile and can be readily adapted to various preference optimization frameworks, including direct preference optimization (DPO). Our experiments with robotic control and natural language generation with large language models (LLMs) show that our method not only improves policy performance but also aligns reward function selection more closely with policy optimization, simplifying the hyperparameter tuning process.
Data Diversity Matters for Robust Instruction Tuning
Nov 21, 2023Abstract:Instruction tuning has emerged as a key step in aligning large language models. One of the central challenges of instruction tuning is dataset selection, as the composition of the instruction tuning dataset can significantly impact downstream performance. In particular, researchers have hypothesized that dataset diversity and dataset quality are important indicators of downstream performance. However, it is not clear how to automatically select high quality and diverse data or how exactly quality and diversity affect instruction following ability. To resolve these issues, we propose a new algorithm, Quality-Diversity Instruction Tuning (QDIT). QDIT provides a principled algorithm to control dataset diversity and quality, allowing us to conduct an in depth study on the effect of diversity and quality on instruction tuning performance. From this study we draw two key insights (1) there is a natural tradeoff between dataset diversity and quality and (2) increasing dataset diversity significantly improves the worst case instruction following performance, therefore improving robustness. We validate the performance of QDIT on several large scale instruction tuning datasets, where we find it can improve worst case performance by 18% while maintaining or improving average performance compared to quality driven baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge