Liyuan Liu
Test-time Recursive Thinking: Self-Improvement without External Feedback
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Modern Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown rapid improvements in reasoning capabilities, driven largely by reinforcement learning (RL) with verifiable rewards. Here, we ask whether these LLMs can self-improve without the need for additional training. We identify two core challenges for such systems: (i) efficiently generating diverse, high-quality candidate solutions, and (ii) reliably selecting correct answers in the absence of ground-truth supervision. To address these challenges, we propose Test-time Recursive Thinking (TRT), an iterative self-improvement framework that conditions generation on rollout-specific strategies, accumulated knowledge, and self-generated verification signals. Using TRT, open-source models reach 100% accuracy on AIME-25/24, and on LiveCodeBench's most difficult problems, closed-source models improve by 10.4-14.8 percentage points without external feedback.
Adaptation of Agentic AI
Dec 22, 2025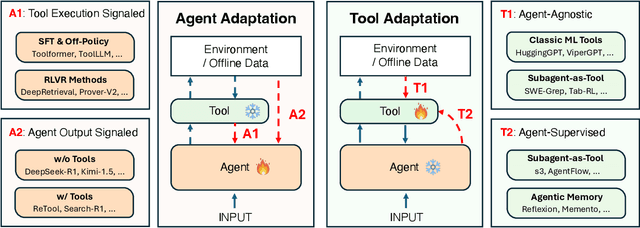
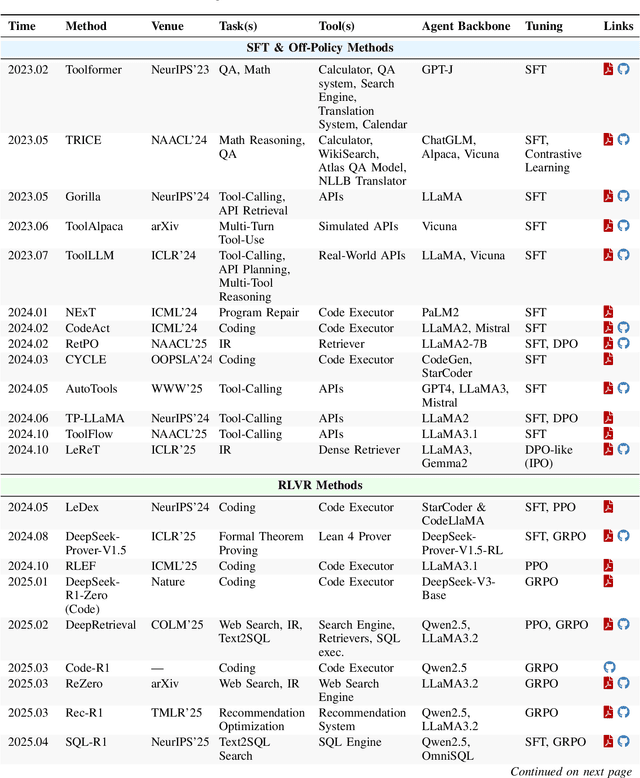
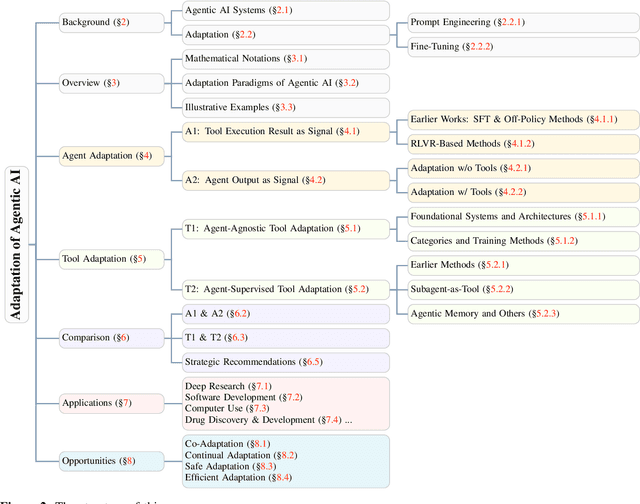
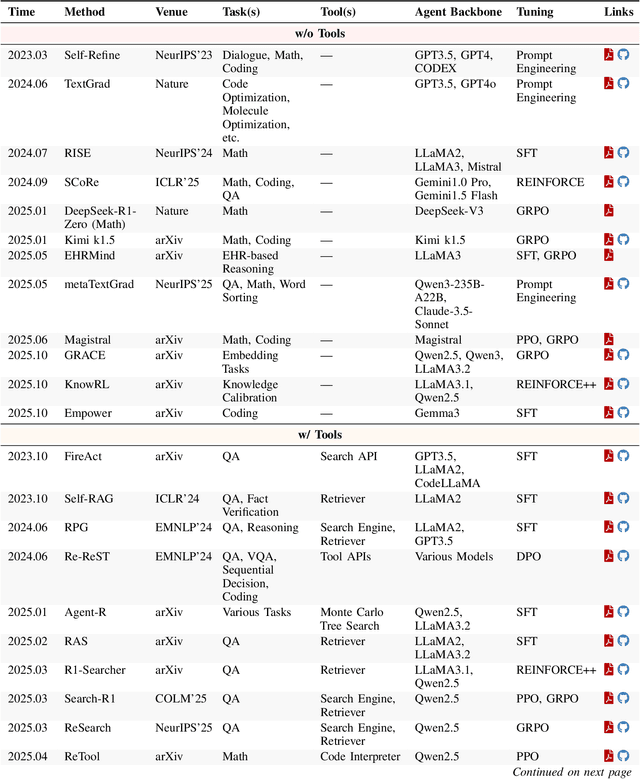
Abstract:Cutting-edge agentic AI systems are built on foundation models that can be adapted to plan, reason, and interact with external tools to perform increasingly complex and specialized tasks. As these systems grow in capability and scope, adaptation becomes a central mechanism for improving performance, reliability, and generalization. In this paper, we unify the rapidly expanding research landscape into a systematic framework that spans both agent adaptations and tool adaptations. We further decompose these into tool-execution-signaled and agent-output-signaled forms of agent adaptation, as well as agent-agnostic and agent-supervised forms of tool adaptation. We demonstrate that this framework helps clarify the design space of adaptation strategies in agentic AI, makes their trade-offs explicit, and provides practical guidance for selecting or switching among strategies during system design. We then review the representative approaches in each category, analyze their strengths and limitations, and highlight key open challenges and future opportunities. Overall, this paper aims to offer a conceptual foundation and practical roadmap for researchers and practitioners seeking to build more capable, efficient, and reliable agentic AI systems.
A digital SRAM-based compute-in-memory macro for weight-stationary dynamic matrix multiplication in Transformer attention score computation
Nov 15, 2025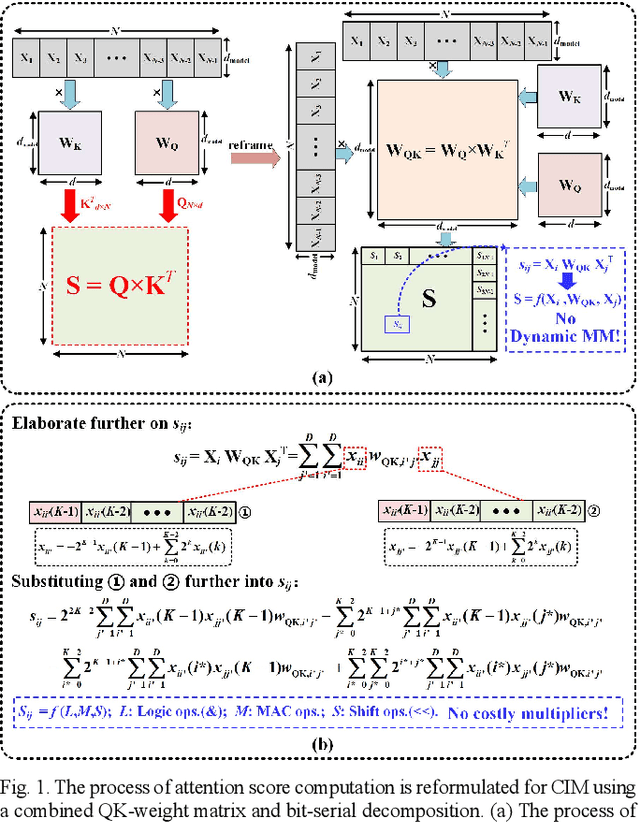
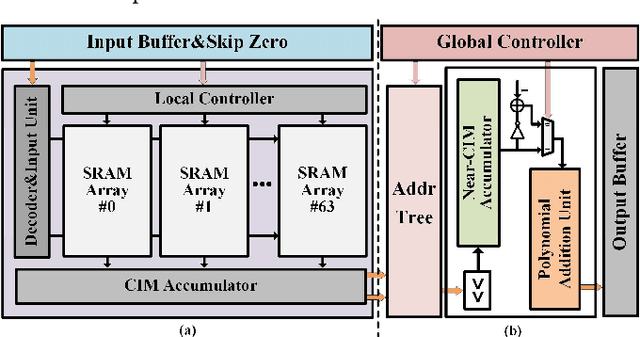


Abstract:Compute-in-memory (CIM) techniques are widely employed in energy-efficient artificial intelligent (AI) processors. They alleviate power and latency bottlenecks caused by extensive data movements between compute and storage units. This work proposes a digital CIM macro to compute Transformer attention. To mitigate dynamic matrix multiplication that is unsuitable for the common weight-stationary CIM paradigm, we reformulate the attention score computation process based on a combined QK-weight matrix, so that inputs can be directly fed to CIM cells to obtain the score results. Moreover, the involved binomial matrix multiplication operation is decomposed into 4 groups of bit-serial shifting and additions, without costly physical multipliers in the CIM. We maximize the energy efficiency of the CIM circuit through zero-value bit-skipping, data-driven word line activation, read-write separate 6T cells and bit-alternating 14T/28T adders. The proposed CIM macro was implemented using a 65-nm process. It occupied only 0.35 mm2 area, and delivered a 42.27 GOPS peak performance with 1.24 mW power consumption at a 1.0 V power supply and a 100 MHz clock frequency, resulting in 34.1 TOPS/W energy efficiency and 120.77 GOPS/mm2 area efficiency. When compared to the CPU and GPU, our CIM macro is 25x and 13x more energy efficient on practical tasks, respectively. Compared with other Transformer-CIMs, our design exhibits at least 7x energy efficiency and at least 2x area efficiency improvements when scaled to the same technology node, showcasing its potential for edge-side intelligent applications.
Decoder-Hybrid-Decoder Architecture for Efficient Reasoning with Long Generation
Jul 09, 2025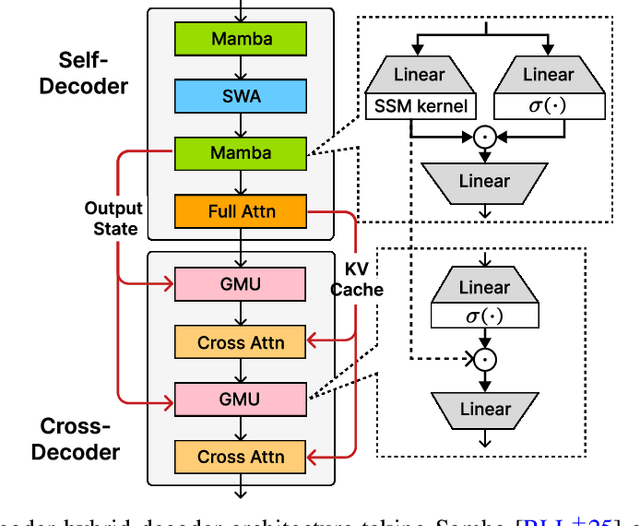
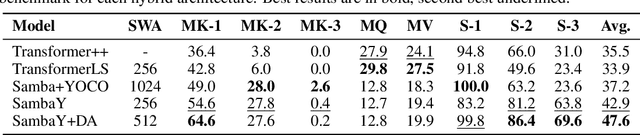
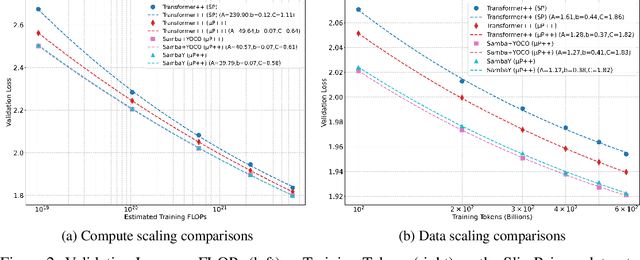
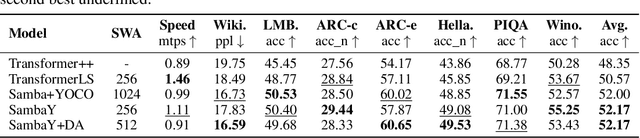
Abstract:Recent advances in language modeling have demonstrated the effectiveness of State Space Models (SSMs) for efficient sequence modeling. While hybrid architectures such as Samba and the decoder-decoder architecture, YOCO, have shown promising performance gains over Transformers, prior works have not investigated the efficiency potential of representation sharing between SSM layers. In this paper, we introduce the Gated Memory Unit (GMU), a simple yet effective mechanism for efficient memory sharing across layers. We apply it to create SambaY, a decoder-hybrid-decoder architecture that incorporates GMUs in the cross-decoder to share memory readout states from a Samba-based self-decoder. SambaY significantly enhances decoding efficiency, preserves linear pre-filling time complexity, and boosts long-context performance, all while eliminating the need for explicit positional encoding. Through extensive scaling experiments, we demonstrate that our model exhibits a significantly lower irreducible loss compared to a strong YOCO baseline, indicating superior performance scalability under large-scale compute regimes. Our largest model enhanced with Differential Attention, Phi4-mini-Flash-Reasoning, achieves significantly better performance than Phi4-mini-Reasoning on reasoning tasks such as Math500, AIME24/25, and GPQA Diamond without any reinforcement learning, while delivering up to 10x higher decoding throughput on 2K-length prompts with 32K generation length under the vLLM inference framework. We release our training codebase on open-source data at https://github.com/microsoft/ArchScale.
Optimal Embedding Learning Rate in LLMs: The Effect of Vocabulary Size
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:Pretraining large language models is a costly process. To make this process more efficient, several methods have been proposed to optimize model architecture/parametrization and hardware use. On the parametrization side, $\mu P$ (Maximal Update Parametrization) parametrizes model weights and learning rate (LR) in a way that makes hyperparameters (HPs) transferable with width (embedding dimension): HPs can be tuned for a small model and used for larger models without additional tuning. While $\mu$P showed impressive results in practice, recent empirical studies have reported conflicting observations when applied to LLMs. One limitation of the theory behind $\mu$P is the fact that input dimension (vocabulary size in LLMs) is considered fixed when taking the width to infinity. This is unrealistic since vocabulary size is generally much larger than width in practice. In this work, we provide a theoretical analysis of the effect of vocabulary size on training dynamics, and subsequently show that as vocabulary size increases, the training dynamics \emph{interpolate between the $\mu$P regime and another regime that we call Large Vocab (LV) Regime}, where optimal scaling rules are different from those predicted by $\mu$P. Our analysis reveals that in the LV regime, the optimal embedding LR to hidden LR ratio should roughly scale as $\Theta(\sqrt{width})$, surprisingly close to the empirical findings previously reported in the literature, and different from the $\Theta(width)$ ratio predicted by $\mu$P. We conduct several experiments to validate our theory, and pretrain a 1B model from scratch to show the benefit of our suggested scaling rule for the embedding LR.
Training Language Models to Generate Quality Code with Program Analysis Feedback
May 28, 2025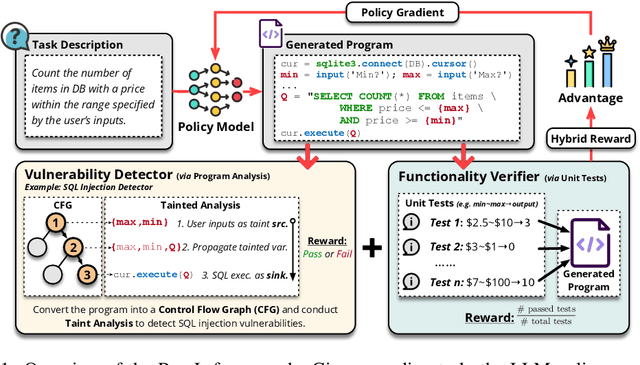
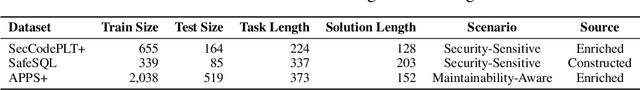
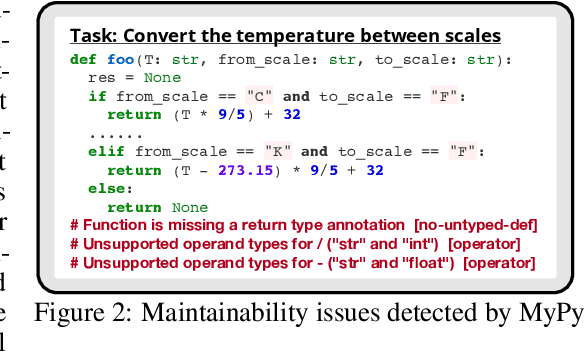
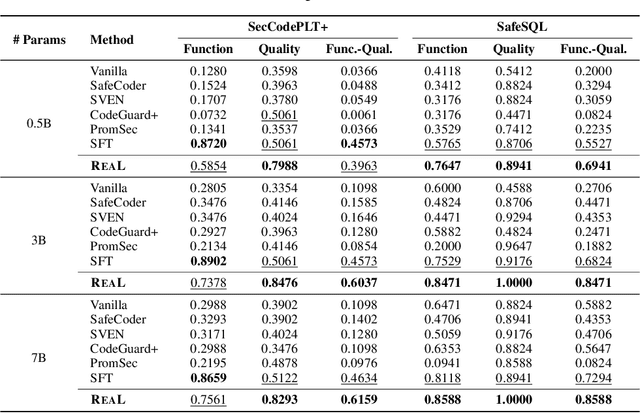
Abstract:Code generation with large language models (LLMs), often termed vibe coding, is increasingly adopted in production but fails to ensure code quality, particularly in security (e.g., SQL injection vulnerabilities) and maintainability (e.g., missing type annotations). Existing methods, such as supervised fine-tuning and rule-based post-processing, rely on labor-intensive annotations or brittle heuristics, limiting their scalability and effectiveness. We propose REAL, a reinforcement learning framework that incentivizes LLMs to generate production-quality code using program analysis-guided feedback. Specifically, REAL integrates two automated signals: (1) program analysis detecting security or maintainability defects and (2) unit tests ensuring functional correctness. Unlike prior work, our framework is prompt-agnostic and reference-free, enabling scalable supervision without manual intervention. Experiments across multiple datasets and model scales demonstrate that REAL outperforms state-of-the-art methods in simultaneous assessments of functionality and code quality. Our work bridges the gap between rapid prototyping and production-ready code, enabling LLMs to deliver both speed and quality.
Text Generation Beyond Discrete Token Sampling
May 20, 2025
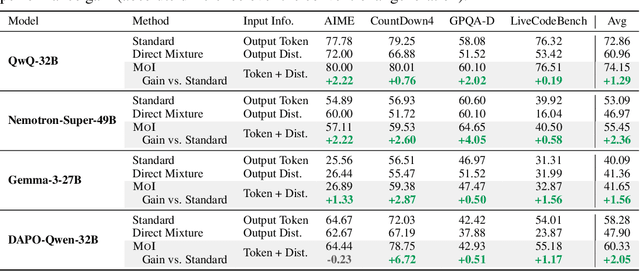


Abstract:In standard autoregressive generation, an LLM predicts the next-token distribution, samples a discrete token, and then discards the distribution, passing only the sampled token as new input. To preserve this distribution's rich information, we propose Mixture of Inputs (MoI), a training-free method for autoregressive generation. After generating a token following the standard paradigm, we construct a new input that blends the generated discrete token with the previously discarded token distribution. Specifically, we employ a Bayesian estimation method that treats the token distribution as the prior, the sampled token as the observation, and replaces the conventional one-hot vector with the continuous posterior expectation as the new model input. MoI allows the model to maintain a richer internal representation throughout the generation process, resulting in improved text quality and reasoning capabilities. On mathematical reasoning, code generation, and PhD-level QA tasks, MoI consistently improves performance across multiple models including QwQ-32B, Nemotron-Super-49B, Gemma-3-27B, and DAPO-Qwen-32B, with no additional training and negligible computational overhead.
An Introduction to Discrete Variational Autoencoders
May 15, 2025Abstract:Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) are well-established as a principled approach to probabilistic unsupervised learning with neural networks. Typically, an encoder network defines the parameters of a Gaussian distributed latent space from which we can sample and pass realizations to a decoder network. This model is trained to reconstruct its inputs and is optimized through the evidence lower bound. In recent years, discrete latent spaces have grown in popularity, suggesting that they may be a natural choice for many data modalities (e.g. text). In this tutorial, we provide a rigorous, yet practical, introduction to discrete variational autoencoders -- specifically, VAEs in which the latent space is made up of latent variables that follow a categorical distribution. We assume only a basic mathematical background with which we carefully derive each step from first principles. From there, we develop a concrete training recipe and provide an example implementation, hosted at https://github.com/alanjeffares/discreteVAE.
MamKPD: A Simple Mamba Baseline for Real-Time 2D Keypoint Detection
Dec 02, 2024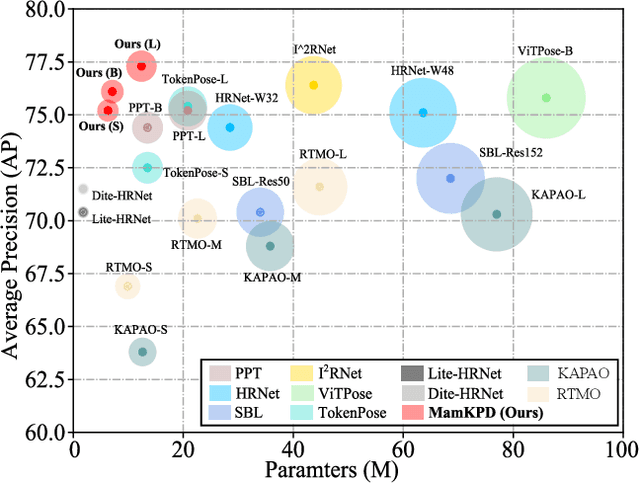
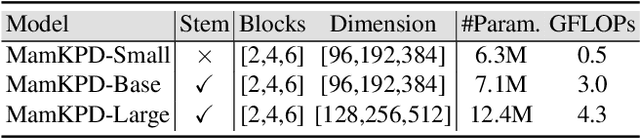
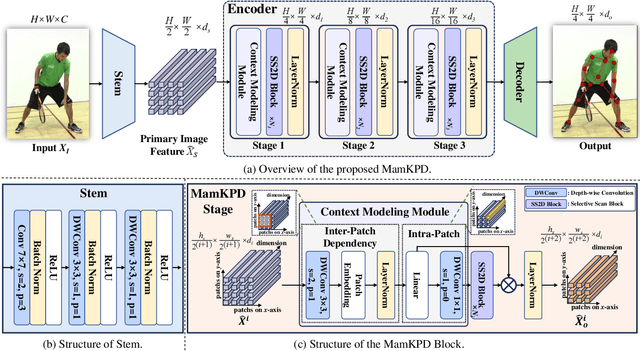
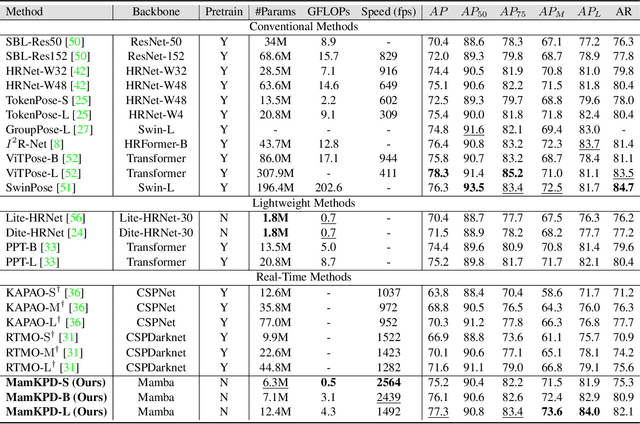
Abstract:Real-time 2D keypoint detection plays an essential role in computer vision. Although CNN-based and Transformer-based methods have achieved breakthrough progress, they often fail to deliver superior performance and real-time speed. This paper introduces MamKPD, the first efficient yet effective mamba-based pose estimation framework for 2D keypoint detection. The conventional Mamba module exhibits limited information interaction between patches. To address this, we propose a lightweight contextual modeling module (CMM) that uses depth-wise convolutions to model inter-patch dependencies and linear layers to distill the pose cues within each patch. Subsequently, by combining Mamba for global modeling across all patches, MamKPD effectively extracts instances' pose information. We conduct extensive experiments on human and animal pose estimation datasets to validate the effectiveness of MamKPD. Our MamKPD-L achieves 77.3% AP on the COCO dataset with 1492 FPS on an NVIDIA GTX 4090 GPU. Moreover, MamKPD achieves state-of-the-art results on the MPII dataset and competitive results on the AP-10K dataset while saving 85% of the parameters compared to ViTPose. Our project page is available at https://mamkpd.github.io/.
STOP: Spatiotemporal Orthogonal Propagation for Weight-Threshold-Leakage Synergistic Training of Deep Spiking Neural Networks
Nov 17, 2024



Abstract:The prevailing of artificial intelligence-of-things calls for higher energy-efficient edge computing paradigms, such as neuromorphic agents leveraging brain-inspired spiking neural network (SNN) models based on spatiotemporally sparse binary activations. However, the lack of efficient and high-accuracy deep SNN learning algorithms prevents them from practical edge deployments with a strictly bounded cost. In this paper, we propose a spatiotemporal orthogonal propagation (STOP) algorithm to tack this challenge. Our algorithm enables fully synergistic learning of synaptic weights as well as firing thresholds and leakage factors in spiking neurons to improve SNN accuracy, while under a unified temporally-forward trace-based framework to mitigate the huge memory requirement for storing neural states of all time-steps in the forward pass. Characteristically, the spatially-backward neuronal errors and temporally-forward traces propagate orthogonally to and independently of each other, substantially reducing computational overhead. Our STOP algorithm obtained high recognition accuracies of 99.53%, 94.84%, 74.92%, 98.26% and 77.10% on the MNIST, CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, DVS-Gesture and DVS-CIFAR10 datasets with adequate SNNs of intermediate scales from LeNet-5 to ResNet-18. Compared with other deep SNN training works, our method is more plausible for edge intelligent scenarios where resources are limited but high-accuracy in-situ learning is desired.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge