Siqi Yang
Length-Unbiased Sequence Policy Optimization: Revealing and Controlling Response Length Variation in RLVR
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Recent applications of Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) to Large Language Models (LLMs) and Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have demonstrated significant success in enhancing reasoning capabilities for complex tasks. During RLVR training, an increase in response length is often regarded as a key factor contributing to the growth of reasoning ability. However, the patterns of change in response length vary significantly across different RLVR algorithms during the training process. To provide a fundamental explanation for these variations, this paper conducts an in-depth analysis of the components of mainstream RLVR algorithms. We present a theoretical analysis of the factors influencing response length and validate our theory through extensive experimentation. Building upon these theoretical findings, we propose the Length-Unbiased Sequence Policy Optimization (LUSPO) algorithm. Specifically, we rectify the length bias inherent in Group Sequence Policy Optimization (GSPO), rendering its loss function unbiased with respect to response length and thereby resolving the issue of response length collapse. We conduct extensive experiments across mathematical reasoning benchmarks and multimodal reasoning scenarios, where LUSPO consistently achieves superior performance. Empirical results demonstrate that LUSPO represents a novel, state-of-the-art optimization strategy compared to existing methods such as GRPO and GSPO.
Proof-RM: A Scalable and Generalizable Reward Model for Math Proof
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:While Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong math reasoning abilities through Reinforcement Learning with *Verifiable Rewards* (RLVR), many advanced mathematical problems are proof-based, with no guaranteed way to determine the authenticity of a proof by simple answer matching. To enable automatic verification, a Reward Model (RM) capable of reliably evaluating full proof processes is required. In this work, we design a *scalable* data-construction pipeline that, with minimal human effort, leverages LLMs to generate a large quantity of high-quality "**question-proof-check**" triplet data. By systematically varying problem sources, generation methods, and model configurations, we create diverse problem-proof pairs spanning multiple difficulty levels, linguistic styles, and error types, subsequently filtered through hierarchical human review for label alignment. Utilizing these data, we train a proof-checking RM, incorporating additional process reward and token weight balance to stabilize the RL process. Our experiments validate the model's scalability and strong performance from multiple perspectives, including reward accuracy, generalization ability and test-time guidance, providing important practical recipes and tools for strengthening LLM mathematical capabilities.
V-FAT: Benchmarking Visual Fidelity Against Text-bias
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Recent advancements in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated impressive performance on standard visual reasoning benchmarks. However, there is growing concern that these models rely excessively on linguistic shortcuts rather than genuine visual grounding, a phenomenon we term Text Bias. In this paper, we investigate the fundamental tension between visual perception and linguistic priors. We decouple the sources of this bias into two dimensions: Internal Corpus Bias, stemming from statistical correlations in pretraining, and External Instruction Bias, arising from the alignment-induced tendency toward sycophancy. To quantify this effect, we introduce V-FAT (Visual Fidelity Against Text-bias), a diagnostic benchmark comprising 4,026 VQA instances across six semantic domains. V-FAT employs a Three-Level Evaluation Framework that systematically increases the conflict between visual evidence and textual information: (L1) internal bias from atypical images, (L2) external bias from misleading instructions, and (L3) synergistic bias where both coincide. We introduce the Visual Robustness Score (VRS), a metric designed to penalize "lucky" linguistic guesses and reward true visual fidelity. Our evaluation of 12 frontier MLLMs reveals that while models excel in existing benchmarks, they experience significant visual collapse under high linguistic dominance.
MeniMV: A Multi-view Benchmark for Meniscus Injury Severity Grading
Dec 20, 2025Abstract:Precise grading of meniscal horn tears is critical in knee injury diagnosis but remains underexplored in automated MRI analysis. Existing methods often rely on coarse study-level labels or binary classification, lacking localization and severity information. In this paper, we introduce MeniMV, a multi-view benchmark dataset specifically designed for horn-specific meniscus injury grading. MeniMV comprises 3,000 annotated knee MRI exams from 750 patients across three medical centers, providing 6,000 co-registered sagittal and coronal images. Each exam is meticulously annotated with four-tier (grade 0-3) severity labels for both anterior and posterior meniscal horns, verified by chief orthopedic physicians. Notably, MeniMV offers more than double the pathology-labeled data volume of prior datasets while uniquely capturing the dual-view diagnostic context essential in clinical practice. To demonstrate the utility of MeniMV, we benchmark multiple state-of-the-art CNN and Transformer-based models. Our extensive experiments establish strong baselines and highlight challenges in severity grading, providing a valuable foundation for future research in automated musculoskeletal imaging.
Learning When to Look: A Disentangled Curriculum for Strategic Perception in Multimodal Reasoning
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) demonstrate significant potential but remain brittle in complex, long-chain visual reasoning tasks. A critical failure mode is "visual forgetting", where models progressively lose visual grounding as reasoning extends, a phenomenon aptly described as "think longer, see less". We posit this failure stems from current training paradigms prematurely entangling two distinct cognitive skills: (1) abstract logical reasoning "how-to-think") and (2) strategic visual perception ("when-to-look"). This creates a foundational cold-start deficiency -- weakening abstract reasoning -- and a strategic perception deficit, as models lack a policy for when to perceive. In this paper, we propose a novel curriculum-based framework to disentangle these skills. First, we introduce a disentangled Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) curriculum that builds a robust abstract reasoning backbone on text-only data before anchoring it to vision with a novel Perception-Grounded Chain-of-Thought (PG-CoT) paradigm. Second, we resolve the strategic perception deficit by formulating timing as a reinforcement learning problem. We design a Pivotal Perception Reward that teaches the model when to look by coupling perceptual actions to linguistic markers of cognitive uncertainty (e.g., "wait", "verify"), thereby learning an autonomous grounding policy. Our contributions include the formalization of these two deficiencies and the development of a principled, two-stage framework to address them, transforming the model from a heuristic-driven observer to a strategic, grounded reasoner. \textbf{Code}: \url{https://github.com/gaozilve-max/learning-when-to-look}.
RecGPT-V2 Technical Report
Dec 16, 2025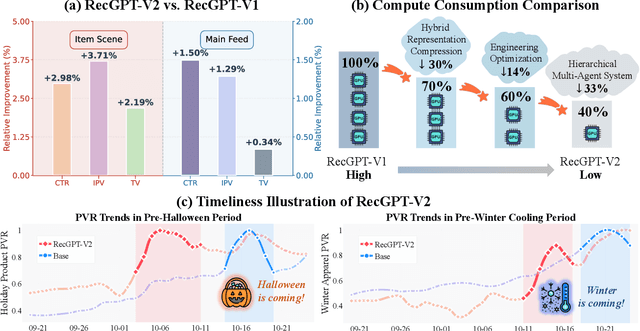
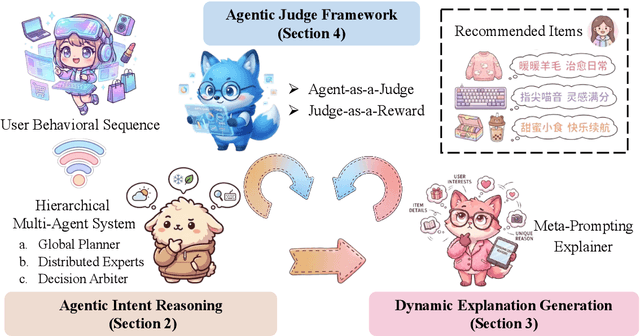
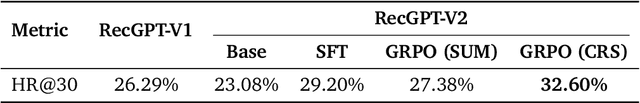
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable potential in transforming recommender systems from implicit behavioral pattern matching to explicit intent reasoning. While RecGPT-V1 successfully pioneered this paradigm by integrating LLM-based reasoning into user interest mining and item tag prediction, it suffers from four fundamental limitations: (1) computational inefficiency and cognitive redundancy across multiple reasoning routes; (2) insufficient explanation diversity in fixed-template generation; (3) limited generalization under supervised learning paradigms; and (4) simplistic outcome-focused evaluation that fails to match human standards. To address these challenges, we present RecGPT-V2 with four key innovations. First, a Hierarchical Multi-Agent System restructures intent reasoning through coordinated collaboration, eliminating cognitive duplication while enabling diverse intent coverage. Combined with Hybrid Representation Inference that compresses user-behavior contexts, our framework reduces GPU consumption by 60% and improves exclusive recall from 9.39% to 10.99%. Second, a Meta-Prompting framework dynamically generates contextually adaptive prompts, improving explanation diversity by +7.3%. Third, constrained reinforcement learning mitigates multi-reward conflicts, achieving +24.1% improvement in tag prediction and +13.0% in explanation acceptance. Fourth, an Agent-as-a-Judge framework decomposes assessment into multi-step reasoning, improving human preference alignment. Online A/B tests on Taobao demonstrate significant improvements: +2.98% CTR, +3.71% IPV, +2.19% TV, and +11.46% NER. RecGPT-V2 establishes both the technical feasibility and commercial viability of deploying LLM-powered intent reasoning at scale, bridging the gap between cognitive exploration and industrial utility.
Audio-sync Video Instance Editing with Granularity-Aware Mask Refiner
Dec 11, 2025



Abstract:Recent advancements in video generation highlight that realistic audio-visual synchronization is crucial for engaging content creation. However, existing video editing methods largely overlook audio-visual synchronization and lack the fine-grained spatial and temporal controllability required for precise instance-level edits. In this paper, we propose AVI-Edit, a framework for audio-sync video instance editing. We propose a granularity-aware mask refiner that iteratively refines coarse user-provided masks into precise instance-level regions. We further design a self-feedback audio agent to curate high-quality audio guidance, providing fine-grained temporal control. To facilitate this task, we additionally construct a large-scale dataset with instance-centric correspondence and comprehensive annotations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that AVI-Edit outperforms state-of-the-art methods in visual quality, condition following, and audio-visual synchronization. Project page: https://hjzheng.net/projects/AVI-Edit/.
Metis-HOME: Hybrid Optimized Mixture-of-Experts for Multimodal Reasoning
Oct 23, 2025Abstract:Inspired by recent advancements in LLM reasoning, the field of multimodal reasoning has seen remarkable progress, achieving significant performance gains on intricate tasks such as mathematical problem-solving. Despite this progress, current multimodal large reasoning models exhibit two key limitations. They tend to employ computationally expensive reasoning even for simple queries, leading to inefficiency. Furthermore, this focus on specialized reasoning often impairs their broader, more general understanding capabilities. In this paper, we propose Metis-HOME: a Hybrid Optimized Mixture-of-Experts framework designed to address this trade-off. Metis-HOME enables a ''Hybrid Thinking'' paradigm by structuring the original dense model into two distinct expert branches: a thinking branch tailored for complex, multi-step reasoning, and a non-thinking branch optimized for rapid, direct inference on tasks like general VQA and OCR. A lightweight, trainable router dynamically allocates queries to the most suitable expert. We instantiate Metis-HOME by adapting the Qwen2.5-VL-7B into an MoE architecture. Comprehensive evaluations reveal that our approach not only substantially enhances complex reasoning abilities but also improves the model's general capabilities, reversing the degradation trend observed in other reasoning-specialized models. Our work establishes a new paradigm for building powerful and versatile MLLMs, effectively resolving the prevalent reasoning-vs-generalization dilemma.
DocTron-Formula: Generalized Formula Recognition in Complex and Structured Scenarios
Aug 01, 2025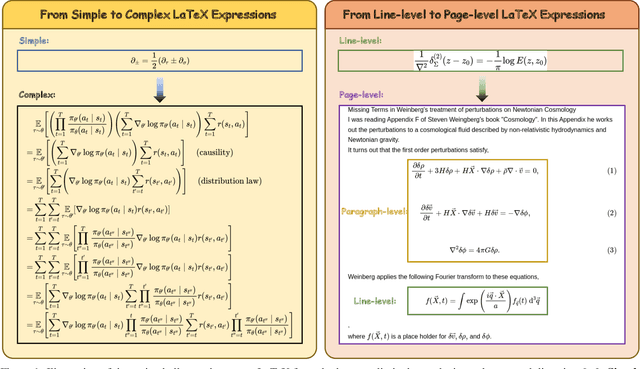

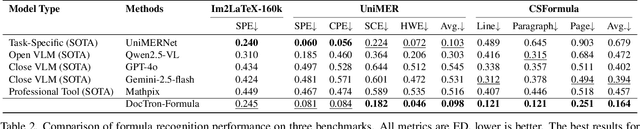
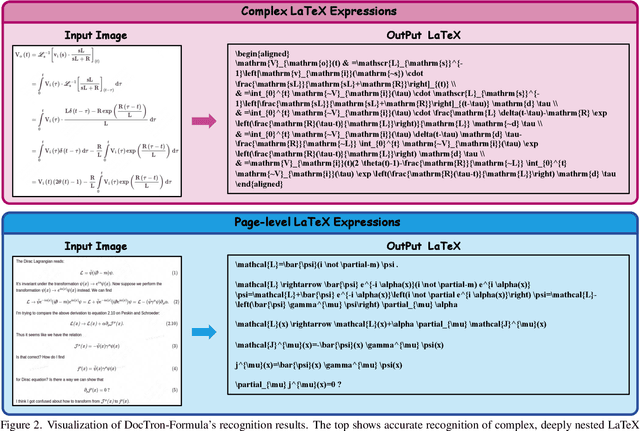
Abstract:Optical Character Recognition (OCR) for mathematical formula is essential for the intelligent analysis of scientific literature. However, both task-specific and general vision-language models often struggle to handle the structural diversity, complexity, and real-world variability inherent in mathematical content. In this work, we present DocTron-Formula, a unified framework built upon general vision-language models, thereby eliminating the need for specialized architectures. Furthermore, we introduce CSFormula, a large-scale and challenging dataset that encompasses multidisciplinary and structurally complex formulas at the line, paragraph, and page levels. Through straightforward supervised fine-tuning, our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance across a variety of styles, scientific domains, and complex layouts. Experimental results demonstrate that our method not only surpasses specialized models in terms of accuracy and robustness, but also establishes a new paradigm for the automated understanding of complex scientific documents.
PanoWan: Lifting Diffusion Video Generation Models to 360° with Latitude/Longitude-aware Mechanisms
May 28, 2025Abstract:Panoramic video generation enables immersive 360{\deg} content creation, valuable in applications that demand scene-consistent world exploration. However, existing panoramic video generation models struggle to leverage pre-trained generative priors from conventional text-to-video models for high-quality and diverse panoramic videos generation, due to limited dataset scale and the gap in spatial feature representations. In this paper, we introduce PanoWan to effectively lift pre-trained text-to-video models to the panoramic domain, equipped with minimal modules. PanoWan employs latitude-aware sampling to avoid latitudinal distortion, while its rotated semantic denoising and padded pixel-wise decoding ensure seamless transitions at longitude boundaries. To provide sufficient panoramic videos for learning these lifted representations, we contribute PanoVid, a high-quality panoramic video dataset with captions and diverse scenarios. Consequently, PanoWan achieves state-of-the-art performance in panoramic video generation and demonstrates robustness for zero-shot downstream tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge