Yiyang Gan
UniViTAR: Unified Vision Transformer with Native Resolution
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:Conventional Vision Transformer simplifies visual modeling by standardizing input resolutions, often disregarding the variability of natural visual data and compromising spatial-contextual fidelity. While preliminary explorations have superficially investigated native resolution modeling, existing approaches still lack systematic analysis from a visual representation perspective. To bridge this gap, we introduce UniViTAR, a family of homogeneous vision foundation models tailored for unified visual modality and native resolution scenario in the era of multimodal. Our framework first conducts architectural upgrades to the vanilla paradigm by integrating multiple advanced components. Building upon these improvements, a progressive training paradigm is introduced, which strategically combines two core mechanisms: (1) resolution curriculum learning, transitioning from fixed-resolution pretraining to native resolution tuning, thereby leveraging ViT's inherent adaptability to variable-length sequences, and (2) visual modality adaptation via inter-batch image-video switching, which balances computational efficiency with enhanced temporal reasoning. In parallel, a hybrid training framework further synergizes sigmoid-based contrastive loss with feature distillation from a frozen teacher model, thereby accelerating early-stage convergence. Finally, trained exclusively on public datasets, externsive experiments across multiple model scales from 0.3B to 1B demonstrate its effectiveness.
SoccerNet 2023 Challenges Results
Sep 12, 2023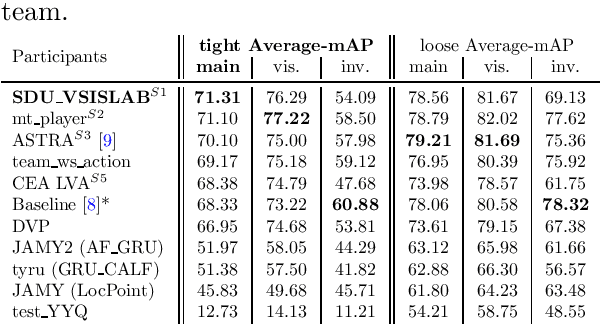
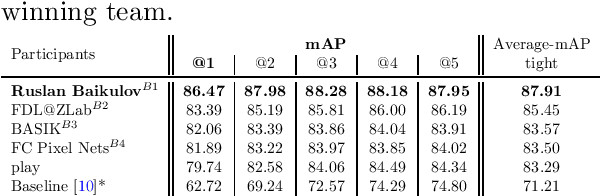
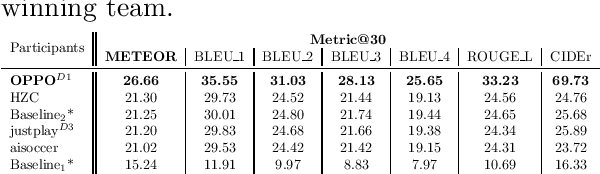
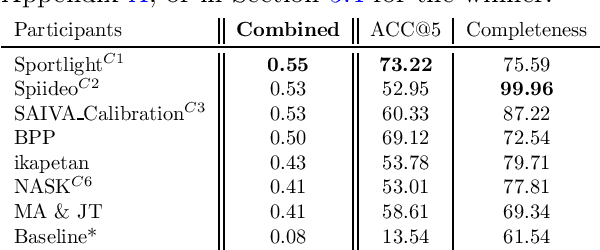
Abstract:The SoccerNet 2023 challenges were the third annual video understanding challenges organized by the SoccerNet team. For this third edition, the challenges were composed of seven vision-based tasks split into three main themes. The first theme, broadcast video understanding, is composed of three high-level tasks related to describing events occurring in the video broadcasts: (1) action spotting, focusing on retrieving all timestamps related to global actions in soccer, (2) ball action spotting, focusing on retrieving all timestamps related to the soccer ball change of state, and (3) dense video captioning, focusing on describing the broadcast with natural language and anchored timestamps. The second theme, field understanding, relates to the single task of (4) camera calibration, focusing on retrieving the intrinsic and extrinsic camera parameters from images. The third and last theme, player understanding, is composed of three low-level tasks related to extracting information about the players: (5) re-identification, focusing on retrieving the same players across multiple views, (6) multiple object tracking, focusing on tracking players and the ball through unedited video streams, and (7) jersey number recognition, focusing on recognizing the jersey number of players from tracklets. Compared to the previous editions of the SoccerNet challenges, tasks (2-3-7) are novel, including new annotations and data, task (4) was enhanced with more data and annotations, and task (6) now focuses on end-to-end approaches. More information on the tasks, challenges, and leaderboards are available on https://www.soccer-net.org. Baselines and development kits can be found on https://github.com/SoccerNet.
Bridging the Gap Between End-to-end and Non-End-to-end Multi-Object Tracking
May 22, 2023



Abstract:Existing end-to-end Multi-Object Tracking (e2e-MOT) methods have not surpassed non-end-to-end tracking-by-detection methods. One potential reason is its label assignment strategy during training that consistently binds the tracked objects with tracking queries and then assigns the few newborns to detection queries. With one-to-one bipartite matching, such an assignment will yield unbalanced training, i.e., scarce positive samples for detection queries, especially for an enclosed scene, as the majority of the newborns come on stage at the beginning of videos. Thus, e2e-MOT will be easier to yield a tracking terminal without renewal or re-initialization, compared to other tracking-by-detection methods. To alleviate this problem, we present Co-MOT, a simple and effective method to facilitate e2e-MOT by a novel coopetition label assignment with a shadow concept. Specifically, we add tracked objects to the matching targets for detection queries when performing the label assignment for training the intermediate decoders. For query initialization, we expand each query by a set of shadow counterparts with limited disturbance to itself. With extensive ablations, Co-MOT achieves superior performance without extra costs, e.g., 69.4% HOTA on DanceTrack and 52.8% TETA on BDD100K. Impressively, Co-MOT only requires 38\% FLOPs of MOTRv2 to attain a similar performance, resulting in the 1.4$\times$ faster inference speed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge