Tianlei Hu
TexSpot: 3D Texture Enhancement with Spatially-uniform Point Latent Representation
Feb 14, 2026Abstract:High-quality 3D texture generation remains a fundamental challenge due to the view-inconsistency inherent in current mainstream multi-view diffusion pipelines. Existing representations either rely on UV maps, which suffer from distortion during unwrapping, or point-based methods, which tightly couple texture fidelity to geometric density that limits high-resolution texture generation. To address these limitations, we introduce TexSpot, a diffusion-based texture enhancement framework. At its core is Texlet, a novel 3D texture representation that merges the geometric expressiveness of point-based 3D textures with the compactness of UV-based representation. Each Texlet latent vector encodes a local texture patch via a 2D encoder and is further aggregated using a 3D encoder to incorporate global shape context. A cascaded 3D-to-2D decoder reconstructs high-quality texture patches, enabling the Texlet space learning. Leveraging this representation, we train a diffusion transformer conditioned on Texlets to refine and enhance textures produced by multi-view diffusion methods. Extensive experiments demonstrate that TexSpot significantly improves visual fidelity, geometric consistency, and robustness over existing state-of-the-art 3D texture generation and enhancement approaches. Project page: https://texlet-arch.github.io/TexSpot-page.
UniPart: Part-Level 3D Generation with Unified 3D Geom-Seg Latents
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:Part-level 3D generation is essential for applications requiring decomposable and structured 3D synthesis. However, existing methods either rely on implicit part segmentation with limited granularity control or depend on strong external segmenters trained on large annotated datasets. In this work, we observe that part awareness emerges naturally during whole-object geometry learning and propose Geom-Seg VecSet, a unified geometry-segmentation latent representation that jointly encodes object geometry and part-level structure. Building on this representation, we introduce UniPart, a two-stage latent diffusion framework for image-guided part-level 3D generation. The first stage performs joint geometry generation and latent part segmentation, while the second stage conditions part-level diffusion on both whole-object and part-specific latents. A dual-space generation scheme further enhances geometric fidelity by predicting part latents in both global and canonical spaces. Extensive experiments demonstrate that UniPart achieves superior segmentation controllability and part-level geometric quality compared with existing approaches.
Unsupervised Cross-Domain Regression for Fine-grained 3D Game Character Reconstruction
Dec 11, 2024Abstract:With the rise of the ``metaverse'' and the rapid development of games, it has become more and more critical to reconstruct characters in the virtual world faithfully. The immersive experience is one of the most central themes of the ``metaverse'', while the reducibility of the avatar is the crucial point. Meanwhile, the game is the carrier of the metaverse, in which players can freely edit the facial appearance of the game character. In this paper, we propose a simple but powerful cross-domain framework that can reconstruct fine-grained 3D game characters from single-view images in an end-to-end manner. Different from the previous methods, which do not resolve the cross-domain gap, we propose an effective regressor that can greatly reduce the discrepancy between the real-world domain and the game domain. To figure out the drawbacks of no ground truth, our unsupervised framework has accomplished the knowledge transfer of the target domain. Additionally, an innovative contrastive loss is proposed to solve the instance-wise disparity, which keeps the person-specific details of the reconstructed character. In contrast, an auxiliary 3D identity-aware extractor is activated to make the results of our model more impeccable. Then a large set of physically meaningful facial parameters is generated robustly and exquisitely. Experiments demonstrate that our method yields state-of-the-art performance in 3D game character reconstruction.
Deep Partial Multi-Label Learning with Graph Disambiguation
May 10, 2023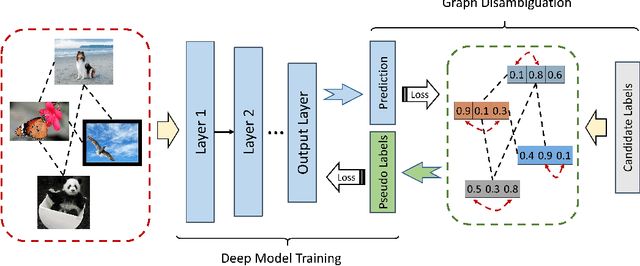
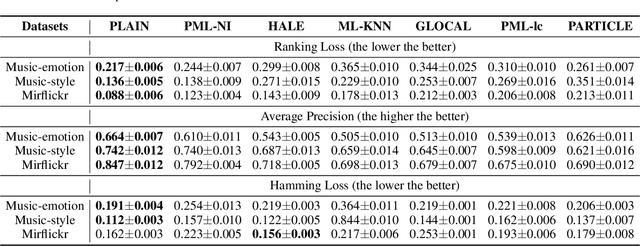
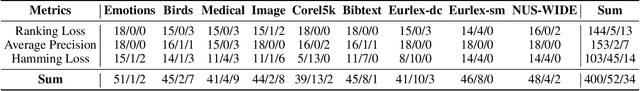
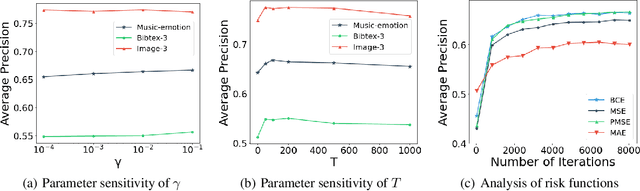
Abstract:In partial multi-label learning (PML), each data example is equipped with a candidate label set, which consists of multiple ground-truth labels and other false-positive labels. Recently, graph-based methods, which demonstrate a good ability to estimate accurate confidence scores from candidate labels, have been prevalent to deal with PML problems. However, we observe that existing graph-based PML methods typically adopt linear multi-label classifiers and thus fail to achieve superior performance. In this work, we attempt to remove several obstacles for extending them to deep models and propose a novel deep Partial multi-Label model with grAph-disambIguatioN (PLAIN). Specifically, we introduce the instance-level and label-level similarities to recover label confidences as well as exploit label dependencies. At each training epoch, labels are propagated on the instance and label graphs to produce relatively accurate pseudo-labels; then, we train the deep model to fit the numerical labels. Moreover, we provide a careful analysis of the risk functions to guarantee the robustness of the proposed model. Extensive experiments on various synthetic datasets and three real-world PML datasets demonstrate that PLAIN achieves significantly superior results to state-of-the-art methods.
Guided Interpolation for Adversarial Training
Feb 15, 2021
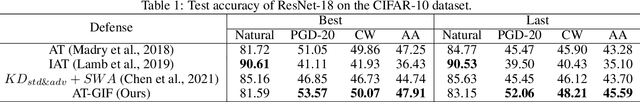
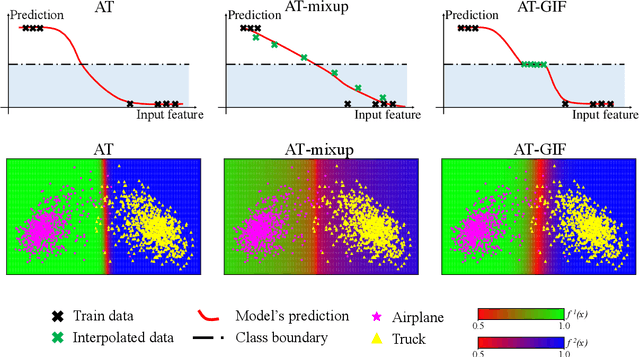
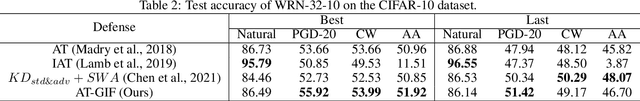
Abstract:To enhance adversarial robustness, adversarial training learns deep neural networks on the adversarial variants generated by their natural data. However, as the training progresses, the training data becomes less and less attackable, undermining the robustness enhancement. A straightforward remedy is to incorporate more training data, but sometimes incurring an unaffordable cost. In this paper, to mitigate this issue, we propose the guided interpolation framework (GIF): in each epoch, the GIF employs the previous epoch's meta information to guide the data's interpolation. Compared with the vanilla mixup, the GIF can provide a higher ratio of attackable data, which is beneficial to the robustness enhancement; it meanwhile mitigates the model's linear behavior between classes, where the linear behavior is favorable to generalization but not to the robustness. As a result, the GIF encourages the model to predict invariantly in the cluster of each class. Experiments demonstrate that the GIF can indeed enhance adversarial robustness on various adversarial training methods and various datasets.
A Simple but Effective Classification Model for Grammatical Error Correction
Jul 02, 2018



Abstract:We treat grammatical error correction (GEC) as a classification problem in this study, where for different types of errors, a target word is identified, and the classifier predicts the correct word form from a set of possible choices. We propose a novel neural network based feature representation and classification model, trained using large text corpora without human annotations. Specifically we use RNNs with attention to represent both the left and right context of a target word. All feature embeddings are learned jointly in an end-to-end fashion. Experimental results show that our novel approach outperforms other classifier methods on the CoNLL-2014 test set (F0.5 45.05%). Our model is simple but effective, and is suitable for industrial production.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge