Bingfeng Han
Unsupervised Cross-Domain Regression for Fine-grained 3D Game Character Reconstruction
Dec 11, 2024Abstract:With the rise of the ``metaverse'' and the rapid development of games, it has become more and more critical to reconstruct characters in the virtual world faithfully. The immersive experience is one of the most central themes of the ``metaverse'', while the reducibility of the avatar is the crucial point. Meanwhile, the game is the carrier of the metaverse, in which players can freely edit the facial appearance of the game character. In this paper, we propose a simple but powerful cross-domain framework that can reconstruct fine-grained 3D game characters from single-view images in an end-to-end manner. Different from the previous methods, which do not resolve the cross-domain gap, we propose an effective regressor that can greatly reduce the discrepancy between the real-world domain and the game domain. To figure out the drawbacks of no ground truth, our unsupervised framework has accomplished the knowledge transfer of the target domain. Additionally, an innovative contrastive loss is proposed to solve the instance-wise disparity, which keeps the person-specific details of the reconstructed character. In contrast, an auxiliary 3D identity-aware extractor is activated to make the results of our model more impeccable. Then a large set of physically meaningful facial parameters is generated robustly and exquisitely. Experiments demonstrate that our method yields state-of-the-art performance in 3D game character reconstruction.
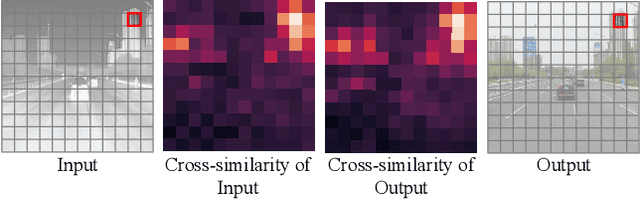
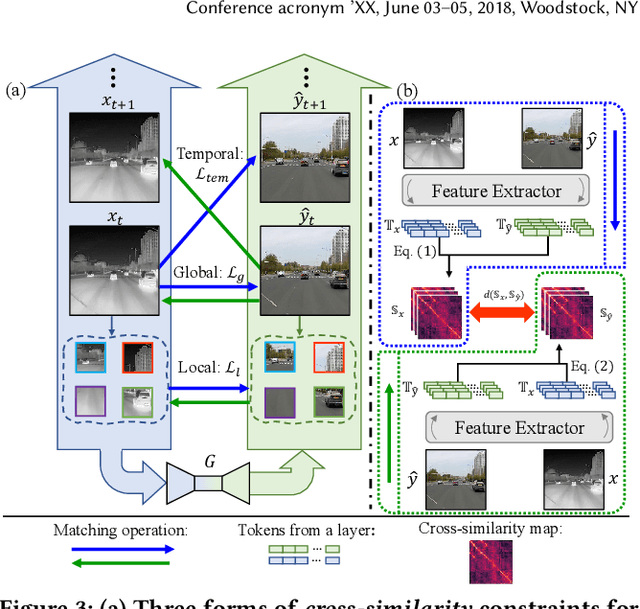
ROMA: Cross-Domain Region Similarity Matching for Unpaired Nighttime Infrared to Daytime Visible Video Translation
Apr 26, 2022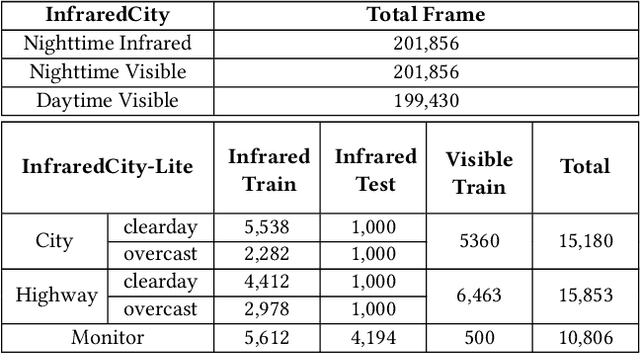
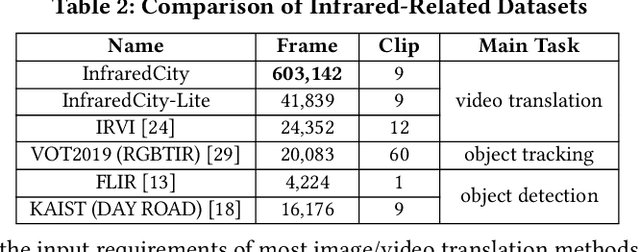
Abstract:Infrared cameras are often utilized to enhance the night vision since the visible light cameras exhibit inferior efficacy without sufficient illumination. However, infrared data possesses inadequate color contrast and representation ability attributed to its intrinsic heat-related imaging principle. This makes it arduous to capture and analyze information for human beings, meanwhile hindering its application. Although, the domain gaps between unpaired nighttime infrared and daytime visible videos are even huger than paired ones that captured at the same time, establishing an effective translation mapping will greatly contribute to various fields. In this case, the structural knowledge within nighttime infrared videos and semantic information contained in the translated daytime visible pairs could be utilized simultaneously. To this end, we propose a tailored framework ROMA that couples with our introduced cRoss-domain regiOn siMilarity mAtching technique for bridging the huge gaps. To be specific, ROMA could efficiently translate the unpaired nighttime infrared videos into fine-grained daytime visible ones, meanwhile maintain the spatiotemporal consistency via matching the cross-domain region similarity. Furthermore, we design a multiscale region-wise discriminator to distinguish the details from synthesized visible results and real references. Extensive experiments and evaluations for specific applications indicate ROMA outperforms the state-of-the-art methods. Moreover, we provide a new and challenging dataset encouraging further research for unpaired nighttime infrared and daytime visible video translation, named InfraredCity. In particular, it consists of 9 long video clips including City, Highway and Monitor scenarios. All clips could be split into 603,142 frames in total, which are 20 times larger than the recently released daytime infrared-to-visible dataset IRVI.
ZiGAN: Fine-grained Chinese Calligraphy Font Generation via a Few-shot Style Transfer Approach
Aug 08, 2021
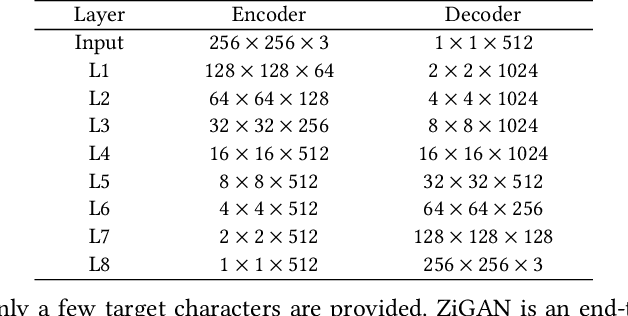
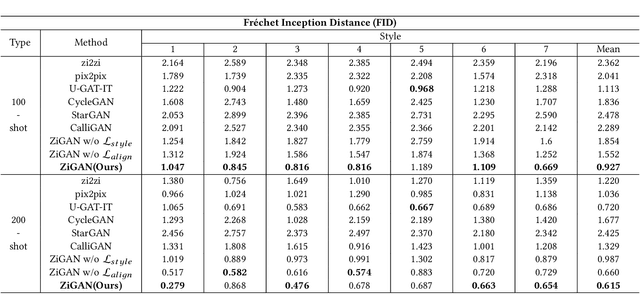

Abstract:Chinese character style transfer is a very challenging problem because of the complexity of the glyph shapes or underlying structures and large numbers of existed characters, when comparing with English letters. Moreover, the handwriting of calligraphy masters has a more irregular stroke and is difficult to obtain in real-world scenarios. Recently, several GAN-based methods have been proposed for font synthesis, but some of them require numerous reference data and the other part of them have cumbersome preprocessing steps to divide the character into different parts to be learned and transferred separately. In this paper, we propose a simple but powerful end-to-end Chinese calligraphy font generation framework ZiGAN, which does not require any manual operation or redundant preprocessing to generate fine-grained target-style characters with few-shot references. To be specific, a few paired samples from different character styles are leveraged to attain a fine-grained correlation between structures underlying different glyphs. To capture valuable style knowledge in target and strengthen the coarse-grained understanding of character content, we utilize multiple unpaired samples to align the feature distributions belonging to different character styles. By doing so, only a few target Chinese calligraphy characters are needed to generated expected style transferred characters. Experiments demonstrate that our method has a state-of-the-art generalization ability in few-shot Chinese character style transfer.
I2V-GAN: Unpaired Infrared-to-Visible Video Translation
Aug 04, 2021
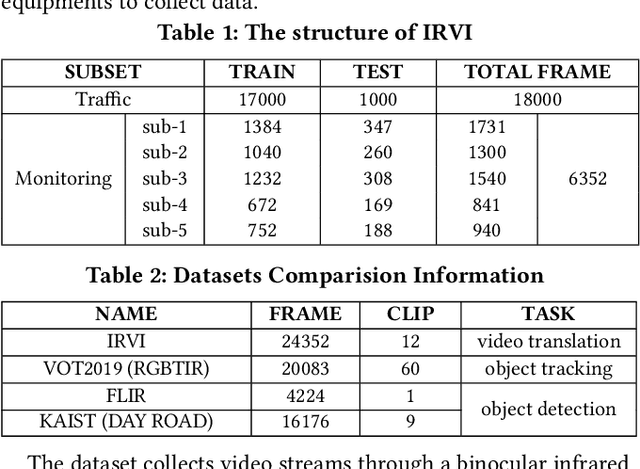
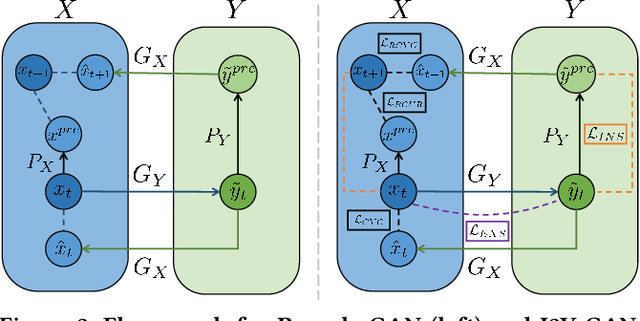
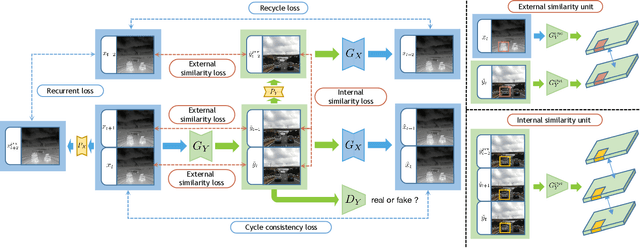
Abstract:Human vision is often adversely affected by complex environmental factors, especially in night vision scenarios. Thus, infrared cameras are often leveraged to help enhance the visual effects via detecting infrared radiation in the surrounding environment, but the infrared videos are undesirable due to the lack of detailed semantic information. In such a case, an effective video-to-video translation method from the infrared domain to the visible light counterpart is strongly needed by overcoming the intrinsic huge gap between infrared and visible fields. To address this challenging problem, we propose an infrared-to-visible (I2V) video translation method I2V-GAN to generate fine-grained and spatial-temporal consistent visible light videos by given unpaired infrared videos. Technically, our model capitalizes on three types of constraints: 1)adversarial constraint to generate synthetic frames that are similar to the real ones, 2)cyclic consistency with the introduced perceptual loss for effective content conversion as well as style preservation, and 3)similarity constraints across and within domains to enhance the content and motion consistency in both spatial and temporal spaces at a fine-grained level. Furthermore, the current public available infrared and visible light datasets are mainly used for object detection or tracking, and some are composed of discontinuous images which are not suitable for video tasks. Thus, we provide a new dataset for I2V video translation, which is named IRVI. Specifically, it has 12 consecutive video clips of vehicle and monitoring scenes, and both infrared and visible light videos could be apart into 24352 frames. Comprehensive experiments validate that I2V-GAN is superior to the compared SOTA methods in the translation of I2V videos with higher fluency and finer semantic details. The code and IRVI dataset are available at https://github.com/BIT-DA/I2V-GAN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge