Shiori Sagawa
OpenFlamingo: An Open-Source Framework for Training Large Autoregressive Vision-Language Models
Aug 07, 2023



Abstract:We introduce OpenFlamingo, a family of autoregressive vision-language models ranging from 3B to 9B parameters. OpenFlamingo is an ongoing effort to produce an open-source replication of DeepMind's Flamingo models. On seven vision-language datasets, OpenFlamingo models average between 80 - 89% of corresponding Flamingo performance. This technical report describes our models, training data, hyperparameters, and evaluation suite. We share our models and code at https://github.com/mlfoundations/open_flamingo.
Out-of-Domain Robustness via Targeted Augmentations
Feb 23, 2023Abstract:Models trained on one set of domains often suffer performance drops on unseen domains, e.g., when wildlife monitoring models are deployed in new camera locations. In this work, we study principles for designing data augmentations for out-of-domain (OOD) generalization. In particular, we focus on real-world scenarios in which some domain-dependent features are robust, i.e., some features that vary across domains are predictive OOD. For example, in the wildlife monitoring application above, image backgrounds vary across camera locations but indicate habitat type, which helps predict the species of photographed animals. Motivated by theoretical analysis on a linear setting, we propose targeted augmentations, which selectively randomize spurious domain-dependent features while preserving robust ones. We prove that targeted augmentations improve OOD performance, allowing models to generalize better with fewer domains. In contrast, existing approaches such as generic augmentations, which fail to randomize domain-dependent features, and domain-invariant augmentations, which randomize all domain-dependent features, both perform poorly OOD. In experiments on three real-world datasets, we show that targeted augmentations set new states-of-the-art for OOD performance by 3.2-15.2%.
Extending the WILDS Benchmark for Unsupervised Adaptation
Dec 09, 2021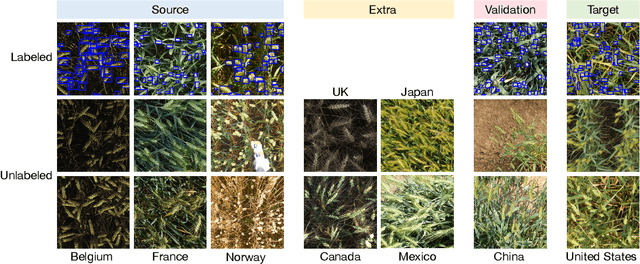

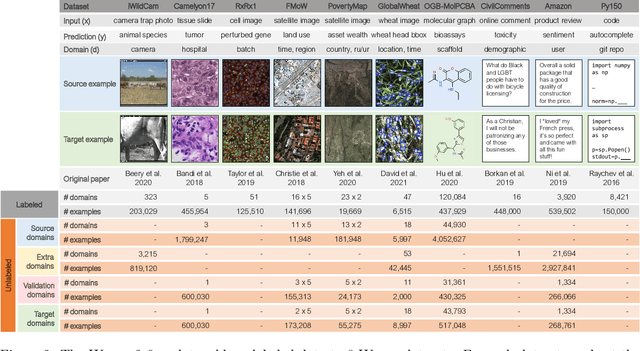
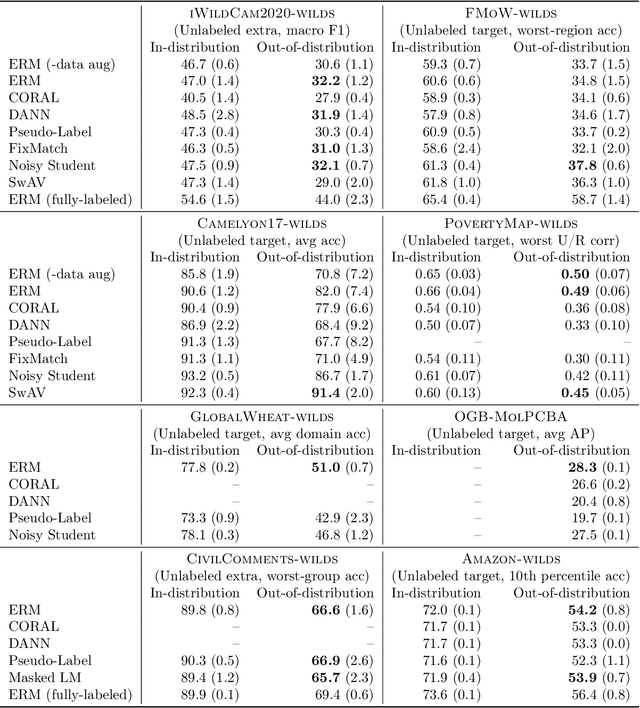
Abstract:Machine learning systems deployed in the wild are often trained on a source distribution but deployed on a different target distribution. Unlabeled data can be a powerful point of leverage for mitigating these distribution shifts, as it is frequently much more available than labeled data. However, existing distribution shift benchmarks for unlabeled data do not reflect the breadth of scenarios that arise in real-world applications. In this work, we present the WILDS 2.0 update, which extends 8 of the 10 datasets in the WILDS benchmark of distribution shifts to include curated unlabeled data that would be realistically obtainable in deployment. To maintain consistency, the labeled training, validation, and test sets, as well as the evaluation metrics, are exactly the same as in the original WILDS benchmark. These datasets span a wide range of applications (from histology to wildlife conservation), tasks (classification, regression, and detection), and modalities (photos, satellite images, microscope slides, text, molecular graphs). We systematically benchmark state-of-the-art methods that leverage unlabeled data, including domain-invariant, self-training, and self-supervised methods, and show that their success on WILDS 2.0 is limited. To facilitate method development and evaluation, we provide an open-source package that automates data loading and contains all of the model architectures and methods used in this paper. Code and leaderboards are available at https://wilds.stanford.edu.
On the Opportunities and Risks of Foundation Models
Aug 18, 2021
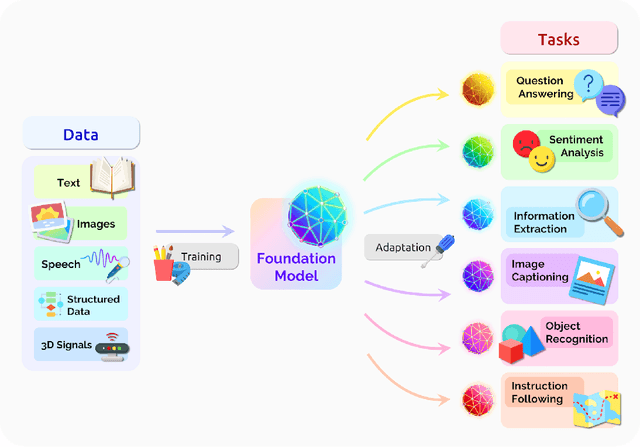
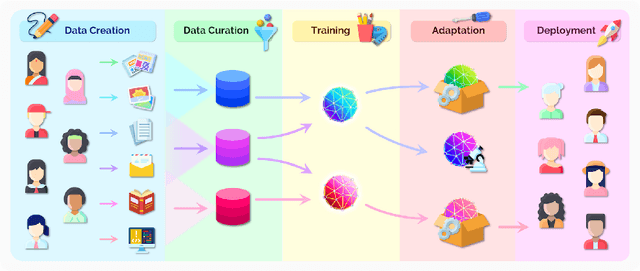
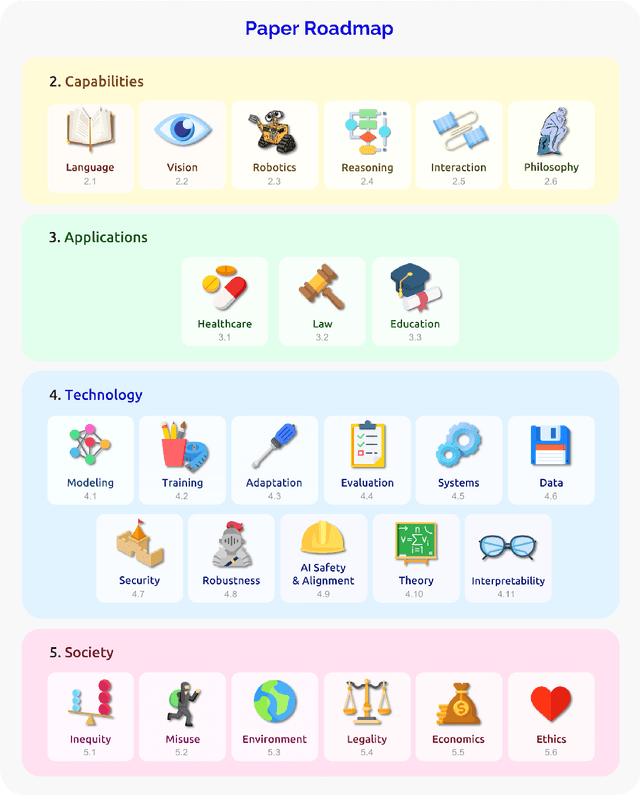
Abstract:AI is undergoing a paradigm shift with the rise of models (e.g., BERT, DALL-E, GPT-3) that are trained on broad data at scale and are adaptable to a wide range of downstream tasks. We call these models foundation models to underscore their critically central yet incomplete character. This report provides a thorough account of the opportunities and risks of foundation models, ranging from their capabilities (e.g., language, vision, robotics, reasoning, human interaction) and technical principles(e.g., model architectures, training procedures, data, systems, security, evaluation, theory) to their applications (e.g., law, healthcare, education) and societal impact (e.g., inequity, misuse, economic and environmental impact, legal and ethical considerations). Though foundation models are based on standard deep learning and transfer learning, their scale results in new emergent capabilities,and their effectiveness across so many tasks incentivizes homogenization. Homogenization provides powerful leverage but demands caution, as the defects of the foundation model are inherited by all the adapted models downstream. Despite the impending widespread deployment of foundation models, we currently lack a clear understanding of how they work, when they fail, and what they are even capable of due to their emergent properties. To tackle these questions, we believe much of the critical research on foundation models will require deep interdisciplinary collaboration commensurate with their fundamentally sociotechnical nature.
Just Train Twice: Improving Group Robustness without Training Group Information
Jul 19, 2021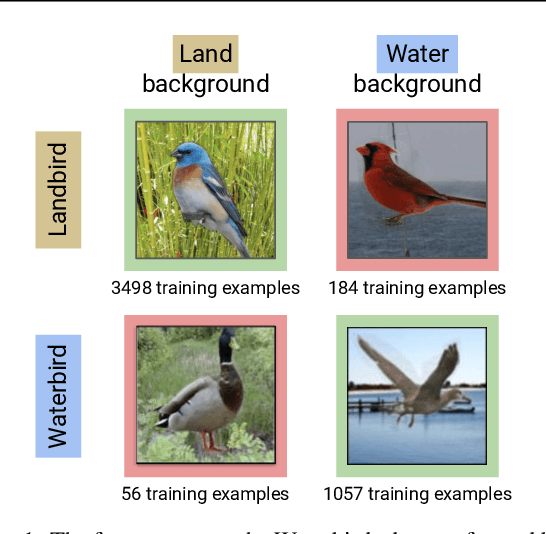
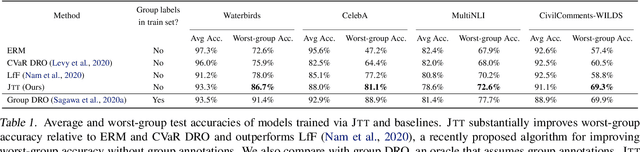

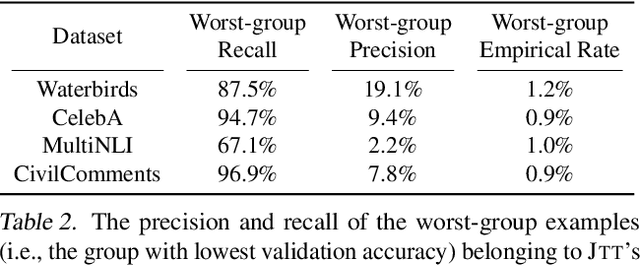
Abstract:Standard training via empirical risk minimization (ERM) can produce models that achieve high accuracy on average but low accuracy on certain groups, especially in the presence of spurious correlations between the input and label. Prior approaches that achieve high worst-group accuracy, like group distributionally robust optimization (group DRO) require expensive group annotations for each training point, whereas approaches that do not use such group annotations typically achieve unsatisfactory worst-group accuracy. In this paper, we propose a simple two-stage approach, JTT, that first trains a standard ERM model for several epochs, and then trains a second model that upweights the training examples that the first model misclassified. Intuitively, this upweights examples from groups on which standard ERM models perform poorly, leading to improved worst-group performance. Averaged over four image classification and natural language processing tasks with spurious correlations, JTT closes 75% of the gap in worst-group accuracy between standard ERM and group DRO, while only requiring group annotations on a small validation set in order to tune hyperparameters.
Accuracy on the Line: On the Strong Correlation Between Out-of-Distribution and In-Distribution Generalization
Jul 09, 2021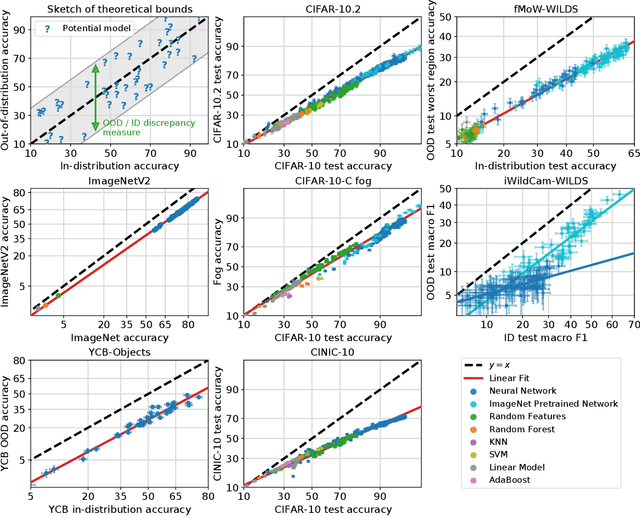
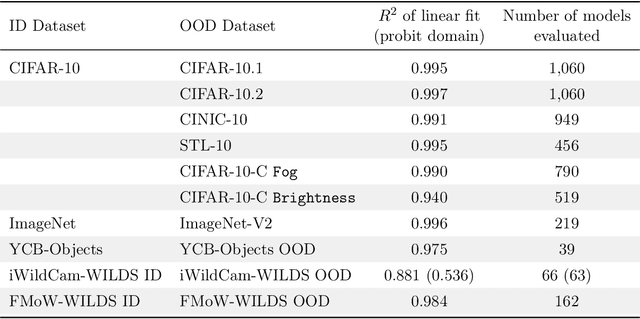
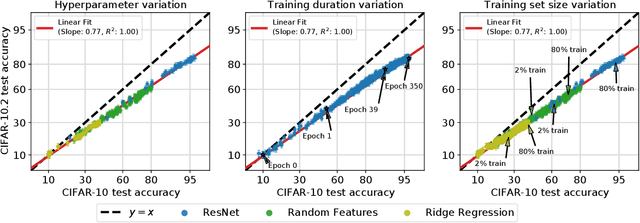
Abstract:For machine learning systems to be reliable, we must understand their performance in unseen, out-of-distribution environments. In this paper, we empirically show that out-of-distribution performance is strongly correlated with in-distribution performance for a wide range of models and distribution shifts. Specifically, we demonstrate strong correlations between in-distribution and out-of-distribution performance on variants of CIFAR-10 & ImageNet, a synthetic pose estimation task derived from YCB objects, satellite imagery classification in FMoW-WILDS, and wildlife classification in iWildCam-WILDS. The strong correlations hold across model architectures, hyperparameters, training set size, and training duration, and are more precise than what is expected from existing domain adaptation theory. To complete the picture, we also investigate cases where the correlation is weaker, for instance some synthetic distribution shifts from CIFAR-10-C and the tissue classification dataset Camelyon17-WILDS. Finally, we provide a candidate theory based on a Gaussian data model that shows how changes in the data covariance arising from distribution shift can affect the observed correlations.
WILDS: A Benchmark of in-the-Wild Distribution Shifts
Dec 14, 2020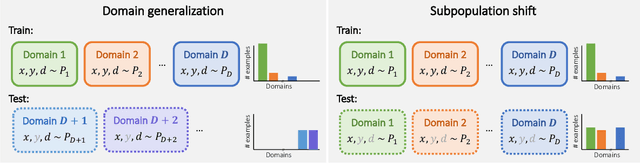
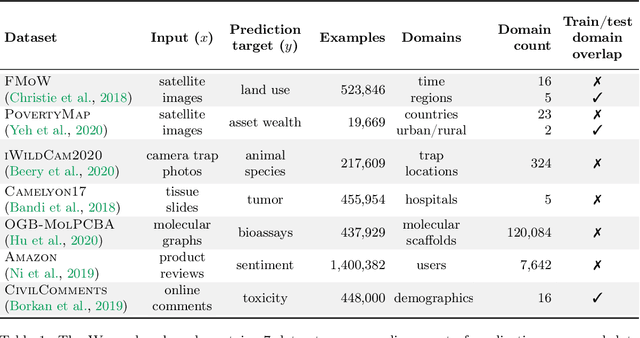
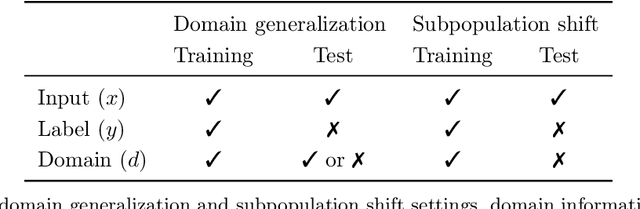
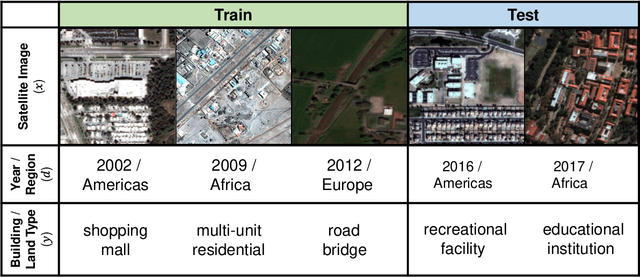
Abstract:Distribution shifts can cause significant degradation in a broad range of machine learning (ML) systems deployed in the wild. However, many widely-used datasets in the ML community today were not designed for evaluating distribution shifts. These datasets typically have training and test sets drawn from the same distribution, and prior work on retrofitting them with distribution shifts has generally relied on artificial shifts that need not represent the kinds of shifts encountered in the wild. In this paper, we present WILDS, a benchmark of in-the-wild distribution shifts spanning diverse data modalities and applications, from tumor identification to wildlife monitoring to poverty mapping. WILDS builds on top of recent data collection efforts by domain experts in these applications and provides a unified collection of datasets with evaluation metrics and train/test splits that are representative of real-world distribution shifts. These datasets reflect distribution shifts arising from training and testing on different hospitals, cameras, countries, time periods, demographics, molecular scaffolds, etc., all of which cause substantial performance drops in our baseline models. Finally, we survey other applications that would be promising additions to the benchmark but for which we did not manage to find appropriate datasets; we discuss their associated challenges and detail datasets and shifts where we did not see an appreciable performance drop. By unifying datasets from a variety of application areas and making them accessible to the ML community, we hope to encourage the development of general-purpose methods that are anchored to real-world distribution shifts and that work well across different applications and problem settings. Data loaders, default models, and leaderboards are available at https://wilds.stanford.edu.
Selective Classification Can Magnify Disparities Across Groups
Oct 27, 2020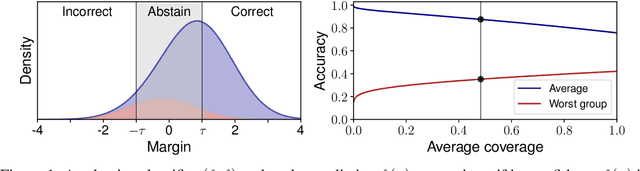
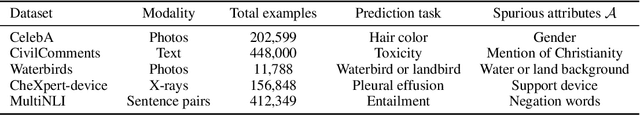
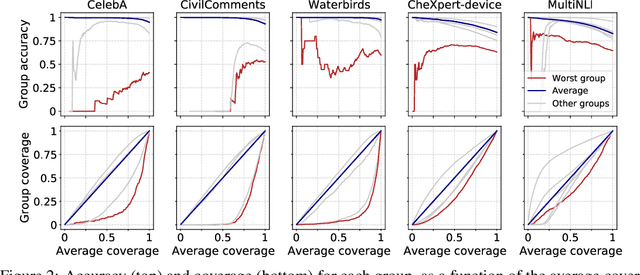
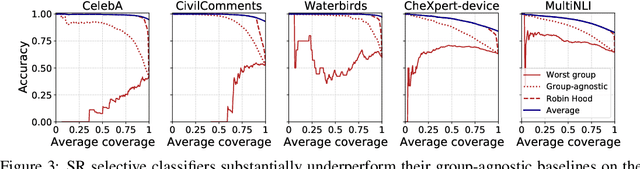
Abstract:Selective classification, in which models are allowed to abstain on uncertain predictions, is a natural approach to improving accuracy in settings where errors are costly but abstentions are manageable. In this paper, we find that while selective classification can improve average accuracies, it can simultaneously magnify existing accuracy disparities between various groups within a population, especially in the presence of spurious correlations. We observe this behavior consistently across five datasets from computer vision and NLP. Surprisingly, increasing the abstention rate can even decrease accuracies on some groups. To better understand when selective classification improves or worsens accuracy on a group, we study its margin distribution, which captures the model's confidences over all predictions. For example, when the margin distribution is symmetric, we prove that whether selective classification monotonically improves or worsens accuracy is fully determined by the accuracy at full coverage (i.e., without any abstentions) and whether the distribution satisfies a property we term left-log-concavity. Our analysis also shows that selective classification tends to magnify accuracy disparities that are present at full coverage. Fortunately, we find that it uniformly improves each group when applied to distributionally-robust models that achieve similar full-coverage accuracies across groups. Altogether, our results imply selective classification should be used with care and underscore the importance of models that perform equally well across groups at full coverage.
An Investigation of Why Overparameterization Exacerbates Spurious Correlations
May 09, 2020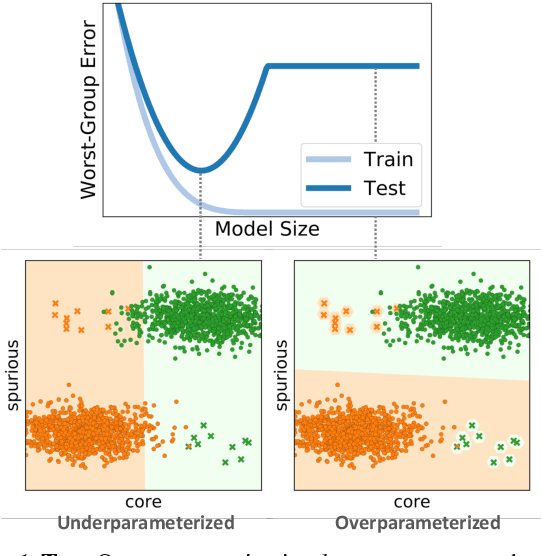
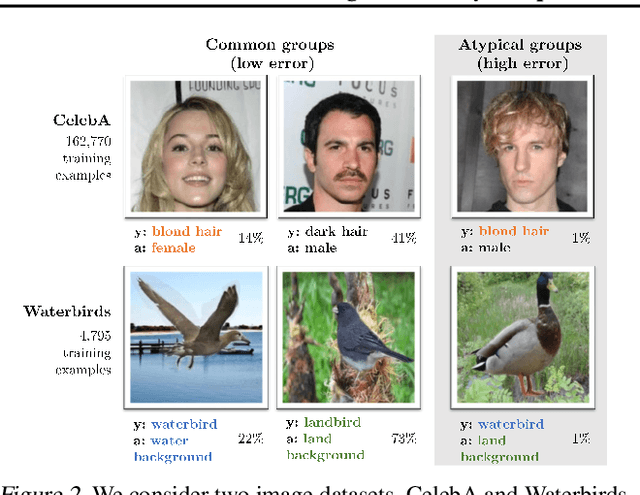
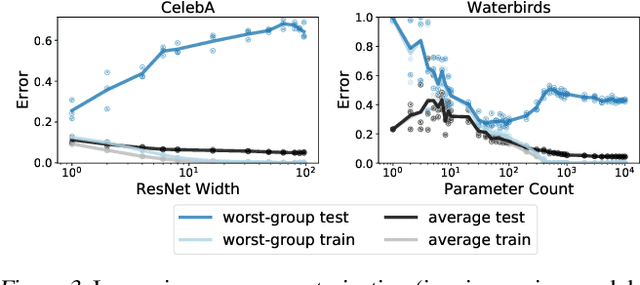
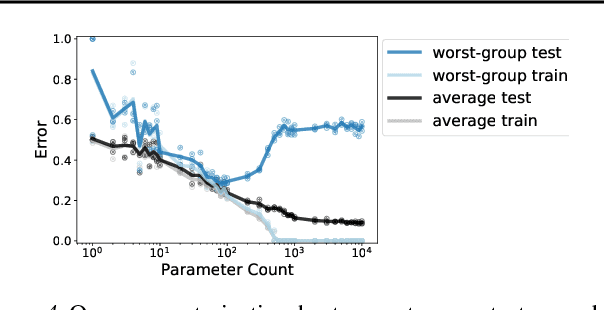
Abstract:We study why overparameterization -- increasing model size well beyond the point of zero training error -- can hurt test error on minority groups despite improving average test error when there are spurious correlations in the data. Through simulations and experiments on two image datasets, we identify two key properties of the training data that drive this behavior: the proportions of majority versus minority groups, and the signal-to-noise ratio of the spurious correlations. We then analyze a linear setting and show theoretically how the inductive bias of models towards "memorizing" fewer examples can cause overparameterization to hurt. Our analysis leads to a counterintuitive approach of subsampling the majority group, which empirically achieves low minority error in the overparameterized regime, even though the standard approach of upweighting the minority fails. Overall, our results suggest a tension between using overparameterized models versus using all the training data for achieving low worst-group error.
Distributionally Robust Neural Networks for Group Shifts: On the Importance of Regularization for Worst-Case Generalization
Nov 20, 2019
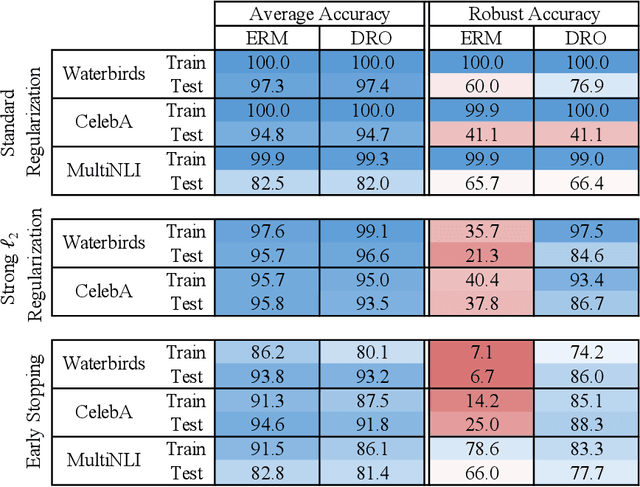
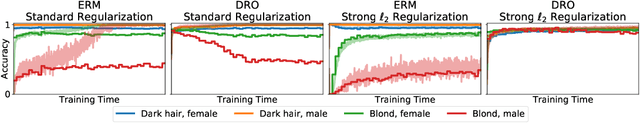
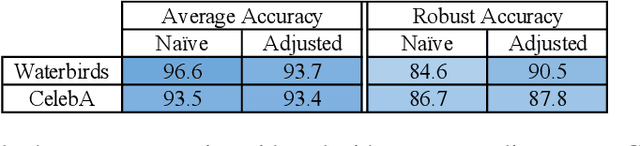
Abstract:Overparameterized neural networks can be highly accurate on average on an i.i.d. test set yet consistently fail on atypical groups of the data (e.g., by learning spurious correlations that hold on average but not in such groups). Distributionally robust optimization (DRO) allows us to learn models that instead minimize the worst-case training loss over a set of pre-defined groups. However, we find that naively applying group DRO to overparameterized neural networks fails: these models can perfectly fit the training data, and any model with vanishing average training loss also already has vanishing worst-case training loss. Instead, their poor worst-case performance arises from poor generalization on some groups. By coupling group DRO models with increased regularization---stronger-than-typical $\ell_2$ regularization or early stopping---we achieve substantially higher worst-group accuracies, with 10-40 percentage point improvements on a natural language inference task and two image tasks, while maintaining high average accuracies. Our results suggest that regularization is critical for worst-group generalization in the overparameterized regime, even if it is not needed for average generalization. Finally, we introduce and give convergence guarantees for a stochastic optimizer for the group DRO setting, underpinning the empirical study above.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge