Pablo Sprechmann
University of Minnesota
Gemini: A Family of Highly Capable Multimodal Models
Dec 19, 2023Abstract:This report introduces a new family of multimodal models, Gemini, that exhibit remarkable capabilities across image, audio, video, and text understanding. The Gemini family consists of Ultra, Pro, and Nano sizes, suitable for applications ranging from complex reasoning tasks to on-device memory-constrained use-cases. Evaluation on a broad range of benchmarks shows that our most-capable Gemini Ultra model advances the state of the art in 30 of 32 of these benchmarks - notably being the first model to achieve human-expert performance on the well-studied exam benchmark MMLU, and improving the state of the art in every one of the 20 multimodal benchmarks we examined. We believe that the new capabilities of Gemini models in cross-modal reasoning and language understanding will enable a wide variety of use cases and we discuss our approach toward deploying them responsibly to users.
TacticAI: an AI assistant for football tactics
Oct 17, 2023Abstract:Identifying key patterns of tactics implemented by rival teams, and developing effective responses, lies at the heart of modern football. However, doing so algorithmically remains an open research challenge. To address this unmet need, we propose TacticAI, an AI football tactics assistant developed and evaluated in close collaboration with domain experts from Liverpool FC. We focus on analysing corner kicks, as they offer coaches the most direct opportunities for interventions and improvements. TacticAI incorporates both a predictive and a generative component, allowing the coaches to effectively sample and explore alternative player setups for each corner kick routine and to select those with the highest predicted likelihood of success. We validate TacticAI on a number of relevant benchmark tasks: predicting receivers and shot attempts and recommending player position adjustments. The utility of TacticAI is validated by a qualitative study conducted with football domain experts at Liverpool FC. We show that TacticAI's model suggestions are not only indistinguishable from real tactics, but also favoured over existing tactics 90% of the time, and that TacticAI offers an effective corner kick retrieval system. TacticAI achieves these results despite the limited availability of gold-standard data, achieving data efficiency through geometric deep learning.
Unlocking the Power of Representations in Long-term Novelty-based Exploration
May 02, 2023



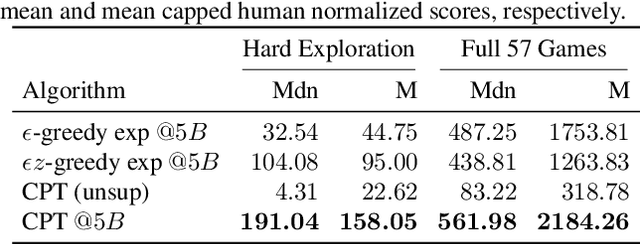
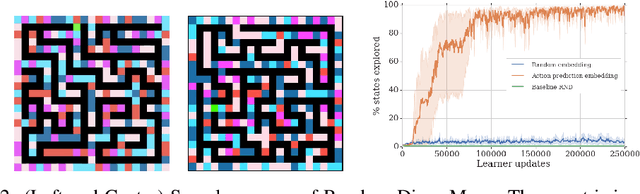
Abstract:We introduce Robust Exploration via Clustering-based Online Density Estimation (RECODE), a non-parametric method for novelty-based exploration that estimates visitation counts for clusters of states based on their similarity in a chosen embedding space. By adapting classical clustering to the nonstationary setting of Deep RL, RECODE can efficiently track state visitation counts over thousands of episodes. We further propose a novel generalization of the inverse dynamics loss, which leverages masked transformer architectures for multi-step prediction; which in conjunction with RECODE achieves a new state-of-the-art in a suite of challenging 3D-exploration tasks in DM-Hard-8. RECODE also sets new state-of-the-art in hard exploration Atari games, and is the first agent to reach the end screen in "Pitfall!".
Coverage as a Principle for Discovering Transferable Behavior in Reinforcement Learning
Feb 24, 2021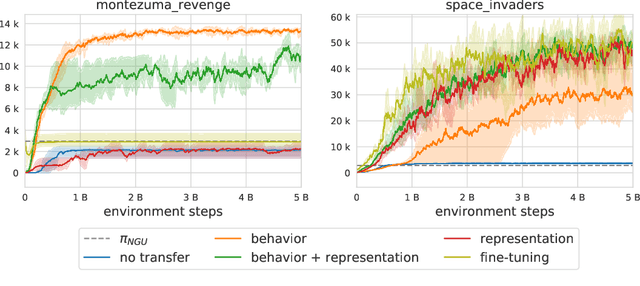
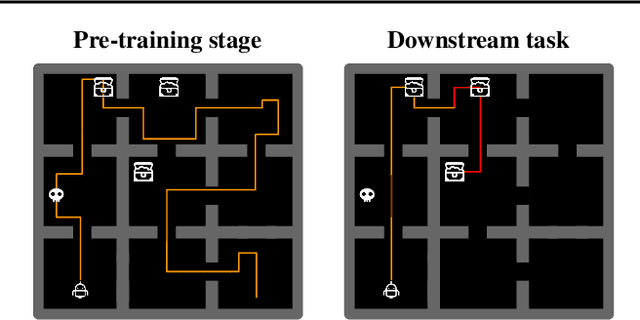
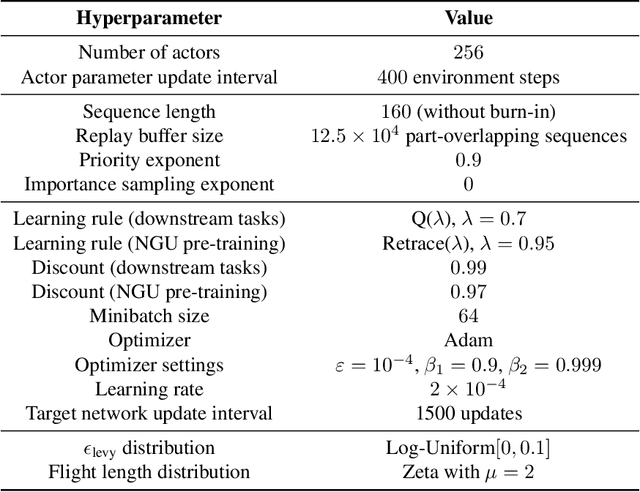
Abstract:Designing agents that acquire knowledge autonomously and use it to solve new tasks efficiently is an important challenge in reinforcement learning, and unsupervised learning provides a useful paradigm for autonomous acquisition of task-agnostic knowledge. In supervised settings, representations discovered through unsupervised pre-training offer important benefits when transferred to downstream tasks. Given the nature of the reinforcement learning problem, we argue that representation alone is not enough for efficient transfer in challenging domains and explore how to transfer knowledge through behavior. The behavior of pre-trained policies may be used for solving the task at hand (exploitation), as well as for collecting useful data to solve the problem (exploration). We argue that policies pre-trained to maximize coverage will produce behavior that is useful for both strategies. When using these policies for both exploitation and exploration, our agents discover better solutions. The largest gains are generally observed in domains requiring structured exploration, including settings where the behavior of the pre-trained policies is misaligned with the downstream task.
Game Plan: What AI can do for Football, and What Football can do for AI
Nov 18, 2020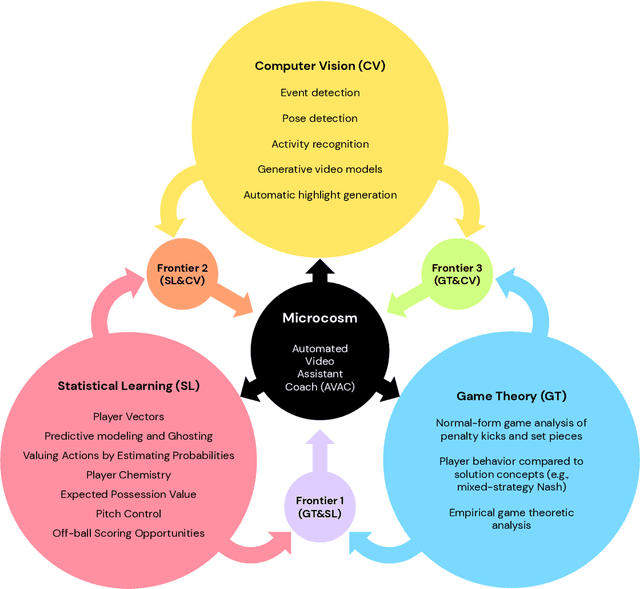

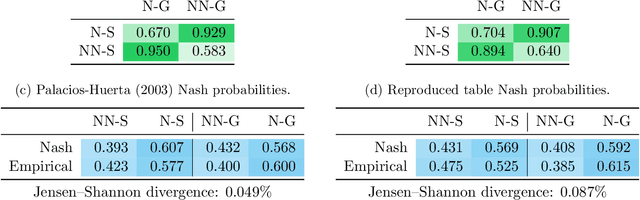
Abstract:The rapid progress in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning has opened unprecedented analytics possibilities in various team and individual sports, including baseball, basketball, and tennis. More recently, AI techniques have been applied to football, due to a huge increase in data collection by professional teams, increased computational power, and advances in machine learning, with the goal of better addressing new scientific challenges involved in the analysis of both individual players' and coordinated teams' behaviors. The research challenges associated with predictive and prescriptive football analytics require new developments and progress at the intersection of statistical learning, game theory, and computer vision. In this paper, we provide an overarching perspective highlighting how the combination of these fields, in particular, forms a unique microcosm for AI research, while offering mutual benefits for professional teams, spectators, and broadcasters in the years to come. We illustrate that this duality makes football analytics a game changer of tremendous value, in terms of not only changing the game of football itself, but also in terms of what this domain can mean for the field of AI. We review the state-of-the-art and exemplify the types of analysis enabled by combining the aforementioned fields, including illustrative examples of counterfactual analysis using predictive models, and the combination of game-theoretic analysis of penalty kicks with statistical learning of player attributes. We conclude by highlighting envisioned downstream impacts, including possibilities for extensions to other sports (real and virtual).
Temporal Difference Uncertainties as a Signal for Exploration
Oct 05, 2020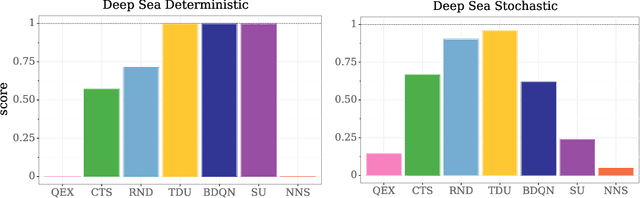
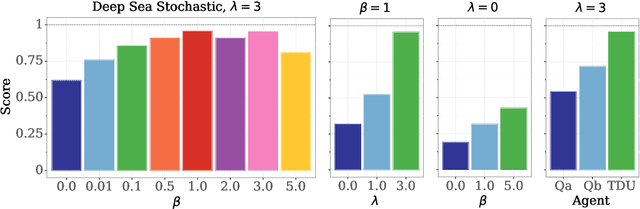
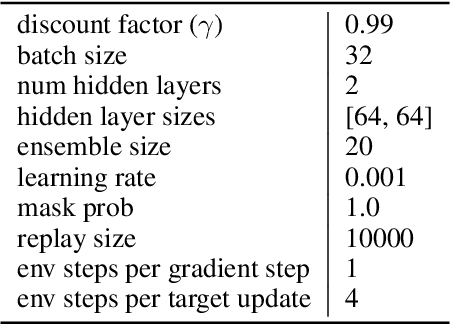
Abstract:An effective approach to exploration in reinforcement learning is to rely on an agent's uncertainty over the optimal policy, which can yield near-optimal exploration strategies in tabular settings. However, in non-tabular settings that involve function approximators, obtaining accurate uncertainty estimates is almost as challenging a problem. In this paper, we highlight that value estimates are easily biased and temporally inconsistent. In light of this, we propose a novel method for estimating uncertainty over the value function that relies on inducing a distribution over temporal difference errors. This exploration signal controls for state-action transitions so as to isolate uncertainty in value that is due to uncertainty over the agent's parameters. Because our measure of uncertainty conditions on state-action transitions, we cannot act on this measure directly. Instead, we incorporate it as an intrinsic reward and treat exploration as a separate learning problem, induced by the agent's temporal difference uncertainties. We introduce a distinct exploration policy that learns to collect data with high estimated uncertainty, which gives rise to a curriculum that smoothly changes throughout learning and vanishes in the limit of perfect value estimates. We evaluate our method on hard exploration tasks, including Deep Sea and Atari 2600 environments and find that our proposed form of exploration facilitates both diverse and deep exploration.
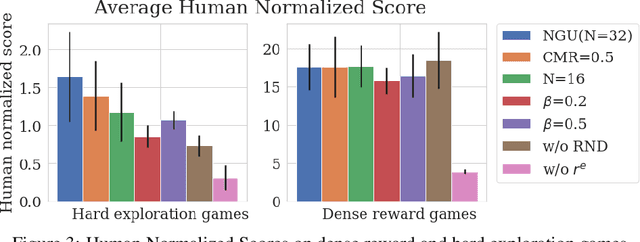
Agent57: Outperforming the Atari Human Benchmark
Mar 30, 2020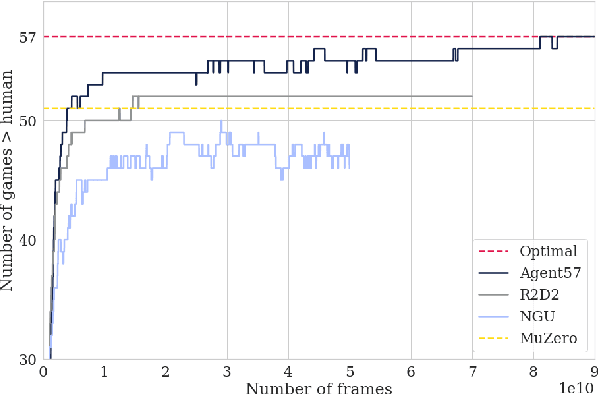
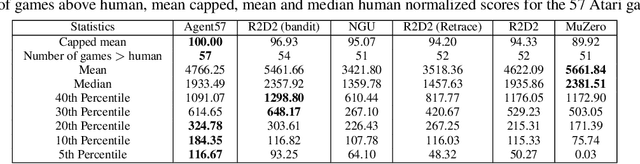
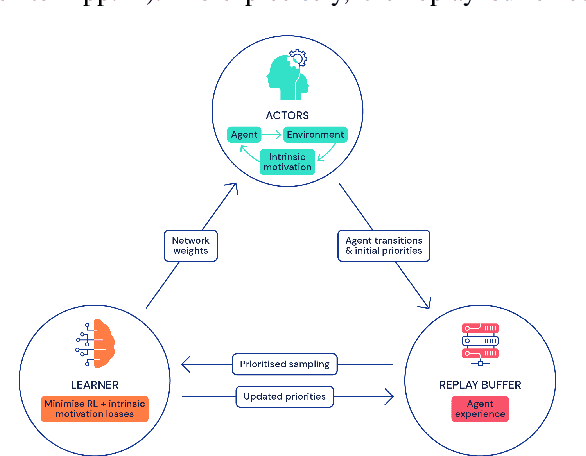
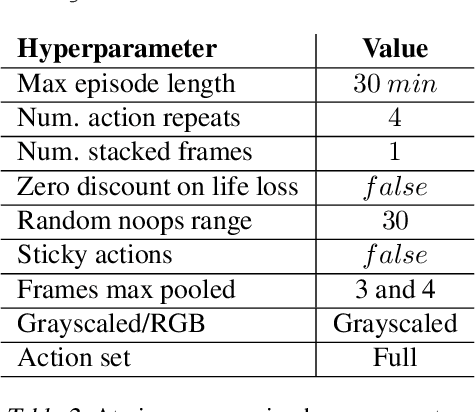
Abstract:Atari games have been a long-standing benchmark in the reinforcement learning (RL) community for the past decade. This benchmark was proposed to test general competency of RL algorithms. Previous work has achieved good average performance by doing outstandingly well on many games of the set, but very poorly in several of the most challenging games. We propose Agent57, the first deep RL agent that outperforms the standard human benchmark on all 57 Atari games. To achieve this result, we train a neural network which parameterizes a family of policies ranging from very exploratory to purely exploitative. We propose an adaptive mechanism to choose which policy to prioritize throughout the training process. Additionally, we utilize a novel parameterization of the architecture that allows for more consistent and stable learning.
Never Give Up: Learning Directed Exploration Strategies
Feb 14, 2020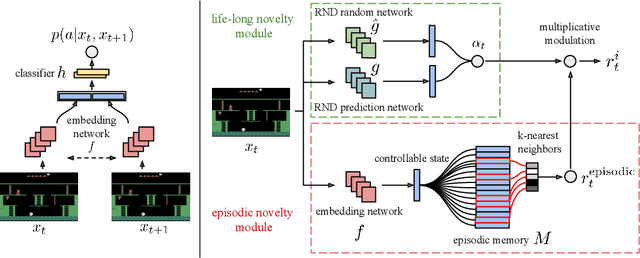
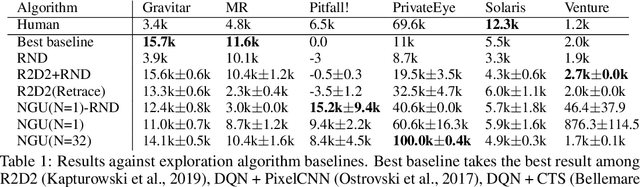
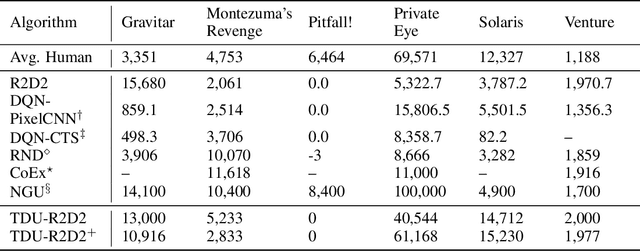
Abstract:We propose a reinforcement learning agent to solve hard exploration games by learning a range of directed exploratory policies. We construct an episodic memory-based intrinsic reward using k-nearest neighbors over the agent's recent experience to train the directed exploratory policies, thereby encouraging the agent to repeatedly revisit all states in its environment. A self-supervised inverse dynamics model is used to train the embeddings of the nearest neighbour lookup, biasing the novelty signal towards what the agent can control. We employ the framework of Universal Value Function Approximators (UVFA) to simultaneously learn many directed exploration policies with the same neural network, with different trade-offs between exploration and exploitation. By using the same neural network for different degrees of exploration/exploitation, transfer is demonstrated from predominantly exploratory policies yielding effective exploitative policies. The proposed method can be incorporated to run with modern distributed RL agents that collect large amounts of experience from many actors running in parallel on separate environment instances. Our method doubles the performance of the base agent in all hard exploration in the Atari-57 suite while maintaining a very high score across the remaining games, obtaining a median human normalised score of 1344.0%. Notably, the proposed method is the first algorithm to achieve non-zero rewards (with a mean score of 8,400) in the game of Pitfall! without using demonstrations or hand-crafted features.
Meta-learning of Sequential Strategies
May 08, 2019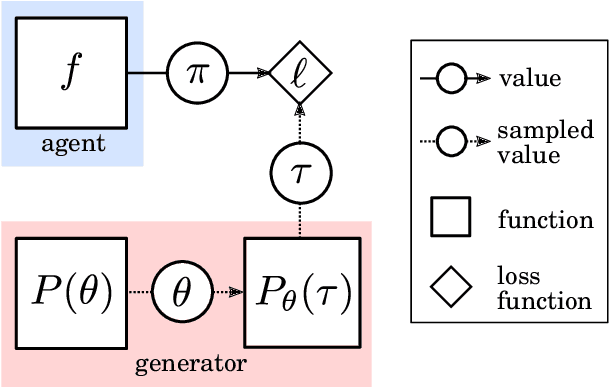
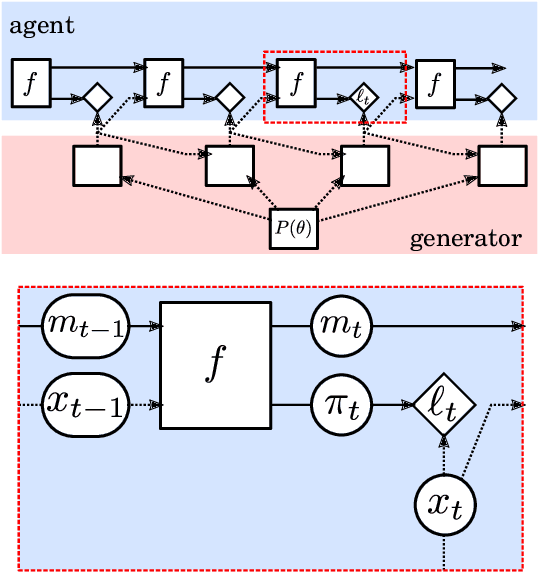
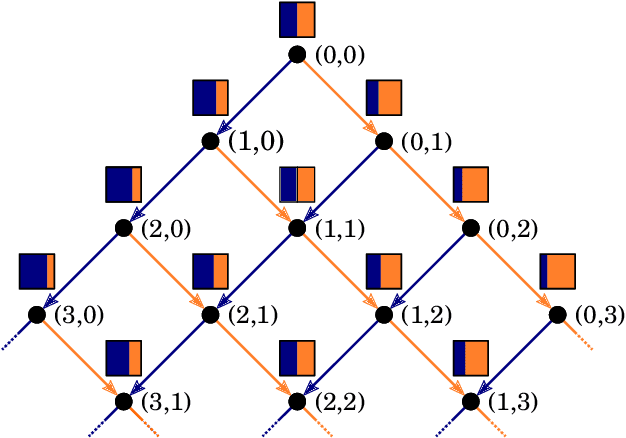
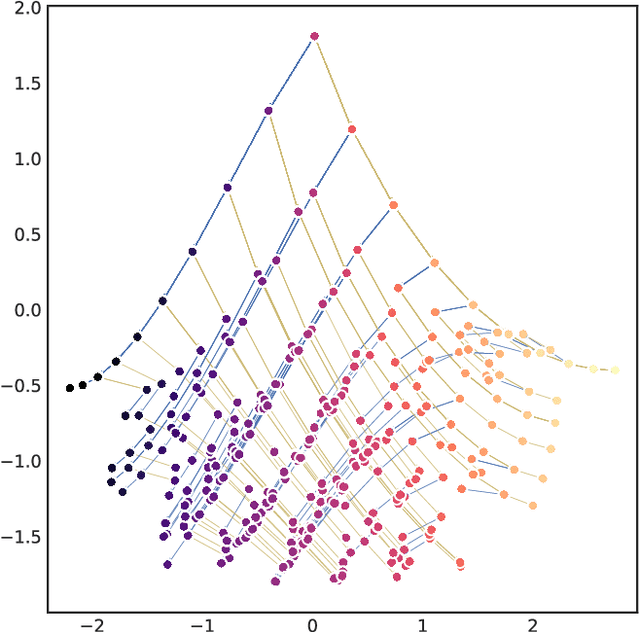
Abstract:In this report we review memory-based meta-learning as a tool for building sample-efficient strategies that learn from past experience to adapt to any task within a target class. Our goal is to equip the reader with the conceptual foundations of this tool for building new, scalable agents that operate on broad domains. To do so, we present basic algorithmic templates for building near-optimal predictors and reinforcement learners which behave as if they had a probabilistic model that allowed them to efficiently exploit task structure. Furthermore, we recast memory-based meta-learning within a Bayesian framework, showing that the meta-learned strategies are near-optimal because they amortize Bayes-filtered data, where the adaptation is implemented in the memory dynamics as a state-machine of sufficient statistics. Essentially, memory-based meta-learning translates the hard problem of probabilistic sequential inference into a regression problem.
Fast deep reinforcement learning using online adjustments from the past
Oct 18, 2018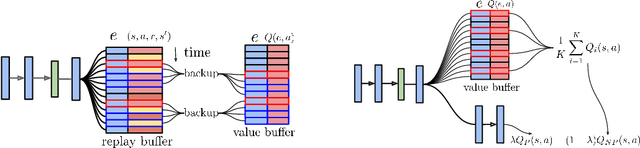
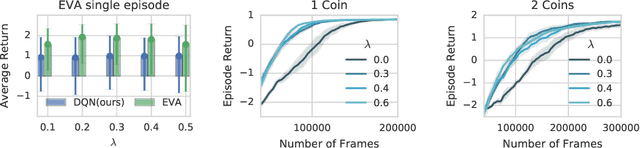
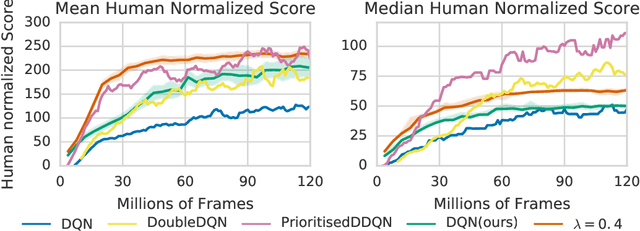
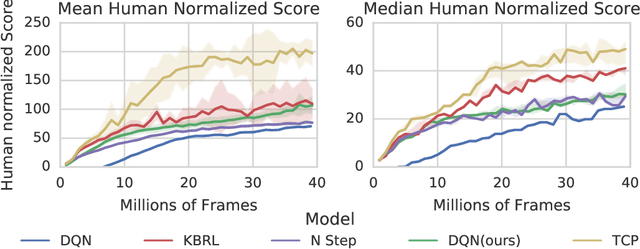
Abstract:We propose Ephemeral Value Adjusments (EVA): a means of allowing deep reinforcement learning agents to rapidly adapt to experience in their replay buffer. EVA shifts the value predicted by a neural network with an estimate of the value function found by planning over experience tuples from the replay buffer near the current state. EVA combines a number of recent ideas around combining episodic memory-like structures into reinforcement learning agents: slot-based storage, content-based retrieval, and memory-based planning. We show that EVAis performant on a demonstration task and Atari games.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge