Daniele Calandriello
Accelerating Nash Learning from Human Feedback via Mirror Prox
May 26, 2025Abstract:Traditional Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) often relies on reward models, frequently assuming preference structures like the Bradley-Terry model, which may not accurately capture the complexities of real human preferences (e.g., intransitivity). Nash Learning from Human Feedback (NLHF) offers a more direct alternative by framing the problem as finding a Nash equilibrium of a game defined by these preferences. In this work, we introduce Nash Mirror Prox ($\mathtt{Nash-MP}$), an online NLHF algorithm that leverages the Mirror Prox optimization scheme to achieve fast and stable convergence to the Nash equilibrium. Our theoretical analysis establishes that Nash-MP exhibits last-iterate linear convergence towards the $\beta$-regularized Nash equilibrium. Specifically, we prove that the KL-divergence to the optimal policy decreases at a rate of order $(1+2\beta)^{-N/2}$, where $N$ is a number of preference queries. We further demonstrate last-iterate linear convergence for the exploitability gap and uniformly for the span semi-norm of log-probabilities, with all these rates being independent of the size of the action space. Furthermore, we propose and analyze an approximate version of Nash-MP where proximal steps are estimated using stochastic policy gradients, making the algorithm closer to applications. Finally, we detail a practical implementation strategy for fine-tuning large language models and present experiments that demonstrate its competitive performance and compatibility with existing methods.
On Teacher Hacking in Language Model Distillation
Feb 04, 2025



Abstract:Post-training of language models (LMs) increasingly relies on the following two stages: (i) knowledge distillation, where the LM is trained to imitate a larger teacher LM, and (ii) reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF), where the LM is aligned by optimizing a reward model. In the second RLHF stage, a well-known challenge is reward hacking, where the LM over-optimizes the reward model. Such phenomenon is in line with Goodhart's law and can lead to degraded performance on the true objective. In this paper, we investigate whether a similar phenomenon, that we call teacher hacking, can occur during knowledge distillation. This could arise because the teacher LM is itself an imperfect approximation of the true distribution. To study this, we propose a controlled experimental setup involving: (i) an oracle LM representing the ground-truth distribution, (ii) a teacher LM distilled from the oracle, and (iii) a student LM distilled from the teacher. Our experiments reveal the following insights. When using a fixed offline dataset for distillation, teacher hacking occurs; moreover, we can detect it by observing when the optimization process deviates from polynomial convergence laws. In contrast, employing online data generation techniques effectively mitigates teacher hacking. More precisely, we identify data diversity as the key factor in preventing hacking. Overall, our findings provide a deeper understanding of the benefits and limitations of distillation for building robust and efficient LMs.
Building Math Agents with Multi-Turn Iterative Preference Learning
Sep 04, 2024



Abstract:Recent studies have shown that large language models' (LLMs) mathematical problem-solving capabilities can be enhanced by integrating external tools, such as code interpreters, and employing multi-turn Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning. While current methods focus on synthetic data generation and Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT), this paper studies the complementary direct preference learning approach to further improve model performance. However, existing direct preference learning algorithms are originally designed for the single-turn chat task, and do not fully address the complexities of multi-turn reasoning and external tool integration required for tool-integrated mathematical reasoning tasks. To fill in this gap, we introduce a multi-turn direct preference learning framework, tailored for this context, that leverages feedback from code interpreters and optimizes trajectory-level preferences. This framework includes multi-turn DPO and multi-turn KTO as specific implementations. The effectiveness of our framework is validated through training of various language models using an augmented prompt set from the GSM8K and MATH datasets. Our results demonstrate substantial improvements: a supervised fine-tuned Gemma-1.1-it-7B model's performance increased from 77.5% to 83.9% on GSM8K and from 46.1% to 51.2% on MATH. Similarly, a Gemma-2-it-9B model improved from 84.1% to 86.3% on GSM8K and from 51.0% to 54.5% on MATH.
Offline Regularised Reinforcement Learning for Large Language Models Alignment
May 29, 2024Abstract:The dominant framework for alignment of large language models (LLM), whether through reinforcement learning from human feedback or direct preference optimisation, is to learn from preference data. This involves building datasets where each element is a quadruplet composed of a prompt, two independent responses (completions of the prompt) and a human preference between the two independent responses, yielding a preferred and a dis-preferred response. Such data is typically scarce and expensive to collect. On the other hand, \emph{single-trajectory} datasets where each element is a triplet composed of a prompt, a response and a human feedback is naturally more abundant. The canonical element of such datasets is for instance an LLM's response to a user's prompt followed by a user's feedback such as a thumbs-up/down. Consequently, in this work, we propose DRO, or \emph{Direct Reward Optimisation}, as a framework and associated algorithms that do not require pairwise preferences. DRO uses a simple mean-squared objective that can be implemented in various ways. We validate our findings empirically, using T5 encoder-decoder language models, and show DRO's performance over selected baselines such as Kahneman-Tversky Optimization (KTO). Thus, we confirm that DRO is a simple and empirically compelling method for single-trajectory policy optimisation.
Multi-turn Reinforcement Learning from Preference Human Feedback
May 23, 2024



Abstract:Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) has become the standard approach for aligning Large Language Models (LLMs) with human preferences, allowing LLMs to demonstrate remarkable abilities in various tasks. Existing methods work by emulating the preferences at the single decision (turn) level, limiting their capabilities in settings that require planning or multi-turn interactions to achieve a long-term goal. In this paper, we address this issue by developing novel methods for Reinforcement Learning (RL) from preference feedback between two full multi-turn conversations. In the tabular setting, we present a novel mirror-descent-based policy optimization algorithm for the general multi-turn preference-based RL problem, and prove its convergence to Nash equilibrium. To evaluate performance, we create a new environment, Education Dialogue, where a teacher agent guides a student in learning a random topic, and show that a deep RL variant of our algorithm outperforms RLHF baselines. Finally, we show that in an environment with explicit rewards, our algorithm recovers the same performance as a reward-based RL baseline, despite relying solely on a weaker preference signal.
Understanding the performance gap between online and offline alignment algorithms
May 14, 2024



Abstract:Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) is the canonical framework for large language model alignment. However, rising popularity in offline alignment algorithms challenge the need for on-policy sampling in RLHF. Within the context of reward over-optimization, we start with an opening set of experiments that demonstrate the clear advantage of online methods over offline methods. This prompts us to investigate the causes to the performance discrepancy through a series of carefully designed experimental ablations. We show empirically that hypotheses such as offline data coverage and data quality by itself cannot convincingly explain the performance difference. We also find that while offline algorithms train policy to become good at pairwise classification, it is worse at generations; in the meantime the policies trained by online algorithms are good at generations while worse at pairwise classification. This hints at a unique interplay between discriminative and generative capabilities, which is greatly impacted by the sampling process. Lastly, we observe that the performance discrepancy persists for both contrastive and non-contrastive loss functions, and appears not to be addressed by simply scaling up policy networks. Taken together, our study sheds light on the pivotal role of on-policy sampling in AI alignment, and hints at certain fundamental challenges of offline alignment algorithms.
Human Alignment of Large Language Models through Online Preference Optimisation
Mar 13, 2024



Abstract:Ensuring alignment of language models' outputs with human preferences is critical to guarantee a useful, safe, and pleasant user experience. Thus, human alignment has been extensively studied recently and several methods such as Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF), Direct Policy Optimisation (DPO) and Sequence Likelihood Calibration (SLiC) have emerged. In this paper, our contribution is two-fold. First, we show the equivalence between two recent alignment methods, namely Identity Policy Optimisation (IPO) and Nash Mirror Descent (Nash-MD). Second, we introduce a generalisation of IPO, named IPO-MD, that leverages the regularised sampling approach proposed by Nash-MD. This equivalence may seem surprising at first sight, since IPO is an offline method whereas Nash-MD is an online method using a preference model. However, this equivalence can be proven when we consider the online version of IPO, that is when both generations are sampled by the online policy and annotated by a trained preference model. Optimising the IPO loss with such a stream of data becomes then equivalent to finding the Nash equilibrium of the preference model through self-play. Building on this equivalence, we introduce the IPO-MD algorithm that generates data with a mixture policy (between the online and reference policy) similarly as the general Nash-MD algorithm. We compare online-IPO and IPO-MD to different online versions of existing losses on preference data such as DPO and SLiC on a summarisation task.
Generalized Preference Optimization: A Unified Approach to Offline Alignment
Feb 08, 2024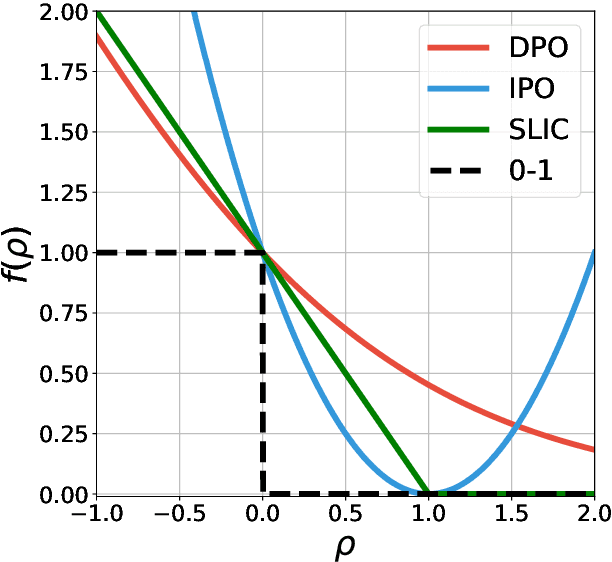
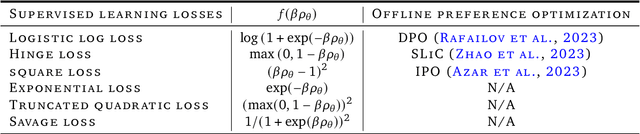
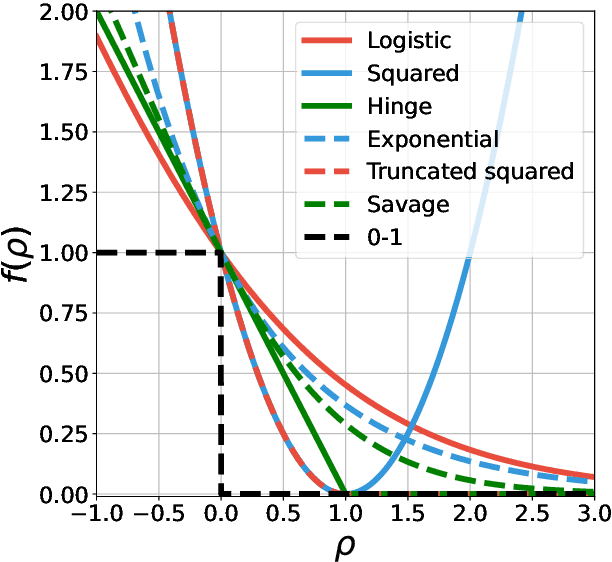
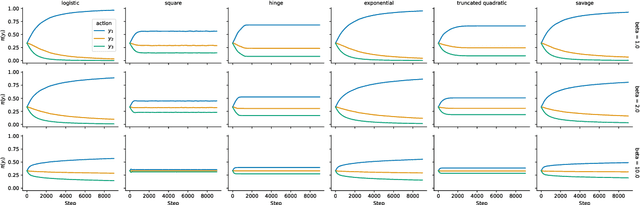
Abstract:Offline preference optimization allows fine-tuning large models directly from offline data, and has proved effective in recent alignment practices. We propose generalized preference optimization (GPO), a family of offline losses parameterized by a general class of convex functions. GPO enables a unified view over preference optimization, encompassing existing algorithms such as DPO, IPO and SLiC as special cases, while naturally introducing new variants. The GPO framework also sheds light on how offline algorithms enforce regularization, through the design of the convex function that defines the loss. Our analysis and experiments reveal the connections and subtle differences between the offline regularization and the KL divergence regularization intended by the canonical RLHF formulation. In all, our results present new algorithmic toolkits and empirical insights to alignment practitioners.
Decoding-time Realignment of Language Models
Feb 05, 2024Abstract:Aligning language models with human preferences is crucial for reducing errors and biases in these models. Alignment techniques, such as reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF), are typically cast as optimizing a tradeoff between human preference rewards and a proximity regularization term that encourages staying close to the unaligned model. Selecting an appropriate level of regularization is critical: insufficient regularization can lead to reduced model capabilities due to reward hacking, whereas excessive regularization hinders alignment. Traditional methods for finding the optimal regularization level require retraining multiple models with varying regularization strengths. This process, however, is resource-intensive, especially for large models. To address this challenge, we propose decoding-time realignment (DeRa), a simple method to explore and evaluate different regularization strengths in aligned models without retraining. DeRa enables control over the degree of alignment, allowing users to smoothly transition between unaligned and aligned models. It also enhances the efficiency of hyperparameter tuning by enabling the identification of effective regularization strengths using a validation dataset.
Nash Learning from Human Feedback
Dec 06, 2023



Abstract:Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) has emerged as the main paradigm for aligning large language models (LLMs) with human preferences. Typically, RLHF involves the initial step of learning a reward model from human feedback, often expressed as preferences between pairs of text generations produced by a pre-trained LLM. Subsequently, the LLM's policy is fine-tuned by optimizing it to maximize the reward model through a reinforcement learning algorithm. However, an inherent limitation of current reward models is their inability to fully represent the richness of human preferences and their dependency on the sampling distribution. In this study, we introduce an alternative pipeline for the fine-tuning of LLMs using pairwise human feedback. Our approach entails the initial learning of a preference model, which is conditioned on two inputs given a prompt, followed by the pursuit of a policy that consistently generates responses preferred over those generated by any competing policy, thus defining the Nash equilibrium of this preference model. We term this approach Nash learning from human feedback (NLHF). In the context of a tabular policy representation, we present a novel algorithmic solution, Nash-MD, founded on the principles of mirror descent. This algorithm produces a sequence of policies, with the last iteration converging to the regularized Nash equilibrium. Additionally, we explore parametric representations of policies and introduce gradient descent algorithms for deep-learning architectures. To demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, we present experimental results involving the fine-tuning of a LLM for a text summarization task. We believe NLHF offers a compelling avenue for preference learning and policy optimization with the potential of advancing the field of aligning LLMs with human preferences.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge