Kexin Yang
additional authors not shown
OPUS: Towards Efficient and Principled Data Selection in Large Language Model Pre-training in Every Iteration
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:As high-quality public text approaches exhaustion, a phenomenon known as the Data Wall, pre-training is shifting from more tokens to better tokens. However, existing methods either rely on heuristic static filters that ignore training dynamics, or use dynamic yet optimizer-agnostic criteria based on raw gradients. We propose OPUS (Optimizer-induced Projected Utility Selection), a dynamic data selection framework that defines utility in the optimizer-induced update space. OPUS scores candidates by projecting their effective updates, shaped by modern optimizers, onto a target direction derived from a stable, in-distribution proxy. To ensure scalability, we employ Ghost technique with CountSketch for computational efficiency, and Boltzmann sampling for data diversity, incurring only 4.7\% additional compute overhead. OPUS achieves remarkable results across diverse corpora, quality tiers, optimizers, and model scales. In pre-training of GPT-2 Large/XL on FineWeb and FineWeb-Edu with 30B tokens, OPUS outperforms industrial-level baselines and even full 200B-token training. Moreover, when combined with industrial-level static filters, OPUS further improves pre-training efficiency, even with lower-quality data. Furthermore, in continued pre-training of Qwen3-8B-Base on SciencePedia, OPUS achieves superior performance using only 0.5B tokens compared to full training with 3B tokens, demonstrating significant data efficiency gains in specialized domains.
PLawBench: A Rubric-Based Benchmark for Evaluating LLMs in Real-World Legal Practice
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) are increasingly applied to legal domain-specific tasks, evaluating their ability to perform legal work in real-world settings has become essential. However, existing legal benchmarks rely on simplified and highly standardized tasks, failing to capture the ambiguity, complexity, and reasoning demands of real legal practice. Moreover, prior evaluations often adopt coarse, single-dimensional metrics and do not explicitly assess fine-grained legal reasoning. To address these limitations, we introduce PLawBench, a Practical Law Benchmark designed to evaluate LLMs in realistic legal practice scenarios. Grounded in real-world legal workflows, PLawBench models the core processes of legal practitioners through three task categories: public legal consultation, practical case analysis, and legal document generation. These tasks assess a model's ability to identify legal issues and key facts, perform structured legal reasoning, and generate legally coherent documents. PLawBench comprises 850 questions across 13 practical legal scenarios, with each question accompanied by expert-designed evaluation rubrics, resulting in approximately 12,500 rubric items for fine-grained assessment. Using an LLM-based evaluator aligned with human expert judgments, we evaluate 10 state-of-the-art LLMs. Experimental results show that none achieves strong performance on PLawBench, revealing substantial limitations in the fine-grained legal reasoning capabilities of current LLMs and highlighting important directions for future evaluation and development of legal LLMs. Data is available at: https://github.com/skylenage/PLawbench.
Qwen3 Technical Report
May 14, 2025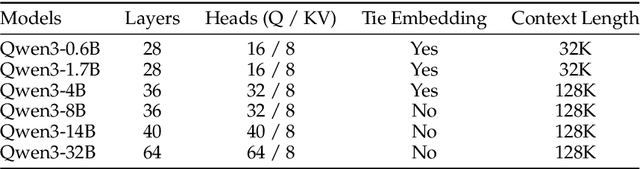
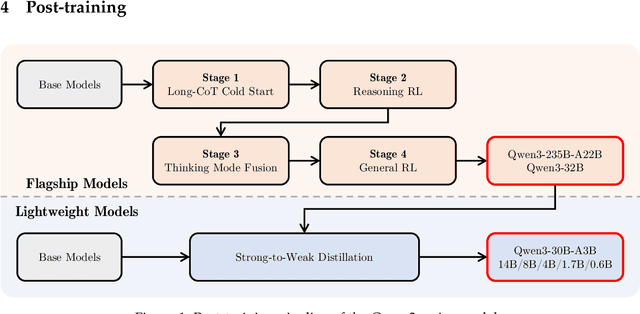
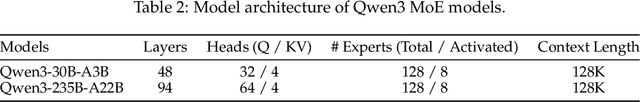
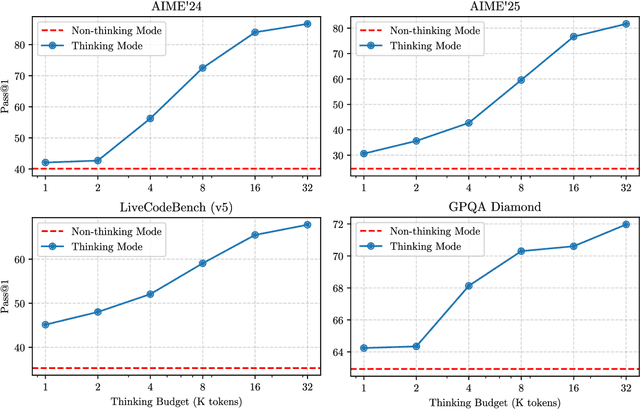
Abstract:In this work, we present Qwen3, the latest version of the Qwen model family. Qwen3 comprises a series of large language models (LLMs) designed to advance performance, efficiency, and multilingual capabilities. The Qwen3 series includes models of both dense and Mixture-of-Expert (MoE) architectures, with parameter scales ranging from 0.6 to 235 billion. A key innovation in Qwen3 is the integration of thinking mode (for complex, multi-step reasoning) and non-thinking mode (for rapid, context-driven responses) into a unified framework. This eliminates the need to switch between different models--such as chat-optimized models (e.g., GPT-4o) and dedicated reasoning models (e.g., QwQ-32B)--and enables dynamic mode switching based on user queries or chat templates. Meanwhile, Qwen3 introduces a thinking budget mechanism, allowing users to allocate computational resources adaptively during inference, thereby balancing latency and performance based on task complexity. Moreover, by leveraging the knowledge from the flagship models, we significantly reduce the computational resources required to build smaller-scale models, while ensuring their highly competitive performance. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that Qwen3 achieves state-of-the-art results across diverse benchmarks, including tasks in code generation, mathematical reasoning, agent tasks, etc., competitive against larger MoE models and proprietary models. Compared to its predecessor Qwen2.5, Qwen3 expands multilingual support from 29 to 119 languages and dialects, enhancing global accessibility through improved cross-lingual understanding and generation capabilities. To facilitate reproducibility and community-driven research and development, all Qwen3 models are publicly accessible under Apache 2.0.
DataMan: Data Manager for Pre-training Large Language Models
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:The performance emergence of large language models (LLMs) driven by data scaling laws makes the selection of pre-training data increasingly important. However, existing methods rely on limited heuristics and human intuition, lacking comprehensive and clear guidelines. To address this, we are inspired by ``reverse thinking'' -- prompting LLMs to self-identify which criteria benefit its performance. As its pre-training capabilities are related to perplexity (PPL), we derive 14 quality criteria from the causes of text perplexity anomalies and introduce 15 common application domains to support domain mixing. In this paper, we train a Data Manager (DataMan) to learn quality ratings and domain recognition from pointwise rating, and use it to annotate a 447B token pre-training corpus with 14 quality ratings and domain type. Our experiments validate our approach, using DataMan to select 30B tokens to train a 1.3B-parameter language model, demonstrating significant improvements in in-context learning (ICL), perplexity, and instruction-following ability over the state-of-the-art baseline. The best-performing model, based on the Overall Score l=5 surpasses a model trained with 50% more data using uniform sampling. We continue pre-training with high-rated, domain-specific data annotated by DataMan to enhance domain-specific ICL performance and thus verify DataMan's domain mixing ability. Our findings emphasize the importance of quality ranking, the complementary nature of quality criteria, and their low correlation with perplexity, analyzing misalignment between PPL and ICL performance. We also thoroughly analyzed our pre-training dataset, examining its composition, the distribution of quality ratings, and the original document sources.
SuperGPQA: Scaling LLM Evaluation across 285 Graduate Disciplines
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable proficiency in mainstream academic disciplines such as mathematics, physics, and computer science. However, human knowledge encompasses over 200 specialized disciplines, far exceeding the scope of existing benchmarks. The capabilities of LLMs in many of these specialized fields-particularly in light industry, agriculture, and service-oriented disciplines-remain inadequately evaluated. To address this gap, we present SuperGPQA, a comprehensive benchmark that evaluates graduate-level knowledge and reasoning capabilities across 285 disciplines. Our benchmark employs a novel Human-LLM collaborative filtering mechanism to eliminate trivial or ambiguous questions through iterative refinement based on both LLM responses and expert feedback. Our experimental results reveal significant room for improvement in the performance of current state-of-the-art LLMs across diverse knowledge domains (e.g., the reasoning-focused model DeepSeek-R1 achieved the highest accuracy of 61.82% on SuperGPQA), highlighting the considerable gap between current model capabilities and artificial general intelligence. Additionally, we present comprehensive insights from our management of a large-scale annotation process, involving over 80 expert annotators and an interactive Human-LLM collaborative system, offering valuable methodological guidance for future research initiatives of comparable scope.
Qwen2.5-1M Technical Report
Jan 26, 2025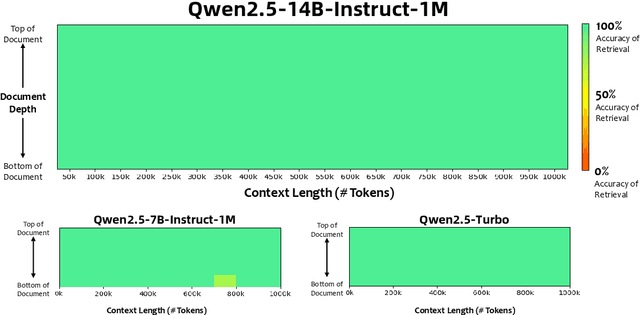
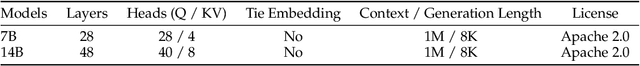
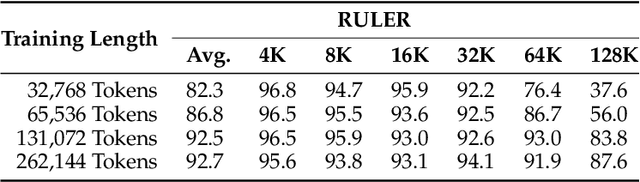
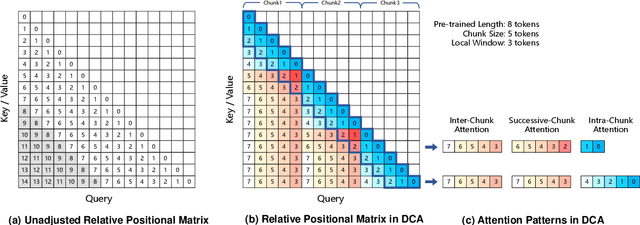
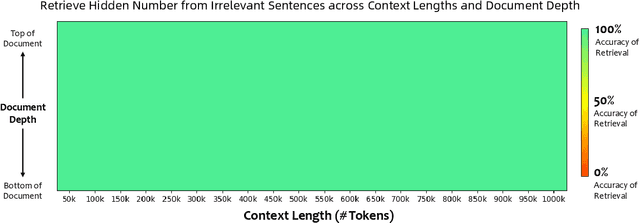
Abstract:We introduce Qwen2.5-1M, a series of models that extend the context length to 1 million tokens. Compared to the previous 128K version, the Qwen2.5-1M series have significantly enhanced long-context capabilities through long-context pre-training and post-training. Key techniques such as long data synthesis, progressive pre-training, and multi-stage supervised fine-tuning are employed to effectively enhance long-context performance while reducing training costs. To promote the use of long-context models among a broader user base, we present and open-source our inference framework. This framework includes a length extrapolation method that can expand the model context lengths by at least four times, or even more, without additional training. To reduce inference costs, we implement a sparse attention method along with chunked prefill optimization for deployment scenarios and a sparsity refinement method to improve precision. Additionally, we detail our optimizations in the inference engine, including kernel optimization, pipeline parallelism, and scheduling optimization, which significantly enhance overall inference performance. By leveraging our inference framework, the Qwen2.5-1M models achieve a remarkable 3x to 7x prefill speedup in scenarios with 1 million tokens of context. This framework provides an efficient and powerful solution for developing applications that require long-context processing using open-source models. The Qwen2.5-1M series currently includes the open-source models Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct-1M and Qwen2.5-14B-Instruct-1M, as well as the API-accessed model Qwen2.5-Turbo. Evaluations show that Qwen2.5-1M models have been greatly improved in long-context tasks without compromising performance in short-context scenarios. Specifically, the Qwen2.5-14B-Instruct-1M model significantly outperforms GPT-4o-mini in long-context tasks and supports contexts eight times longer.
Qwen2.5 Technical Report
Dec 19, 2024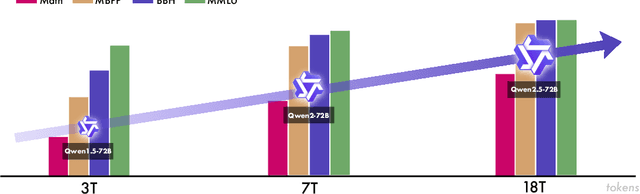

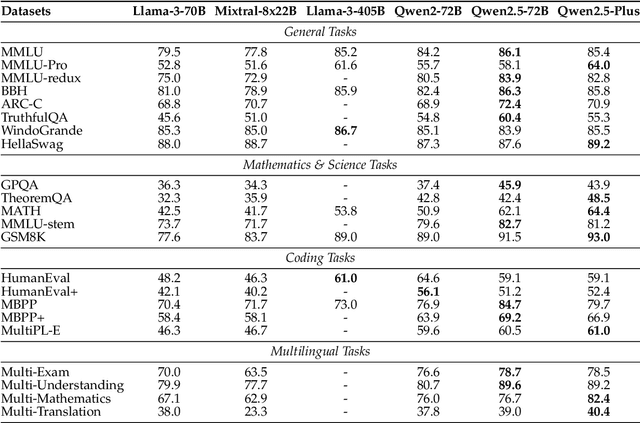
Abstract:In this report, we introduce Qwen2.5, a comprehensive series of large language models (LLMs) designed to meet diverse needs. Compared to previous iterations, Qwen 2.5 has been significantly improved during both the pre-training and post-training stages. In terms of pre-training, we have scaled the high-quality pre-training datasets from the previous 7 trillion tokens to 18 trillion tokens. This provides a strong foundation for common sense, expert knowledge, and reasoning capabilities. In terms of post-training, we implement intricate supervised finetuning with over 1 million samples, as well as multistage reinforcement learning. Post-training techniques enhance human preference, and notably improve long text generation, structural data analysis, and instruction following. To handle diverse and varied use cases effectively, we present Qwen2.5 LLM series in rich sizes. Open-weight offerings include base and instruction-tuned models, with quantized versions available. In addition, for hosted solutions, the proprietary models currently include two mixture-of-experts (MoE) variants: Qwen2.5-Turbo and Qwen2.5-Plus, both available from Alibaba Cloud Model Studio. Qwen2.5 has demonstrated top-tier performance on a wide range of benchmarks evaluating language understanding, reasoning, mathematics, coding, human preference alignment, etc. Specifically, the open-weight flagship Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct outperforms a number of open and proprietary models and demonstrates competitive performance to the state-of-the-art open-weight model, Llama-3-405B-Instruct, which is around 5 times larger. Qwen2.5-Turbo and Qwen2.5-Plus offer superior cost-effectiveness while performing competitively against GPT-4o-mini and GPT-4o respectively. Additionally, as the foundation, Qwen2.5 models have been instrumental in training specialized models such as Qwen2.5-Math, Qwen2.5-Coder, QwQ, and multimodal models.
Robust Simultaneous Multislice MRI Reconstruction Using Deep Generative Priors
Jul 31, 2024



Abstract:Simultaneous multislice (SMS) imaging is a powerful technique for accelerating magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) acquisitions. However, SMS reconstruction remains challenging due to the complex signal interactions between and within the excited slices. This study presents a robust SMS MRI reconstruction method using deep generative priors. Starting from Gaussian noise, we leverage denoising diffusion probabilistic models (DDPM) to gradually recover the individual slices through reverse diffusion iterations while imposing data consistency from the measured k-space under readout concatenation framework. The posterior sampling procedure is designed such that the DDPM training can be performed on single-slice images without special adjustments for SMS tasks. Additionally, our method integrates a low-frequency enhancement (LFE) module to address a practical issue that SMS-accelerated fast spin echo (FSE) and echo-planar imaging (EPI) sequences cannot easily embed autocalibration signals. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms existing methods and generalizes well to unseen datasets. The code is available at https://github.com/Solor-pikachu/ROGER after the review process.
Qwen2 Technical Report
Jul 16, 2024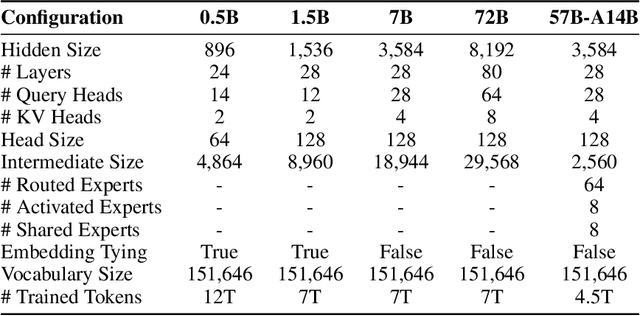
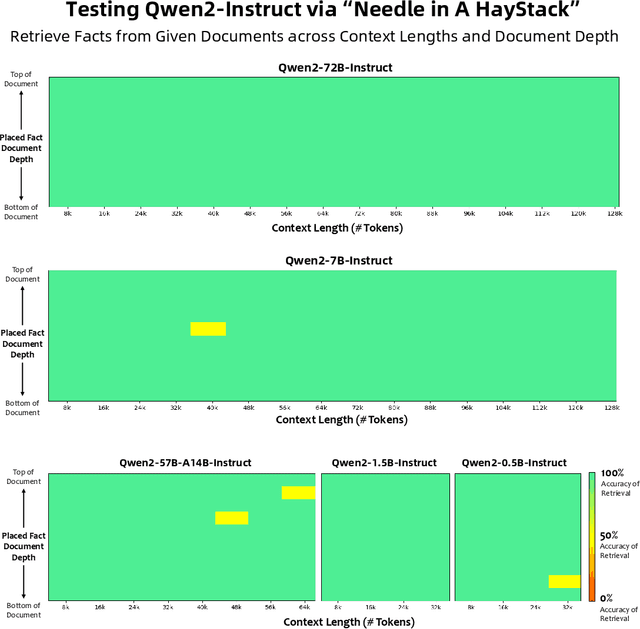
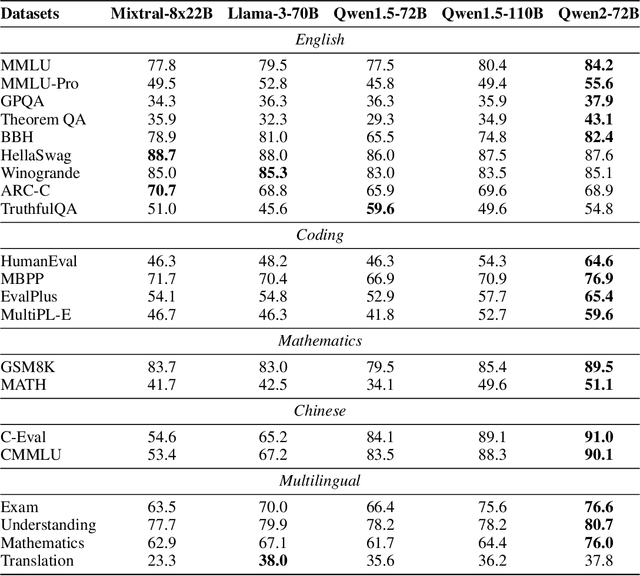
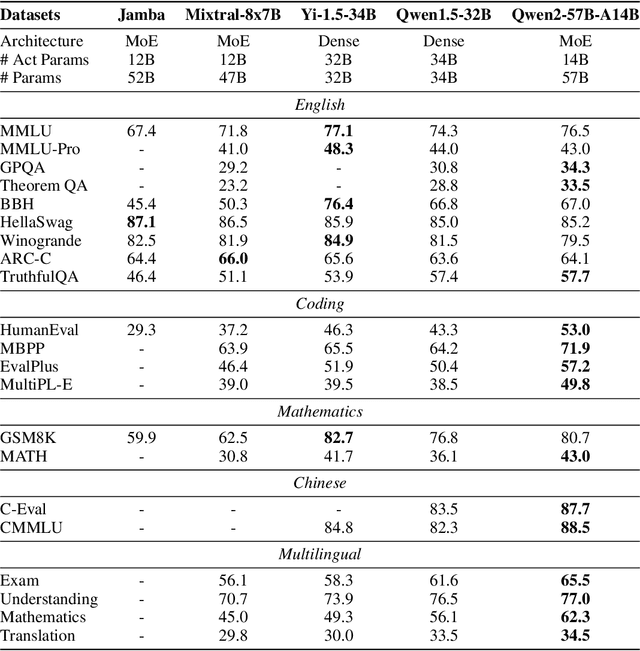
Abstract:This report introduces the Qwen2 series, the latest addition to our large language models and large multimodal models. We release a comprehensive suite of foundational and instruction-tuned language models, encompassing a parameter range from 0.5 to 72 billion, featuring dense models and a Mixture-of-Experts model. Qwen2 surpasses most prior open-weight models, including its predecessor Qwen1.5, and exhibits competitive performance relative to proprietary models across diverse benchmarks on language understanding, generation, multilingual proficiency, coding, mathematics, and reasoning. The flagship model, Qwen2-72B, showcases remarkable performance: 84.2 on MMLU, 37.9 on GPQA, 64.6 on HumanEval, 89.5 on GSM8K, and 82.4 on BBH as a base language model. The instruction-tuned variant, Qwen2-72B-Instruct, attains 9.1 on MT-Bench, 48.1 on Arena-Hard, and 35.7 on LiveCodeBench. Moreover, Qwen2 demonstrates robust multilingual capabilities, proficient in approximately 30 languages, spanning English, Chinese, Spanish, French, German, Arabic, Russian, Korean, Japanese, Thai, Vietnamese, and more, underscoring its versatility and global reach. To foster community innovation and accessibility, we have made the Qwen2 model weights openly available on Hugging Face and ModelScope, and the supplementary materials including example code on GitHub. These platforms also include resources for quantization, fine-tuning, and deployment, facilitating a wide range of applications and research endeavors.
InjectTST: A Transformer Method of Injecting Global Information into Independent Channels for Long Time Series Forecasting
Mar 05, 2024
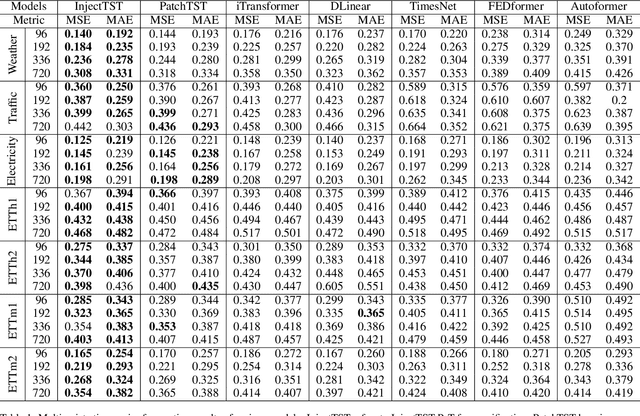

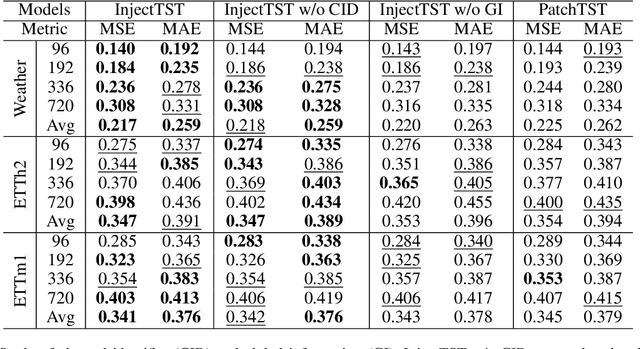
Abstract:Transformer has become one of the most popular architectures for multivariate time series (MTS) forecasting. Recent Transformer-based MTS models generally prefer channel-independent structures with the observation that channel independence can alleviate noise and distribution drift issues, leading to more robustness. Nevertheless, it is essential to note that channel dependency remains an inherent characteristic of MTS, carrying valuable information. Designing a model that incorporates merits of both channel-independent and channel-mixing structures is a key to further improvement of MTS forecasting, which poses a challenging conundrum. To address the problem, an injection method for global information into channel-independent Transformer, InjectTST, is proposed in this paper. Instead of designing a channel-mixing model directly, we retain the channel-independent backbone and gradually inject global information into individual channels in a selective way. A channel identifier, a global mixing module and a self-contextual attention module are devised in InjectTST. The channel identifier can help Transformer distinguish channels for better representation. The global mixing module produces cross-channel global information. Through the self-contextual attention module, the independent channels can selectively concentrate on useful global information without robustness degradation, and channel mixing is achieved implicitly. Experiments indicate that InjectTST can achieve stable improvement compared with state-of-the-art models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge