Jianhong Tu
additional authors not shown
DeepPlanning: Benchmarking Long-Horizon Agentic Planning with Verifiable Constraints
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:While agent evaluation has shifted toward long-horizon tasks, most benchmarks still emphasize local, step-level reasoning rather than the global constrained optimization (e.g., time and financial budgets) that demands genuine planning ability. Meanwhile, existing LLM planning benchmarks underrepresent the active information gathering and fine-grained local constraints typical of real-world settings. To address this, we introduce DeepPlanning, a challenging benchmark for practical long-horizon agent planning. It features multi-day travel planning and multi-product shopping tasks that require proactive information acquisition, local constrained reasoning, and global constrained optimization. Evaluations on DeepPlanning show that even frontier agentic LLMs struggle with these problems, highlighting the importance of reliable explicit reasoning patterns and parallel tool use for achieving better effectiveness-efficiency trade-offs. Error analysis further points to promising directions for improving agentic LLMs over long planning horizons. We open-source the code and data to support future research.
One Model to Critique Them All: Rewarding Agentic Tool-Use via Efficient Reasoning
Oct 30, 2025

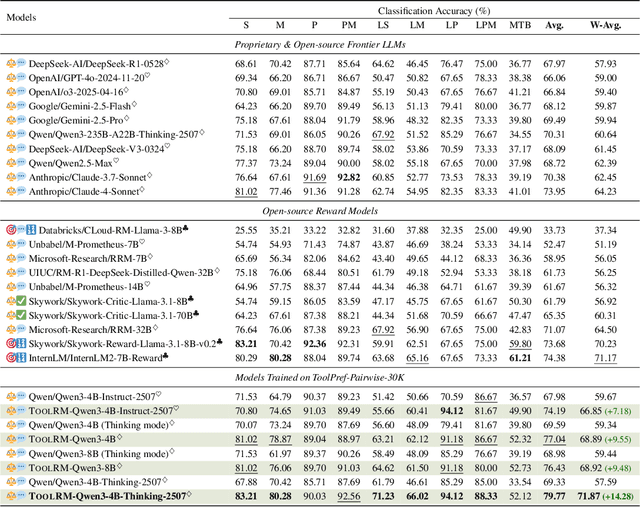

Abstract:Reward models (RMs) play a critical role in aligning large language models (LLMs) with human preferences. Yet in the domain of tool learning, the lack of RMs specifically designed for function-calling tasks has limited progress toward more capable agentic AI. We introduce ToolRM, a family of lightweight generative RMs tailored for general tool-use scenarios. To build these models, we propose a novel pipeline that constructs pairwise preference data using rule-based scoring and multidimensional sampling. This yields ToolPref-Pairwise-30K, a diverse, balanced, and challenging dataset of critique tasks that supports reinforcement learning with verifiable feedback. To evaluate tool-use RMs, we also introduce TRBench$_{BFCL}$, a benchmark built on the agentic evaluation suite BFCL. Trained on our constructed data, models from the Qwen3-4B/8B series achieve up to 14.28% higher accuracy, substantially outperforming frontier models such as Claude 4 and OpenAI o3 in pairwise reward judgments. Beyond training objectives, ToolRM generalizes to broader critique tasks, including Best-of-N sampling and self-correction. Experiments on ACEBench highlight its effectiveness and efficiency, enabling inference-time scaling and reducing output token usage by over 66%. We release data and model checkpoints to facilitate future research.
Qwen3 Technical Report
May 14, 2025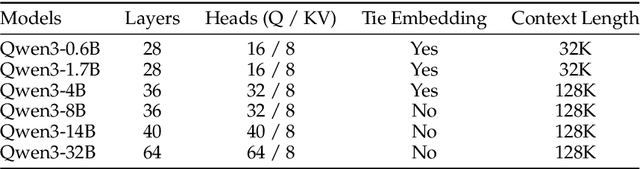
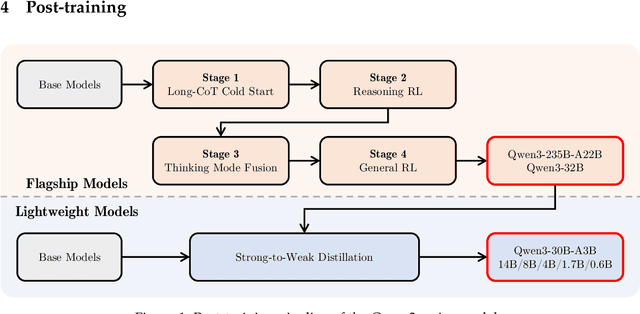
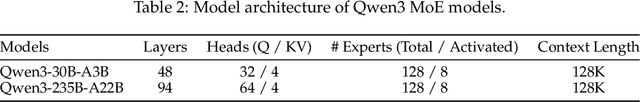
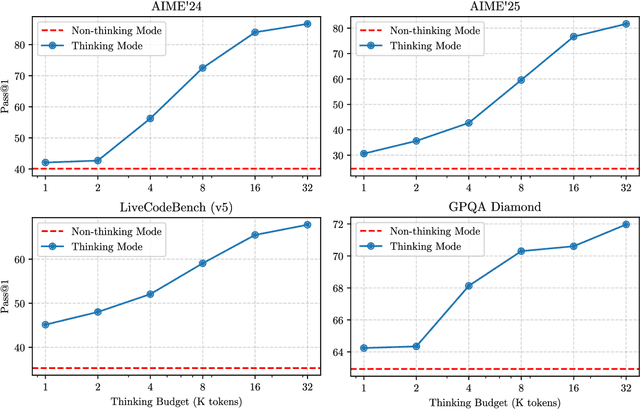
Abstract:In this work, we present Qwen3, the latest version of the Qwen model family. Qwen3 comprises a series of large language models (LLMs) designed to advance performance, efficiency, and multilingual capabilities. The Qwen3 series includes models of both dense and Mixture-of-Expert (MoE) architectures, with parameter scales ranging from 0.6 to 235 billion. A key innovation in Qwen3 is the integration of thinking mode (for complex, multi-step reasoning) and non-thinking mode (for rapid, context-driven responses) into a unified framework. This eliminates the need to switch between different models--such as chat-optimized models (e.g., GPT-4o) and dedicated reasoning models (e.g., QwQ-32B)--and enables dynamic mode switching based on user queries or chat templates. Meanwhile, Qwen3 introduces a thinking budget mechanism, allowing users to allocate computational resources adaptively during inference, thereby balancing latency and performance based on task complexity. Moreover, by leveraging the knowledge from the flagship models, we significantly reduce the computational resources required to build smaller-scale models, while ensuring their highly competitive performance. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that Qwen3 achieves state-of-the-art results across diverse benchmarks, including tasks in code generation, mathematical reasoning, agent tasks, etc., competitive against larger MoE models and proprietary models. Compared to its predecessor Qwen2.5, Qwen3 expands multilingual support from 29 to 119 languages and dialects, enhancing global accessibility through improved cross-lingual understanding and generation capabilities. To facilitate reproducibility and community-driven research and development, all Qwen3 models are publicly accessible under Apache 2.0.
Qwen2.5-1M Technical Report
Jan 26, 2025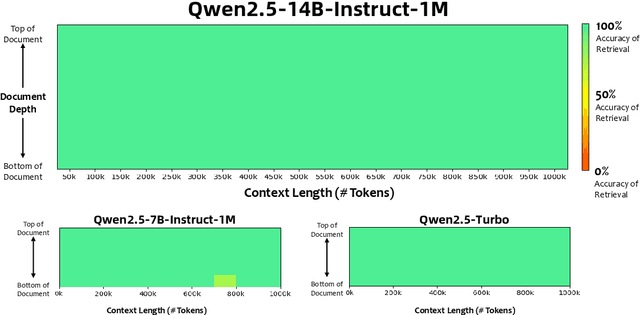
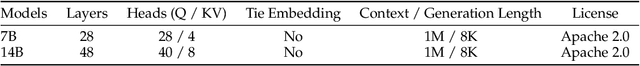
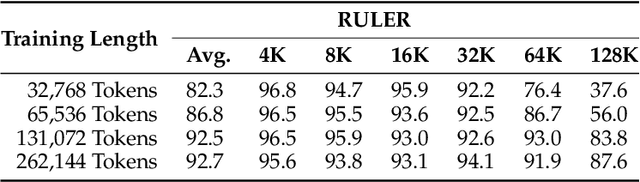
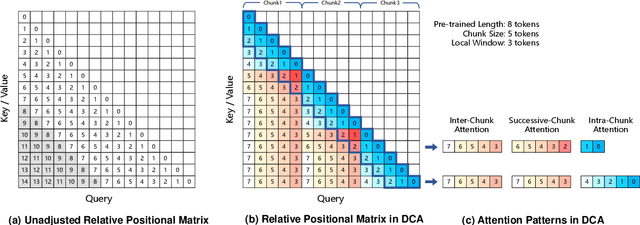
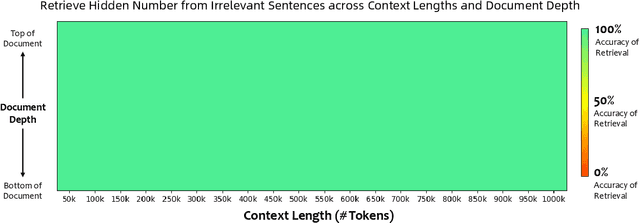
Abstract:We introduce Qwen2.5-1M, a series of models that extend the context length to 1 million tokens. Compared to the previous 128K version, the Qwen2.5-1M series have significantly enhanced long-context capabilities through long-context pre-training and post-training. Key techniques such as long data synthesis, progressive pre-training, and multi-stage supervised fine-tuning are employed to effectively enhance long-context performance while reducing training costs. To promote the use of long-context models among a broader user base, we present and open-source our inference framework. This framework includes a length extrapolation method that can expand the model context lengths by at least four times, or even more, without additional training. To reduce inference costs, we implement a sparse attention method along with chunked prefill optimization for deployment scenarios and a sparsity refinement method to improve precision. Additionally, we detail our optimizations in the inference engine, including kernel optimization, pipeline parallelism, and scheduling optimization, which significantly enhance overall inference performance. By leveraging our inference framework, the Qwen2.5-1M models achieve a remarkable 3x to 7x prefill speedup in scenarios with 1 million tokens of context. This framework provides an efficient and powerful solution for developing applications that require long-context processing using open-source models. The Qwen2.5-1M series currently includes the open-source models Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct-1M and Qwen2.5-14B-Instruct-1M, as well as the API-accessed model Qwen2.5-Turbo. Evaluations show that Qwen2.5-1M models have been greatly improved in long-context tasks without compromising performance in short-context scenarios. Specifically, the Qwen2.5-14B-Instruct-1M model significantly outperforms GPT-4o-mini in long-context tasks and supports contexts eight times longer.
Qwen2.5 Technical Report
Dec 19, 2024

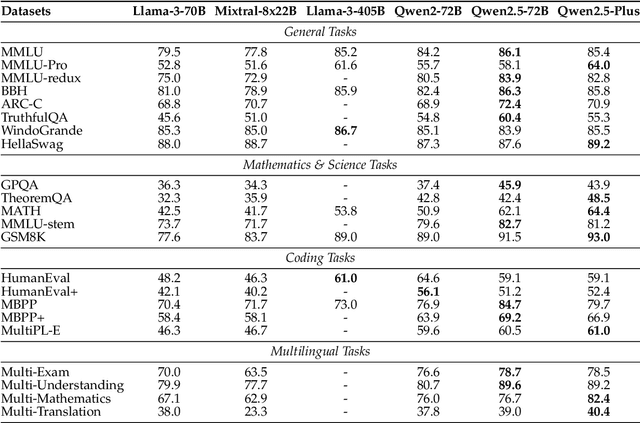
Abstract:In this report, we introduce Qwen2.5, a comprehensive series of large language models (LLMs) designed to meet diverse needs. Compared to previous iterations, Qwen 2.5 has been significantly improved during both the pre-training and post-training stages. In terms of pre-training, we have scaled the high-quality pre-training datasets from the previous 7 trillion tokens to 18 trillion tokens. This provides a strong foundation for common sense, expert knowledge, and reasoning capabilities. In terms of post-training, we implement intricate supervised finetuning with over 1 million samples, as well as multistage reinforcement learning. Post-training techniques enhance human preference, and notably improve long text generation, structural data analysis, and instruction following. To handle diverse and varied use cases effectively, we present Qwen2.5 LLM series in rich sizes. Open-weight offerings include base and instruction-tuned models, with quantized versions available. In addition, for hosted solutions, the proprietary models currently include two mixture-of-experts (MoE) variants: Qwen2.5-Turbo and Qwen2.5-Plus, both available from Alibaba Cloud Model Studio. Qwen2.5 has demonstrated top-tier performance on a wide range of benchmarks evaluating language understanding, reasoning, mathematics, coding, human preference alignment, etc. Specifically, the open-weight flagship Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct outperforms a number of open and proprietary models and demonstrates competitive performance to the state-of-the-art open-weight model, Llama-3-405B-Instruct, which is around 5 times larger. Qwen2.5-Turbo and Qwen2.5-Plus offer superior cost-effectiveness while performing competitively against GPT-4o-mini and GPT-4o respectively. Additionally, as the foundation, Qwen2.5 models have been instrumental in training specialized models such as Qwen2.5-Math, Qwen2.5-Coder, QwQ, and multimodal models.
MLAN: Language-Based Instruction Tuning Improves Zero-Shot Generalization of Multimodal Large Language Models
Nov 19, 2024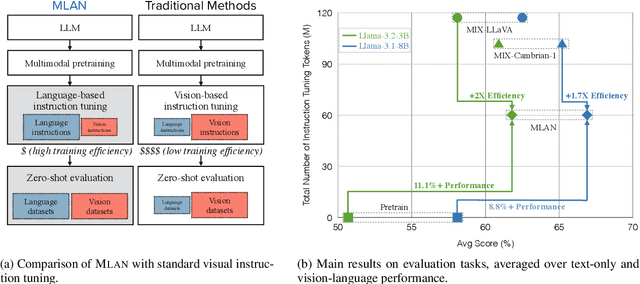
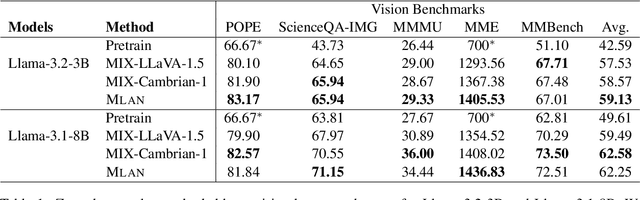
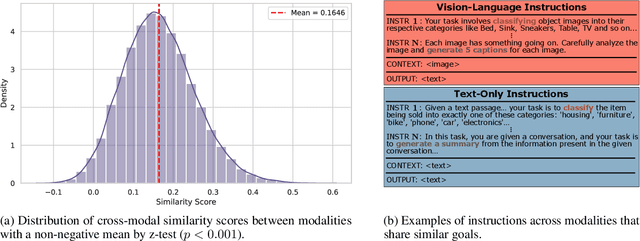
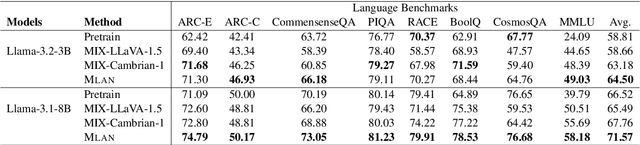
Abstract:We present a novel instruction tuning recipe to improve the zero-shot task generalization of multimodal large language models. In contrast to existing instruction tuning mechanisms that heavily rely on visual instructions, our approach focuses on language-based instruction tuning, offering a distinct and more training efficient path for multimodal instruction tuning. We evaluate the performance of the proposed approach on 9 unseen datasets across both language and vision modalities. Our results show that our language-only instruction tuning is able to significantly improve the performance of two pretrained multimodal models based on Llama 2 and Vicuna on those unseen datasets. Interestingly, the language instruction following ability also helps unlock the models to follow vision instructions without explicit training. Compared to the state of the art multimodal instruction tuning approaches that are mainly based on visual instructions, our language-based method not only achieves superior performance but also significantly enhances training efficiency. For instance, the language-only instruction tuning produces competitive average performance across the evaluated datasets (with even better performance on language datasets) with significant training efficiency improvements (on average 4x), thanks to the striking reduction in the need for vision data. With a small number of visual instructions, this emerging language instruction following ability transfers well to the unseen vision datasets, outperforming the state of the art with greater training efficiency.
Language Models can Self-Lengthen to Generate Long Texts
Oct 31, 2024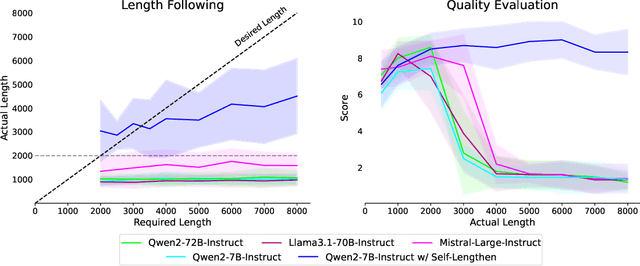
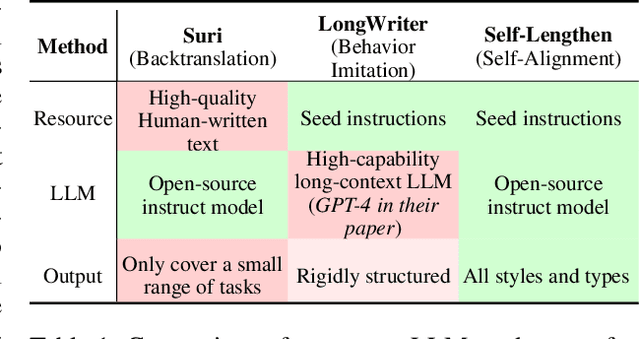
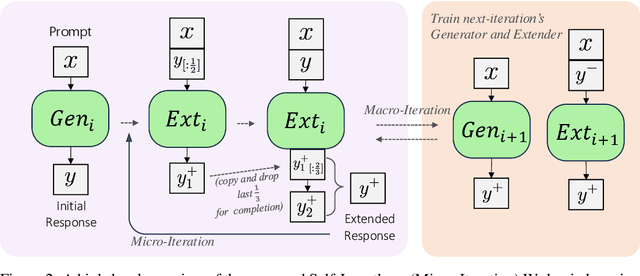
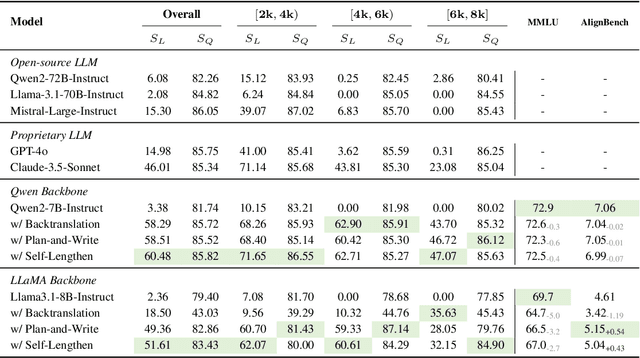
Abstract:Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have significantly enhanced their ability to process long contexts, yet a notable gap remains in generating long, aligned outputs. This limitation stems from a training gap where pre-training lacks effective instructions for long-text generation, and post-training data primarily consists of short query-response pairs. Current approaches, such as instruction backtranslation and behavior imitation, face challenges including data quality, copyright issues, and constraints on proprietary model usage. In this paper, we introduce an innovative iterative training framework called Self-Lengthen that leverages only the intrinsic knowledge and skills of LLMs without the need for auxiliary data or proprietary models. The framework consists of two roles: the Generator and the Extender. The Generator produces the initial response, which is then split and expanded by the Extender. This process results in a new, longer response, which is used to train both the Generator and the Extender iteratively. Through this process, the models are progressively trained to handle increasingly longer responses. Experiments on benchmarks and human evaluations show that Self-Lengthen outperforms existing methods in long-text generation, when applied to top open-source LLMs such as Qwen2 and LLaMA3. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/QwenLM/Self-Lengthen.
Qwen2.5-Math Technical Report: Toward Mathematical Expert Model via Self-Improvement
Sep 18, 2024Abstract:In this report, we present a series of math-specific large language models: Qwen2.5-Math and Qwen2.5-Math-Instruct-1.5B/7B/72B. The core innovation of the Qwen2.5 series lies in integrating the philosophy of self-improvement throughout the entire pipeline, from pre-training and post-training to inference: (1) During the pre-training phase, Qwen2-Math-Instruct is utilized to generate large-scale, high-quality mathematical data. (2) In the post-training phase, we develop a reward model (RM) by conducting massive sampling from Qwen2-Math-Instruct. This RM is then applied to the iterative evolution of data in supervised fine-tuning (SFT). With a stronger SFT model, it's possible to iteratively train and update the RM, which in turn guides the next round of SFT data iteration. On the final SFT model, we employ the ultimate RM for reinforcement learning, resulting in the Qwen2.5-Math-Instruct. (3) Furthermore, during the inference stage, the RM is used to guide sampling, optimizing the model's performance. Qwen2.5-Math-Instruct supports both Chinese and English, and possess advanced mathematical reasoning capabilities, including Chain-of-Thought (CoT) and Tool-Integrated Reasoning (TIR). We evaluate our models on 10 mathematics datasets in both English and Chinese, such as GSM8K, MATH, GaoKao, AMC23, and AIME24, covering a range of difficulties from grade school level to math competition problems.
Qwen2 Technical Report
Jul 16, 2024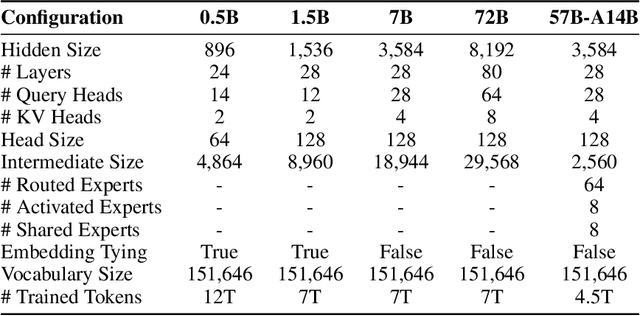
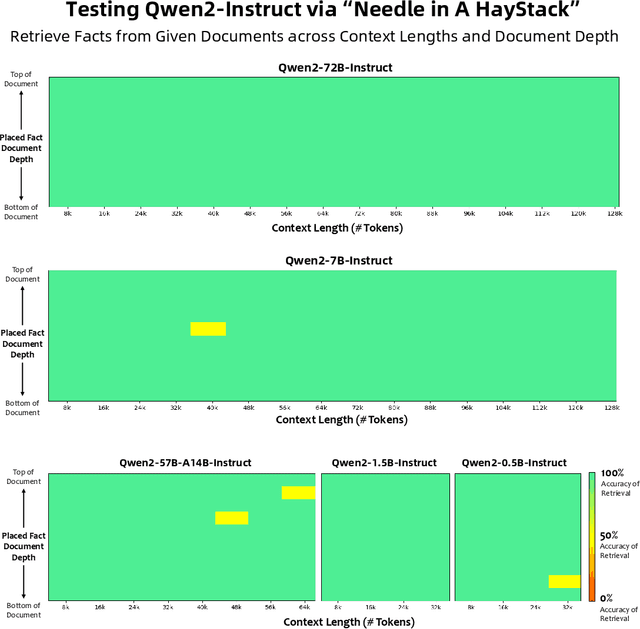
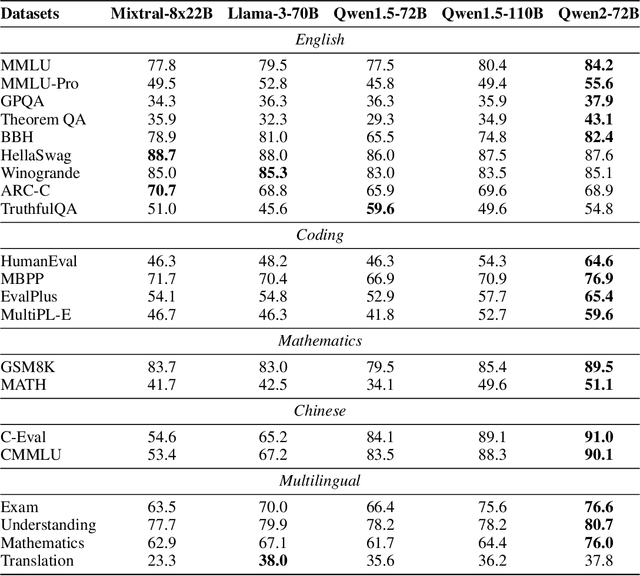
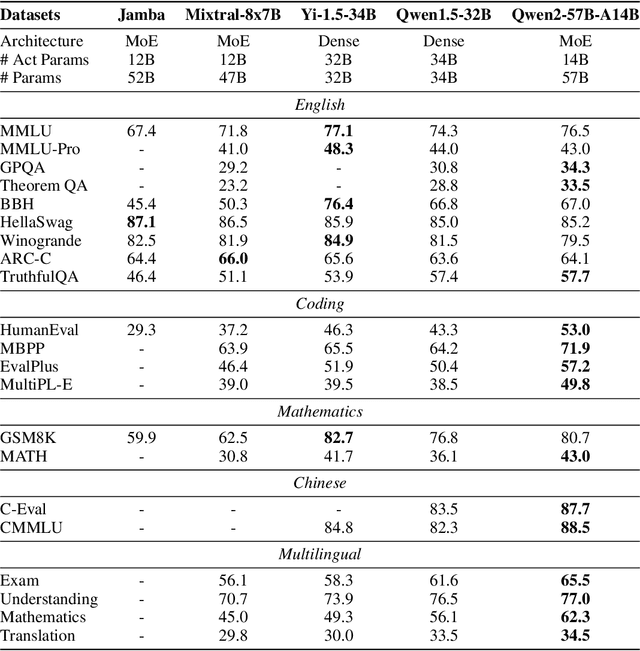
Abstract:This report introduces the Qwen2 series, the latest addition to our large language models and large multimodal models. We release a comprehensive suite of foundational and instruction-tuned language models, encompassing a parameter range from 0.5 to 72 billion, featuring dense models and a Mixture-of-Experts model. Qwen2 surpasses most prior open-weight models, including its predecessor Qwen1.5, and exhibits competitive performance relative to proprietary models across diverse benchmarks on language understanding, generation, multilingual proficiency, coding, mathematics, and reasoning. The flagship model, Qwen2-72B, showcases remarkable performance: 84.2 on MMLU, 37.9 on GPQA, 64.6 on HumanEval, 89.5 on GSM8K, and 82.4 on BBH as a base language model. The instruction-tuned variant, Qwen2-72B-Instruct, attains 9.1 on MT-Bench, 48.1 on Arena-Hard, and 35.7 on LiveCodeBench. Moreover, Qwen2 demonstrates robust multilingual capabilities, proficient in approximately 30 languages, spanning English, Chinese, Spanish, French, German, Arabic, Russian, Korean, Japanese, Thai, Vietnamese, and more, underscoring its versatility and global reach. To foster community innovation and accessibility, we have made the Qwen2 model weights openly available on Hugging Face and ModelScope, and the supplementary materials including example code on GitHub. These platforms also include resources for quantization, fine-tuning, and deployment, facilitating a wide range of applications and research endeavors.
Qwen Technical Report
Sep 28, 2023
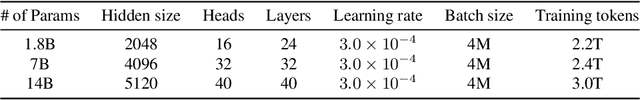
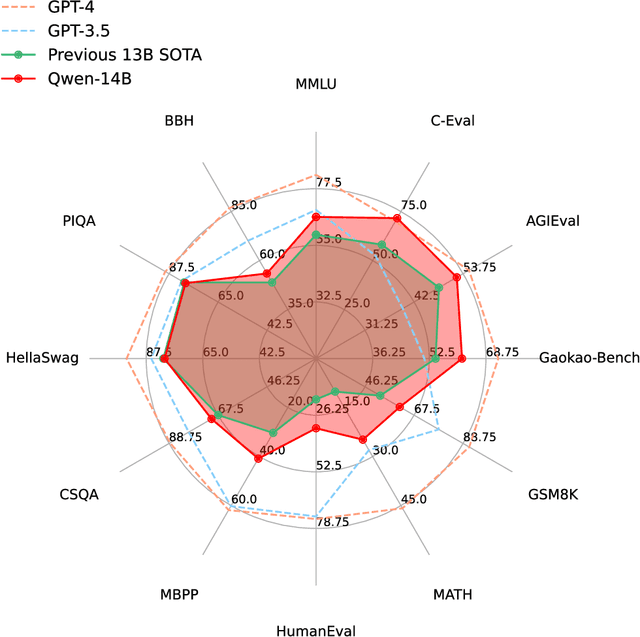
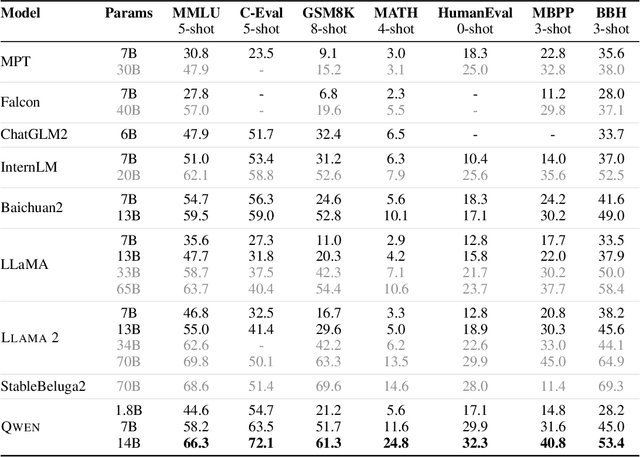
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized the field of artificial intelligence, enabling natural language processing tasks that were previously thought to be exclusive to humans. In this work, we introduce Qwen, the first installment of our large language model series. Qwen is a comprehensive language model series that encompasses distinct models with varying parameter counts. It includes Qwen, the base pretrained language models, and Qwen-Chat, the chat models finetuned with human alignment techniques. The base language models consistently demonstrate superior performance across a multitude of downstream tasks, and the chat models, particularly those trained using Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF), are highly competitive. The chat models possess advanced tool-use and planning capabilities for creating agent applications, showcasing impressive performance even when compared to bigger models on complex tasks like utilizing a code interpreter. Furthermore, we have developed coding-specialized models, Code-Qwen and Code-Qwen-Chat, as well as mathematics-focused models, Math-Qwen-Chat, which are built upon base language models. These models demonstrate significantly improved performance in comparison with open-source models, and slightly fall behind the proprietary models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge