Zhuohao Ni
MLAN: Language-Based Instruction Tuning Improves Zero-Shot Generalization of Multimodal Large Language Models
Nov 19, 2024
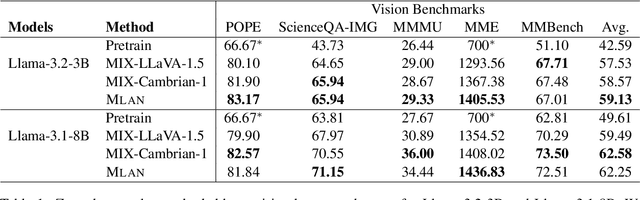
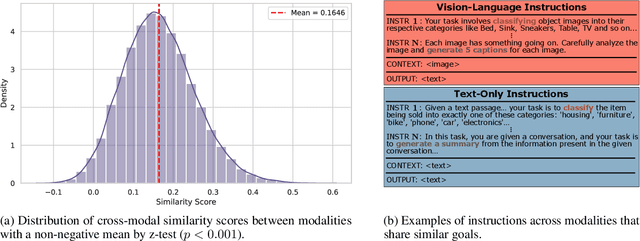
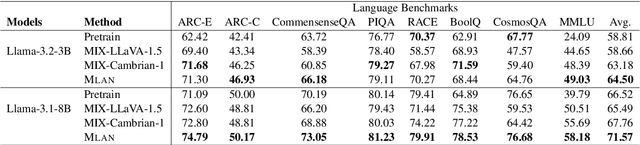
Abstract:We present a novel instruction tuning recipe to improve the zero-shot task generalization of multimodal large language models. In contrast to existing instruction tuning mechanisms that heavily rely on visual instructions, our approach focuses on language-based instruction tuning, offering a distinct and more training efficient path for multimodal instruction tuning. We evaluate the performance of the proposed approach on 9 unseen datasets across both language and vision modalities. Our results show that our language-only instruction tuning is able to significantly improve the performance of two pretrained multimodal models based on Llama 2 and Vicuna on those unseen datasets. Interestingly, the language instruction following ability also helps unlock the models to follow vision instructions without explicit training. Compared to the state of the art multimodal instruction tuning approaches that are mainly based on visual instructions, our language-based method not only achieves superior performance but also significantly enhances training efficiency. For instance, the language-only instruction tuning produces competitive average performance across the evaluated datasets (with even better performance on language datasets) with significant training efficiency improvements (on average 4x), thanks to the striking reduction in the need for vision data. With a small number of visual instructions, this emerging language instruction following ability transfers well to the unseen vision datasets, outperforming the state of the art with greater training efficiency.
Learnable Community-Aware Transformer for Brain Connectome Analysis with Token Clustering
Mar 13, 2024Abstract:Neuroscientific research has revealed that the complex brain network can be organized into distinct functional communities, each characterized by a cohesive group of regions of interest (ROIs) with strong interconnections. These communities play a crucial role in comprehending the functional organization of the brain and its implications for neurological conditions, including Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and biological differences, such as in gender. Traditional models have been constrained by the necessity of predefined community clusters, limiting their flexibility and adaptability in deciphering the brain's functional organization. Furthermore, these models were restricted by a fixed number of communities, hindering their ability to accurately represent the brain's dynamic nature. In this study, we present a token clustering brain transformer-based model ($\texttt{TC-BrainTF}$) for joint community clustering and classification. Our approach proposes a novel token clustering (TC) module based on the transformer architecture, which utilizes learnable prompt tokens with orthogonal loss where each ROI embedding is projected onto the prompt embedding space, effectively clustering ROIs into communities and reducing the dimensions of the node representation via merging with communities. Our results demonstrate that our learnable community-aware model $\texttt{TC-BrainTF}$ offers improved accuracy in identifying ASD and classifying genders through rigorous testing on ABIDE and HCP datasets. Additionally, the qualitative analysis on $\texttt{TC-BrainTF}$ has demonstrated the effectiveness of the designed TC module and its relevance to neuroscience interpretations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge