Jingqun Tang
Dolphin-v2: Universal Document Parsing via Scalable Anchor Prompting
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Document parsing has garnered widespread attention as vision-language models (VLMs) advance OCR capabilities. However, the field remains fragmented across dozens of specialized models with varying strengths, forcing users to navigate complex model selection and limiting system scalability. Moreover, existing two-stage approaches depend on axis-aligned bounding boxes for layout detection, failing to handle distorted or photographed documents effectively. To this end, we present Dolphin-v2, a two-stage document image parsing model that substantially improves upon the original Dolphin. In the first stage, Dolphin-v2 jointly performs document type classification (digital-born versus photographed) alongside layout analysis. For digital-born documents, it conducts finer-grained element detection with reading order prediction. In the second stage, we employ a hybrid parsing strategy: photographed documents are parsed holistically as complete pages to handle geometric distortions, while digital-born documents undergo element-wise parallel parsing guided by the detected layout anchors, enabling efficient content extraction. Compared with the original Dolphin, Dolphin-v2 introduces several crucial enhancements: (1) robust parsing of photographed documents via holistic page-level understanding, (2) finer-grained element detection (21 categories) with semantic attribute extraction such as author information and document metadata, and (3) code block recognition with indentation preservation, which existing systems typically lack. Comprehensive evaluations are conducted on DocPTBench, OmniDocBench, and our self-constructed RealDoc-160 benchmark. The results demonstrate substantial improvements: +14.78 points overall on the challenging OmniDocBench and 91% error reduction on photographed documents, while maintaining efficient inference through parallel processing.
DTP: A Simple yet Effective Distracting Token Pruning Framework for Vision-Language Action Models
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language Action (VLA) models have shown remarkable progress in robotic manipulation by leveraging the powerful perception abilities of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to understand environments and directly output actions. However, by default, VLA models may overly attend to image tokens in the task-irrelevant region, which we describe as 'distracting tokens'. This behavior can disturb the model from the generation of the desired action tokens in each step, affecting the success rate of tasks. In this paper, we introduce a simple yet effective plug-and-play Distracting Token Pruning (DTP) framework, which dynamically detects and prunes these distracting image tokens. By correcting the model's visual attention patterns, we aim to improve the task success rate, as well as exploring the performance upper boundaries of the model without altering its original architecture or adding additional inputs. Experiments on the SIMPLER Benchmark (Li et al., 2024) show that our method consistently achieving relative improvements in task success rates across different types of novel VLA models, demonstrating generalizability to transformer-based VLAs. Further analysis reveals a negative correlation between the task success rate and the amount of attentions in the task-irrelevant region for all models tested, highlighting a common phenomenon of VLA models that could guide future research. We also publish our code at: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/CBD3.
CME-CAD: Heterogeneous Collaborative Multi-Expert Reinforcement Learning for CAD Code Generation
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Computer-Aided Design (CAD) is essential in industrial design, but the complexity of traditional CAD modeling and workflows presents significant challenges for automating the generation of high-precision, editable CAD models. Existing methods that reconstruct 3D models from sketches often produce non-editable and approximate models that fall short of meeting the stringent requirements for precision and editability in industrial design. Moreover, the reliance on text or image-based inputs often requires significant manual annotation, limiting their scalability and applicability in industrial settings. To overcome these challenges, we propose the Heterogeneous Collaborative Multi-Expert Reinforcement Learning (CME-CAD) paradigm, a novel training paradigm for CAD code generation. Our approach integrates the complementary strengths of these models, facilitating collaborative learning and improving the model's ability to generate accurate, constraint-compatible, and fully editable CAD models. We introduce a two-stage training process: Multi-Expert Fine-Tuning (MEFT), and Multi-Expert Reinforcement Learning (MERL). Additionally, we present CADExpert, an open-source benchmark consisting of 17,299 instances, including orthographic projections with precise dimension annotations, expert-generated Chain-of-Thought (CoT) processes, executable CADQuery code, and rendered 3D models.
Beyond Pixel Simulation: Pathology Image Generation via Diagnostic Semantic Tokens and Prototype Control
Dec 24, 2025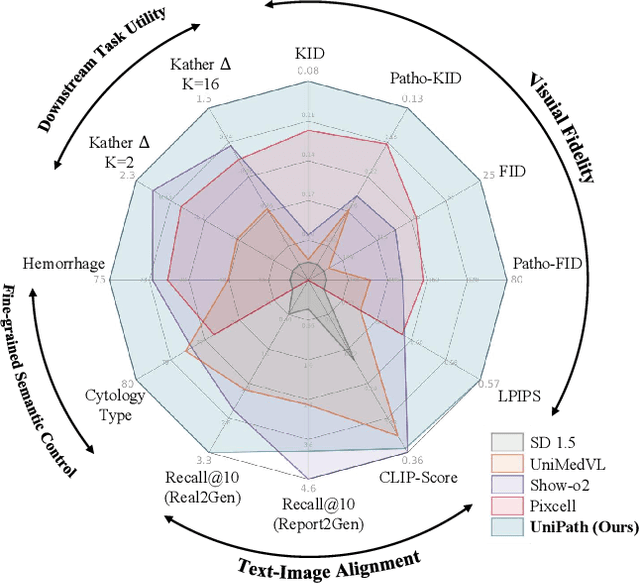
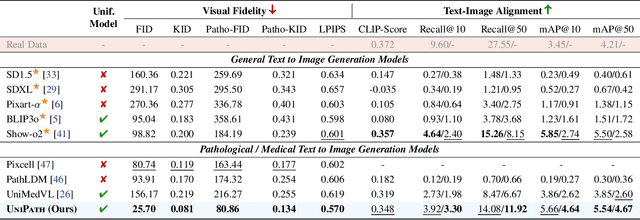
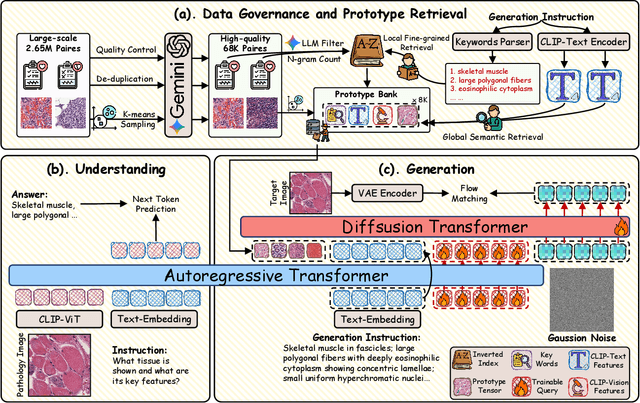
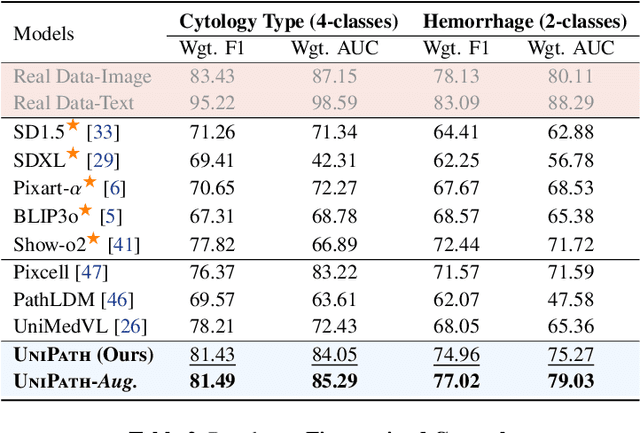
Abstract:In computational pathology, understanding and generation have evolved along disparate paths: advanced understanding models already exhibit diagnostic-level competence, whereas generative models largely simulate pixels. Progress remains hindered by three coupled factors: the scarcity of large, high-quality image-text corpora; the lack of precise, fine-grained semantic control, which forces reliance on non-semantic cues; and terminological heterogeneity, where diverse phrasings for the same diagnostic concept impede reliable text conditioning. We introduce UniPath, a semantics-driven pathology image generation framework that leverages mature diagnostic understanding to enable controllable generation. UniPath implements Multi-Stream Control: a Raw-Text stream; a High-Level Semantics stream that uses learnable queries to a frozen pathology MLLM to distill paraphrase-robust Diagnostic Semantic Tokens and to expand prompts into diagnosis-aware attribute bundles; and a Prototype stream that affords component-level morphological control via a prototype bank. On the data front, we curate a 2.65M image-text corpus and a finely annotated, high-quality 68K subset to alleviate data scarcity. For a comprehensive assessment, we establish a four-tier evaluation hierarchy tailored to pathology. Extensive experiments demonstrate UniPath's SOTA performance, including a Patho-FID of 80.9 (51% better than the second-best) and fine-grained semantic control achieving 98.7% of the real-image. The meticulously curated datasets, complete source code, and pre-trained model weights developed in this study will be made openly accessible to the public.
Prolonged Reasoning Is Not All You Need: Certainty-Based Adaptive Routing for Efficient LLM/MLLM Reasoning
May 21, 2025



Abstract:Recent advancements in reasoning have significantly enhanced the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) and Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) across diverse tasks. However, excessive reliance on chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning can impair model performance and brings unnecessarily lengthened outputs, reducing efficiency. Our work reveals that prolonged reasoning does not universally improve accuracy and even degrade performance on simpler tasks. To address this, we propose Certainty-based Adaptive Reasoning (CAR), a novel framework that dynamically switches between short answers and long-form reasoning based on the model perplexity. CAR first generates a short answer and evaluates its perplexity, triggering reasoning only when the model exhibits low confidence (i.e., high perplexity). Experiments across diverse multimodal VQA/KIE benchmarks and text reasoning datasets show that CAR outperforms both short-answer and long-form reasoning approaches, striking an optimal balance between accuracy and efficiency.
Dolphin: Document Image Parsing via Heterogeneous Anchor Prompting
May 20, 2025Abstract:Document image parsing is challenging due to its complexly intertwined elements such as text paragraphs, figures, formulas, and tables. Current approaches either assemble specialized expert models or directly generate page-level content autoregressively, facing integration overhead, efficiency bottlenecks, and layout structure degradation despite their decent performance. To address these limitations, we present \textit{Dolphin} (\textit{\textbf{Do}cument Image \textbf{P}arsing via \textbf{H}eterogeneous Anchor Prompt\textbf{in}g}), a novel multimodal document image parsing model following an analyze-then-parse paradigm. In the first stage, Dolphin generates a sequence of layout elements in reading order. These heterogeneous elements, serving as anchors and coupled with task-specific prompts, are fed back to Dolphin for parallel content parsing in the second stage. To train Dolphin, we construct a large-scale dataset of over 30 million samples, covering multi-granularity parsing tasks. Through comprehensive evaluations on both prevalent benchmarks and self-constructed ones, Dolphin achieves state-of-the-art performance across diverse page-level and element-level settings, while ensuring superior efficiency through its lightweight architecture and parallel parsing mechanism. The code and pre-trained models are publicly available at https://github.com/ByteDance/Dolphin
Advancing Sequential Numerical Prediction in Autoregressive Models
May 19, 2025Abstract:Autoregressive models have become the de facto choice for sequence generation tasks, but standard approaches treat digits as independent tokens and apply cross-entropy loss, overlooking the coherent structure of numerical sequences. This paper introduces Numerical Token Integrity Loss (NTIL) to address this gap. NTIL operates at two levels: (1) token-level, where it extends the Earth Mover's Distance (EMD) to preserve ordinal relationships between numerical values, and (2) sequence-level, where it penalizes the overall discrepancy between the predicted and actual sequences. This dual approach improves numerical prediction and integrates effectively with LLMs/MLLMs. Extensive experiments show significant performance improvements with NTIL.
WildDoc: How Far Are We from Achieving Comprehensive and Robust Document Understanding in the Wild?
May 16, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancements in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have significantly enhanced capabilities in Document Understanding. However, prevailing benchmarks like DocVQA and ChartQA predominantly comprise \textit{scanned or digital} documents, inadequately reflecting the intricate challenges posed by diverse real-world scenarios, such as variable illumination and physical distortions. This paper introduces WildDoc, the inaugural benchmark designed specifically for assessing document understanding in natural environments. WildDoc incorporates a diverse set of manually captured document images reflecting real-world conditions and leverages document sources from established benchmarks to facilitate comprehensive comparisons with digital or scanned documents. Further, to rigorously evaluate model robustness, each document is captured four times under different conditions. Evaluations of state-of-the-art MLLMs on WildDoc expose substantial performance declines and underscore the models' inadequate robustness compared to traditional benchmarks, highlighting the unique challenges posed by real-world document understanding. Our project homepage is available at https://bytedance.github.io/WildDoc.
Seed1.5-VL Technical Report
May 11, 2025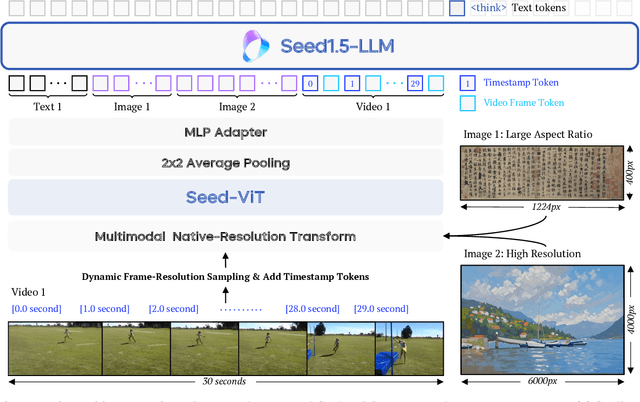

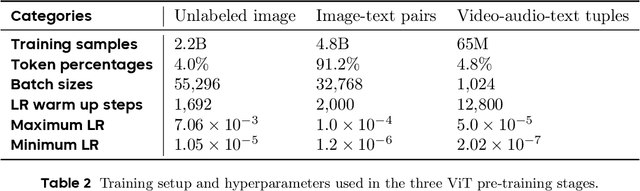
Abstract:We present Seed1.5-VL, a vision-language foundation model designed to advance general-purpose multimodal understanding and reasoning. Seed1.5-VL is composed with a 532M-parameter vision encoder and a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) LLM of 20B active parameters. Despite its relatively compact architecture, it delivers strong performance across a wide spectrum of public VLM benchmarks and internal evaluation suites, achieving the state-of-the-art performance on 38 out of 60 public benchmarks. Moreover, in agent-centric tasks such as GUI control and gameplay, Seed1.5-VL outperforms leading multimodal systems, including OpenAI CUA and Claude 3.7. Beyond visual and video understanding, it also demonstrates strong reasoning abilities, making it particularly effective for multimodal reasoning challenges such as visual puzzles. We believe these capabilities will empower broader applications across diverse tasks. In this report, we mainly provide a comprehensive review of our experiences in building Seed1.5-VL across model design, data construction, and training at various stages, hoping that this report can inspire further research. Seed1.5-VL is now accessible at https://www.volcengine.com/ (Volcano Engine Model ID: doubao-1-5-thinking-vision-pro-250428)
Vision as LoRA
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:We introduce Vision as LoRA (VoRA), a novel paradigm for transforming an LLM into an MLLM. Unlike prevalent MLLM architectures that rely on external vision modules for vision encoding, VoRA internalizes visual capabilities by integrating vision-specific LoRA layers directly into the LLM. This design allows the added parameters to be seamlessly merged into the LLM during inference, eliminating structural complexity and minimizing computational overhead. Moreover, inheriting the LLM's ability of handling flexible context, VoRA can process inputs at arbitrary resolutions. To further strengthen VoRA's visual capabilities, we introduce a block-wise distillation method that transfers visual priors from a pre-trained ViT into the LoRA layers, effectively accelerating training by injecting visual knowledge. Additionally, we apply bi-directional attention masks to better capture the context information of an image. We successfully demonstrate that with additional pre-training data, VoRA can perform comparably with conventional encode-based MLLMs. All training data, codes, and model weights will be released at https://github.com/Hon-Wong/VoRA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge