Yuxiang Nie
Post-Completion Learning for Language Models
Jul 27, 2025Abstract:Current language model training paradigms typically terminate learning upon reaching the end-of-sequence (<eos>}) token, overlooking the potential learning opportunities in the post-completion space. We propose Post-Completion Learning (PCL), a novel training framework that systematically utilizes the sequence space after model output completion, to enhance both the reasoning and self-evaluation abilities. PCL enables models to continue generating self-assessments and reward predictions during training, while maintaining efficient inference by stopping at the completion point. To fully utilize this post-completion space, we design a white-box reinforcement learning method: let the model evaluate the output content according to the reward rules, then calculate and align the score with the reward functions for supervision. We implement dual-track SFT to optimize both reasoning and evaluation capabilities, and mixed it with RL training to achieve multi-objective hybrid optimization. Experimental results on different datasets and models demonstrate consistent improvements over traditional SFT and RL methods. Our method provides a new technical path for language model training that enhances output quality while preserving deployment efficiency.
UniBiomed: A Universal Foundation Model for Grounded Biomedical Image Interpretation
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:Multi-modal interpretation of biomedical images opens up novel opportunities in biomedical image analysis. Conventional AI approaches typically rely on disjointed training, i.e., Large Language Models (LLMs) for clinical text generation and segmentation models for target extraction, which results in inflexible real-world deployment and a failure to leverage holistic biomedical information. To this end, we introduce UniBiomed, the first universal foundation model for grounded biomedical image interpretation. UniBiomed is based on a novel integration of Multi-modal Large Language Model (MLLM) and Segment Anything Model (SAM), which effectively unifies the generation of clinical texts and the segmentation of corresponding biomedical objects for grounded interpretation. In this way, UniBiomed is capable of tackling a wide range of biomedical tasks across ten diverse biomedical imaging modalities. To develop UniBiomed, we curate a large-scale dataset comprising over 27 million triplets of images, annotations, and text descriptions across ten imaging modalities. Extensive validation on 84 internal and external datasets demonstrated that UniBiomed achieves state-of-the-art performance in segmentation, disease recognition, region-aware diagnosis, visual question answering, and report generation. Moreover, unlike previous models that rely on clinical experts to pre-diagnose images and manually craft precise textual or visual prompts, UniBiomed can provide automated and end-to-end grounded interpretation for biomedical image analysis. This represents a novel paradigm shift in clinical workflows, which will significantly improve diagnostic efficiency. In summary, UniBiomed represents a novel breakthrough in biomedical AI, unlocking powerful grounded interpretation capabilities for more accurate and efficient biomedical image analysis.
Vision as LoRA
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:We introduce Vision as LoRA (VoRA), a novel paradigm for transforming an LLM into an MLLM. Unlike prevalent MLLM architectures that rely on external vision modules for vision encoding, VoRA internalizes visual capabilities by integrating vision-specific LoRA layers directly into the LLM. This design allows the added parameters to be seamlessly merged into the LLM during inference, eliminating structural complexity and minimizing computational overhead. Moreover, inheriting the LLM's ability of handling flexible context, VoRA can process inputs at arbitrary resolutions. To further strengthen VoRA's visual capabilities, we introduce a block-wise distillation method that transfers visual priors from a pre-trained ViT into the LoRA layers, effectively accelerating training by injecting visual knowledge. Additionally, we apply bi-directional attention masks to better capture the context information of an image. We successfully demonstrate that with additional pre-training data, VoRA can perform comparably with conventional encode-based MLLMs. All training data, codes, and model weights will be released at https://github.com/Hon-Wong/VoRA.
ConceptCLIP: Towards Trustworthy Medical AI via Concept-Enhanced Contrastive Langauge-Image Pre-training
Jan 26, 2025Abstract:Trustworthiness is essential for the precise and interpretable application of artificial intelligence (AI) in medical imaging. Traditionally, precision and interpretability have been addressed as separate tasks, namely medical image analysis and explainable AI, each developing its own models independently. In this study, for the first time, we investigate the development of a unified medical vision-language pre-training model that can achieve both accurate analysis and interpretable understanding of medical images across various modalities. To build the model, we construct MedConcept-23M, a large-scale dataset comprising 23 million medical image-text pairs extracted from 6.2 million scientific articles, enriched with concepts from the Unified Medical Language System (UMLS). Based on MedConcept-23M, we introduce ConceptCLIP, a medical AI model utilizing concept-enhanced contrastive language-image pre-training. The pre-training of ConceptCLIP involves two primary components: image-text alignment learning (IT-Align) and patch-concept alignment learning (PC-Align). This dual alignment strategy enhances the model's capability to associate specific image regions with relevant concepts, thereby improving both the precision of analysis and the interpretability of the AI system. We conducted extensive experiments on 5 diverse types of medical image analysis tasks, spanning 51 subtasks across 10 image modalities, with the broadest range of downstream tasks. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed vision-language pre-training model. Further explainability analysis across 6 modalities reveals that ConceptCLIP achieves superior performance, underscoring its robust ability to advance explainable AI in medical imaging. These findings highlight ConceptCLIP's capability in promoting trustworthy AI in the field of medicine.
Dynamic-VLM: Simple Dynamic Visual Token Compression for VideoLLM
Dec 12, 2024



Abstract:The application of Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) for analyzing images and videos is an exciting and rapidly evolving field. In recent years, we've seen significant growth in high-quality image-text datasets for fine-tuning image understanding, but there is still a lack of comparable datasets for videos. Additionally, many VideoLLMs are extensions of single-image VLMs, which may not efficiently handle the complexities of longer videos. In this study, we introduce a large-scale synthetic dataset created from proprietary models, using carefully designed prompts to tackle a wide range of questions. We also explore a dynamic visual token compression architecture that strikes a balance between computational efficiency and performance. Our proposed \model{} achieves state-of-the-art results across various video tasks and shows impressive generalization, setting new baselines in multi-image understanding. Notably, \model{} delivers an absolute improvement of 2.7\% over LLaVA-OneVision on VideoMME and 10.7\% on MuirBench. Codes are available at https://github.com/Hon-Wong/ByteVideoLLM
MedDr: Diagnosis-Guided Bootstrapping for Large-Scale Medical Vision-Language Learning
Apr 23, 2024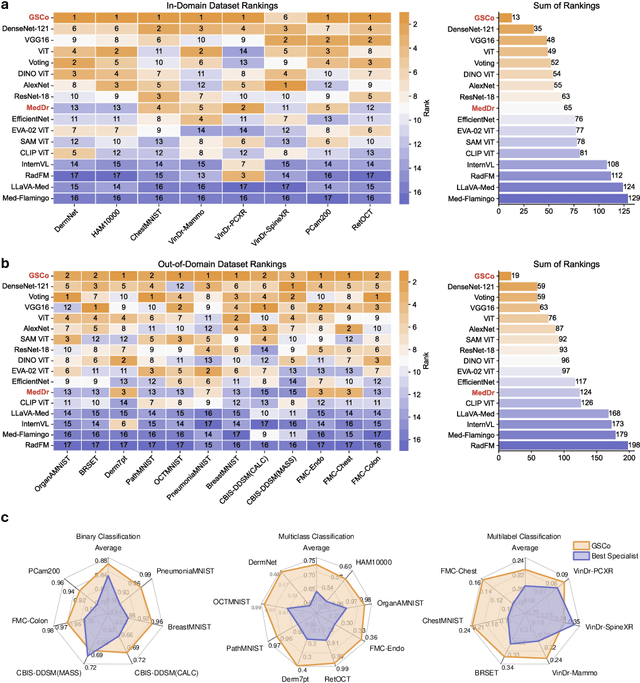

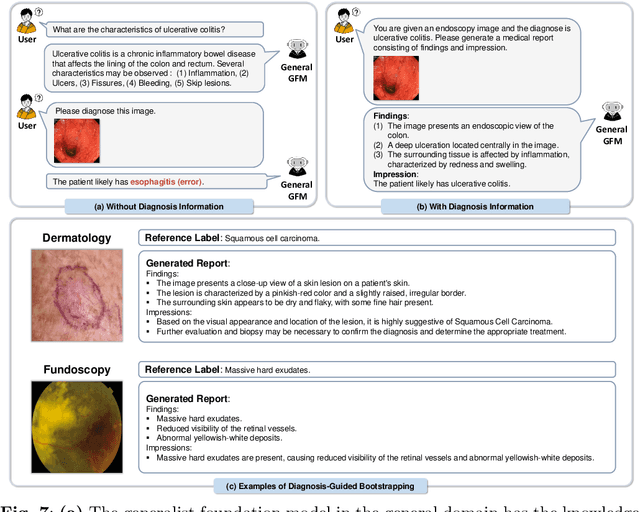
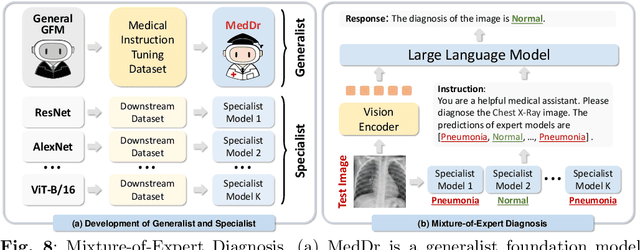
Abstract:The rapid advancement of large-scale vision-language models has showcased remarkable capabilities across various tasks. However, the lack of extensive and high-quality image-text data in medicine has greatly hindered the development of large-scale medical vision-language models. In this work, we present a diagnosis-guided bootstrapping strategy that exploits both image and label information to construct vision-language datasets. Based on the constructed dataset, we developed MedDr, a generalist foundation model for healthcare capable of handling diverse medical data modalities, including radiology, pathology, dermatology, retinography, and endoscopy. Moreover, during inference, we propose a simple but effective retrieval-augmented medical diagnosis strategy, which enhances the model's generalization ability. Extensive experiments on visual question answering, medical report generation, and medical image diagnosis demonstrate the superiority of our method.
Foundation Model for Advancing Healthcare: Challenges, Opportunities, and Future Directions
Apr 04, 2024



Abstract:Foundation model, which is pre-trained on broad data and is able to adapt to a wide range of tasks, is advancing healthcare. It promotes the development of healthcare artificial intelligence (AI) models, breaking the contradiction between limited AI models and diverse healthcare practices. Much more widespread healthcare scenarios will benefit from the development of a healthcare foundation model (HFM), improving their advanced intelligent healthcare services. Despite the impending widespread deployment of HFMs, there is currently a lack of clear understanding about how they work in the healthcare field, their current challenges, and where they are headed in the future. To answer these questions, a comprehensive and deep survey of the challenges, opportunities, and future directions of HFMs is presented in this survey. It first conducted a comprehensive overview of the HFM including the methods, data, and applications for a quick grasp of the current progress. Then, it made an in-depth exploration of the challenges present in data, algorithms, and computing infrastructures for constructing and widespread application of foundation models in healthcare. This survey also identifies emerging and promising directions in this field for future development. We believe that this survey will enhance the community's comprehension of the current progress of HFM and serve as a valuable source of guidance for future development in this field. The latest HFM papers and related resources are maintained on our website: https://github.com/YutingHe-list/Awesome-Foundation-Models-for-Advancing-Healthcare.
Elysium: Exploring Object-level Perception in Videos via MLLM
Mar 29, 2024Abstract:Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated their ability to perceive objects in still images, but their application in video-related tasks, such as object tracking, remains understudied. This lack of exploration is primarily due to two key challenges. Firstly, extensive pretraining on large-scale video datasets is required to equip MLLMs with the capability to perceive objects across multiple frames and understand inter-frame relationships. Secondly, processing a large number of frames within the context window of Large Language Models (LLMs) can impose a significant computational burden. To address the first challenge, we introduce ElysiumTrack-1M, a large-scale video dataset supported for three tasks: Single Object Tracking (SOT), Referring Single Object Tracking (RSOT), and Video Referring Expression Generation (Video-REG). ElysiumTrack-1M contains 1.27 million annotated video frames with corresponding object boxes and descriptions. Leveraging this dataset, we conduct training of MLLMs and propose a token-compression model T-Selector to tackle the second challenge. Our proposed approach, Elysium: Exploring Object-level Perception in Videos via MLLM, is an end-to-end trainable MLLM that attempts to conduct object-level tasks in videos without requiring any additional plug-in or expert models. All codes and datasets are available at https://github.com/Hon-Wong/Elysium.
Mix-Initiative Response Generation with Dynamic Prefix Tuning
Mar 27, 2024



Abstract:Mixed initiative serves as one of the key factors in controlling conversation directions. For a speaker, responding passively or leading proactively would result in rather different responses. However, most dialogue systems focus on training a holistic response generation model without any distinction among different initiatives. It leads to the cross-contamination problem, where the model confuses different initiatives and generates inappropriate responses. Moreover, obtaining plenty of human annotations for initiative labels can be expensive. To address this issue, we propose a general mix-Initiative Dynamic Prefix Tuning framework (IDPT) to decouple different initiatives from the generation model, which learns initiative-aware prefixes in both supervised and unsupervised settings. Specifically, IDPT decouples initiative factors into different prefix parameters and uses the attention mechanism to adjust the selection of initiatives in guiding generation dynamically. The prefix parameters can be tuned towards accurate initiative prediction as well as mix-initiative response generation. Extensive experiments on two public dialogue datasets show that the proposed IDPT outperforms previous baselines on both automatic metrics and human evaluations. It also manages to generate appropriate responses with manipulated initiatives.
SciMRC: Multi-perspective Scientific Machine Reading Comprehension
Jun 25, 2023



Abstract:Scientific machine reading comprehension (SMRC) aims to understand scientific texts through interactions with humans by given questions. As far as we know, there is only one dataset focused on exploring full-text scientific machine reading comprehension. However, the dataset has ignored the fact that different readers may have different levels of understanding of the text, and only includes single-perspective question-answer pairs, leading to a lack of consideration of different perspectives. To tackle the above problem, we propose a novel multi-perspective SMRC dataset, called SciMRC, which includes perspectives from beginners, students and experts. Our proposed SciMRC is constructed from 741 scientific papers and 6,057 question-answer pairs. Each perspective of beginners, students and experts contains 3,306, 1,800 and 951 QA pairs, respectively. The extensive experiments on SciMRC by utilizing pre-trained models suggest the importance of considering perspectives of SMRC, and demonstrate its challenging nature for machine comprehension.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge