Huadong Wang
Distance between Relevant Information Pieces Causes Bias in Long-Context LLMs
Oct 18, 2024



Abstract:Positional bias in large language models (LLMs) hinders their ability to effectively process long inputs. A prominent example is the "lost in the middle" phenomenon, where LLMs struggle to utilize relevant information situated in the middle of the input. While prior research primarily focuses on single pieces of relevant information, real-world applications often involve multiple relevant information pieces. To bridge this gap, we present LongPiBench, a benchmark designed to assess positional bias involving multiple pieces of relevant information. Thorough experiments are conducted with five commercial and six open-source models. These experiments reveal that while most current models are robust against the "lost in the middle" issue, there exist significant biases related to the spacing of relevant information pieces. These findings highlight the importance of evaluating and reducing positional biases to advance LLM's capabilities.
Proactive Agent: Shifting LLM Agents from Reactive Responses to Active Assistance
Oct 16, 2024



Abstract:Agents powered by large language models have shown remarkable abilities in solving complex tasks. However, most agent systems remain reactive, limiting their effectiveness in scenarios requiring foresight and autonomous decision-making. In this paper, we tackle the challenge of developing proactive agents capable of anticipating and initiating tasks without explicit human instructions. We propose a novel data-driven approach for this problem. Firstly, we collect real-world human activities to generate proactive task predictions. These predictions are then labeled by human annotators as either accepted or rejected. The labeled data is used to train a reward model that simulates human judgment and serves as an automatic evaluator of the proactiveness of LLM agents. Building on this, we develop a comprehensive data generation pipeline to create a diverse dataset, ProactiveBench, containing 6,790 events. Finally, we demonstrate that fine-tuning models with the proposed ProactiveBench can significantly elicit the proactiveness of LLM agents. Experimental results show that our fine-tuned model achieves an F1-Score of 66.47% in proactively offering assistance, outperforming all open-source and close-source models. These results highlight the potential of our method in creating more proactive and effective agent systems, paving the way for future advancements in human-agent collaboration.
ProAgent: From Robotic Process Automation to Agentic Process Automation
Nov 02, 2023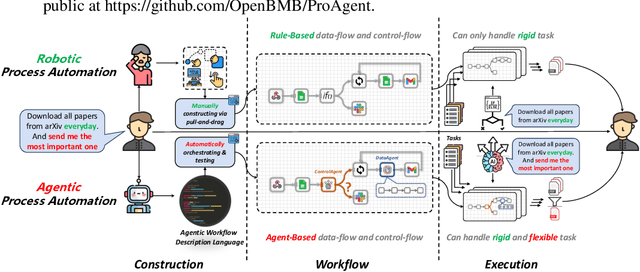
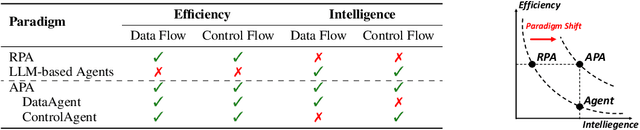
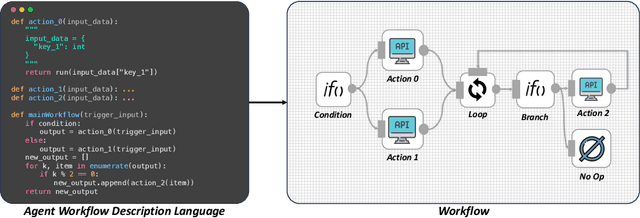
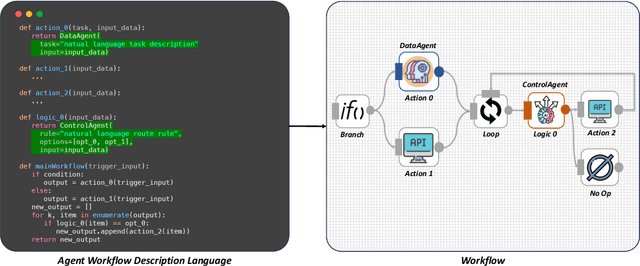
Abstract:From ancient water wheels to robotic process automation (RPA), automation technology has evolved throughout history to liberate human beings from arduous tasks. Yet, RPA struggles with tasks needing human-like intelligence, especially in elaborate design of workflow construction and dynamic decision-making in workflow execution. As Large Language Models (LLMs) have emerged human-like intelligence, this paper introduces Agentic Process Automation (APA), a groundbreaking automation paradigm using LLM-based agents for advanced automation by offloading the human labor to agents associated with construction and execution. We then instantiate ProAgent, an LLM-based agent designed to craft workflows from human instructions and make intricate decisions by coordinating specialized agents. Empirical experiments are conducted to detail its construction and execution procedure of workflow, showcasing the feasibility of APA, unveiling the possibility of a new paradigm of automation driven by agents. Our code is public at https://github.com/OpenBMB/ProAgent.
Exploring Format Consistency for Instruction Tuning
Jul 28, 2023



Abstract:Instruction tuning has emerged as a promising approach to enhancing large language models in following human instructions. It is shown that increasing the diversity and number of instructions in the training data can consistently enhance generalization performance, which facilitates a recent endeavor to collect various instructions and integrate existing instruction tuning datasets into larger collections. However, different users have their unique ways of expressing instructions, and there often exist variations across different datasets in the instruction styles and formats, i.e., format inconsistency. In this work, we study how format inconsistency may impact the performance of instruction tuning. We propose a framework called "Unified Instruction Tuning" (UIT), which calls OpenAI APIs for automatic format transfer among different instruction tuning datasets. We show that UIT successfully improves the generalization performance on unseen instructions, which highlights the importance of format consistency for instruction tuning. To make the UIT framework more practical, we further propose a novel perplexity-based denoising method to reduce the noise of automatic format transfer. We also train a smaller offline model that achieves comparable format transfer capability than OpenAI APIs to reduce costs in practice.
Won't Get Fooled Again: Answering Questions with False Premises
Jul 05, 2023



Abstract:Pre-trained language models (PLMs) have shown unprecedented potential in various fields, especially as the backbones for question-answering (QA) systems. However, they tend to be easily deceived by tricky questions such as "How many eyes does the sun have?". Such frailties of PLMs often allude to the lack of knowledge within them. In this paper, we find that the PLMs already possess the knowledge required to rebut such questions, and the key is how to activate the knowledge. To systematize this observation, we investigate the PLMs' responses to one kind of tricky questions, i.e., the false premises questions (FPQs). We annotate a FalseQA dataset containing 2365 human-written FPQs, with the corresponding explanations for the false premises and the revised true premise questions. Using FalseQA, we discover that PLMs are capable of discriminating FPQs by fine-tuning on moderate numbers (e.g., 256) of examples. PLMs also generate reasonable explanations for the false premise, which serve as rebuttals. Further replaying a few general questions during training allows PLMs to excel on FPQs and general questions simultaneously. Our work suggests that once the rebuttal ability is stimulated, knowledge inside the PLMs can be effectively utilized to handle FPQs, which incentivizes the research on PLM-based QA systems.
Plug-and-Play Knowledge Injection for Pre-trained Language Models
May 28, 2023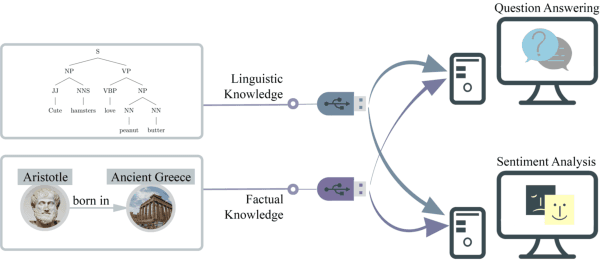
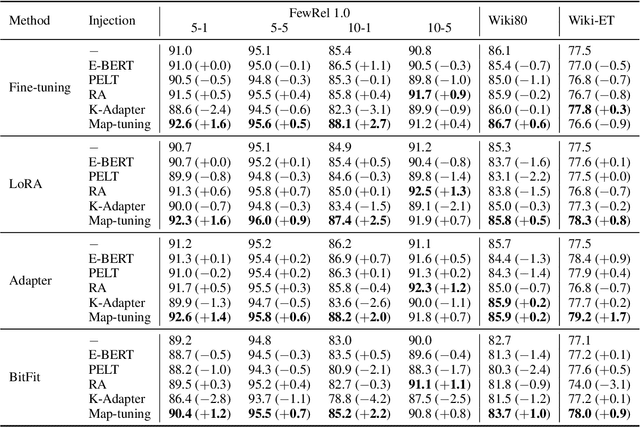
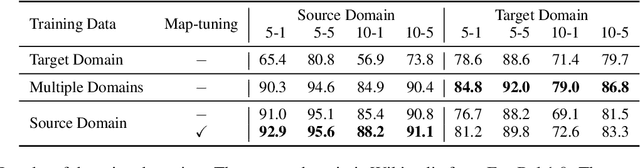
Abstract:Injecting external knowledge can improve the performance of pre-trained language models (PLMs) on various downstream NLP tasks. However, massive retraining is required to deploy new knowledge injection methods or knowledge bases for downstream tasks. In this work, we are the first to study how to improve the flexibility and efficiency of knowledge injection by reusing existing downstream models. To this end, we explore a new paradigm plug-and-play knowledge injection, where knowledge bases are injected into frozen existing downstream models by a knowledge plugin. Correspondingly, we propose a plug-and-play injection method map-tuning, which trains a mapping of knowledge embeddings to enrich model inputs with mapped embeddings while keeping model parameters frozen. Experimental results on three knowledge-driven NLP tasks show that existing injection methods are not suitable for the new paradigm, while map-tuning effectively improves the performance of downstream models. Moreover, we show that a frozen downstream model can be well adapted to different domains with different mapping networks of domain knowledge. Our code and models are available at https://github.com/THUNLP/Knowledge-Plugin.
WebCPM: Interactive Web Search for Chinese Long-form Question Answering
May 23, 2023

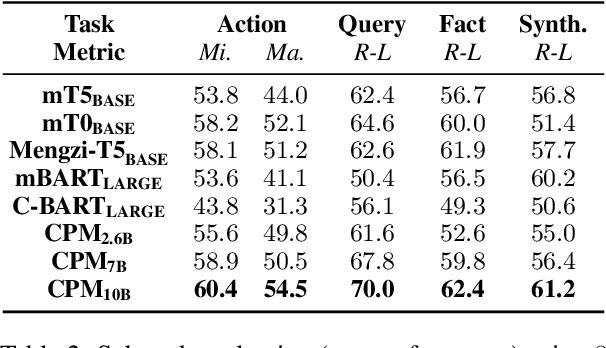

Abstract:Long-form question answering (LFQA) aims at answering complex, open-ended questions with detailed, paragraph-length responses. The de facto paradigm of LFQA necessitates two procedures: information retrieval, which searches for relevant supporting facts, and information synthesis, which integrates these facts into a coherent answer. In this paper, we introduce WebCPM, the first Chinese LFQA dataset. One unique feature of WebCPM is that its information retrieval is based on interactive web search, which engages with a search engine in real time. Following WebGPT, we develop a web search interface. We recruit annotators to search for relevant information using our interface and then answer questions. Meanwhile, the web search behaviors of our annotators would be recorded. In total, we collect 5,500 high-quality question-answer pairs, together with 14,315 supporting facts and 121,330 web search actions. We fine-tune pre-trained language models to imitate human behaviors for web search and to generate answers based on the collected facts. Our LFQA pipeline, built on these fine-tuned models, generates answers that are no worse than human-written ones in 32.5% and 47.5% of the cases on our dataset and DuReader, respectively.
Recyclable Tuning for Continual Pre-training
May 15, 2023



Abstract:Continual pre-training is the paradigm where pre-trained language models (PLMs) continually acquire fresh knowledge from growing data and gradually get upgraded. Before an upgraded PLM is released, we may have tuned the original PLM for various tasks and stored the adapted weights. However, when tuning the upgraded PLM, these outdated adapted weights will typically be ignored and discarded, causing a potential waste of resources. We bring this issue to the forefront and contend that proper algorithms for recycling outdated adapted weights should be developed. To this end, we formulate the task of recyclable tuning for continual pre-training. In pilot studies, we find that after continual pre-training, the upgraded PLM remains compatible with the outdated adapted weights to some extent. Motivated by this finding, we analyze the connection between continually pre-trained PLMs from two novel aspects, i.e., mode connectivity, and functional similarity. Based on the corresponding findings, we propose both an initialization-based method and a distillation-based method for our task. We demonstrate their feasibility in improving the convergence and performance for tuning the upgraded PLM. We also show that both methods can be combined to achieve better performance. The source codes are publicly available at https://github.com/thunlp/RecyclableTuning.
Tool Learning with Foundation Models
Apr 17, 2023Abstract:Humans possess an extraordinary ability to create and utilize tools, allowing them to overcome physical limitations and explore new frontiers. With the advent of foundation models, AI systems have the potential to be equally adept in tool use as humans. This paradigm, i.e., tool learning with foundation models, combines the strengths of specialized tools and foundation models to achieve enhanced accuracy, efficiency, and automation in problem-solving. Despite its immense potential, there is still a lack of a comprehensive understanding of key challenges, opportunities, and future endeavors in this field. To this end, we present a systematic investigation of tool learning in this paper. We first introduce the background of tool learning, including its cognitive origins, the paradigm shift of foundation models, and the complementary roles of tools and models. Then we recapitulate existing tool learning research into tool-augmented and tool-oriented learning. We formulate a general tool learning framework: starting from understanding the user instruction, models should learn to decompose a complex task into several subtasks, dynamically adjust their plan through reasoning, and effectively conquer each sub-task by selecting appropriate tools. We also discuss how to train models for improved tool-use capabilities and facilitate the generalization in tool learning. Considering the lack of a systematic tool learning evaluation in prior works, we experiment with 17 representative tools and show the potential of current foundation models in skillfully utilizing tools. Finally, we discuss several open problems that require further investigation for tool learning. Overall, we hope this paper could inspire future research in integrating tools with foundation models.
Human Emotion Knowledge Representation Emerges in Large Language Model and Supports Discrete Emotion Inference
Feb 21, 2023


Abstract:How humans infer discrete emotions is a fundamental research question in the field of psychology. While conceptual knowledge about emotions (emotion knowledge) has been suggested to be essential for emotion inference, evidence to date is mostly indirect and inconclusive. As the large language models (LLMs) have been shown to support effective representations of various human conceptual knowledge, the present study further employed artificial neurons in LLMs to investigate the mechanism of human emotion inference. With artificial neurons activated by prompts, the LLM (RoBERTa) demonstrated a similar conceptual structure of 27 discrete emotions as that of human behaviors. Furthermore, the LLM-based conceptual structure revealed a human-like reliance on 14 underlying conceptual attributes of emotions for emotion inference. Most importantly, by manipulating attribute-specific neurons, we found that the corresponding LLM's emotion inference performance deteriorated, and the performance deterioration was correlated to the effectiveness of representations of the conceptual attributes on the human side. Our findings provide direct evidence for the emergence of emotion knowledge representation in large language models and suggest its casual support for discrete emotion inference.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge