Hongda Zhang
Pheromone-Focused Ant Colony Optimization algorithm for path planning
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) is a prominent swarm intelligence algorithm extensively applied to path planning. However, traditional ACO methods often exhibit shortcomings, such as blind search behavior and slow convergence within complex environments. To address these challenges, this paper proposes the Pheromone-Focused Ant Colony Optimization (PFACO) algorithm, which introduces three key strategies to enhance the problem-solving ability of the ant colony. First, the initial pheromone distribution is concentrated in more promising regions based on the Euclidean distances of nodes to the start and end points, balancing the trade-off between exploration and exploitation. Second, promising solutions are reinforced during colony iterations to intensify pheromone deposition along high-quality paths, accelerating convergence while maintaining solution diversity. Third, a forward-looking mechanism is implemented to penalize redundant path turns, promoting smoother and more efficient solutions. These strategies collectively produce the focused pheromones to guide the ant colony's search, which enhances the global optimization capabilities of the PFACO algorithm, significantly improving convergence speed and solution quality across diverse optimization problems. The experimental results demonstrate that PFACO consistently outperforms comparative ACO algorithms in terms of convergence speed and solution quality.
AiEDA: An Open-Source AI-Aided Design Library for Design-to-Vector
Nov 08, 2025Abstract:Recent research has demonstrated that artificial intelligence (AI) can assist electronic design automation (EDA) in improving both the quality and efficiency of chip design. But current AI for EDA (AI-EDA) infrastructures remain fragmented, lacking comprehensive solutions for the entire data pipeline from design execution to AI integration. Key challenges include fragmented flow engines that generate raw data, heterogeneous file formats for data exchange, non-standardized data extraction methods, and poorly organized data storage. This work introduces a unified open-source library for EDA (AiEDA) that addresses these issues. AiEDA integrates multiple design-to-vector data representation techniques that transform diverse chip design data into universal multi-level vector representations, establishing an AI-aided design (AAD) paradigm optimized for AI-EDA workflows. AiEDA provides complete physical design flows with programmatic data extraction and standardized Python interfaces bridging EDA datasets and AI frameworks. Leveraging the AiEDA library, we generate iDATA, a 600GB dataset of structured data derived from 50 real chip designs (28nm), and validate its effectiveness through seven representative AAD tasks spanning prediction, generation, optimization and analysis. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/OSCC-Project/AiEDA, while the full iDATA dataset is being prepared for public release, providing a foundation for future AI-EDA research.
ViG3D-UNet: Volumetric Vascular Connectivity-Aware Segmentation via 3D Vision Graph Representation
Apr 18, 2025Abstract:Accurate vascular segmentation is essential for coronary visualization and the diagnosis of coronary heart disease. This task involves the extraction of sparse tree-like vascular branches from the volumetric space. However, existing methods have faced significant challenges due to discontinuous vascular segmentation and missing endpoints. To address this issue, a 3D vision graph neural network framework, named ViG3D-UNet, was introduced. This method integrates 3D graph representation and aggregation within a U-shaped architecture to facilitate continuous vascular segmentation. The ViG3D module captures volumetric vascular connectivity and topology, while the convolutional module extracts fine vascular details. These two branches are combined through channel attention to form the encoder feature. Subsequently, a paperclip-shaped offset decoder minimizes redundant computations in the sparse feature space and restores the feature map size to match the original input dimensions. To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed approach for continuous vascular segmentation, evaluations were performed on two public datasets, ASOCA and ImageCAS. The segmentation results show that the ViG3D-UNet surpassed competing methods in maintaining vascular segmentation connectivity while achieving high segmentation accuracy. Our code will be available soon.
Baichuan-M1: Pushing the Medical Capability of Large Language Models
Feb 18, 2025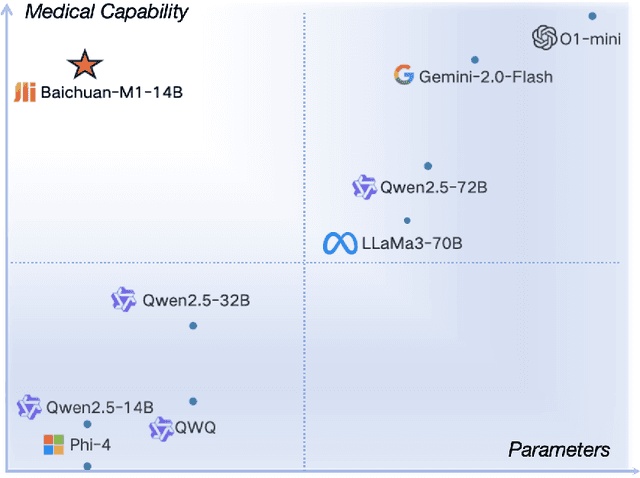
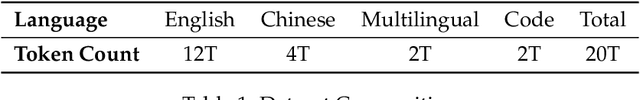
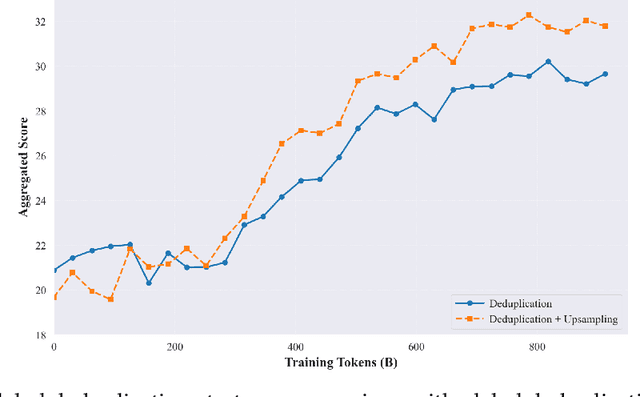
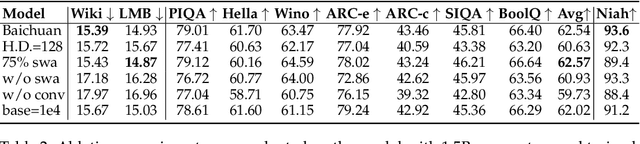
Abstract:The current generation of large language models (LLMs) is typically designed for broad, general-purpose applications, while domain-specific LLMs, especially in vertical fields like medicine, remain relatively scarce. In particular, the development of highly efficient and practical LLMs for the medical domain is challenging due to the complexity of medical knowledge and the limited availability of high-quality data. To bridge this gap, we introduce Baichuan-M1, a series of large language models specifically optimized for medical applications. Unlike traditional approaches that simply continue pretraining on existing models or apply post-training to a general base model, Baichuan-M1 is trained from scratch with a dedicated focus on enhancing medical capabilities. Our model is trained on 20 trillion tokens and incorporates a range of effective training methods that strike a balance between general capabilities and medical expertise. As a result, Baichuan-M1 not only performs strongly across general domains such as mathematics and coding but also excels in specialized medical fields. We have open-sourced Baichuan-M1-14B, a mini version of our model, which can be accessed through the following links.
Baichuan-Omni-1.5 Technical Report
Jan 26, 2025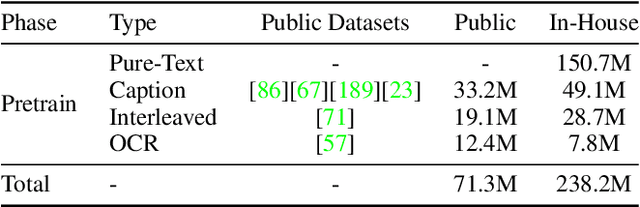
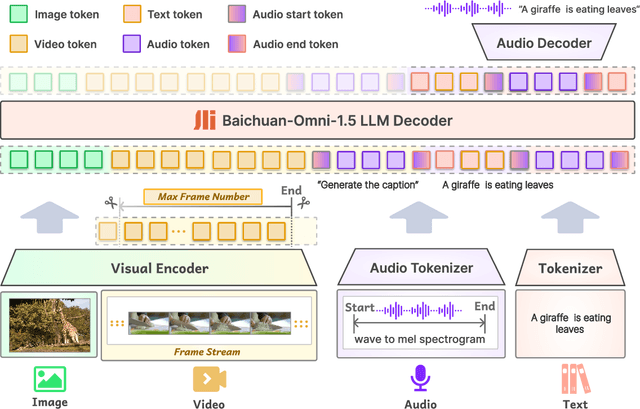
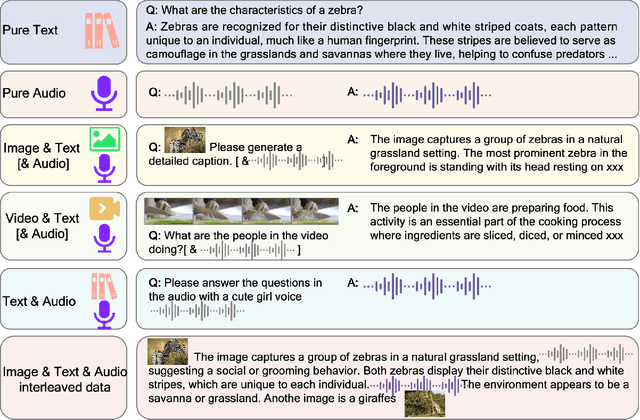
Abstract:We introduce Baichuan-Omni-1.5, an omni-modal model that not only has omni-modal understanding capabilities but also provides end-to-end audio generation capabilities. To achieve fluent and high-quality interaction across modalities without compromising the capabilities of any modality, we prioritized optimizing three key aspects. First, we establish a comprehensive data cleaning and synthesis pipeline for multimodal data, obtaining about 500B high-quality data (text, audio, and vision). Second, an audio-tokenizer (Baichuan-Audio-Tokenizer) has been designed to capture both semantic and acoustic information from audio, enabling seamless integration and enhanced compatibility with MLLM. Lastly, we designed a multi-stage training strategy that progressively integrates multimodal alignment and multitask fine-tuning, ensuring effective synergy across all modalities. Baichuan-Omni-1.5 leads contemporary models (including GPT4o-mini and MiniCPM-o 2.6) in terms of comprehensive omni-modal capabilities. Notably, it achieves results comparable to leading models such as Qwen2-VL-72B across various multimodal medical benchmarks.
CTA-Net: A CNN-Transformer Aggregation Network for Improving Multi-Scale Feature Extraction
Oct 15, 2024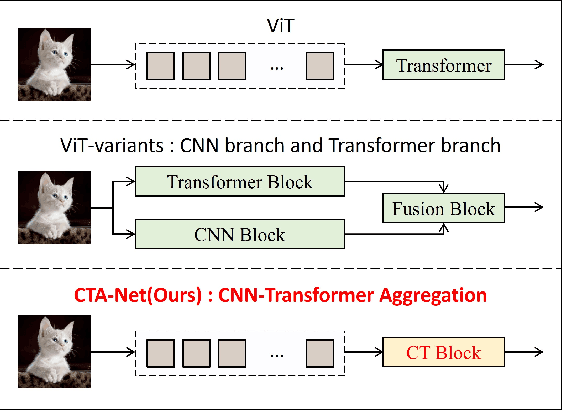
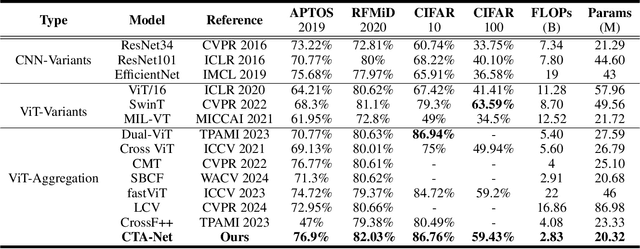
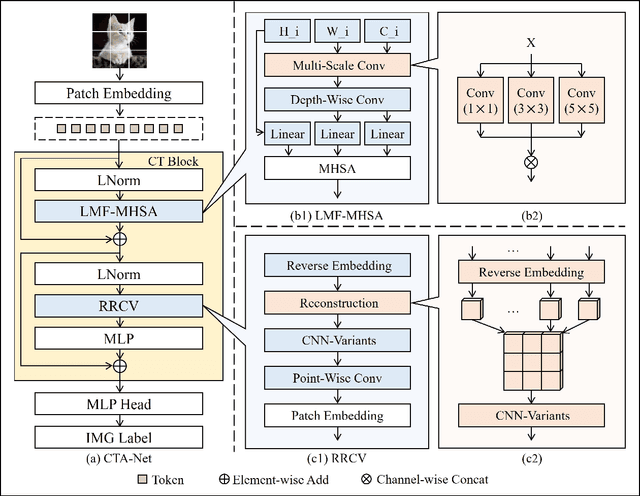
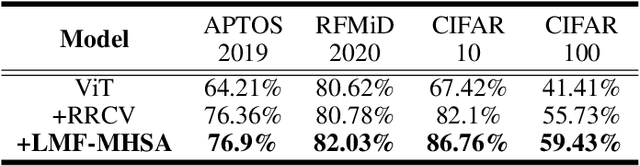
Abstract:Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and vision transformers (ViTs) have become essential in computer vision for local and global feature extraction. However, aggregating these architectures in existing methods often results in inefficiencies. To address this, the CNN-Transformer Aggregation Network (CTA-Net) was developed. CTA-Net combines CNNs and ViTs, with transformers capturing long-range dependencies and CNNs extracting localized features. This integration enables efficient processing of detailed local and broader contextual information. CTA-Net introduces the Light Weight Multi-Scale Feature Fusion Multi-Head Self-Attention (LMF-MHSA) module for effective multi-scale feature integration with reduced parameters. Additionally, the Reverse Reconstruction CNN-Variants (RRCV) module enhances the embedding of CNNs within the transformer architecture. Extensive experiments on small-scale datasets with fewer than 100,000 samples show that CTA-Net achieves superior performance (TOP-1 Acc 86.76\%), fewer parameters (20.32M), and greater efficiency (FLOPs 2.83B), making it a highly efficient and lightweight solution for visual tasks on small-scale datasets (fewer than 100,000).
Baichuan 2: Open Large-scale Language Models
Sep 20, 2023Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance on a variety of natural language tasks based on just a few examples of natural language instructions, reducing the need for extensive feature engineering. However, most powerful LLMs are closed-source or limited in their capability for languages other than English. In this technical report, we present Baichuan 2, a series of large-scale multilingual language models containing 7 billion and 13 billion parameters, trained from scratch, on 2.6 trillion tokens. Baichuan 2 matches or outperforms other open-source models of similar size on public benchmarks like MMLU, CMMLU, GSM8K, and HumanEval. Furthermore, Baichuan 2 excels in vertical domains such as medicine and law. We will release all pre-training model checkpoints to benefit the research community in better understanding the training dynamics of Baichuan 2.
MRS-VPR: a multi-resolution sampling based global visual place recognition method
Feb 26, 2019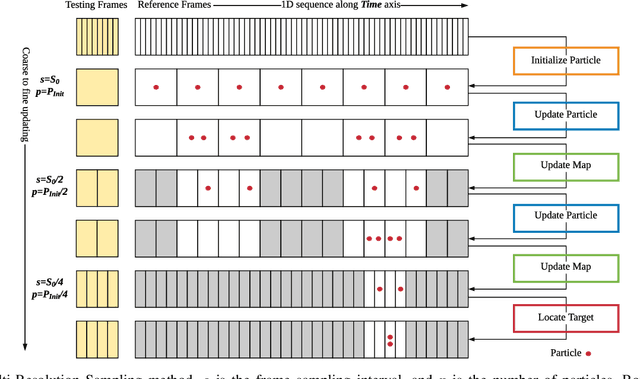
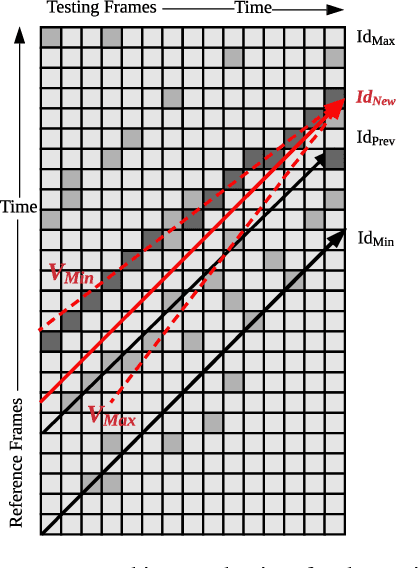
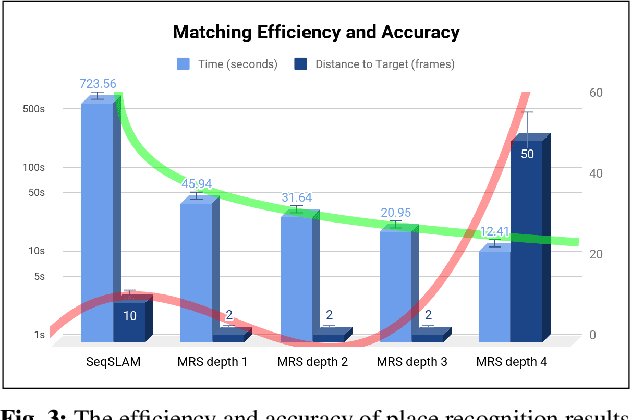
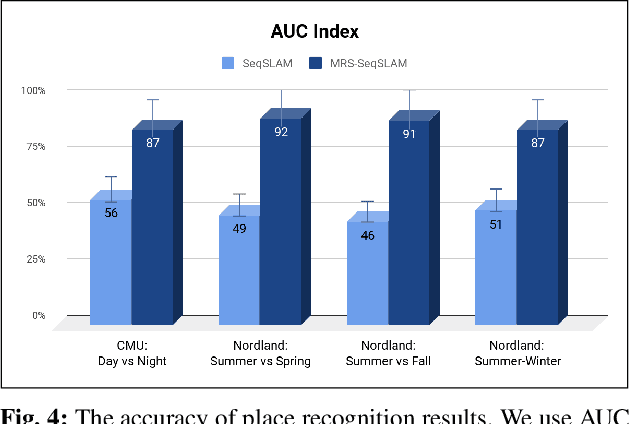
Abstract:Place recognition and loop closure detection are challenging for long-term visual navigation tasks. SeqSLAM is considered to be one of the most successful approaches to achieving long-term localization under varying environmental conditions and changing viewpoints. It depends on a brute-force, time-consuming sequential matching method. We propose MRS-VPR, a multi-resolution, sampling-based place recognition method, which can significantly improve the matching efficiency and accuracy in sequential matching. The novelty of this method lies in the coarse-to-fine searching pipeline and a particle filter-based global sampling scheme, that can balance the matching efficiency and accuracy in the long-term navigation task. Moreover, our model works much better than SeqSLAM when the testing sequence has a much smaller scale than the reference sequence. Our experiments demonstrate that the proposed method is efficient in locating short temporary trajectories within long-term reference ones without losing accuracy compared to SeqSLAM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge