Jiacheng Yang
StreamFusion: Scalable Sequence Parallelism for Distributed Inference of Diffusion Transformers on GPUs
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Diffusion Transformers (DiTs) have gained increasing adoption in high-quality image and video generation. As demand for higher-resolution images and longer videos increases, single-GPU inference becomes inefficient due to increased latency and large activation sizes. Current frameworks employ sequence parallelism (SP) techniques such as Ulysses Attention and Ring Attention to scale inference. However, these implementations have three primary limitations: (1) suboptimal communication patterns for network topologies on modern GPU machines, (2) latency bottlenecks from all-to-all operations in inter-machine communication, and (3) GPU sender-receiver synchronization and computation overheads from using two-sided communication libraries. To address these issues, we present StreamFusion, a topology-aware efficient DiT serving engine. StreamFusion incorporates three key innovations: (1) a topology-aware sequence parallelism technique that accounts for inter- and intra-machine bandwidth differences, (2) Torus Attention, a novel SP technique enabling overlapping of inter-machine all-to-all operations with computation, and (3) a one-sided communication implementation that minimizes GPU sender-receiver synchronization and computation overheads. Our experiments demonstrate that StreamFusion outperforms the state-of-the-art approach by an average of $1.35\times$ (up to $1.77\times$).
FUSE-RSVLM: Feature Fusion Vision-Language Model for Remote Sensing
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Large vision-language models (VLMs) exhibit strong performance across various tasks. However, these VLMs encounter significant challenges when applied to the remote sensing domain due to the inherent differences between remote sensing images and natural images. Existing remote sensing VLMs often fail to extract fine-grained visual features and suffer from visual forgetting during deep language processing. To address this, we introduce MF-RSVLM, a Multi-Feature Fusion Remote Sensing Vision--Language Model that effectively extracts and fuses visual features for RS understanding. MF-RSVLM learns multi-scale visual representations and combines global context with local details, improving the capture of small and complex structures in RS scenes. A recurrent visual feature injection scheme ensures the language model remains grounded in visual evidence and reduces visual forgetting during generation. Extensive experiments on diverse RS benchmarks show that MF-RSVLM achieves state-of-the-art or highly competitive performance across remote sensing classification, image captioning, and VQA tasks. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/Yunkaidang/RSVLM.
A Benchmark for Ultra-High-Resolution Remote Sensing MLLMs
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) demonstrate strong perception and reasoning performance on existing remote sensing (RS) benchmarks. However, most prior benchmarks rely on low-resolution imagery, and some high-resolution benchmarks suffer from flawed reasoning-task designs. We show that text-only LLMs can perform competitively with multimodal vision-language models on RS reasoning tasks without access to images, revealing a critical mismatch between current benchmarks and the intended evaluation of visual understanding. To enable faithful assessment, we introduce RSHR-Bench, a super-high-resolution benchmark for RS visual understanding and reasoning. RSHR-Bench contains 5,329 full-scene images with a long side of at least 4,000 pixels, with up to about 3 x 10^8 pixels per image, sourced from widely used RS corpora and UAV collections. We design four task families: multiple-choice VQA, open-ended VQA, image captioning, and single-image evaluation. These tasks cover nine perception categories and four reasoning types, supporting multi-turn and multi-image dialog. To reduce reliance on language priors, we apply adversarial filtering with strong LLMs followed by rigorous human verification. Overall, we construct 3,864 VQA tasks, 3,913 image captioning tasks, and 500 fully human-written or verified single-image evaluation VQA pairs. Evaluations across open-source, closed-source, and RS-specific VLMs reveal persistent performance gaps in super-high-resolution scenarios. Code: https://github.com/Yunkaidang/RSHR
Static Batching of Irregular Workloads on GPUs: Framework and Application to Efficient MoE Model Inference
Jan 27, 2025
Abstract:It has long been a problem to arrange and execute irregular workloads on massively parallel devices. We propose a general framework for statically batching irregular workloads into a single kernel with a runtime task mapping mechanism on GPUs. We further apply this framework to Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model inference and implement an optimized and efficient CUDA kernel. Our MoE kernel achieves up to 91% of the peak Tensor Core throughput on NVIDIA H800 GPU and 95% on NVIDIA H20 GPU.
CTA-Net: A CNN-Transformer Aggregation Network for Improving Multi-Scale Feature Extraction
Oct 15, 2024
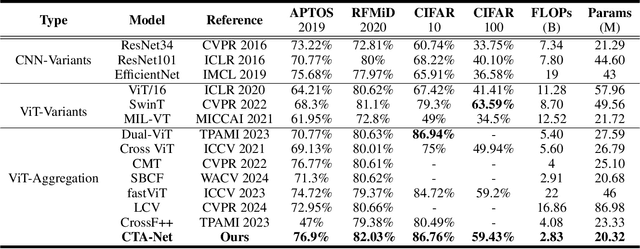
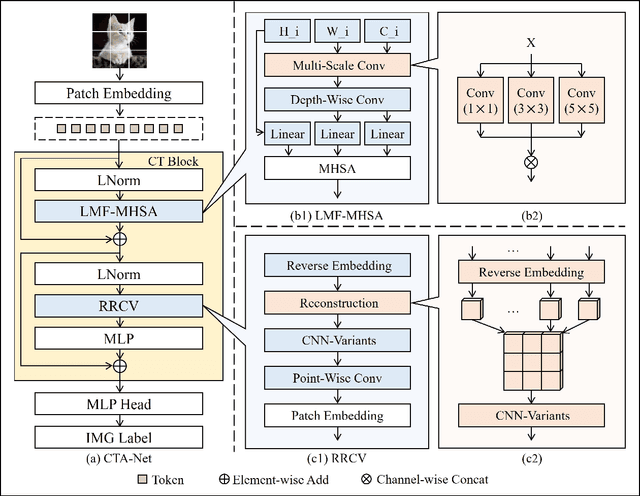
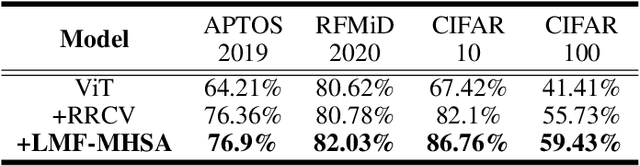
Abstract:Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and vision transformers (ViTs) have become essential in computer vision for local and global feature extraction. However, aggregating these architectures in existing methods often results in inefficiencies. To address this, the CNN-Transformer Aggregation Network (CTA-Net) was developed. CTA-Net combines CNNs and ViTs, with transformers capturing long-range dependencies and CNNs extracting localized features. This integration enables efficient processing of detailed local and broader contextual information. CTA-Net introduces the Light Weight Multi-Scale Feature Fusion Multi-Head Self-Attention (LMF-MHSA) module for effective multi-scale feature integration with reduced parameters. Additionally, the Reverse Reconstruction CNN-Variants (RRCV) module enhances the embedding of CNNs within the transformer architecture. Extensive experiments on small-scale datasets with fewer than 100,000 samples show that CTA-Net achieves superior performance (TOP-1 Acc 86.76\%), fewer parameters (20.32M), and greater efficiency (FLOPs 2.83B), making it a highly efficient and lightweight solution for visual tasks on small-scale datasets (fewer than 100,000).
Accelerating Graph Neural Networks on Real Processing-In-Memory Systems
Feb 26, 2024



Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) are emerging ML models to analyze graph-structure data. Graph Neural Network (GNN) execution involves both compute-intensive and memory-intensive kernels, the latter dominates the total time, being significantly bottlenecked by data movement between memory and processors. Processing-In-Memory (PIM) systems can alleviate this data movement bottleneck by placing simple processors near or inside to memory arrays. In this work, we introduce PyGim, an efficient ML framework that accelerates GNNs on real PIM systems. We propose intelligent parallelization techniques for memory-intensive kernels of GNNs tailored for real PIM systems, and develop handy Python API for them. We provide hybrid GNN execution, in which the compute-intensive and memory-intensive kernels are executed in processor-centric and memory-centric computing systems, respectively, to match their algorithmic nature. We extensively evaluate PyGim on a real-world PIM system with 1992 PIM cores using emerging GNN models, and demonstrate that it outperforms its state-of-the-art CPU counterpart on Intel Xeon by on average 3.04x, and achieves higher resource utilization than CPU and GPU systems. Our work provides useful recommendations for software, system and hardware designers. PyGim will be open-sourced to enable the widespread use of PIM systems in GNNs.
LOGEN: Few-shot Logical Knowledge-Conditioned Text Generation with Self-training
Dec 02, 2021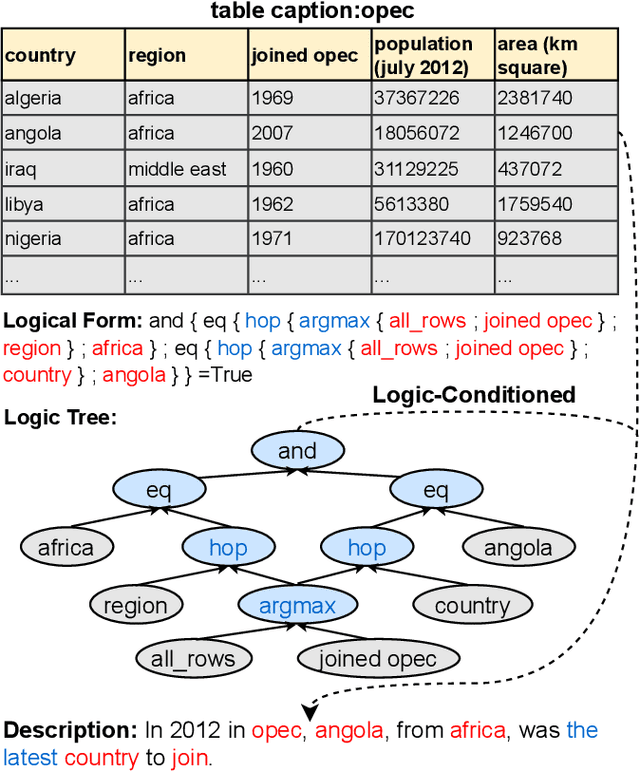
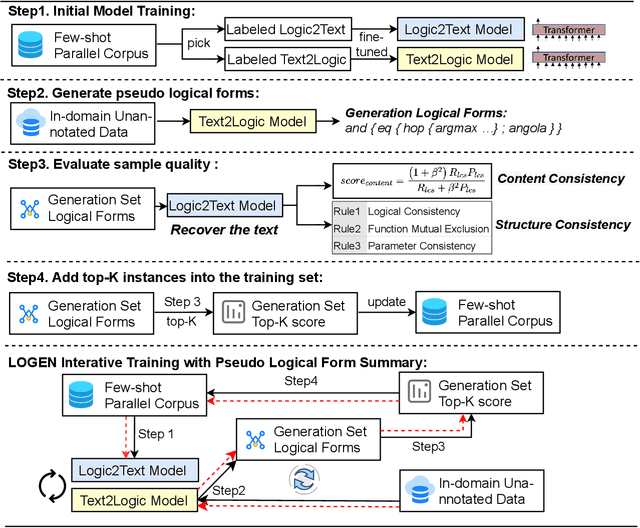
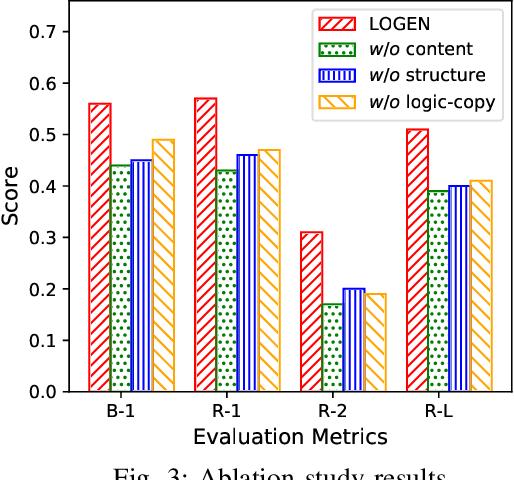
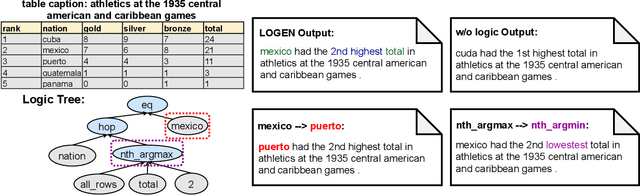
Abstract:Natural language generation from structured data mainly focuses on surface-level descriptions, suffering from uncontrollable content selection and low fidelity. Previous works leverage logical forms to facilitate logical knowledge-conditioned text generation. Though achieving remarkable progress, they are data-hungry, which makes the adoption for real-world applications challenging with limited data. To this end, this paper proposes a unified framework for logical knowledge-conditioned text generation in the few-shot setting. With only a few seeds logical forms (e.g., 20/100 shot), our approach leverages self-training and samples pseudo logical forms based on content and structure consistency. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach can obtain better few-shot performance than baselines.
GCN-RL Circuit Designer: Transferable Transistor Sizing with Graph Neural Networks and Reinforcement Learning
Apr 30, 2020



Abstract:Automatic transistor sizing is a challenging problem in circuit design due to the large design space, complex performance trade-offs, and fast technological advancements. Although there has been plenty of work on transistor sizing targeting on one circuit, limited research has been done on transferring the knowledge from one circuit to another to reduce the re-design overhead. In this paper, we present GCN-RL Circuit Designer, leveraging reinforcement learning (RL) to transfer the knowledge between different technology nodes and topologies. Moreover, inspired by the simple fact that circuit is a graph, we learn on the circuit topology representation with graph convolutional neural networks (GCN). The GCN-RL agent extracts features of the topology graph whose vertices are transistors, edges are wires. Our learning-based optimization consistently achieves the highest Figures of Merit (FoM) on four different circuits compared with conventional black-box optimization methods (Bayesian Optimization, Evolutionary Algorithms), random search, and human expert designs. Experiments on transfer learning between five technology nodes and two circuit topologies demonstrate that RL with transfer learning can achieve much higher FoMs than methods without knowledge transfer. Our transferable optimization method makes transistor sizing and design porting more effective and efficient.
Towards Making the Most of BERT in Neural Machine Translation
Aug 30, 2019



Abstract:GPT-2 and BERT demonstrate the effectiveness of using pre-trained language models (LMs) on various natural language processing tasks. However, LM fine-tuning often suffers from catastrophic forgetting when applied to resource-rich tasks. In this work, we introduce a concerted training framework (\method) that is the key to integrate the pre-trained LMs to neural machine translation (NMT). Our proposed Cnmt consists of three techniques: a) asymptotic distillation to ensure that the NMT model can retain the previous pre-trained knowledge; \item a dynamic switching gate to avoid catastrophic forgetting of pre-trained knowledge; and b)a strategy to adjust the learning paces according to a scheduled policy. Our experiments in machine translation show \method gains of up to 3 BLEU score on the WMT14 English-German language pair which even surpasses the previous state-of-the-art pre-training aided NMT by 1.4 BLEU score. While for the large WMT14 English-French task with 40 millions of sentence-pairs, our base model still significantly improves upon the state-of-the-art Transformer big model by more than 1 BLEU score.
Learning to Design Circuits
Jan 17, 2019



Abstract:Analog IC design relies on human experts to search for parameters that satisfy circuit specifications with their experience and intuitions, which is highly labor intensive, time consuming and suboptimal. Machine learning is a promising tool to automate this process. However, supervised learning is difficult for this task due to the low availability of training data: 1) Circuit simulation is slow, thus generating large-scale dataset is time-consuming; 2) Most circuit designs are propitiatory IPs within individual IC companies, making it expensive to collect large-scale datasets. We propose Learning to Design Circuits (L2DC) to leverage reinforcement learning that learns to efficiently generate new circuits data and to optimize circuits. We fix the schematic, and optimize the parameters of the transistors automatically by training an RL agent with no prior knowledge about optimizing circuits. After iteratively getting observations, generating a new set of transistor parameters, getting a reward, and adjusting the model, L2DC is able to optimize circuits. We evaluate L2DC on two transimpedance amplifiers. Trained for a day, our RL agent can achieve comparable or better performance than human experts trained for a quarter. It first learns to meet hard-constraints (eg. gain, bandwidth), and then learns to optimize good-to-have targets (eg. area, power). Compared with grid search-aided human design, L2DC can achieve $\mathbf{250}\boldsymbol{\times}$ higher sample efficiency with comparable performance. Under the same runtime constraint, the performance of L2DC is also better than Bayesian Optimization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge