Chunlei Meng
NeuroPareto: Calibrated Acquisition for Costly Many-Goal Search in Vast Parameter Spaces
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:The pursuit of optimal trade-offs in high-dimensional search spaces under stringent computational constraints poses a fundamental challenge for contemporary multi-objective optimization. We develop NeuroPareto, a cohesive architecture that integrates rank-centric filtering, uncertainty disentanglement, and history-conditioned acquisition strategies to navigate complex objective landscapes. A calibrated Bayesian classifier estimates epistemic uncertainty across non-domination tiers, enabling rapid generation of high-quality candidates with minimal evaluation cost. Deep Gaussian Process surrogates further separate predictive uncertainty into reducible and irreducible components, providing refined predictive means and risk-aware signals for downstream selection. A lightweight acquisition network, trained online from historical hypervolume improvements, guides expensive evaluations toward regions balancing convergence and diversity. With hierarchical screening and amortized surrogate updates, the method maintains accuracy while keeping computational overhead low. Experiments on DTLZ and ZDT suites and a subsurface energy extraction task show that NeuroPareto consistently outperforms classifier-enhanced and surrogate-assisted baselines in Pareto proximity and hypervolume.
SwiftRepertoire: Few-Shot Immune-Signature Synthesis via Dynamic Kernel Codes
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Repertoire-level analysis of T cell receptors offers a biologically grounded signal for disease detection and immune monitoring, yet practical deployment is impeded by label sparsity, cohort heterogeneity, and the computational burden of adapting large encoders to new tasks. We introduce a framework that synthesizes compact task-specific parameterizations from a learned dictionary of prototypes conditioned on lightweight task descriptors derived from repertoire probes and pooled embedding statistics. This synthesis produces small adapter modules applied to a frozen pretrained backbone, enabling immediate adaptation to novel tasks with only a handful of support examples and without full model fine-tuning. The architecture preserves interpretability through motif-aware probes and a calibrated motif discovery pipeline that links predictive decisions to sequence-level signals. Together, these components yield a practical, sample-efficient, and interpretable pathway for translating repertoire-informed models into diverse clinical and research settings where labeled data are scarce and computational resources are constrained.
Temporal-Spatial Decouple before Act: Disentangled Representation Learning for Multimodal Sentiment Analysis
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Multimodal Sentiment Analysis integrates Linguistic, Visual, and Acoustic. Mainstream approaches based on modality-invariant and modality-specific factorization or on complex fusion still rely on spatiotemporal mixed modeling. This ignores spatiotemporal heterogeneity, leading to spatiotemporal information asymmetry and thus limited performance. Hence, we propose TSDA, Temporal-Spatial Decouple before Act, which explicitly decouples each modality into temporal dynamics and spatial structural context before any interaction. For every modality, a temporal encoder and a spatial encoder project signals into separate temporal and spatial body. Factor-Consistent Cross-Modal Alignment then aligns temporal features only with their temporal counterparts across modalities, and spatial features only with their spatial counterparts. Factor specific supervision and decorrelation regularization reduce cross factor leakage while preserving complementarity. A Gated Recouple module subsequently recouples the aligned streams for task. Extensive experiments show that TSDA outperforms baselines. Ablation analysis studies confirm the necessity and interpretability of the design.
QuantEval: A Benchmark for Financial Quantitative Tasks in Large Language Models
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown strong capabilities across many domains, yet their evaluation in financial quantitative tasks remains fragmented and mostly limited to knowledge-centric question answering. We introduce QuantEval, a benchmark that evaluates LLMs across three essential dimensions of quantitative finance: knowledge-based QA, quantitative mathematical reasoning, and quantitative strategy coding. Unlike prior financial benchmarks, QuantEval integrates a CTA-style backtesting framework that executes model-generated strategies and evaluates them using financial performance metrics, enabling a more realistic assessment of quantitative coding ability. We evaluate some state-of-the-art open-source and proprietary LLMs and observe substantial gaps to human experts, particularly in reasoning and strategy coding. Finally, we conduct large-scale supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning experiments on domain-aligned data, demonstrating consistent improvements. We hope QuantEval will facilitate research on LLMs' quantitative finance capabilities and accelerate their practical adoption in real-world trading workflows. We additionally release the full deterministic backtesting configuration (asset universe, cost model, and metric definitions) to ensure strict reproducibility.
How Order-Sensitive Are LLMs? OrderProbe for Deterministic Structural Reconstruction
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) excel at semantic understanding, yet their ability to reconstruct internal structure from scrambled inputs remains underexplored. Sentence-level restoration is ill-posed for automated evaluation because multiple valid word orders often exist. We introduce OrderProbe, a deterministic benchmark for structural reconstruction using fixed four-character expressions in Chinese, Japanese, and Korean, which have a unique canonical order and thus support exact-match scoring. We further propose a diagnostic framework that evaluates models beyond recovery accuracy, including semantic fidelity, logical validity, consistency, robustness sensitivity, and information density. Experiments on twelve widely used LLMs show that structural reconstruction remains difficult even for frontier systems: zero-shot recovery frequently falls below 35%. We also observe a consistent dissociation between semantic recall and structural planning, suggesting that structural robustness is not an automatic byproduct of semantic competence.
DIVER: Dynamic Iterative Visual Evidence Reasoning for Multimodal Fake News Detection
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Multimodal fake news detection is crucial for mitigating adversarial misinformation. Existing methods, relying on static fusion or LLMs, face computational redundancy and hallucination risks due to weak visual foundations. To address this, we propose DIVER (Dynamic Iterative Visual Evidence Reasoning), a framework grounded in a progressive, evidence-driven reasoning paradigm. DIVER first establishes a strong text-based baseline through language analysis, leveraging intra-modal consistency to filter unreliable or hallucinated claims. Only when textual evidence is insufficient does the framework introduce visual information, where inter-modal alignment verification adaptively determines whether deeper visual inspection is necessary. For samples exhibiting significant cross-modal semantic discrepancies, DIVER selectively invokes fine-grained visual tools (e.g., OCR and dense captioning) to extract task-relevant evidence, which is iteratively aggregated via uncertainty-aware fusion to refine multimodal reasoning. Experiments on Weibo, Weibo21, and GossipCop demonstrate that DIVER outperforms state-of-the-art baselines by an average of 2.72\%, while optimizing inference efficiency with a reduced latency of 4.12 s.
Pheromone-Focused Ant Colony Optimization algorithm for path planning
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) is a prominent swarm intelligence algorithm extensively applied to path planning. However, traditional ACO methods often exhibit shortcomings, such as blind search behavior and slow convergence within complex environments. To address these challenges, this paper proposes the Pheromone-Focused Ant Colony Optimization (PFACO) algorithm, which introduces three key strategies to enhance the problem-solving ability of the ant colony. First, the initial pheromone distribution is concentrated in more promising regions based on the Euclidean distances of nodes to the start and end points, balancing the trade-off between exploration and exploitation. Second, promising solutions are reinforced during colony iterations to intensify pheromone deposition along high-quality paths, accelerating convergence while maintaining solution diversity. Third, a forward-looking mechanism is implemented to penalize redundant path turns, promoting smoother and more efficient solutions. These strategies collectively produce the focused pheromones to guide the ant colony's search, which enhances the global optimization capabilities of the PFACO algorithm, significantly improving convergence speed and solution quality across diverse optimization problems. The experimental results demonstrate that PFACO consistently outperforms comparative ACO algorithms in terms of convergence speed and solution quality.
ViG3D-UNet: Volumetric Vascular Connectivity-Aware Segmentation via 3D Vision Graph Representation
Apr 18, 2025Abstract:Accurate vascular segmentation is essential for coronary visualization and the diagnosis of coronary heart disease. This task involves the extraction of sparse tree-like vascular branches from the volumetric space. However, existing methods have faced significant challenges due to discontinuous vascular segmentation and missing endpoints. To address this issue, a 3D vision graph neural network framework, named ViG3D-UNet, was introduced. This method integrates 3D graph representation and aggregation within a U-shaped architecture to facilitate continuous vascular segmentation. The ViG3D module captures volumetric vascular connectivity and topology, while the convolutional module extracts fine vascular details. These two branches are combined through channel attention to form the encoder feature. Subsequently, a paperclip-shaped offset decoder minimizes redundant computations in the sparse feature space and restores the feature map size to match the original input dimensions. To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed approach for continuous vascular segmentation, evaluations were performed on two public datasets, ASOCA and ImageCAS. The segmentation results show that the ViG3D-UNet surpassed competing methods in maintaining vascular segmentation connectivity while achieving high segmentation accuracy. Our code will be available soon.
CTA-Net: A CNN-Transformer Aggregation Network for Improving Multi-Scale Feature Extraction
Oct 15, 2024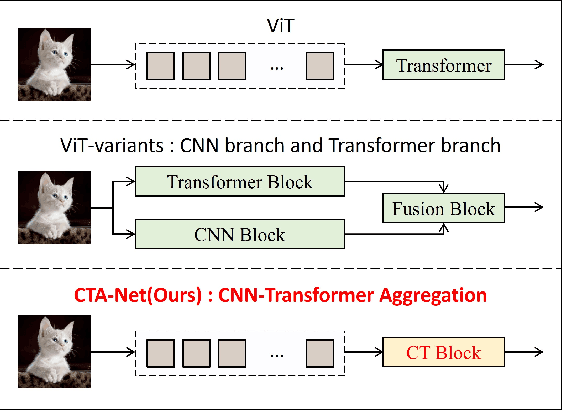
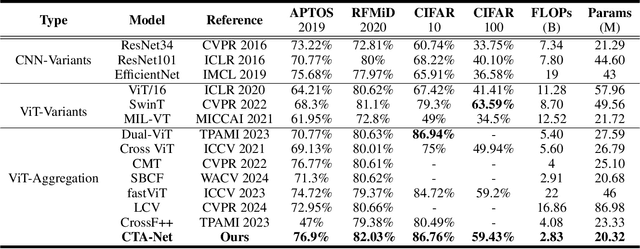
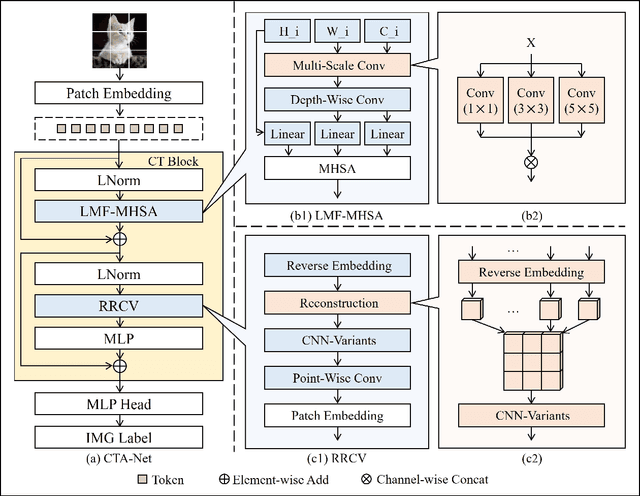
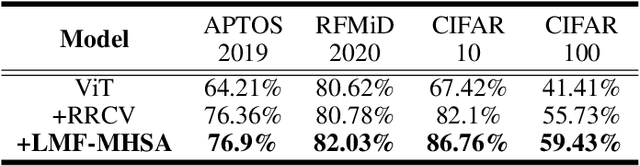
Abstract:Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and vision transformers (ViTs) have become essential in computer vision for local and global feature extraction. However, aggregating these architectures in existing methods often results in inefficiencies. To address this, the CNN-Transformer Aggregation Network (CTA-Net) was developed. CTA-Net combines CNNs and ViTs, with transformers capturing long-range dependencies and CNNs extracting localized features. This integration enables efficient processing of detailed local and broader contextual information. CTA-Net introduces the Light Weight Multi-Scale Feature Fusion Multi-Head Self-Attention (LMF-MHSA) module for effective multi-scale feature integration with reduced parameters. Additionally, the Reverse Reconstruction CNN-Variants (RRCV) module enhances the embedding of CNNs within the transformer architecture. Extensive experiments on small-scale datasets with fewer than 100,000 samples show that CTA-Net achieves superior performance (TOP-1 Acc 86.76\%), fewer parameters (20.32M), and greater efficiency (FLOPs 2.83B), making it a highly efficient and lightweight solution for visual tasks on small-scale datasets (fewer than 100,000).
A physics-constrained machine learning method for mapping gapless land surface temperature
Jul 03, 2023Abstract:More accurate, spatio-temporally, and physically consistent LST estimation has been a main interest in Earth system research. Developing physics-driven mechanism models and data-driven machine learning (ML) models are two major paradigms for gapless LST estimation, which have their respective advantages and disadvantages. In this paper, a physics-constrained ML model, which combines the strengths in the mechanism model and ML model, is proposed to generate gapless LST with physical meanings and high accuracy. The hybrid model employs ML as the primary architecture, under which the input variable physical constraints are incorporated to enhance the interpretability and extrapolation ability of the model. Specifically, the light gradient-boosting machine (LGBM) model, which uses only remote sensing data as input, serves as the pure ML model. Physical constraints (PCs) are coupled by further incorporating key Community Land Model (CLM) forcing data (cause) and CLM simulation data (effect) as inputs into the LGBM model. This integration forms the PC-LGBM model, which incorporates surface energy balance (SEB) constraints underlying the data in CLM-LST modeling within a biophysical framework. Compared with a pure physical method and pure ML methods, the PC-LGBM model improves the prediction accuracy and physical interpretability of LST. It also demonstrates a good extrapolation ability for the responses to extreme weather cases, suggesting that the PC-LGBM model enables not only empirical learning from data but also rationally derived from theory. The proposed method represents an innovative way to map accurate and physically interpretable gapless LST, and could provide insights to accelerate knowledge discovery in land surface processes and data mining in geographical parameter estimation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge