Huanfeng Shen
Weakly Supervised Cloud Detection Combining Spectral Features and Multi-Scale Deep Network
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:Clouds significantly affect the quality of optical satellite images, which seriously limits their precise application. Recently, deep learning has been widely applied to cloud detection and has achieved satisfactory results. However, the lack of distinctive features in thin clouds and the low quality of training samples limit the cloud detection accuracy of deep learning methods, leaving space for further improvements. In this paper, we propose a weakly supervised cloud detection method that combines spectral features and multi-scale scene-level deep network (SpecMCD) to obtain highly accurate pixel-level cloud masks. The method first utilizes a progressive training framework with a multi-scale scene-level dataset to train the multi-scale scene-level cloud detection network. Pixel-level cloud probability maps are then obtained by combining the multi-scale probability maps and cloud thickness map based on the characteristics of clouds in dense cloud coverage and large cloud-area coverage images. Finally, adaptive thresholds are generated based on the differentiated regions of the scene-level cloud masks at different scales and combined with distance-weighted optimization to obtain binary cloud masks. Two datasets, WDCD and GF1MS-WHU, comprising a total of 60 Gaofen-1 multispectral (GF1-MS) images, were used to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method. Compared to the other weakly supervised cloud detection methods such as WDCD and WSFNet, the F1-score of the proposed SpecMCD method shows an improvement of over 7.82%, highlighting the superiority and potential of the SpecMCD method for cloud detection under different cloud coverage conditions.
High-Resolution Global Land Surface Temperature Retrieval via a Coupled Mechanism-Machine Learning Framework
Sep 05, 2025Abstract:Land surface temperature (LST) is vital for land-atmosphere interactions and climate processes. Accurate LST retrieval remains challenging under heterogeneous land cover and extreme atmospheric conditions. Traditional split window (SW) algorithms show biases in humid environments; purely machine learning (ML) methods lack interpretability and generalize poorly with limited data. We propose a coupled mechanism model-ML (MM-ML) framework integrating physical constraints with data-driven learning for robust LST retrieval. Our approach fuses radiative transfer modeling with data components, uses MODTRAN simulations with global atmospheric profiles, and employs physics-constrained optimization. Validation against 4,450 observations from 29 global sites shows MM-ML achieves MAE=1.84K, RMSE=2.55K, and R-squared=0.966, outperforming conventional methods. Under extreme conditions, MM-ML reduces errors by over 50%. Sensitivity analysis indicates LST estimates are most sensitive to sensor radiance, then water vapor, and less to emissivity, with MM-ML showing superior stability. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of our coupled modeling strategy for retrieving geophysical parameters. The MM-ML framework combines physical interpretability with nonlinear modeling capacity, enabling reliable LST retrieval in complex environments and supporting climate monitoring and ecosystem studies.
A Mechanism-Learning Deeply Coupled Model for Remote Sensing Retrieval of Global Land Surface Temperature
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:Land surface temperature (LST) retrieval from remote sensing data is pivotal for analyzing climate processes and surface energy budgets. However, LST retrieval is an ill-posed inverse problem, which becomes particularly severe when only a single band is available. In this paper, we propose a deeply coupled framework integrating mechanistic modeling and machine learning to enhance the accuracy and generalizability of single-channel LST retrieval. Training samples are generated using a physically-based radiative transfer model and a global collection of 5810 atmospheric profiles. A physics-informed machine learning framework is proposed to systematically incorporate the first principles from classical physical inversion models into the learning workflow, with optimization constrained by radiative transfer equations. Global validation demonstrated a 30% reduction in root-mean-square error versus standalone methods. Under extreme humidity, the mean absolute error decreased from 4.87 K to 2.29 K (53% improvement). Continental-scale tests across five continents confirmed the superior generalizability of this model.
Super-Resolution for Remote Sensing Imagery via the Coupling of a Variational Model and Deep Learning
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:Image super-resolution (SR) is an effective way to enhance the spatial resolution and detail information of remote sensing images, to obtain a superior visual quality. As SR is severely ill-conditioned, effective image priors are necessary to regularize the solution space and generate the corresponding high-resolution (HR) image. In this paper, we propose a novel gradient-guided multi-frame super-resolution (MFSR) framework for remote sensing imagery reconstruction. The framework integrates a learned gradient prior as the regularization term into a model-based optimization method. Specifically, the local gradient regularization (LGR) prior is derived from the deep residual attention network (DRAN) through gradient profile transformation. The non-local total variation (NLTV) prior is characterized using the spatial structure similarity of the gradient patches with the maximum a posteriori (MAP) model. The modeled prior performs well in preserving edge smoothness and suppressing visual artifacts, while the learned prior is effective in enhancing sharp edges and recovering fine structures. By incorporating the two complementary priors into an adaptive norm based reconstruction framework, the mixed L1 and L2 regularization minimization problem is optimized to achieve the required HR remote sensing image. Extensive experimental results on remote sensing data demonstrate that the proposed method can produce visually pleasant images and is superior to several of the state-of-the-art SR algorithms in terms of the quantitative evaluation.
A Single-Frame and Multi-Frame Cascaded Image Super-Resolution Method
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:The objective of image super-resolution is to reconstruct a high-resolution (HR) image with the prior knowledge from one or several low-resolution (LR) images. However, in the real world, due to the limited complementary information, the performance of both single-frame and multi-frame super-resolution reconstruction degrades rapidly as the magnification increases. In this paper, we propose a novel two-step image super resolution method concatenating multi-frame super-resolution (MFSR) with single-frame super-resolution (SFSR), to progressively upsample images to the desired resolution. The proposed method consisting of an L0-norm constrained reconstruction scheme and an enhanced residual back-projection network, integrating the flexibility of the variational modelbased method and the feature learning capacity of the deep learning-based method. To verify the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm, extensive experiments with both simulated and real world sequences were implemented. The experimental results show that the proposed method yields superior performance in both objective and perceptual quality measurements. The average PSNRs of the cascade model in set5 and set14 are 33.413 dB and 29.658 dB respectively, which are 0.76 dB and 0.621 dB more than the baseline method. In addition, the experiment indicates that this cascade model can be robustly applied to different SFSR and MFSR methods.
* 20 pages, 13 figures
PGCS: Physical Law embedded Generative Cloud Synthesis in Remote Sensing Images
Oct 22, 2024



Abstract:Data quantity and quality are both critical for information extraction and analyzation in remote sensing. However, the current remote sensing datasets often fail to meet these two requirements, for which cloud is a primary factor degrading the data quantity and quality. This limitation affects the precision of results in remote sensing application, particularly those derived from data-driven techniques. In this paper, a physical law embedded generative cloud synthesis method (PGCS) is proposed to generate diverse realistic cloud images to enhance real data and promote the development of algorithms for subsequent tasks, such as cloud correction, cloud detection, and data augmentation for classification, recognition, and segmentation. The PGCS method involves two key phases: spatial synthesis and spectral synthesis. In the spatial synthesis phase, a style-based generative adversarial network is utilized to simulate the spatial characteristics, generating an infinite number of single-channel clouds. In the spectral synthesis phase, the atmospheric scattering law is embedded through a local statistics and global fitting method, converting the single-channel clouds into multi-spectral clouds. The experimental results demonstrate that PGCS achieves a high accuracy in both phases and performs better than three other existing cloud synthesis methods. Two cloud correction methods are developed from PGCS and exhibits a superior performance compared to state-of-the-art methods in the cloud correction task. Furthermore, the application of PGCS with data from various sensors was investigated and successfully extended. Code will be provided at https://github.com/Liying-Xu/PGCS.
Adaptive Regularized Low-Rank Tensor Decomposition for Hyperspectral Image Denoising and Destriping
Jan 11, 2024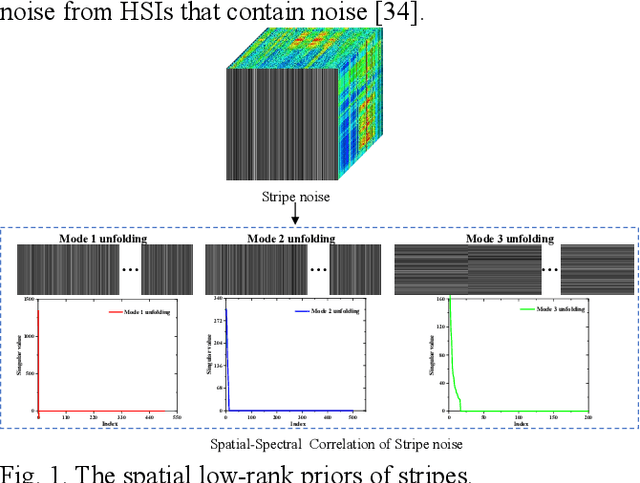

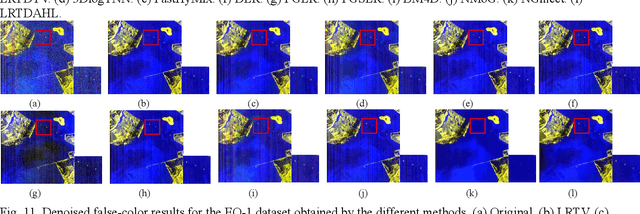
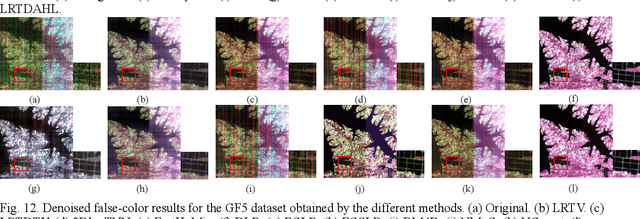
Abstract:Hyperspectral images (HSIs) are inevitably degraded by a mixture of various types of noise, such as Gaussian noise, impulse noise, stripe noise, and dead pixels, which greatly limits the subsequent applications. Although various denoising methods have already been developed, accurately recovering the spatial-spectral structure of HSIs remains a challenging problem to be addressed. Furthermore, serious stripe noise, which is common in real HSIs, is still not fully separated by the previous models. In this paper, we propose an adaptive hyperLaplacian regularized low-rank tensor decomposition (LRTDAHL) method for HSI denoising and destriping. On the one hand, the stripe noise is separately modeled by the tensor decomposition, which can effectively encode the spatial-spectral correlation of the stripe noise. On the other hand, adaptive hyper-Laplacian spatial-spectral regularization is introduced to represent the distribution structure of different HSI gradient data by adaptively estimating the optimal hyper-Laplacian parameter, which can reduce the spatial information loss and over-smoothing caused by the previous total variation regularization. The proposed model is solved using the alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) algorithm. Extensive simulation and real-data experiments all demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed method.
A physics-constrained machine learning method for mapping gapless land surface temperature
Jul 03, 2023Abstract:More accurate, spatio-temporally, and physically consistent LST estimation has been a main interest in Earth system research. Developing physics-driven mechanism models and data-driven machine learning (ML) models are two major paradigms for gapless LST estimation, which have their respective advantages and disadvantages. In this paper, a physics-constrained ML model, which combines the strengths in the mechanism model and ML model, is proposed to generate gapless LST with physical meanings and high accuracy. The hybrid model employs ML as the primary architecture, under which the input variable physical constraints are incorporated to enhance the interpretability and extrapolation ability of the model. Specifically, the light gradient-boosting machine (LGBM) model, which uses only remote sensing data as input, serves as the pure ML model. Physical constraints (PCs) are coupled by further incorporating key Community Land Model (CLM) forcing data (cause) and CLM simulation data (effect) as inputs into the LGBM model. This integration forms the PC-LGBM model, which incorporates surface energy balance (SEB) constraints underlying the data in CLM-LST modeling within a biophysical framework. Compared with a pure physical method and pure ML methods, the PC-LGBM model improves the prediction accuracy and physical interpretability of LST. It also demonstrates a good extrapolation ability for the responses to extreme weather cases, suggesting that the PC-LGBM model enables not only empirical learning from data but also rationally derived from theory. The proposed method represents an innovative way to map accurate and physically interpretable gapless LST, and could provide insights to accelerate knowledge discovery in land surface processes and data mining in geographical parameter estimation.
An attention mechanism based convolutional network for satellite precipitation downscaling over China
Mar 28, 2022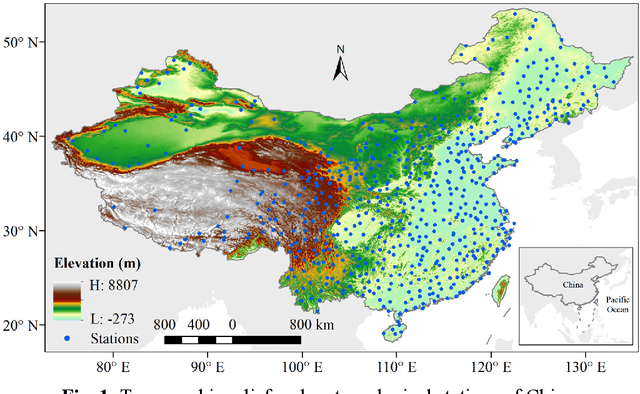
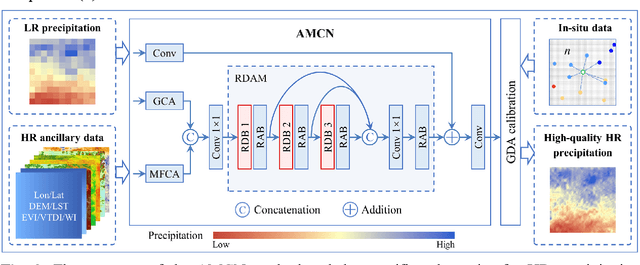
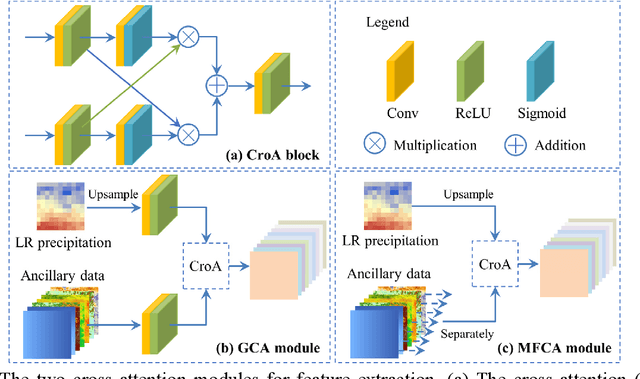
Abstract:Precipitation is a key part of hydrological circulation and is a sensitive indicator of climate change. The Integrated Multi-satellitE Retrievals for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission (IMERG) datasets are widely used for global and regional precipitation investigations. However, their local application is limited by the relatively coarse spatial resolution. Therefore, in this paper, an attention mechanism based convolutional network (AMCN) is proposed to downscale GPM IMERG monthly precipitation data. The proposed method is an end-to-end network, which consists of a global cross-attention module, a multi-factor cross-attention module, and a residual convolutional module, comprehensively considering the potential relationships between precipitation and complicated surface characteristics. In addition, a degradation loss function based on low-resolution precipitation is designed to physically constrain the network training, to improve the robustness of the proposed network under different time and scale variations. The experiments demonstrate that the proposed network significantly outperforms three baseline methods. Finally, a geographic difference analysis method is introduced to further improve the downscaled results by incorporating in-situ measurements for high-quality and fine-scale precipitation estimation.
Generating gapless land surface temperature with a high spatio-temporal resolution by fusing multi-source satellite-observed and model-simulated data
Nov 29, 2021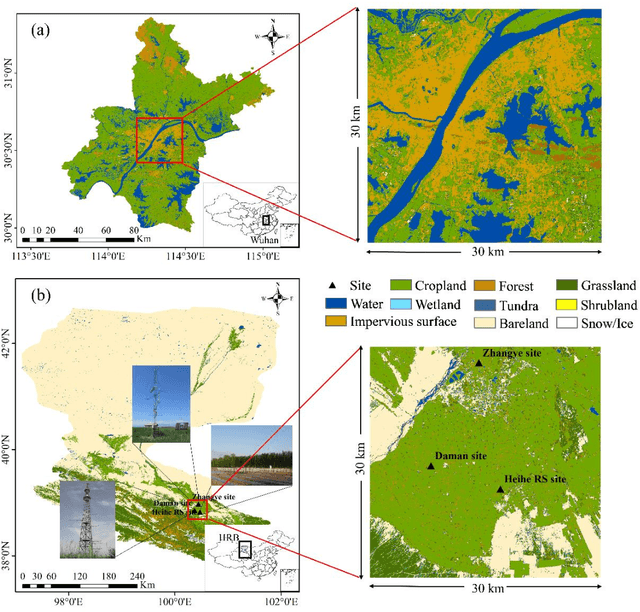
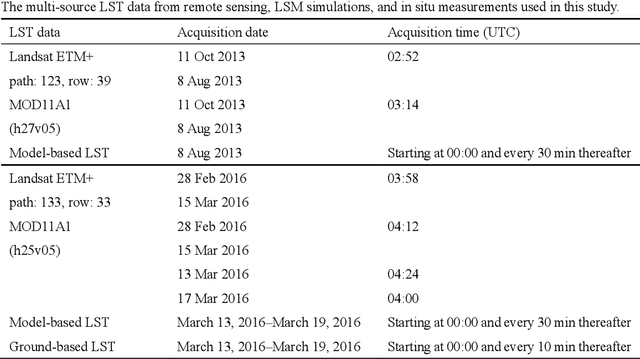
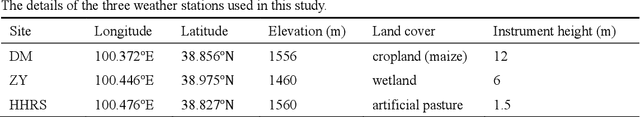
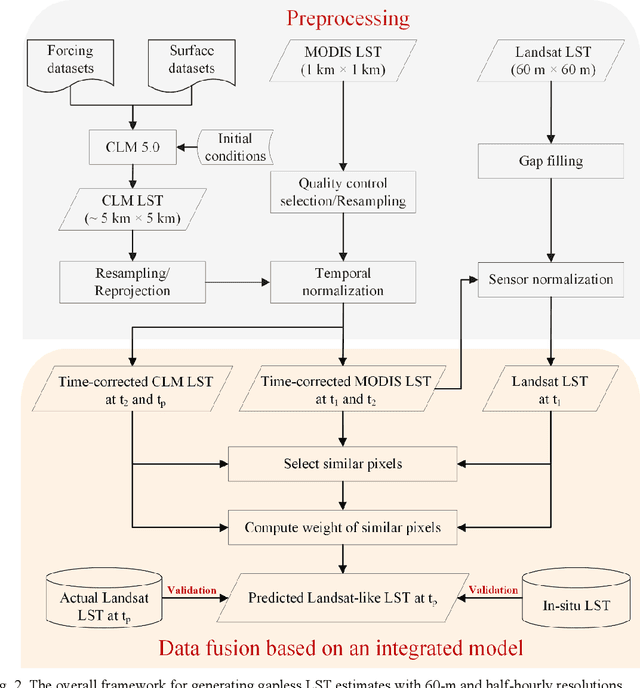
Abstract:Land surface temperature (LST) is a key parameter when monitoring land surface processes. However, cloud contamination and the tradeoff between the spatial and temporal resolutions greatly impede the access to high-quality thermal infrared (TIR) remote sensing data. Despite the massive efforts made to solve these dilemmas, it is still difficult to generate LST estimates with concurrent spatial completeness and a high spatio-temporal resolution. Land surface models (LSMs) can be used to simulate gapless LST with a high temporal resolution, but this usually comes with a low spatial resolution. In this paper, we present an integrated temperature fusion framework for satellite-observed and LSM-simulated LST data to map gapless LST at a 60-m spatial resolution and half-hourly temporal resolution. The global linear model (GloLM) model and the diurnal land surface temperature cycle (DTC) model are respectively performed as preprocessing steps for sensor and temporal normalization between the different LST data. The Landsat LST, Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) LST, and Community Land Model Version 5.0 (CLM 5.0)-simulated LST are then fused using a filter-based spatio-temporal integrated fusion model. Evaluations were implemented in an urban-dominated region (the city of Wuhan in China) and a natural-dominated region (the Heihe River Basin in China), in terms of accuracy, spatial variability, and diurnal temporal dynamics. Results indicate that the fused LST is highly consistent with actual Landsat LST data (in situ LST measurements), in terms of a Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.94 (0.97-0.99), a mean absolute error of 0.71-0.98 K (0.82-3.17 K), and a root-mean-square error of 0.97-1.26 K (1.09-3.97 K).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge