Jing Sun
Adaptive Plan-Execute Framework for Smart Contract Security Auditing
May 21, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown great promise in code analysis and auditing; however, they still struggle with hallucinations and limited context-aware reasoning. We introduce SmartAuditFlow, a novel Plan-Execute framework that enhances smart contract security analysis through dynamic audit planning and structured execution. Unlike conventional LLM-based auditing approaches that follow fixed workflows and predefined steps, SmartAuditFlow dynamically generates and refines audit plans based on the unique characteristics of each smart contract. It continuously adjusts its auditing strategy in response to intermediate LLM outputs and newly detected vulnerabilities, ensuring a more adaptive and precise security assessment. The framework then executes these plans step by step, applying a structured reasoning process to enhance vulnerability detection accuracy while minimizing hallucinations and false positives. To further improve audit precision, SmartAuditFlow integrates iterative prompt optimization and external knowledge sources, such as static analysis tools and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). This ensures audit decisions are contextually informed and backed by real-world security knowledge, producing comprehensive security reports. Extensive evaluations across multiple benchmarks demonstrate that SmartAuditFlow outperforms existing methods, achieving 100 percent accuracy on common and critical vulnerabilities, 41.2 percent accuracy for comprehensive coverage of known smart contract weaknesses in real-world projects, and successfully identifying all 13 tested CVEs. These results highlight SmartAuditFlow's scalability, cost-effectiveness, and superior adaptability over traditional static analysis tools and contemporary LLM-based approaches, establishing it as a robust solution for automated smart contract auditing.
Streamlining Biomedical Research with Specialized LLMs
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel system that integrates state-of-the-art, domain-specific large language models with advanced information retrieval techniques to deliver comprehensive and context-aware responses. Our approach facilitates seamless interaction among diverse components, enabling cross-validation of outputs to produce accurate, high-quality responses enriched with relevant data, images, tables, and other modalities. We demonstrate the system's capability to enhance response precision by leveraging a robust question-answering model, significantly improving the quality of dialogue generation. The system provides an accessible platform for real-time, high-fidelity interactions, allowing users to benefit from efficient human-computer interaction, precise retrieval, and simultaneous access to a wide range of literature and data. This dramatically improves the research efficiency of professionals in the biomedical and pharmaceutical domains and facilitates faster, more informed decision-making throughout the R\&D process. Furthermore, the system proposed in this paper is available at https://synapse-chat.patsnap.com.
Aligning First, Then Fusing: A Novel Weakly Supervised Multimodal Violence Detection Method
Jan 13, 2025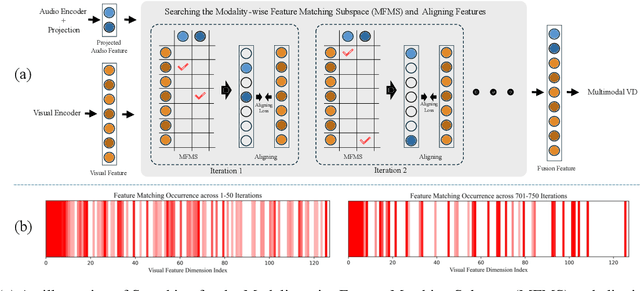
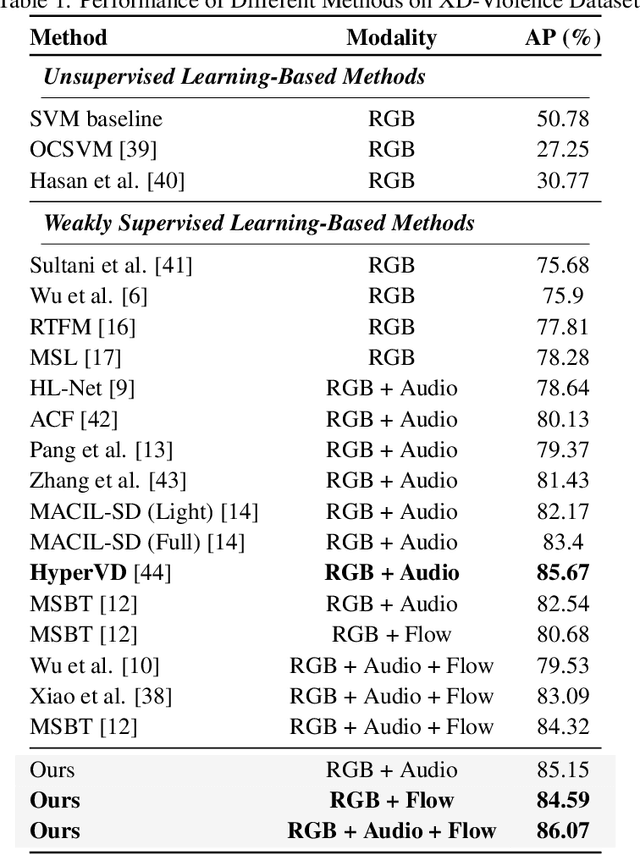
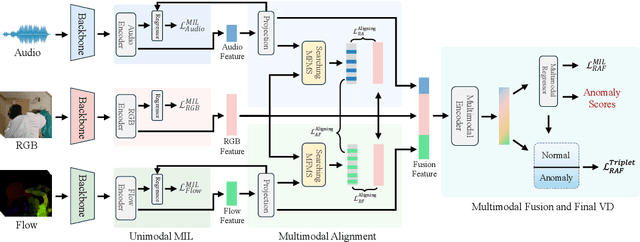
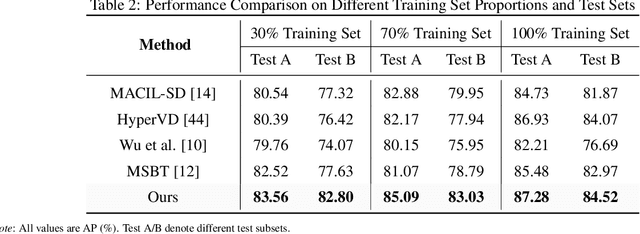
Abstract:Weakly supervised violence detection refers to the technique of training models to identify violent segments in videos using only video-level labels. Among these approaches, multimodal violence detection, which integrates modalities such as audio and optical flow, holds great potential. Existing methods in this domain primarily focus on designing multimodal fusion models to address modality discrepancies. In contrast, we take a different approach; leveraging the inherent discrepancies across modalities in violence event representation to propose a novel multimodal semantic feature alignment method. This method sparsely maps the semantic features of local, transient, and less informative modalities ( such as audio and optical flow ) into the more informative RGB semantic feature space. Through an iterative process, the method identifies the suitable no-zero feature matching subspace and aligns the modality-specific event representations based on this subspace, enabling the full exploitation of information from all modalities during the subsequent modality fusion stage. Building on this, we design a new weakly supervised violence detection framework that consists of unimodal multiple-instance learning for extracting unimodal semantic features, multimodal alignment, multimodal fusion, and final detection. Experimental results on benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, achieving an average precision (AP) of 86.07% on the XD-Violence dataset. Our code is available at https://github.com/xjpp2016/MAVD.
Super-Resolution for Remote Sensing Imagery via the Coupling of a Variational Model and Deep Learning
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:Image super-resolution (SR) is an effective way to enhance the spatial resolution and detail information of remote sensing images, to obtain a superior visual quality. As SR is severely ill-conditioned, effective image priors are necessary to regularize the solution space and generate the corresponding high-resolution (HR) image. In this paper, we propose a novel gradient-guided multi-frame super-resolution (MFSR) framework for remote sensing imagery reconstruction. The framework integrates a learned gradient prior as the regularization term into a model-based optimization method. Specifically, the local gradient regularization (LGR) prior is derived from the deep residual attention network (DRAN) through gradient profile transformation. The non-local total variation (NLTV) prior is characterized using the spatial structure similarity of the gradient patches with the maximum a posteriori (MAP) model. The modeled prior performs well in preserving edge smoothness and suppressing visual artifacts, while the learned prior is effective in enhancing sharp edges and recovering fine structures. By incorporating the two complementary priors into an adaptive norm based reconstruction framework, the mixed L1 and L2 regularization minimization problem is optimized to achieve the required HR remote sensing image. Extensive experimental results on remote sensing data demonstrate that the proposed method can produce visually pleasant images and is superior to several of the state-of-the-art SR algorithms in terms of the quantitative evaluation.
A Single-Frame and Multi-Frame Cascaded Image Super-Resolution Method
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:The objective of image super-resolution is to reconstruct a high-resolution (HR) image with the prior knowledge from one or several low-resolution (LR) images. However, in the real world, due to the limited complementary information, the performance of both single-frame and multi-frame super-resolution reconstruction degrades rapidly as the magnification increases. In this paper, we propose a novel two-step image super resolution method concatenating multi-frame super-resolution (MFSR) with single-frame super-resolution (SFSR), to progressively upsample images to the desired resolution. The proposed method consisting of an L0-norm constrained reconstruction scheme and an enhanced residual back-projection network, integrating the flexibility of the variational modelbased method and the feature learning capacity of the deep learning-based method. To verify the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm, extensive experiments with both simulated and real world sequences were implemented. The experimental results show that the proposed method yields superior performance in both objective and perceptual quality measurements. The average PSNRs of the cascade model in set5 and set14 are 33.413 dB and 29.658 dB respectively, which are 0.76 dB and 0.621 dB more than the baseline method. In addition, the experiment indicates that this cascade model can be robustly applied to different SFSR and MFSR methods.
* 20 pages, 13 figures
The Fusion of Large Language Models and Formal Methods for Trustworthy AI Agents: A Roadmap
Dec 09, 2024


Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have emerged as a transformative AI paradigm, profoundly influencing daily life through their exceptional language understanding and contextual generation capabilities. Despite their remarkable performance, LLMs face a critical challenge: the propensity to produce unreliable outputs due to the inherent limitations of their learning-based nature. Formal methods (FMs), on the other hand, are a well-established computation paradigm that provides mathematically rigorous techniques for modeling, specifying, and verifying the correctness of systems. FMs have been extensively applied in mission-critical software engineering, embedded systems, and cybersecurity. However, the primary challenge impeding the deployment of FMs in real-world settings lies in their steep learning curves, the absence of user-friendly interfaces, and issues with efficiency and adaptability. This position paper outlines a roadmap for advancing the next generation of trustworthy AI systems by leveraging the mutual enhancement of LLMs and FMs. First, we illustrate how FMs, including reasoning and certification techniques, can help LLMs generate more reliable and formally certified outputs. Subsequently, we highlight how the advanced learning capabilities and adaptability of LLMs can significantly enhance the usability, efficiency, and scalability of existing FM tools. Finally, we show that unifying these two computation paradigms -- integrating the flexibility and intelligence of LLMs with the rigorous reasoning abilities of FMs -- has transformative potential for the development of trustworthy AI software systems. We acknowledge that this integration has the potential to enhance both the trustworthiness and efficiency of software engineering practices while fostering the development of intelligent FM tools capable of addressing complex yet real-world challenges.
Recent development of optical electric current transformer and its obstacles
Dec 09, 2024Abstract:Conventional electromagnetic induction-based current transformers suffer from issues such as bulky and complex structures, slow response times, and low safety levels. Consequently, researchers have explored combining various sensing technologies with optical fibers to develop optical current transformers that could become the primary choice for power systems in the future. With the maturation of optoelectronic technology, optical current transformers have emerged. They offer outstanding advantages, including high sensitivity, integration, stability, and the ability to operate in complex environments. This review categorizes optical current transformers based on different principles, including all-fiber current transformers, those based on magnetostrictive effects, magneto-optic effects, and thermal effects. It also discusses their principles, structures, manufacturing techniques, and signal processing, while forecasting their future development trends.
VisionCoder: Empowering Multi-Agent Auto-Programming for Image Processing with Hybrid LLMs
Oct 25, 2024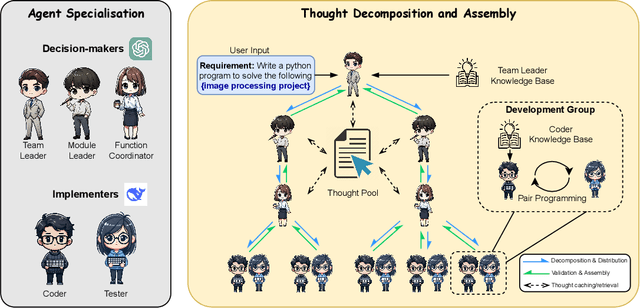



Abstract:In the field of automated programming, large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated foundational generative capabilities when given detailed task descriptions. However, their current functionalities are primarily limited to function-level development, restricting their effectiveness in complex project environments and specific application scenarios, such as complicated image-processing tasks. This paper presents a multi-agent framework that utilises a hybrid set of LLMs, including GPT-4o and locally deployed open-source models, which collaboratively complete auto-programming tasks. Each agent plays a distinct role in the software development cycle, collectively forming a virtual organisation that works together to produce software products. By establishing a tree-structured thought distribution and development mechanism across project, module, and function levels, this framework offers a cost-effective and efficient solution for code generation. We evaluated our approach using benchmark datasets, and the experimental results demonstrate that VisionCoder significantly outperforms existing methods in image processing auto-programming tasks.
Leveraging Fine-Tuned Language Models for Efficient and Accurate Smart Contract Auditing
Oct 17, 2024Abstract:The rise of blockchain technologies has greatly accelerated the development and deployment of smart contracts. However, their inherent vulnerabilities and susceptibility to bugs have led to significant financial losses, underscoring the challenges in securing smart contracts. While traditional auditing methods are crucial, they often fall short in addressing the increasing complexity and volume of smart contracts. Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) offer promising solutions for enhancing software auditing by automatically identifying security vulnerabilities. Despite their potential, the practical application of these models is hindered by substantial computational demands. This paper investigates the feasibility of using smaller, fine-tuned models to achieve comparable or even superior results in smart contract auditing. We introduce the FTSmartAudit framework, which is designed to develop cost-effective, specialized models for smart contract auditing through the fine-tuning of LLMs. Our contributions include: (1) a single-task learning framework that streamlines data preparation, training, evaluation, and continuous learning; (2) a robust dataset generation method utilizing domain-special knowledge distillation to produce high-quality datasets from advanced models like GPT-4o; (3) an adaptive learning strategy to maintain model accuracy and robustness; (4) the proven effectiveness of fine-tuned models in detecting specific vulnerabilities and complex logical errors; and (5) a framework that can be extended to other domains requiring LLM solutions. Our experimental results demonstrate that smaller models can surpass state-of-the-art commercial models and tools in detecting vulnerabilities in smart contracts.
Deep learning-based shot-domain seismic deblending
Sep 13, 2024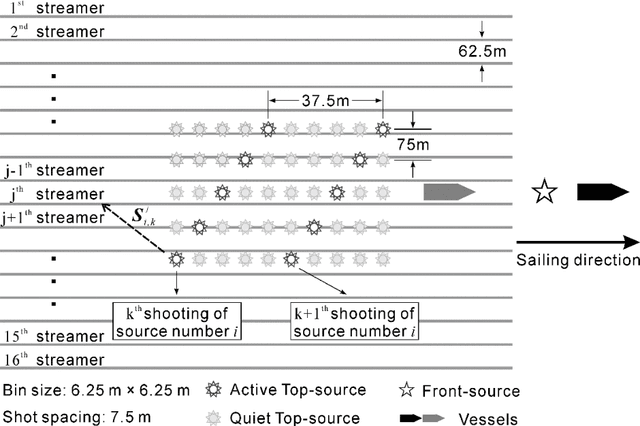
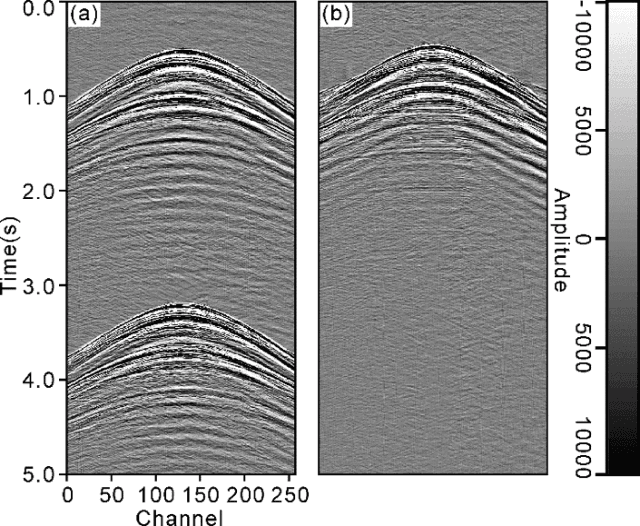
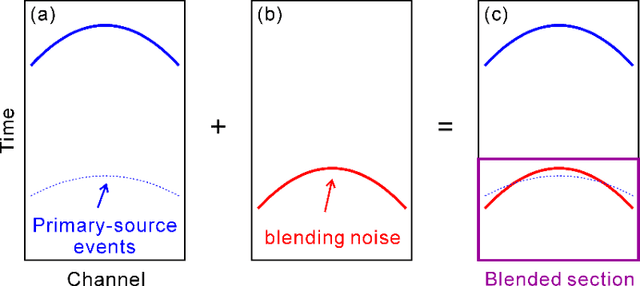

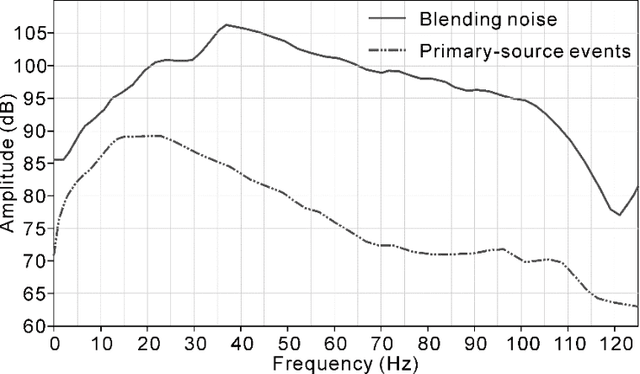
Abstract:To streamline fast-track processing of large data volumes, we have developed a deep learning approach to deblend seismic data in the shot domain based on a practical strategy for generating high-quality training data along with a list of data conditioning techniques to improve performance of the data-driven model. We make use of unblended shot gathers acquired at the end of each sail line, to which the access requires no additional time or labor costs beyond the blended acquisition. By manually blending these data we obtain training data with good control of the ground truth and fully adapted to the given survey. Furthermore, we train a deep neural network using multi-channel inputs that include adjacent blended shot gathers as additional channels. The prediction of the blending noise is added in as a related and auxiliary task with the main task of the network being the prediction of the primary-source events. Blending noise in the ground truth is scaled down during the training and validation process due to its excessively strong amplitudes. As part of the process, the to-be-deblended shot gathers are aligned by the blending noise. Implementation on field blended-by-acquisition data demonstrates that introducing the suggested data conditioning steps can considerably reduce the leakage of primary-source events in the deep part of the blended section. The complete proposed approach performs almost as well as a conventional algorithm in the shallow section and shows great advantage in efficiency. It performs slightly worse for larger traveltimes, but still removes the blending noise efficiently.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge