Zhiyuan Wei
Adaptive Plan-Execute Framework for Smart Contract Security Auditing
May 21, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown great promise in code analysis and auditing; however, they still struggle with hallucinations and limited context-aware reasoning. We introduce SmartAuditFlow, a novel Plan-Execute framework that enhances smart contract security analysis through dynamic audit planning and structured execution. Unlike conventional LLM-based auditing approaches that follow fixed workflows and predefined steps, SmartAuditFlow dynamically generates and refines audit plans based on the unique characteristics of each smart contract. It continuously adjusts its auditing strategy in response to intermediate LLM outputs and newly detected vulnerabilities, ensuring a more adaptive and precise security assessment. The framework then executes these plans step by step, applying a structured reasoning process to enhance vulnerability detection accuracy while minimizing hallucinations and false positives. To further improve audit precision, SmartAuditFlow integrates iterative prompt optimization and external knowledge sources, such as static analysis tools and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). This ensures audit decisions are contextually informed and backed by real-world security knowledge, producing comprehensive security reports. Extensive evaluations across multiple benchmarks demonstrate that SmartAuditFlow outperforms existing methods, achieving 100 percent accuracy on common and critical vulnerabilities, 41.2 percent accuracy for comprehensive coverage of known smart contract weaknesses in real-world projects, and successfully identifying all 13 tested CVEs. These results highlight SmartAuditFlow's scalability, cost-effectiveness, and superior adaptability over traditional static analysis tools and contemporary LLM-based approaches, establishing it as a robust solution for automated smart contract auditing.
The Fusion of Large Language Models and Formal Methods for Trustworthy AI Agents: A Roadmap
Dec 09, 2024


Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have emerged as a transformative AI paradigm, profoundly influencing daily life through their exceptional language understanding and contextual generation capabilities. Despite their remarkable performance, LLMs face a critical challenge: the propensity to produce unreliable outputs due to the inherent limitations of their learning-based nature. Formal methods (FMs), on the other hand, are a well-established computation paradigm that provides mathematically rigorous techniques for modeling, specifying, and verifying the correctness of systems. FMs have been extensively applied in mission-critical software engineering, embedded systems, and cybersecurity. However, the primary challenge impeding the deployment of FMs in real-world settings lies in their steep learning curves, the absence of user-friendly interfaces, and issues with efficiency and adaptability. This position paper outlines a roadmap for advancing the next generation of trustworthy AI systems by leveraging the mutual enhancement of LLMs and FMs. First, we illustrate how FMs, including reasoning and certification techniques, can help LLMs generate more reliable and formally certified outputs. Subsequently, we highlight how the advanced learning capabilities and adaptability of LLMs can significantly enhance the usability, efficiency, and scalability of existing FM tools. Finally, we show that unifying these two computation paradigms -- integrating the flexibility and intelligence of LLMs with the rigorous reasoning abilities of FMs -- has transformative potential for the development of trustworthy AI software systems. We acknowledge that this integration has the potential to enhance both the trustworthiness and efficiency of software engineering practices while fostering the development of intelligent FM tools capable of addressing complex yet real-world challenges.
VisionCoder: Empowering Multi-Agent Auto-Programming for Image Processing with Hybrid LLMs
Oct 25, 2024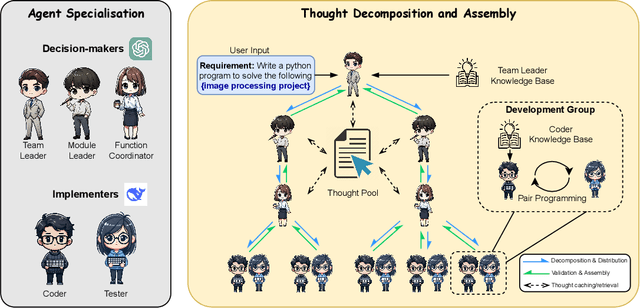



Abstract:In the field of automated programming, large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated foundational generative capabilities when given detailed task descriptions. However, their current functionalities are primarily limited to function-level development, restricting their effectiveness in complex project environments and specific application scenarios, such as complicated image-processing tasks. This paper presents a multi-agent framework that utilises a hybrid set of LLMs, including GPT-4o and locally deployed open-source models, which collaboratively complete auto-programming tasks. Each agent plays a distinct role in the software development cycle, collectively forming a virtual organisation that works together to produce software products. By establishing a tree-structured thought distribution and development mechanism across project, module, and function levels, this framework offers a cost-effective and efficient solution for code generation. We evaluated our approach using benchmark datasets, and the experimental results demonstrate that VisionCoder significantly outperforms existing methods in image processing auto-programming tasks.
Leveraging Fine-Tuned Language Models for Efficient and Accurate Smart Contract Auditing
Oct 17, 2024Abstract:The rise of blockchain technologies has greatly accelerated the development and deployment of smart contracts. However, their inherent vulnerabilities and susceptibility to bugs have led to significant financial losses, underscoring the challenges in securing smart contracts. While traditional auditing methods are crucial, they often fall short in addressing the increasing complexity and volume of smart contracts. Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) offer promising solutions for enhancing software auditing by automatically identifying security vulnerabilities. Despite their potential, the practical application of these models is hindered by substantial computational demands. This paper investigates the feasibility of using smaller, fine-tuned models to achieve comparable or even superior results in smart contract auditing. We introduce the FTSmartAudit framework, which is designed to develop cost-effective, specialized models for smart contract auditing through the fine-tuning of LLMs. Our contributions include: (1) a single-task learning framework that streamlines data preparation, training, evaluation, and continuous learning; (2) a robust dataset generation method utilizing domain-special knowledge distillation to produce high-quality datasets from advanced models like GPT-4o; (3) an adaptive learning strategy to maintain model accuracy and robustness; (4) the proven effectiveness of fine-tuned models in detecting specific vulnerabilities and complex logical errors; and (5) a framework that can be extended to other domains requiring LLM solutions. Our experimental results demonstrate that smaller models can surpass state-of-the-art commercial models and tools in detecting vulnerabilities in smart contracts.
The Invisible COVID-19 Crisis: Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Risk Among Frontline Physicians Treating COVID-19 Patients
Oct 25, 2021



Abstract:This study evaluated post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) among frontline US physicians (treating COVID-19 patients) in comparison with second-line physicians (not treating COVID-19 patients), and identified the significance and patterns of factors associated with higher PTSD risk. A cross-sectional, web-based survey was deployed during August and September, 2020, to practicing physicians in the 18 states with the largest COVID-19 cases. Among 1,478 responding physicians, 1,017 completed the PTSD Checklist (PCL-5). First, the PCL-5 was used to compare symptom endorsement between the two physician groups. A greater percentage of frontline than second-line physicians had clinically significant endorsement of PCL-5 symptoms and higher PCL-5 scores. Second, logistic regression and seven nonlinear machine learning (ML) algorithms were leveraged to identify potential predictors of PTSD risk by analyzing variable importance and partial dependence plots. Predictors of PTSD risk included cognitive/psychological measures, occupational characteristics, work experiences, social support, demographics, and workplace characteristics. Importantly, the final ML model random forest, identified patterns of both damaging and protective predictors of PTSD risk among frontline physicians. Key damaging factors included depression, burnout, negative coping, fears of contracting/transmitting COVID-19, perceived stigma, and insufficient resources to treat COVID-19 patients. Protective factors included resilience and support from employers/friends/family/significant others. This study underscores the value of ML algorithms to uncover nonlinear relationships among protective/damaging risk factors for PTSD in frontline physicians, which may better inform interventions to prepare healthcare systems for future epidemics/pandemics.
Health-behaviors associated with the growing risk of adolescent suicide attempts: A data-driven cross-sectional study
Sep 08, 2020

Abstract:Purpose: Identify and examine the associations between health behaviors and increased risk of adolescent suicide attempts, while controlling for socioeconomic and demographic differences. Design: A data-driven analysis using cross-sectional data. Setting: Communities in the state of Montana from 1999 to 2017. Subjects: Selected 22,447 adolescents of whom 1,631 adolescents attempted suicide at least once. Measures: Overall 29 variables (predictors) accounting for psychological behaviors, illegal substances consumption, daily activities at schools and demographic backgrounds, were considered. Analysis: A library of machine learning algorithms along with the traditionally-used logistic regression were used to model and predict suicide attempt risk. Model performances (goodness-of-fit and predictive accuracy) were measured using accuracy, precision, recall and F-score metrics. Results: The non-parametric Bayesian tree ensemble model outperformed all other models, with 80.0% accuracy in goodness-of-fit (F-score:0.802) and 78.2% in predictive accuracy (F-score:0.785). Key health-behaviors identified include: being sad/hopeless, followed by safety concerns at school, physical fighting, inhalant usage, illegal drugs consumption at school, current cigarette usage, and having first sex at an early age (below 15 years of age). Additionally, the minority groups (American Indian/Alaska Natives, Hispanics/Latinos), and females are also found to be highly vulnerable to attempting suicides. Conclusion: Significant contribution of this work is understanding the key health-behaviors and health disparities that lead to higher frequency of suicide attempts among adolescents, while accounting for the non-linearity and complex interactions among the outcome and the exposure variables.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge