Chengqi Zhao
BLEURT Has Universal Translations: An Analysis of Automatic Metrics by Minimum Risk Training
Jul 10, 2023
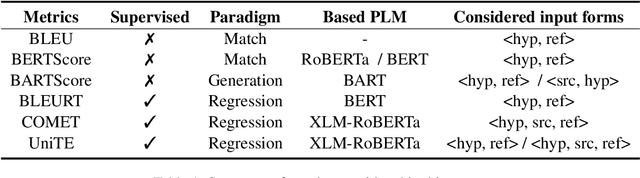
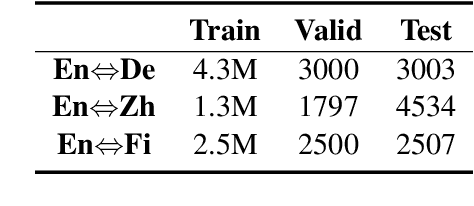
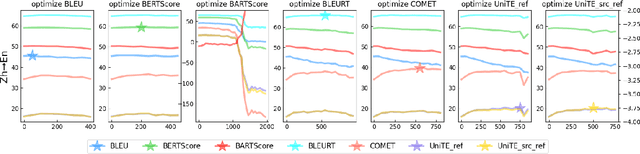
Abstract:Automatic metrics play a crucial role in machine translation. Despite the widespread use of n-gram-based metrics, there has been a recent surge in the development of pre-trained model-based metrics that focus on measuring sentence semantics. However, these neural metrics, while achieving higher correlations with human evaluations, are often considered to be black boxes with potential biases that are difficult to detect. In this study, we systematically analyze and compare various mainstream and cutting-edge automatic metrics from the perspective of their guidance for training machine translation systems. Through Minimum Risk Training (MRT), we find that certain metrics exhibit robustness defects, such as the presence of universal adversarial translations in BLEURT and BARTScore. In-depth analysis suggests two main causes of these robustness deficits: distribution biases in the training datasets, and the tendency of the metric paradigm. By incorporating token-level constraints, we enhance the robustness of evaluation metrics, which in turn leads to an improvement in the performance of machine translation systems. Codes are available at \url{https://github.com/powerpuffpomelo/fairseq_mrt}.
Recent Advances in Direct Speech-to-text Translation
Jun 20, 2023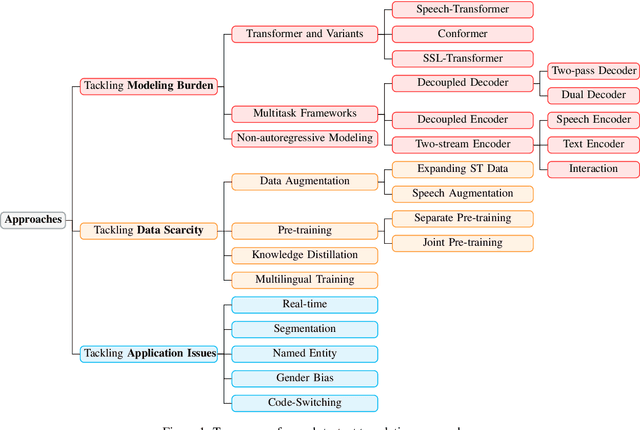
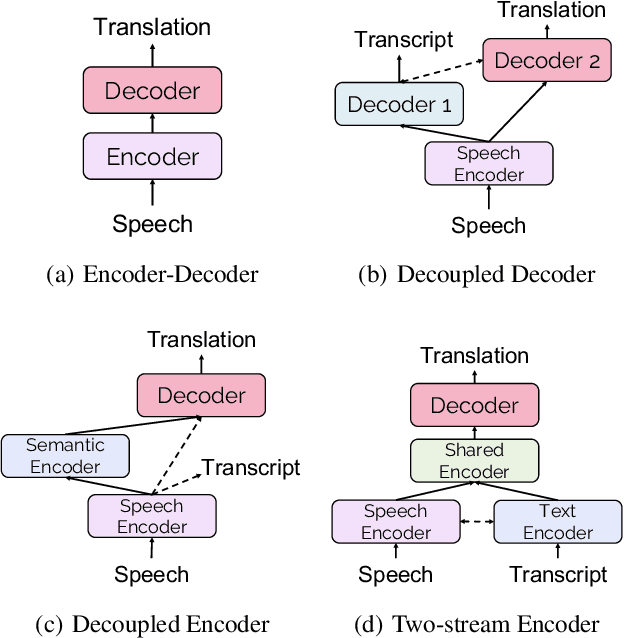
Abstract:Recently, speech-to-text translation has attracted more and more attention and many studies have emerged rapidly. In this paper, we present a comprehensive survey on direct speech translation aiming to summarize the current state-of-the-art techniques. First, we categorize the existing research work into three directions based on the main challenges -- modeling burden, data scarcity, and application issues. To tackle the problem of modeling burden, two main structures have been proposed, encoder-decoder framework (Transformer and the variants) and multitask frameworks. For the challenge of data scarcity, recent work resorts to many sophisticated techniques, such as data augmentation, pre-training, knowledge distillation, and multilingual modeling. We analyze and summarize the application issues, which include real-time, segmentation, named entity, gender bias, and code-switching. Finally, we discuss some promising directions for future work.
Improving speech translation by fusing speech and text
May 23, 2023Abstract:In speech translation, leveraging multimodal data to improve model performance and address limitations of individual modalities has shown significant effectiveness. In this paper, we harness the complementary strengths of speech and text, which are disparate modalities. We observe three levels of modality gap between them, denoted by Modal input representation, Modal semantic, and Modal hidden states. To tackle these gaps, we propose \textbf{F}use-\textbf{S}peech-\textbf{T}ext (\textbf{FST}), a cross-modal model which supports three distinct input modalities for translation: speech, text, and fused speech-text. We leverage multiple techniques for cross-modal alignment and conduct a comprehensive analysis to assess its impact on speech translation, machine translation, and fused speech-text translation. We evaluate FST on MuST-C, GigaST, and newstest benchmark. Experiments show that the proposed FST achieves an average 34.0 BLEU on MuST-C En$\rightarrow$De/Es/Fr (vs SOTA +1.1 BLEU). Further experiments demonstrate that FST does not degrade on MT task, as observed in prior works. Instead, it yields an average improvement of 3.2 BLEU over the pre-trained MT model.
Selective Knowledge Distillation for Non-Autoregressive Neural Machine Translation
Mar 31, 2023



Abstract:Benefiting from the sequence-level knowledge distillation, the Non-Autoregressive Transformer (NAT) achieves great success in neural machine translation tasks. However, existing knowledge distillation has side effects, such as propagating errors from the teacher to NAT students, which may limit further improvements of NAT models and are rarely discussed in existing research. In this paper, we introduce selective knowledge distillation by introducing an NAT evaluator to select NAT-friendly targets that are of high quality and easy to learn. In addition, we introduce a simple yet effective progressive distillation method to boost NAT performance. Experiment results on multiple WMT language directions and several representative NAT models show that our approach can realize a flexible trade-off between the quality and complexity of training data for NAT models, achieving strong performances. Further analysis shows that distilling only 5% of the raw translations can help an NAT outperform its counterpart trained on raw data by about 2.4 BLEU.
WavCaps: A ChatGPT-Assisted Weakly-Labelled Audio Captioning Dataset for Audio-Language Multimodal Research
Mar 30, 2023



Abstract:The advancement of audio-language (AL) multimodal learning tasks has been significant in recent years. However, researchers face challenges due to the costly and time-consuming collection process of existing audio-language datasets, which are limited in size. To address this data scarcity issue, we introduce WavCaps, the first large-scale weakly-labelled audio captioning dataset, comprising approximately 400k audio clips with paired captions. We sourced audio clips and their raw descriptions from web sources and a sound event detection dataset. However, the online-harvested raw descriptions are highly noisy and unsuitable for direct use in tasks such as automated audio captioning. To overcome this issue, we propose a three-stage processing pipeline for filtering noisy data and generating high-quality captions, where ChatGPT, a large language model, is leveraged to filter and transform raw descriptions automatically. We conduct a comprehensive analysis of the characteristics of WavCaps dataset and evaluate it on multiple downstream audio-language multimodal learning tasks. The systems trained on WavCaps outperform previous state-of-the-art (SOTA) models by a significant margin. Our aspiration is for the WavCaps dataset we have proposed to facilitate research in audio-language multimodal learning and demonstrate the potential of utilizing ChatGPT to enhance academic research. Our dataset and codes are available at https://github.com/XinhaoMei/WavCaps.
GigaST: A 10,000-hour Pseudo Speech Translation Corpus
Apr 08, 2022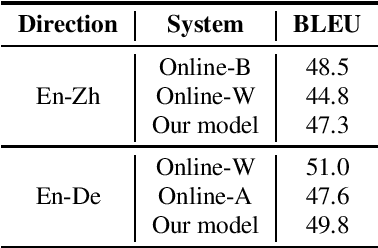
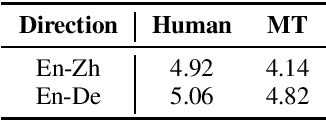
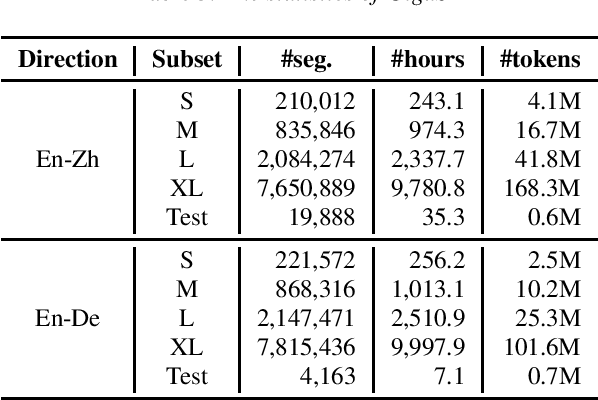
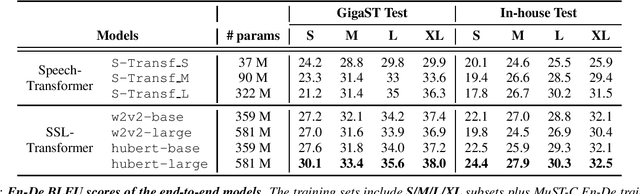
Abstract:This paper introduces GigaST, a large-scale pseudo speech translation (ST) corpus. We create the corpus by translating the text in GigaSpeech, an English ASR corpus, into German and Chinese. The training set is translated by a strong machine translation system and the test set is translated by human. ST models trained with an addition of our corpus obtain new state-of-the-art results on the MuST-C English-German benchmark test set. We provide a detailed description of the translation process and verify its quality. We make the translated text data public and hope to facilitate research in speech translation. Additionally, we also release the training scripts on NeurST to make it easy to replicate our systems. GigaST dataset is available at https://st-benchmark.github.io/resources/GigaST.
Secoco: Self-Correcting Encoding for Neural Machine Translation
Aug 27, 2021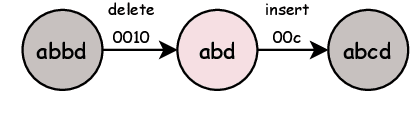
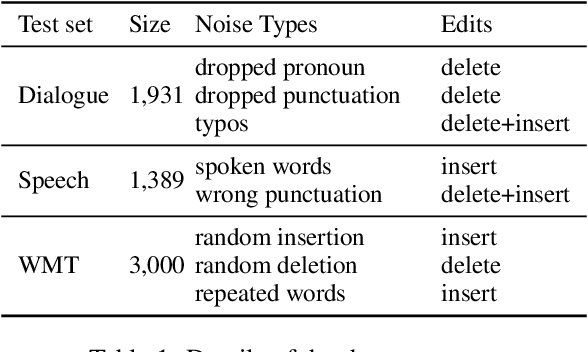
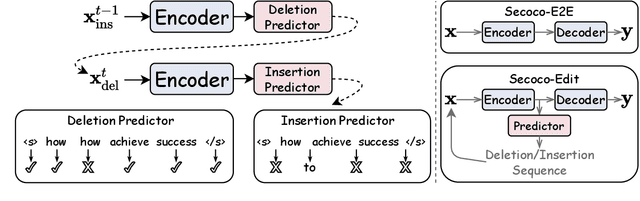
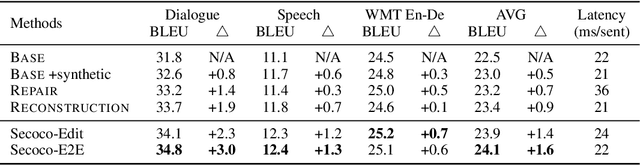
Abstract:This paper presents Self-correcting Encoding (Secoco), a framework that effectively deals with input noise for robust neural machine translation by introducing self-correcting predictors. Different from previous robust approaches, Secoco enables NMT to explicitly correct noisy inputs and delete specific errors simultaneously with the translation decoding process. Secoco is able to achieve significant improvements over strong baselines on two real-world test sets and a benchmark WMT dataset with good interpretability. We will make our code and dataset publicly available soon.
The Volctrans Neural Speech Translation System for IWSLT 2021
May 16, 2021
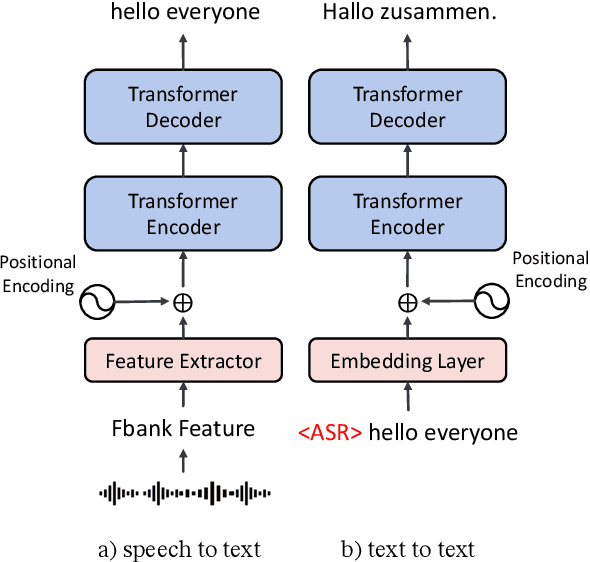
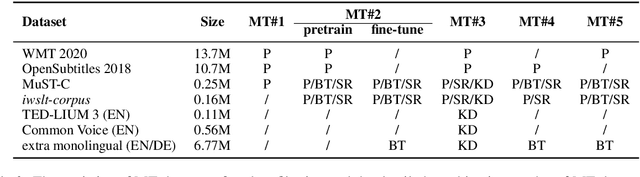
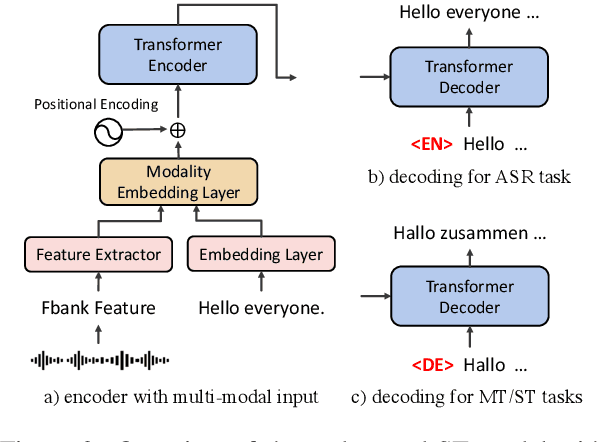
Abstract:This paper describes the systems submitted to IWSLT 2021 by the Volctrans team. We participate in the offline speech translation and text-to-text simultaneous translation tracks. For offline speech translation, our best end-to-end model achieves 8.1 BLEU improvements over the benchmark on the MuST-C test set and is even approaching the results of a strong cascade solution. For text-to-text simultaneous translation, we explore the best practice to optimize the wait-k model. As a result, our final submitted systems exceed the benchmark at around 7 BLEU on the same latency regime. We will publish our code and model to facilitate both future research works and industrial applications.
Autocorrect in the Process of Translation -- Multi-task Learning Improves Dialogue Machine Translation
Apr 21, 2021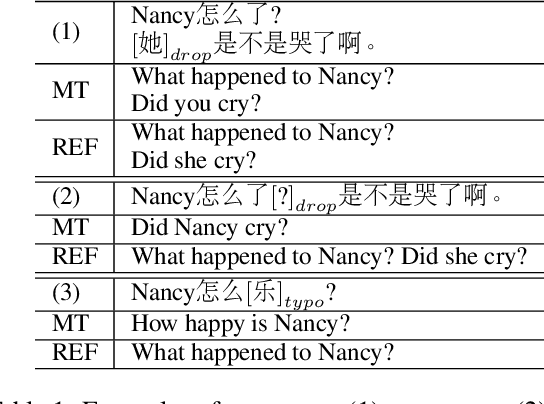
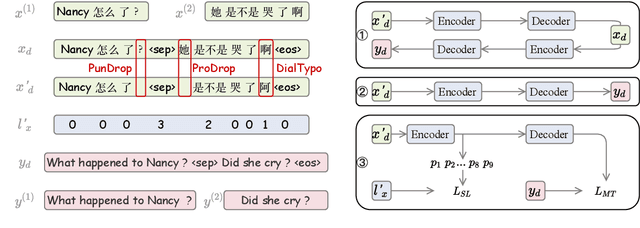
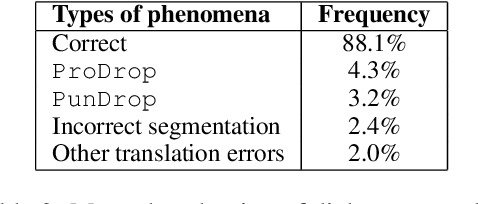
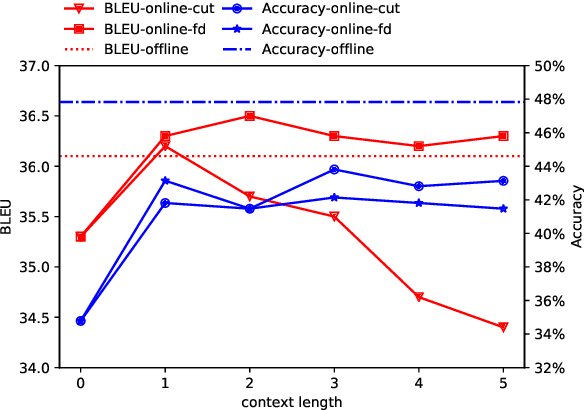
Abstract:Automatic translation of dialogue texts is a much needed demand in many real life scenarios. However, the currently existing neural machine translation delivers unsatisfying results. In this paper, we conduct a deep analysis of a dialogue corpus and summarize three major issues on dialogue translation, including pronoun dropping (\droppro), punctuation dropping (\droppun), and typos (\typo). In response to these challenges, we propose a joint learning method to identify omission and typo, and utilize context to translate dialogue utterances. To properly evaluate the performance, we propose a manually annotated dataset with 1,931 Chinese-English parallel utterances from 300 dialogues as a benchmark testbed for dialogue translation. Our experiments show that the proposed method improves translation quality by 3.2 BLEU over the baselines. It also elevates the recovery rate of omitted pronouns from 26.09% to 47.16%. We will publish the code and dataset publicly at https://github.com/rgwt123/DialogueMT.
Serial or Parallel? Plug-able Adapter for multilingual machine translation
Apr 16, 2021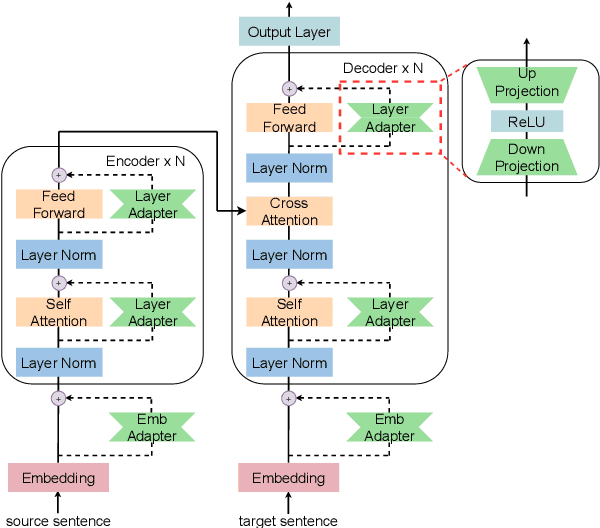
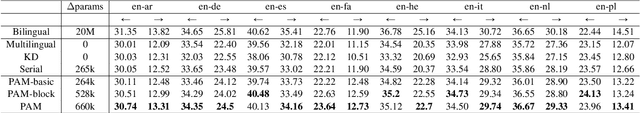
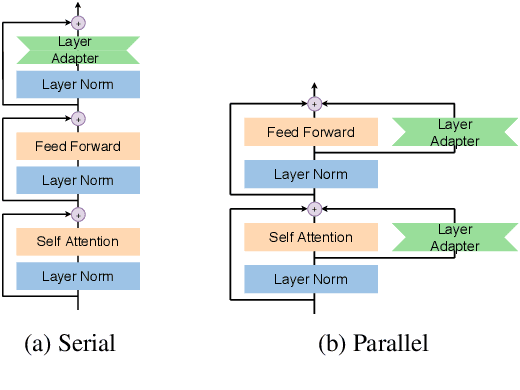
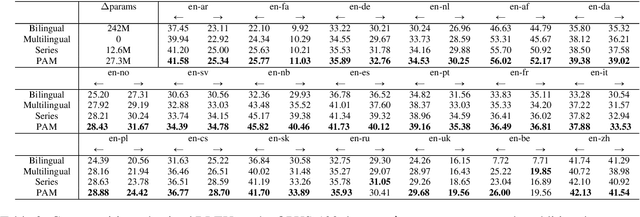
Abstract:Developing a unified multilingual translation model is a key topic in machine translation research. However, existing approaches suffer from performance degradation: multilingual models yield inferior performance compared to the ones trained separately on rich bilingual data. We attribute the performance degradation to two issues: multilingual embedding conflation and multilingual fusion effects. To address the two issues, we propose PAM, a Transformer model augmented with defusion adaptation for multilingual machine translation. Specifically, PAM consists of embedding and layer adapters to shift the word and intermediate representations towards language-specific ones. Extensive experiment results on IWSLT, OPUS-100, and WMT benchmarks show that \method outperforms several strong competitors, including series adapter and multilingual knowledge distillation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge