Zhicheng Liu
and Other Contributors
TrafficSimAgent: A Hierarchical Agent Framework for Autonomous Traffic Simulation with MCP Control
Dec 24, 2025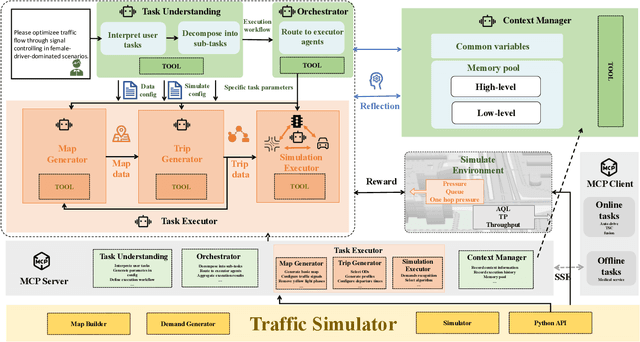
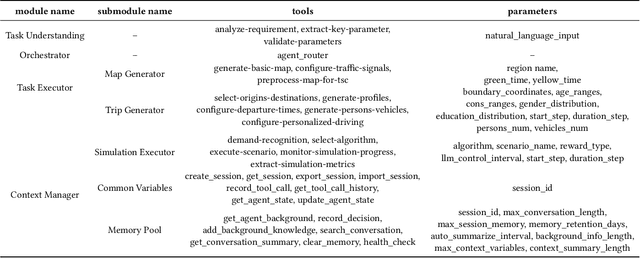
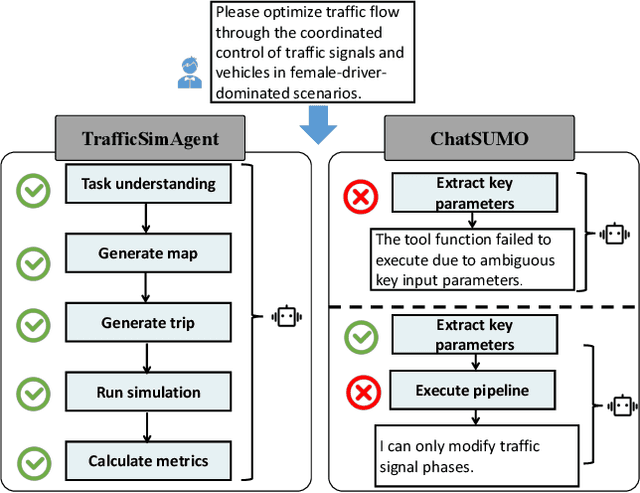
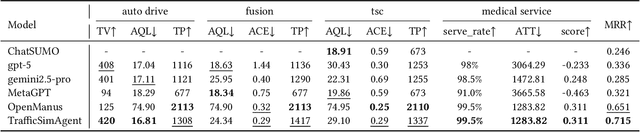
Abstract:Traffic simulation is important for transportation optimization and policy making. While existing simulators such as SUMO and MATSim offer fully-featured platforms and utilities, users without too much knowledge about these platforms often face significant challenges when conducting experiments from scratch and applying them to their daily work. To solve this challenge, we propose TrafficSimAgent, an LLM-based agent framework that serves as an expert in experiment design and decision optimization for general-purpose traffic simulation tasks. The framework facilitates execution through cross-level collaboration among expert agents: high-level expert agents comprehend natural language instructions with high flexibility, plan the overall experiment workflow, and invoke corresponding MCP-compatible tools on demand; meanwhile, low-level expert agents select optimal action plans for fundamental elements based on real-time traffic conditions. Extensive experiments across multiple scenarios show that TrafficSimAgent effectively executes simulations under various conditions and consistently produces reasonable outcomes even when user instructions are ambiguous. Besides, the carefully designed expert-level autonomous decision-driven optimization in TrafficSimAgent yields superior performance when compared with other systems and SOTA LLM based methods.
Pangu Pro MoE: Mixture of Grouped Experts for Efficient Sparsity
May 28, 2025Abstract:The surgence of Mixture of Experts (MoE) in Large Language Models promises a small price of execution cost for a much larger model parameter count and learning capacity, because only a small fraction of parameters are activated for each input token. However, it is commonly observed that some experts are activated far more often than others, leading to system inefficiency when running the experts on different devices in parallel. Therefore, we introduce Mixture of Grouped Experts (MoGE), which groups the experts during selection and balances the expert workload better than MoE in nature. It constrains tokens to activate an equal number of experts within each predefined expert group. When a model execution is distributed on multiple devices, this architectural design ensures a balanced computational load across devices, significantly enhancing throughput, particularly for the inference phase. Further, we build Pangu Pro MoE on Ascend NPUs, a sparse model based on MoGE with 72 billion total parameters, 16 billion of which are activated for each token. The configuration of Pangu Pro MoE is optimized for Ascend 300I Duo and 800I A2 through extensive system simulation studies. Our experiments indicate that MoGE indeed leads to better expert load balancing and more efficient execution for both model training and inference on Ascend NPUs. The inference performance of Pangu Pro MoE achieves 1148 tokens/s per card and can be further improved to 1528 tokens/s per card by speculative acceleration, outperforming comparable 32B and 72B Dense models. Furthermore, we achieve an excellent cost-to-performance ratio for model inference on Ascend 300I Duo. Our studies show that Ascend NPUs are capable of training Pangu Pro MoE with massive parallelization to make it a leading model within the sub-100B total parameter class, outperforming prominent open-source models like GLM-Z1-32B and Qwen3-32B.
Pangu Ultra MoE: How to Train Your Big MoE on Ascend NPUs
May 07, 2025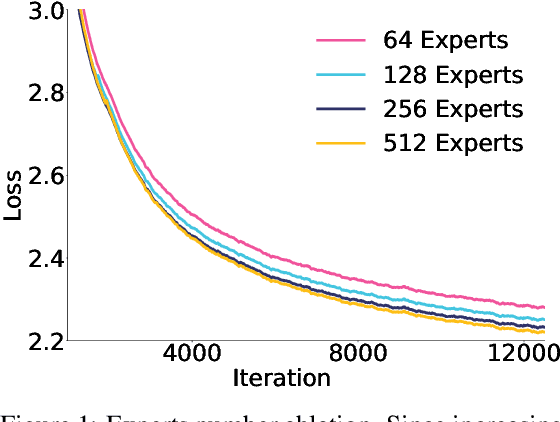

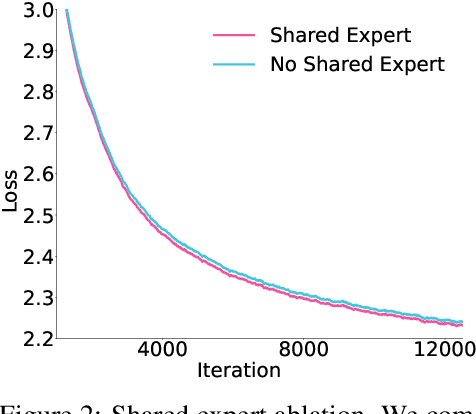
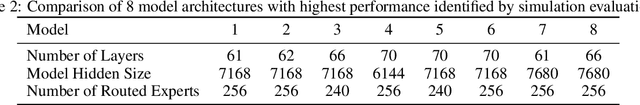
Abstract:Sparse large language models (LLMs) with Mixture of Experts (MoE) and close to a trillion parameters are dominating the realm of most capable language models. However, the massive model scale poses significant challenges for the underlying software and hardware systems. In this paper, we aim to uncover a recipe to harness such scale on Ascend NPUs. The key goals are better usage of the computing resources under the dynamic sparse model structures and materializing the expected performance gain on the actual hardware. To select model configurations suitable for Ascend NPUs without repeatedly running the expensive experiments, we leverage simulation to compare the trade-off of various model hyperparameters. This study led to Pangu Ultra MoE, a sparse LLM with 718 billion parameters, and we conducted experiments on the model to verify the simulation results. On the system side, we dig into Expert Parallelism to optimize the communication between NPU devices to reduce the synchronization overhead. We also optimize the memory efficiency within the devices to further reduce the parameter and activation management overhead. In the end, we achieve an MFU of 30.0% when training Pangu Ultra MoE, with performance comparable to that of DeepSeek R1, on 6K Ascend NPUs, and demonstrate that the Ascend system is capable of harnessing all the training stages of the state-of-the-art language models. Extensive experiments indicate that our recipe can lead to efficient training of large-scale sparse language models with MoE. We also study the behaviors of such models for future reference.
Pangu Ultra: Pushing the Limits of Dense Large Language Models on Ascend NPUs
Apr 10, 2025



Abstract:We present Pangu Ultra, a Large Language Model (LLM) with 135 billion parameters and dense Transformer modules trained on Ascend Neural Processing Units (NPUs). Although the field of LLM has been witnessing unprecedented advances in pushing the scale and capability of LLM in recent years, training such a large-scale model still involves significant optimization and system challenges. To stabilize the training process, we propose depth-scaled sandwich normalization, which effectively eliminates loss spikes during the training process of deep models. We pre-train our model on 13.2 trillion diverse and high-quality tokens and further enhance its reasoning capabilities during post-training. To perform such large-scale training efficiently, we utilize 8,192 Ascend NPUs with a series of system optimizations. Evaluations on multiple diverse benchmarks indicate that Pangu Ultra significantly advances the state-of-the-art capabilities of dense LLMs such as Llama 405B and Mistral Large 2, and even achieves competitive results with DeepSeek-R1, whose sparse model structure contains much more parameters. Our exploration demonstrates that Ascend NPUs are capable of efficiently and effectively training dense models with more than 100 billion parameters. Our model and system will be available for our commercial customers.
Comparing Native and Non-native English Speakers' Behaviors in Collaborative Writing through Visual Analytics
Feb 25, 2025Abstract:Understanding collaborative writing dynamics between native speakers (NS) and non-native speakers (NNS) is critical for enhancing collaboration quality and team inclusivity. In this paper, we partnered with communication researchers to develop visual analytics solutions for comparing NS and NNS behaviors in 162 writing sessions across 27 teams. The primary challenges in analyzing writing behaviors are data complexity and the uncertainties introduced by automated methods. In response, we present \textsc{COALA}, a novel visual analytics tool that improves model interpretability by displaying uncertainties in author clusters, generating behavior summaries using large language models, and visualizing writing-related actions at multiple granularities. We validated the effectiveness of \textsc{COALA} through user studies with domain experts (N=2+2) and researchers with relevant experience (N=8). We present the insights discovered by participants using \textsc{COALA}, suggest features for future AI-assisted collaborative writing tools, and discuss the broader implications for analyzing collaborative processes beyond writing.
Evaluating the Semantic Profiling Abilities of LLMs for Natural Language Utterances in Data Visualization
Jul 09, 2024Abstract:Automatically generating data visualizations in response to human utterances on datasets necessitates a deep semantic understanding of the data utterance, including implicit and explicit references to data attributes, visualization tasks, and necessary data preparation steps. Natural Language Interfaces (NLIs) for data visualization have explored ways to infer such information, yet challenges persist due to inherent uncertainty in human speech. Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) provide an avenue to address these challenges, but their ability to extract the relevant semantic information remains unexplored. In this study, we evaluate four publicly available LLMs (GPT-4, Gemini-Pro, Llama3, and Mixtral), investigating their ability to comprehend utterances even in the presence of uncertainty and identify the relevant data context and visual tasks. Our findings reveal that LLMs are sensitive to uncertainties in utterances. Despite this sensitivity, they are able to extract the relevant data context. However, LLMs struggle with inferring visualization tasks. Based on these results, we highlight future research directions on using LLMs for visualization generation.
From Pixels to Progress: Generating Road Network from Satellite Imagery for Socioeconomic Insights in Impoverished Areas
Jun 17, 2024Abstract:The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) aim to resolve societal challenges, such as eradicating poverty and improving the lives of vulnerable populations in impoverished areas. Those areas rely on road infrastructure construction to promote accessibility and economic development. Although publicly available data like OpenStreetMap is available to monitor road status, data completeness in impoverished areas is limited. Meanwhile, the development of deep learning techniques and satellite imagery shows excellent potential for earth monitoring. To tackle the challenge of road network assessment in impoverished areas, we develop a systematic road extraction framework combining an encoder-decoder architecture and morphological operations on satellite imagery, offering an integrated workflow for interdisciplinary researchers. Extensive experiments of road network extraction on real-world data in impoverished regions achieve a 42.7% enhancement in the F1-score over the baseline methods and reconstruct about 80% of the actual roads. We also propose a comprehensive road network dataset covering approximately 794,178 km2 area and 17.048 million people in 382 impoverished counties in China. The generated dataset is further utilized to conduct socioeconomic analysis in impoverished counties, showing that road network construction positively impacts regional economic development. The technical appendix, code, and generated dataset can be found at https://github.com/tsinghua-fib-lab/Road_network_extraction_impoverished_counties.
G-DIG: Towards Gradient-based DIverse and hiGh-quality Instruction Data Selection for Machine Translation
May 21, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable abilities in general scenarios. Instruction finetuning empowers them to align with humans in various tasks. Nevertheless, the Diversity and Quality of the instruction data remain two main challenges for instruction finetuning. With regard to this, in this paper, we propose a novel gradient-based method to automatically select high-quality and diverse instruction finetuning data for machine translation. Our key innovation centers around analyzing how individual training examples influence the model during training. Specifically, we select training examples that exert beneficial influences on the model as high-quality ones by means of Influence Function plus a small high-quality seed dataset. Moreover, to enhance the diversity of the training data we maximize the variety of influences they have on the model by clustering on their gradients and resampling. Extensive experiments on WMT22 and FLORES translation tasks demonstrate the superiority of our methods, and in-depth analysis further validates their effectiveness and generalization.
WordDecipher: Enhancing Digital Workspace Communication with Explainable AI for Non-native English Speakers
Apr 10, 2024Abstract:Non-native English speakers (NNES) face challenges in digital workspace communication (e.g., emails, Slack messages), often inadvertently translating expressions from their native languages, which can lead to awkward or incorrect usage. Current AI-assisted writing tools are equipped with fluency enhancement and rewriting suggestions; however, NNES may struggle to grasp the subtleties among various expressions, making it challenging to choose the one that accurately reflects their intent. Such challenges are exacerbated in high-stake text-based communications, where the absence of non-verbal cues heightens the risk of misinterpretation. By leveraging the latest advancements in large language models (LLM) and word embeddings, we propose WordDecipher, an explainable AI-assisted writing tool to enhance digital workspace communication for NNES. WordDecipher not only identifies the perceived social intentions detected in users' writing, but also generates rewriting suggestions aligned with users' intended messages, either numerically or by inferring from users' writing in their native language. Then, WordDecipher provides an overview of nuances to help NNES make selections. Through a usage scenario, we demonstrate how WordDecipher can significantly enhance an NNES's ability to communicate her request, showcasing its potential to transform workspace communication for NNES.
ASAP: Interpretable Analysis and Summarization of AI-generated Image Patterns at Scale
Apr 03, 2024



Abstract:Generative image models have emerged as a promising technology to produce realistic images. Despite potential benefits, concerns grow about its misuse, particularly in generating deceptive images that could raise significant ethical, legal, and societal issues. Consequently, there is growing demand to empower users to effectively discern and comprehend patterns of AI-generated images. To this end, we developed ASAP, an interactive visualization system that automatically extracts distinct patterns of AI-generated images and allows users to interactively explore them via various views. To uncover fake patterns, ASAP introduces a novel image encoder, adapted from CLIP, which transforms images into compact "distilled" representations, enriched with information for differentiating authentic and fake images. These representations generate gradients that propagate back to the attention maps of CLIP's transformer block. This process quantifies the relative importance of each pixel to image authenticity or fakeness, exposing key deceptive patterns. ASAP enables the at scale interactive analysis of these patterns through multiple, coordinated visualizations. This includes a representation overview with innovative cell glyphs to aid in the exploration and qualitative evaluation of fake patterns across a vast array of images, as well as a pattern view that displays authenticity-indicating patterns in images and quantifies their impact. ASAP supports the analysis of cutting-edge generative models with the latest architectures, including GAN-based models like proGAN and diffusion models like the latent diffusion model. We demonstrate ASAP's usefulness through two usage scenarios using multiple fake image detection benchmark datasets, revealing its ability to identify and understand hidden patterns in AI-generated images, especially in detecting fake human faces produced by diffusion-based techniques.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge