Sasu Tarkoma
Bio-inspired Agentic Self-healing Framework for Resilient Distributed Computing Continuum Systems
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:Human biological systems sustain life through extraordinary resilience, continually detecting damage, orchestrating targeted responses, and restoring function through self-healing. Inspired by these capabilities, this paper introduces ReCiSt, a bio-inspired agentic self-healing framework designed to achieve resilience in Distributed Computing Continuum Systems (DCCS). Modern DCCS integrate heterogeneous computing resources, ranging from resource-constrained IoT devices to high-performance cloud infrastructures, and their inherent complexity, mobility, and dynamic operating conditions expose them to frequent faults that disrupt service continuity. These challenges underscore the need for scalable, adaptive, and self-regulated resilience strategies. ReCiSt reconstructs the biological phases of Hemostasis, Inflammation, Proliferation, and Remodeling into the computational layers Containment, Diagnosis, Meta-Cognitive, and Knowledge for DCCS. These four layers perform autonomous fault isolation, causal diagnosis, adaptive recovery, and long-term knowledge consolidation through Language Model (LM)-powered agents. These agents interpret heterogeneous logs, infer root causes, refine reasoning pathways, and reconfigure resources with minimal human intervention. The proposed ReCiSt framework is evaluated on public fault datasets using multiple LMs, and no baseline comparison is included due to the scarcity of similar approaches. Nevertheless, our results, evaluated under different LMs, confirm ReCiSt's self-healing capabilities within tens of seconds with minimum of 10% of agent CPU usage. Our results also demonstrated depth of analysis to over come uncertainties and amount of micro-agents invoked to achieve resilience.
Towards Efficient Multi-LLM Inference: Characterization and Analysis of LLM Routing and Hierarchical Techniques
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Recent progress in Language Models (LMs) has dramatically advanced the field of natural language processing (NLP), excelling at tasks like text generation, summarization, and question answering. However, their inference remains computationally expensive and energy intensive, especially in settings with limited hardware, power, or bandwidth. This makes it difficult to deploy LMs in mobile, edge, or cost sensitive environments. To address these challenges, recent approaches have introduced multi LLM intelligent model selection strategies that dynamically allocate computational resources based on query complexity -- using lightweight models for simpler queries and escalating to larger models only when necessary. This survey explores two complementary strategies for efficient LLM inference: (i) routing, which selects the most suitable model based on the query, and (ii) cascading or hierarchical inference (HI), which escalates queries through a sequence of models until a confident response is found. Both approaches aim to reduce computation by using lightweight models for simpler tasks while offloading only when needed. We provide a comparative analysis of these techniques across key performance metrics, discuss benchmarking efforts, and outline open challenges. Finally, we outline future research directions to enable faster response times, adaptive model selection based on task complexity, and scalable deployment across heterogeneous environments, making LLM based systems more efficient and accessible for real world applications.
UserCentrix: An Agentic Memory-augmented AI Framework for Smart Spaces
May 01, 2025Abstract:Agentic AI, with its autonomous and proactive decision-making, has transformed smart environments. By integrating Generative AI (GenAI) and multi-agent systems, modern AI frameworks can dynamically adapt to user preferences, optimize data management, and improve resource allocation. This paper introduces UserCentrix, an agentic memory-augmented AI framework designed to enhance smart spaces through dynamic, context-aware decision-making. This framework integrates personalized Large Language Model (LLM) agents that leverage user preferences and LLM memory management to deliver proactive and adaptive assistance. Furthermore, it incorporates a hybrid hierarchical control system, balancing centralized and distributed processing to optimize real-time responsiveness while maintaining global situational awareness. UserCentrix achieves resource-efficient AI interactions by embedding memory-augmented reasoning, cooperative agent negotiation, and adaptive orchestration strategies. Our key contributions include (i) a self-organizing framework with proactive scaling based on task urgency, (ii) a Value of Information (VoI)-driven decision-making process, (iii) a meta-reasoning personal LLM agent, and (iv) an intelligent multi-agent coordination system for seamless environment adaptation. Experimental results across various models confirm the effectiveness of our approach in enhancing response accuracy, system efficiency, and computational resource management in real-world application.
Exponentially Weighted Instance-Aware Repeat Factor Sampling for Long-Tailed Object Detection Model Training in Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Surveillance Scenarios
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:Object detection models often struggle with class imbalance, where rare categories appear significantly less frequently than common ones. Existing sampling-based rebalancing strategies, such as Repeat Factor Sampling (RFS) and Instance-Aware Repeat Factor Sampling (IRFS), mitigate this issue by adjusting sample frequencies based on image and instance counts. However, these methods are based on linear adjustments, which limit their effectiveness in long-tailed distributions. This work introduces Exponentially Weighted Instance-Aware Repeat Factor Sampling (E-IRFS), an extension of IRFS that applies exponential scaling to better differentiate between rare and frequent classes. E-IRFS adjusts sampling probabilities using an exponential function applied to the geometric mean of image and instance frequencies, ensuring a more adaptive rebalancing strategy. We evaluate E-IRFS on a dataset derived from the Fireman-UAV-RGBT Dataset and four additional public datasets, using YOLOv11 object detection models to identify fire, smoke, people and lakes in emergency scenarios. The results show that E-IRFS improves detection performance by 22\% over the baseline and outperforms RFS and IRFS, particularly for rare categories. The analysis also highlights that E-IRFS has a stronger effect on lightweight models with limited capacity, as these models rely more on data sampling strategies to address class imbalance. The findings demonstrate that E-IRFS improves rare object detection in resource-constrained environments, making it a suitable solution for real-time applications such as UAV-based emergency monitoring.
Sometimes Painful but Certainly Promising: Feasibility and Trade-offs of Language Model Inference at the Edge
Mar 12, 2025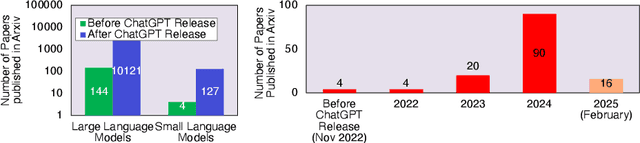
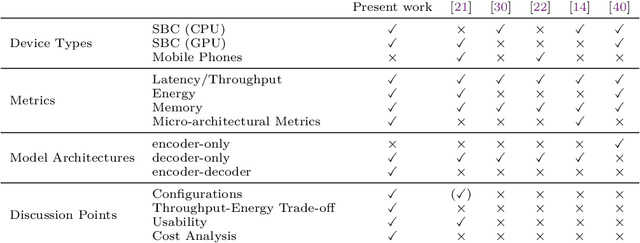
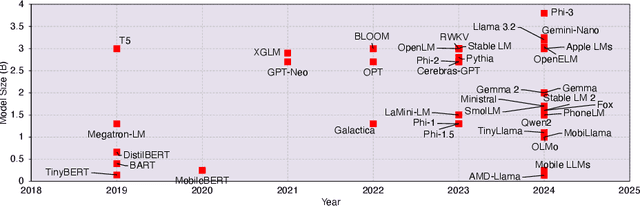
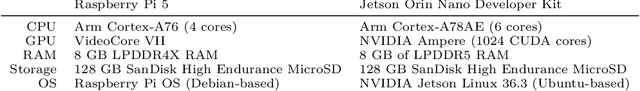
Abstract:The rapid rise of Language Models (LMs) has expanded the capabilities of natural language processing, powering applications from text generation to complex decision-making. While state-of-the-art LMs often boast hundreds of billions of parameters and are primarily deployed in data centers, recent trends show a growing focus on compact models-typically under 10 billion parameters-enabled by techniques such as quantization and other model compression techniques. This shift paves the way for LMs on edge devices, offering potential benefits such as enhanced privacy, reduced latency, and improved data sovereignty. However, the inherent complexity of even these smaller models, combined with the limited computing resources of edge hardware, raises critical questions about the practical trade-offs in executing LM inference outside the cloud. To address these challenges, we present a comprehensive evaluation of generative LM inference on representative CPU-based and GPU-accelerated edge devices. Our study measures key performance indicators-including memory usage, inference speed, and energy consumption-across various device configurations. Additionally, we examine throughput-energy trade-offs, cost considerations, and usability, alongside an assessment of qualitative model performance. While quantization helps mitigate memory overhead, it does not fully eliminate resource bottlenecks, especially for larger models. Our findings quantify the memory and energy constraints that must be considered for practical real-world deployments, offering concrete insights into the trade-offs between model size, inference performance, and efficiency. The exploration of LMs at the edge is still in its early stages. We hope this study provides a foundation for future research, guiding the refinement of models, the enhancement of inference efficiency, and the advancement of edge-centric AI systems.
Large Language Model Based Multi-Agent System Augmented Complex Event Processing Pipeline for Internet of Multimedia Things
Jan 03, 2025Abstract:This paper presents the development and evaluation of a Large Language Model (LLM), also known as foundation models, based multi-agent system framework for complex event processing (CEP) with a focus on video query processing use cases. The primary goal is to create a proof-of-concept (POC) that integrates state-of-the-art LLM orchestration frameworks with publish/subscribe (pub/sub) tools to address the integration of LLMs with current CEP systems. Utilizing the Autogen framework in conjunction with Kafka message brokers, the system demonstrates an autonomous CEP pipeline capable of handling complex workflows. Extensive experiments evaluate the system's performance across varying configurations, complexities, and video resolutions, revealing the trade-offs between functionality and latency. The results show that while higher agent count and video complexities increase latency, the system maintains high consistency in narrative coherence. This research builds upon and contributes to, existing novel approaches to distributed AI systems, offering detailed insights into integrating such systems into existing infrastructures.
Creation of AI-driven Smart Spaces for Enhanced Indoor Environments -- A Survey
Dec 19, 2024Abstract:Smart spaces are ubiquitous computing environments that integrate diverse sensing and communication technologies to enhance space functionality, optimize energy utilization, and improve user comfort and well-being. The integration of emerging AI methodologies into these environments facilitates the formation of AI-driven smart spaces, which further enhance functionalities of the spaces by enabling advanced applications such as personalized comfort settings, interactive living spaces, and automatization of the space systems, all resulting in enhanced indoor experiences of the users. In this paper, we present a systematic survey of existing research on the foundational components of AI-driven smart spaces, including sensor technologies, data communication protocols, sensor network management and maintenance strategies, as well as the data collection, processing and analytics. Given the pivotal role of AI in establishing AI-powered smart spaces, we explore the opportunities and challenges associated with traditional machine learning (ML) approaches, such as deep learning (DL), and emerging methodologies including large language models (LLMs). Finally, we provide key insights necessary for the development of AI-driven smart spaces, propose future research directions, and sheds light on the path forward.
Future-Proofing Mobile Networks: A Digital Twin Approach to Multi-Signal Management
Jul 22, 2024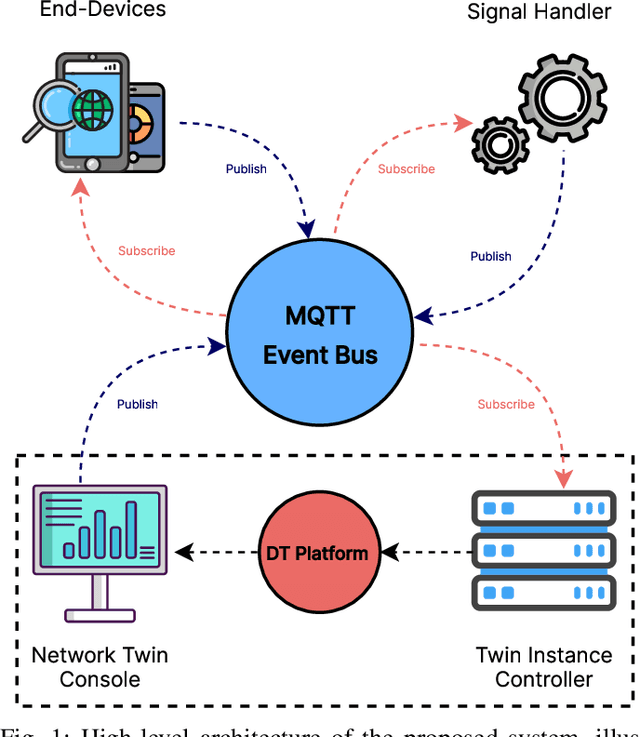
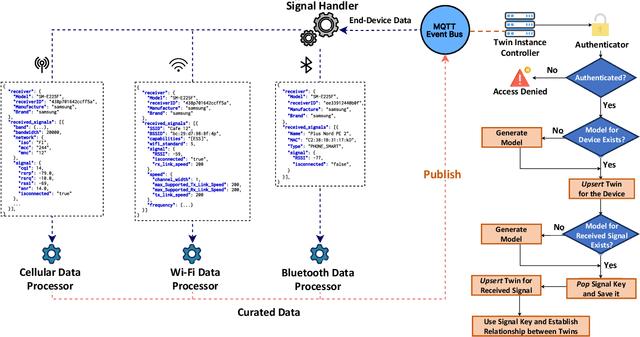
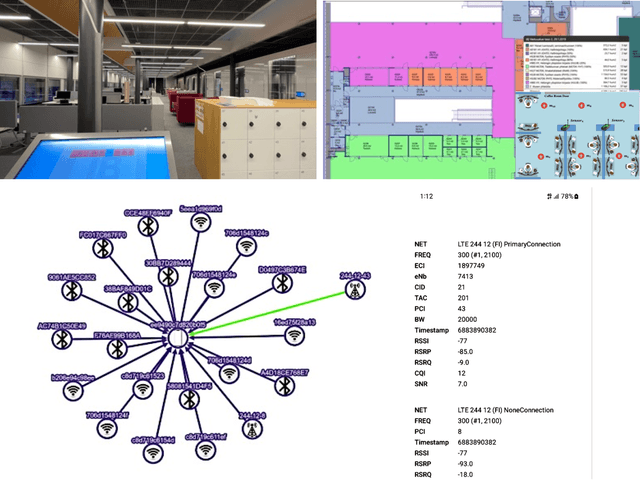
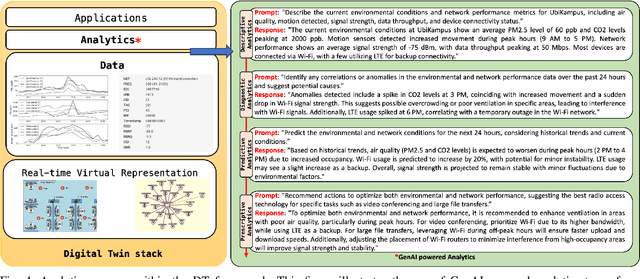
Abstract:Digital Twins (DTs) are set to become a key enabling technology in future wireless networks, with their use in network management increasing significantly. We developed a DT framework that leverages the heterogeneity of network access technologies as a resource for enhanced network performance and management, enabling smart data handling in the physical network. Tested in a \textit{Campus Area Network} environment, our framework integrates diverse data sources to provide real-time, holistic insights into network performance and environmental sensing. We also envision that traditional analytics will evolve to rely on emerging AI models, such as Generative AI (GenAI), while leveraging current analytics capabilities. This capacity can simplify analytics processes through advanced ML models, enabling descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics in a unified fashion. Finally, we present specific research opportunities concerning interoperability aspects and envision aligning advancements in DT technology with evolved AI integration.
From Pixels to Progress: Generating Road Network from Satellite Imagery for Socioeconomic Insights in Impoverished Areas
Jun 17, 2024Abstract:The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) aim to resolve societal challenges, such as eradicating poverty and improving the lives of vulnerable populations in impoverished areas. Those areas rely on road infrastructure construction to promote accessibility and economic development. Although publicly available data like OpenStreetMap is available to monitor road status, data completeness in impoverished areas is limited. Meanwhile, the development of deep learning techniques and satellite imagery shows excellent potential for earth monitoring. To tackle the challenge of road network assessment in impoverished areas, we develop a systematic road extraction framework combining an encoder-decoder architecture and morphological operations on satellite imagery, offering an integrated workflow for interdisciplinary researchers. Extensive experiments of road network extraction on real-world data in impoverished regions achieve a 42.7% enhancement in the F1-score over the baseline methods and reconstruct about 80% of the actual roads. We also propose a comprehensive road network dataset covering approximately 794,178 km2 area and 17.048 million people in 382 impoverished counties in China. The generated dataset is further utilized to conduct socioeconomic analysis in impoverished counties, showing that road network construction positively impacts regional economic development. The technical appendix, code, and generated dataset can be found at https://github.com/tsinghua-fib-lab/Road_network_extraction_impoverished_counties.
AI-native Interconnect Framework for Integration of Large Language Model Technologies in 6G Systems
Nov 10, 2023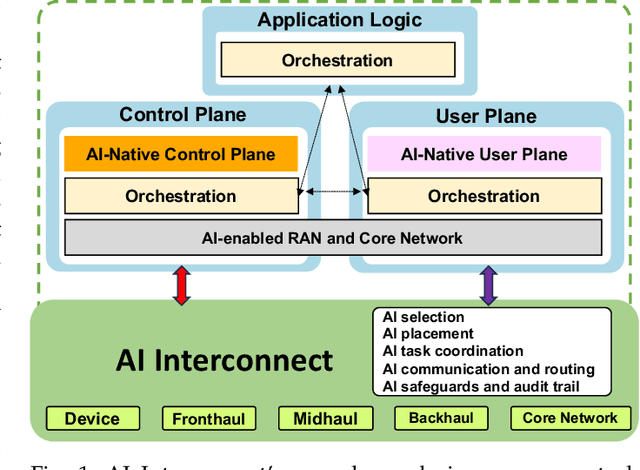
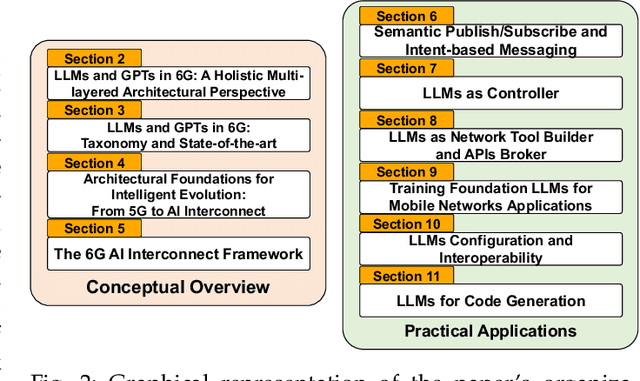
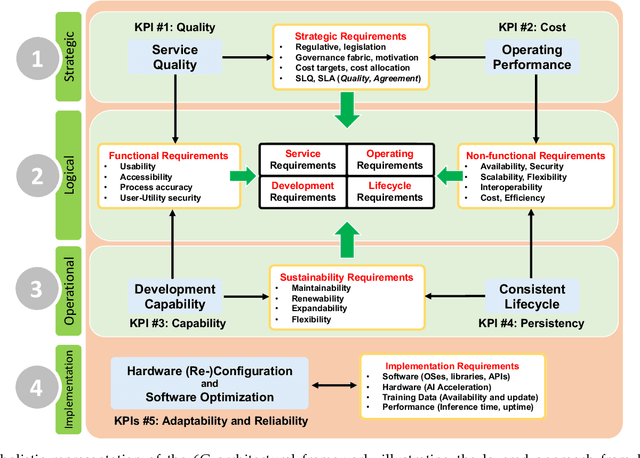
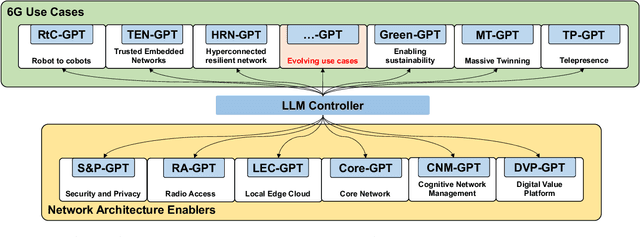
Abstract:The evolution towards 6G architecture promises a transformative shift in communication networks, with artificial intelligence (AI) playing a pivotal role. This paper delves deep into the seamless integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) and Generalized Pretrained Transformers (GPT) within 6G systems. Their ability to grasp intent, strategize, and execute intricate commands will be pivotal in redefining network functionalities and interactions. Central to this is the AI Interconnect framework, intricately woven to facilitate AI-centric operations within the network. Building on the continuously evolving current state-of-the-art, we present a new architectural perspective for the upcoming generation of mobile networks. Here, LLMs and GPTs will collaboratively take center stage alongside traditional pre-generative AI and machine learning (ML) algorithms. This union promises a novel confluence of the old and new, melding tried-and-tested methods with transformative AI technologies. Along with providing a conceptual overview of this evolution, we delve into the nuances of practical applications arising from such an integration. Through this paper, we envisage a symbiotic integration where AI becomes the cornerstone of the next-generation communication paradigm, offering insights into the structural and functional facets of an AI-native 6G network.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge