Rong Ye
Signed Graph Learning with Hidden Nodes
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:Signed graphs, which are characterized by both positive and negative edge weights, have recently attracted significant attention in the field of graph signal processing (GSP). Existing works on signed graph learning typically assume that all graph nodes are available. However, in some specific applications, only a subset of nodes can be observed while the remaining nodes stay hidden. To address this challenge, we propose a novel method for identifying signed graph that accounts for hidden nodes, termed \textit{signed graph learning with hidden nodes under column-sparsity regularization} (SGL-HNCS). Our method is based on the assumption that graph signals are smooth over signed graphs, i.e., signal values of two nodes connected by positive (negative) edges are similar (dissimilar). Rooted in this prior assumption, the topology inference of a signed graph is formulated as a constrained optimization problem with column-sparsity regularization, where the goal is to reconstruct the signed graph Laplacian matrix without disregarding the influence of hidden nodes. We solve the constrained optimization problem using a tailored block coordinate descent (BCD) approach. Experimental results using synthetic data and real-world data demonstrate the efficiency of the proposed SGL-HNCS method.
* 25 pages, 7 figures, published to Signal Processing
Seed LiveInterpret 2.0: End-to-end Simultaneous Speech-to-speech Translation with Your Voice
Jul 24, 2025



Abstract:Simultaneous Interpretation (SI) represents one of the most daunting frontiers in the translation industry, with product-level automatic systems long plagued by intractable challenges: subpar transcription and translation quality, lack of real-time speech generation, multi-speaker confusion, and translated speech inflation, especially in long-form discourses. In this study, we introduce Seed-LiveInterpret 2.0, an end-to-end SI model that delivers high-fidelity, ultra-low-latency speech-to-speech generation with voice cloning capabilities. As a fully operational product-level solution, Seed-LiveInterpret 2.0 tackles these challenges head-on through our novel duplex speech-to-speech understanding-generating framework. Experimental results demonstrate that through large-scale pretraining and reinforcement learning, the model achieves a significantly better balance between translation accuracy and latency, validated by human interpreters to exceed 70% correctness in complex scenarios. Notably, Seed-LiveInterpret 2.0 outperforms commercial SI solutions by significant margins in translation quality, while slashing the average latency of cloned speech from nearly 10 seconds to a near-real-time 3 seconds, which is around a near 70% reduction that drastically enhances practical usability.
Multi-agent KTO: Reinforcing Strategic Interactions of Large Language Model in Language Game
Jan 24, 2025



Abstract:Achieving Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) requires AI agents that can not only make stratigic decisions but also engage in flexible and meaningful communication. Inspired by Wittgenstein's language game theory in Philosophical Investigations, we propose that language agents can learn through in-context interaction rather than traditional multi-stage frameworks that separate decision-making from language expression. Using Werewolf, a social deduction game that tests language understanding, strategic interaction, and adaptability, we develop the Multi-agent Kahneman & Tversky's Optimization (MaKTO). MaKTO engages diverse models in extensive gameplay to generate unpaired desirable and unacceptable responses, then employs KTO to refine the model's decision-making process. In 9-player Werewolf games, MaKTO achieves a 61% average win rate across various models, outperforming GPT-4o and two-stage RL agents by relative improvements of 23.0% and 10.9%, respectively. Notably, MaKTO also demonstrates human-like performance, winning 60% against expert players and showing only 49% detectability in Turing-style blind tests. These results showcase MaKTO's superior decision-making, strategic adaptation, and natural language generation in complex social deduction games.
AgentSense: Benchmarking Social Intelligence of Language Agents through Interactive Scenarios
Oct 25, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly leveraged to empower autonomous agents to simulate human beings in various fields of behavioral research. However, evaluating their capacity to navigate complex social interactions remains a challenge. Previous studies face limitations due to insufficient scenario diversity, complexity, and a single-perspective focus. To this end, we introduce AgentSense: Benchmarking Social Intelligence of Language Agents through Interactive Scenarios. Drawing on Dramaturgical Theory, AgentSense employs a bottom-up approach to create 1,225 diverse social scenarios constructed from extensive scripts. We evaluate LLM-driven agents through multi-turn interactions, emphasizing both goal completion and implicit reasoning. We analyze goals using ERG theory and conduct comprehensive experiments. Our findings highlight that LLMs struggle with goals in complex social scenarios, especially high-level growth needs, and even GPT-4o requires improvement in private information reasoning.
Debatrix: Multi-dimensinal Debate Judge with Iterative Chronological Analysis Based on LLM
Mar 12, 2024



Abstract:How can we construct an automated debate judge to evaluate an extensive, vibrant, multi-turn debate? This task is challenging, as judging a debate involves grappling with lengthy texts, intricate argument relationships, and multi-dimensional assessments. At the same time, current research mainly focuses on short dialogues, rarely touching upon the evaluation of an entire debate. In this paper, by leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs), we propose Debatrix, which makes the analysis and assessment of multi-turn debates more aligned with majority preferences. Specifically, Debatrix features a vertical, iterative chronological analysis and a horizontal, multi-dimensional evaluation collaboration. To align with real-world debate scenarios, we introduced the PanelBench benchmark, comparing our system's performance to actual debate outcomes. The findings indicate a notable enhancement over directly using LLMs for debate evaluation. Source code and benchmark data are available online at https://github.com/ljcleo/Debatrix .
Speech Translation with Large Language Models: An Industrial Practice
Dec 21, 2023



Abstract:Given the great success of large language models (LLMs) across various tasks, in this paper, we introduce LLM-ST, a novel and effective speech translation model constructed upon a pre-trained LLM. By integrating the large language model (LLM) with a speech encoder and employing multi-task instruction tuning, LLM-ST can produce accurate timestamped transcriptions and translations, even from long audio inputs. Furthermore, our findings indicate that the implementation of Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting can yield advantages in the context of LLM-ST. Through rigorous experimentation on English and Chinese datasets, we showcase the exceptional performance of LLM-ST, establishing a new benchmark in the field of speech translation. Demo: https://speechtranslation.github.io/llm-st/.
Argue with Me Tersely: Towards Sentence-Level Counter-Argument Generation
Dec 21, 2023



Abstract:Counter-argument generation -- a captivating area in computational linguistics -- seeks to craft statements that offer opposing views. While most research has ventured into paragraph-level generation, sentence-level counter-argument generation beckons with its unique constraints and brevity-focused challenges. Furthermore, the diverse nature of counter-arguments poses challenges for evaluating model performance solely based on n-gram-based metrics. In this paper, we present the ArgTersely benchmark for sentence-level counter-argument generation, drawing from a manually annotated dataset from the ChangeMyView debate forum. We also propose Arg-LlaMA for generating high-quality counter-argument. For better evaluation, we trained a BERT-based evaluator Arg-Judge with human preference data. We conducted comparative experiments involving various baselines such as LlaMA, Alpaca, GPT-3, and others. The results show the competitiveness of our proposed framework and evaluator in counter-argument generation tasks. Code and data are available at https://github.com/amazingljy1206/ArgTersely.
Hi-ArG: Exploring the Integration of Hierarchical Argumentation Graphs in Language Pretraining
Dec 01, 2023



Abstract:The knowledge graph is a structure to store and represent knowledge, and recent studies have discussed its capability to assist language models for various applications. Some variations of knowledge graphs aim to record arguments and their relations for computational argumentation tasks. However, many must simplify semantic types to fit specific schemas, thus losing flexibility and expression ability. In this paper, we propose the Hierarchical Argumentation Graph (Hi-ArG), a new structure to organize arguments. We also introduce two approaches to exploit Hi-ArG, including a text-graph multi-modal model GreaseArG and a new pre-training framework augmented with graph information. Experiments on two argumentation tasks have shown that after further pre-training and fine-tuning, GreaseArG supersedes same-scale language models on these tasks, while incorporating graph information during further pre-training can also improve the performance of vanilla language models. Code for this paper is available at https://github.com/ljcleo/Hi-ArG .
Put Your Money Where Your Mouth Is: Evaluating Strategic Planning and Execution of LLM Agents in an Auction Arena
Oct 09, 2023Abstract:Can Large Language Models (LLMs) simulate human behavior in complex environments? LLMs have recently been shown to exhibit advanced reasoning skills but much of NLP evaluation still relies on static benchmarks. Answering this requires evaluation environments that probe strategic reasoning in competitive, dynamic scenarios that involve long-term planning. We introduce AucArena, a novel simulation environment for evaluating LLMs within auctions, a setting chosen for being highly unpredictable and involving many skills related to resource and risk management, while also being easy to evaluate. We conduct several controlled simulations using state-of-the-art LLMs as bidding agents. We find that through simple prompting, LLMs do indeed demonstrate many of the skills needed for effectively engaging in auctions (e.g., managing budget, adhering to long-term goals and priorities), skills that we find can be sharpened by explicitly encouraging models to be adaptive and observe strategies in past auctions. These results are significant as they show the potential of using LLM agents to model intricate social dynamics, especially in competitive settings. However, we also observe considerable variability in the capabilities of individual LLMs. Notably, even our most advanced models (GPT-4) are occasionally surpassed by heuristic baselines and human agents, highlighting the potential for further improvements in the design of LLM agents and the important role that our simulation environment can play in further testing and refining agent architectures.
Recent Advances in Direct Speech-to-text Translation
Jun 20, 2023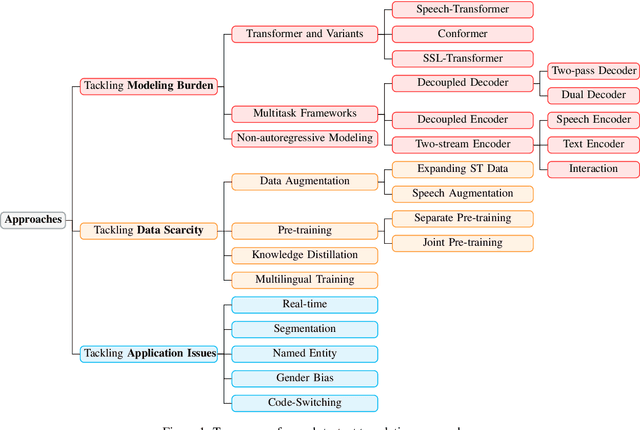
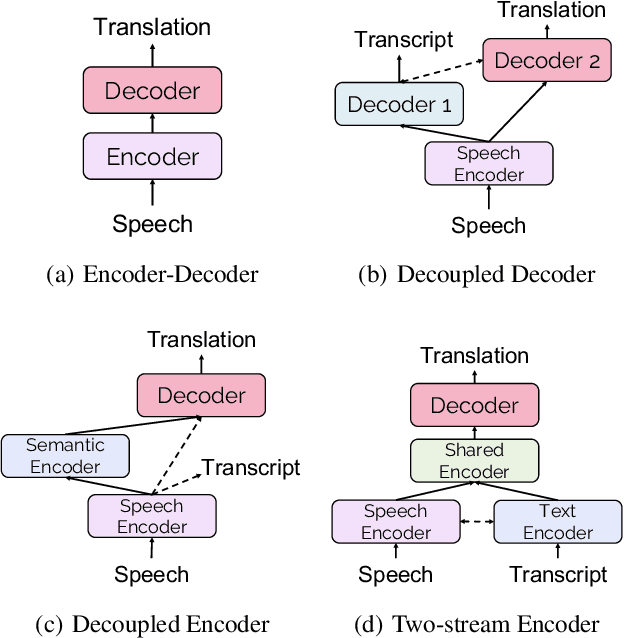
Abstract:Recently, speech-to-text translation has attracted more and more attention and many studies have emerged rapidly. In this paper, we present a comprehensive survey on direct speech translation aiming to summarize the current state-of-the-art techniques. First, we categorize the existing research work into three directions based on the main challenges -- modeling burden, data scarcity, and application issues. To tackle the problem of modeling burden, two main structures have been proposed, encoder-decoder framework (Transformer and the variants) and multitask frameworks. For the challenge of data scarcity, recent work resorts to many sophisticated techniques, such as data augmentation, pre-training, knowledge distillation, and multilingual modeling. We analyze and summarize the application issues, which include real-time, segmentation, named entity, gender bias, and code-switching. Finally, we discuss some promising directions for future work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge