Yongxin Zhang
Multi-agent KTO: Reinforcing Strategic Interactions of Large Language Model in Language Game
Jan 24, 2025



Abstract:Achieving Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) requires AI agents that can not only make stratigic decisions but also engage in flexible and meaningful communication. Inspired by Wittgenstein's language game theory in Philosophical Investigations, we propose that language agents can learn through in-context interaction rather than traditional multi-stage frameworks that separate decision-making from language expression. Using Werewolf, a social deduction game that tests language understanding, strategic interaction, and adaptability, we develop the Multi-agent Kahneman & Tversky's Optimization (MaKTO). MaKTO engages diverse models in extensive gameplay to generate unpaired desirable and unacceptable responses, then employs KTO to refine the model's decision-making process. In 9-player Werewolf games, MaKTO achieves a 61% average win rate across various models, outperforming GPT-4o and two-stage RL agents by relative improvements of 23.0% and 10.9%, respectively. Notably, MaKTO also demonstrates human-like performance, winning 60% against expert players and showing only 49% detectability in Turing-style blind tests. These results showcase MaKTO's superior decision-making, strategic adaptation, and natural language generation in complex social deduction games.
Actively Supervised Clustering for Open Relation Extraction
Jun 08, 2023Abstract:Current clustering-based Open Relation Extraction (OpenRE) methods usually adopt a two-stage pipeline. The first stage simultaneously learns relation representations and assignments. The second stage manually labels several instances and thus names the relation for each cluster. However, unsupervised objectives struggle to optimize the model to derive accurate clustering assignments, and the number of clusters has to be supplied in advance. In this paper, we present a novel setting, named actively supervised clustering for OpenRE. Our insight lies in that clustering learning and relation labeling can be alternately performed, providing the necessary guidance for clustering without a significant increase in human effort. The key to the setting is selecting which instances to label. Instead of using classical active labeling strategies designed for fixed known classes, we propose a new strategy, which is applicable to dynamically discover clusters of unknown relations. Experimental results show that our method is able to discover almost all relational clusters in the data and improve the SOTA methods by 10.3\% and 5.2\%, on two datasets respectively.
Mastering Strategy Card Game (Hearthstone) with Improved Techniques
Mar 09, 2023Abstract:Strategy card game is a well-known genre that is demanding on the intelligent game-play and can be an ideal test-bench for AI. Previous work combines an end-to-end policy function and an optimistic smooth fictitious play, which shows promising performances on the strategy card game Legend of Code and Magic. In this work, we apply such algorithms to Hearthstone, a famous commercial game that is more complicated in game rules and mechanisms. We further propose several improved techniques and consequently achieve significant progress. For a machine-vs-human test we invite a Hearthstone streamer whose best rank was top 10 of the official league in China region that is estimated to be of millions of players. Our models defeat the human player in all Best-of-5 tournaments of full games (including both deck building and battle), showing a strong capability of decision making.
Mastering Strategy Card Game via End-to-End Policy and Optimistic Smooth Fictitious Play
Mar 07, 2023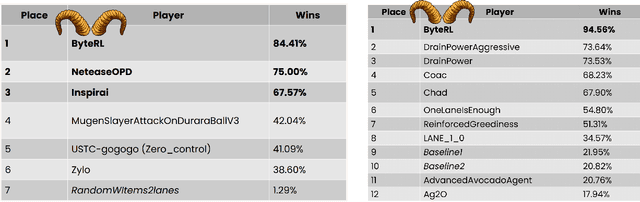
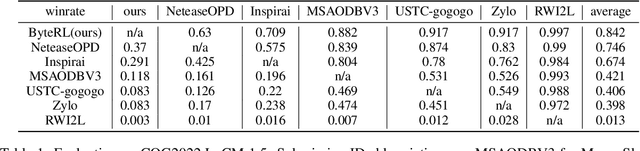

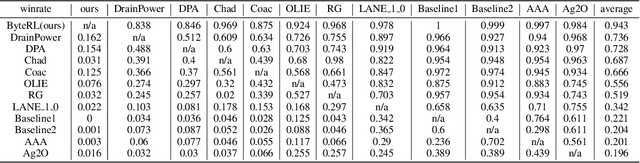
Abstract:Deep Reinforcement Learning combined with Fictitious Play shows impressive results on many benchmark games, most of which are, however, single-stage. In contrast, real-world decision making problems may consist of multiple stages, where the observation spaces and the action spaces can be completely different across stages. We study a two-stage strategy card game Legends of Code and Magic and propose an end-to-end policy to address the difficulties that arise in multi-stage game. We also propose an optimistic smooth fictitious play algorithm to find the Nash Equilibrium for the two-player game. Our approach wins double championships of COG2022 competition. Extensive studies verify and show the advancement of our approach.
Unitail: Detecting, Reading, and Matching in Retail Scene
Apr 01, 2022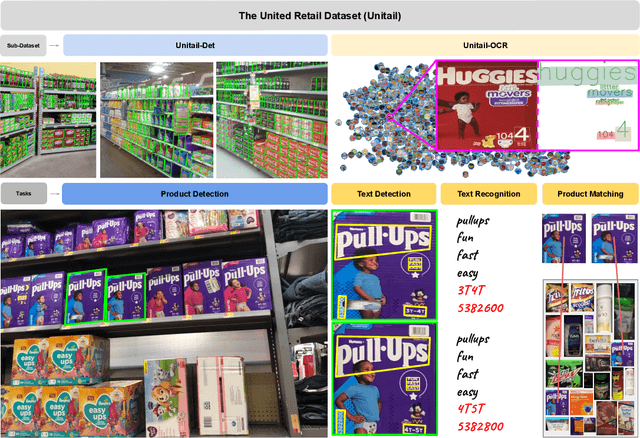
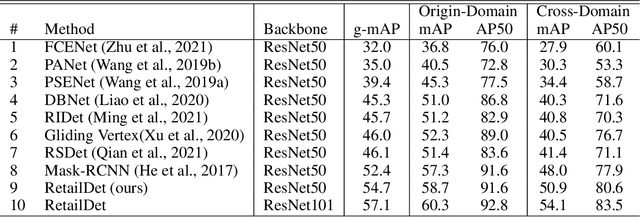
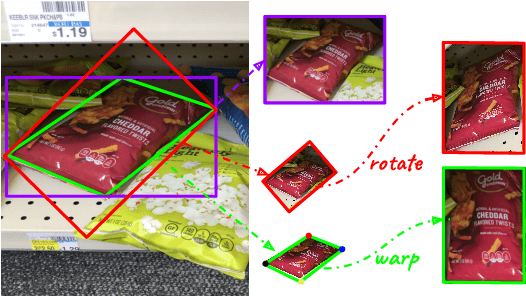
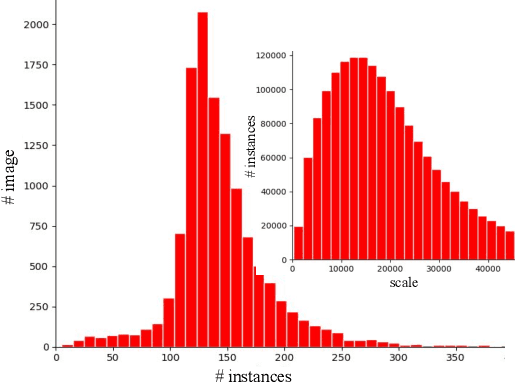
Abstract:To make full use of computer vision technology in stores, it is required to consider the actual needs that fit the characteristics of the retail scene. Pursuing this goal, we introduce the United Retail Datasets (Unitail), a large-scale benchmark of basic visual tasks on products that challenges algorithms for detecting, reading, and matching. With 1.8M quadrilateral-shaped instances annotated, the Unitail offers a detection dataset to align product appearance better. Furthermore, it provides a gallery-style OCR dataset containing 1454 product categories, 30k text regions, and 21k transcriptions to enable robust reading on products and motivate enhanced product matching. Besides benchmarking the datasets using various state-of-the-arts, we customize a new detector for product detection and provide a simple OCR-based matching solution that verifies its effectiveness.
MODRL/D-EL: Multiobjective Deep Reinforcement Learning with Evolutionary Learning for Multiobjective Optimization
Jul 16, 2021



Abstract:Learning-based heuristics for solving combinatorial optimization problems has recently attracted much academic attention. While most of the existing works only consider the single objective problem with simple constraints, many real-world problems have the multiobjective perspective and contain a rich set of constraints. This paper proposes a multiobjective deep reinforcement learning with evolutionary learning algorithm for a typical complex problem called the multiobjective vehicle routing problem with time windows (MO-VRPTW). In the proposed algorithm, the decomposition strategy is applied to generate subproblems for a set of attention models. The comprehensive context information is introduced to further enhance the attention models. The evolutionary learning is also employed to fine-tune the parameters of the models. The experimental results on MO-VRPTW instances demonstrate the superiority of the proposed algorithm over other learning-based and iterative-based approaches.
TextFlint: Unified Multilingual Robustness Evaluation Toolkit for Natural Language Processing
Apr 06, 2021



Abstract:Various robustness evaluation methodologies from different perspectives have been proposed for different natural language processing (NLP) tasks. These methods have often focused on either universal or task-specific generalization capabilities. In this work, we propose a multilingual robustness evaluation platform for NLP tasks (TextFlint) that incorporates universal text transformation, task-specific transformation, adversarial attack, subpopulation, and their combinations to provide comprehensive robustness analysis. TextFlint enables practitioners to automatically evaluate their models from all aspects or to customize their evaluations as desired with just a few lines of code. To guarantee user acceptability, all the text transformations are linguistically based, and we provide a human evaluation for each one. TextFlint generates complete analytical reports as well as targeted augmented data to address the shortcomings of the model's robustness. To validate TextFlint's utility, we performed large-scale empirical evaluations (over 67,000 evaluations) on state-of-the-art deep learning models, classic supervised methods, and real-world systems. Almost all models showed significant performance degradation, including a decline of more than 50% of BERT's prediction accuracy on tasks such as aspect-level sentiment classification, named entity recognition, and natural language inference. Therefore, we call for the robustness to be included in the model evaluation, so as to promote the healthy development of NLP technology.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge